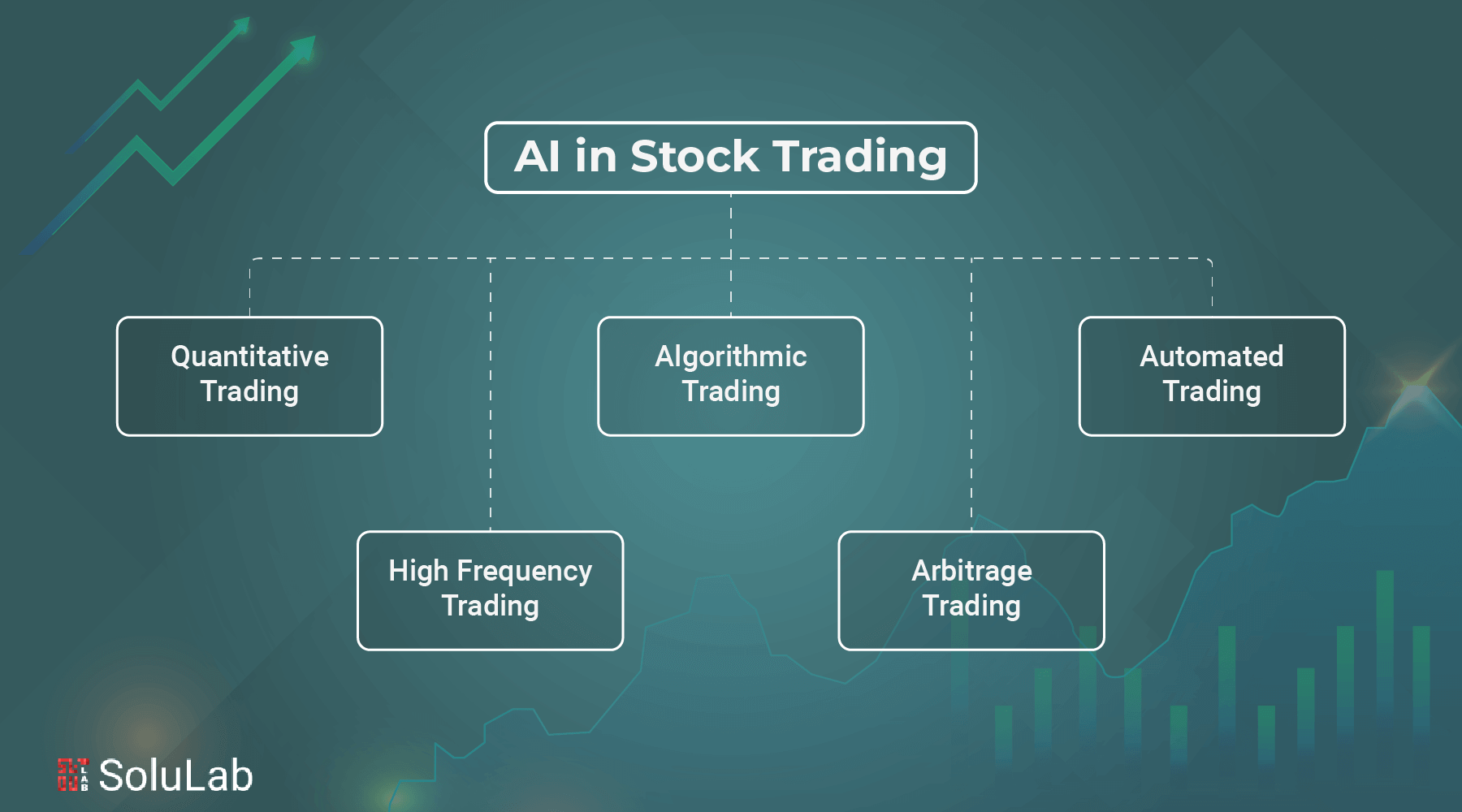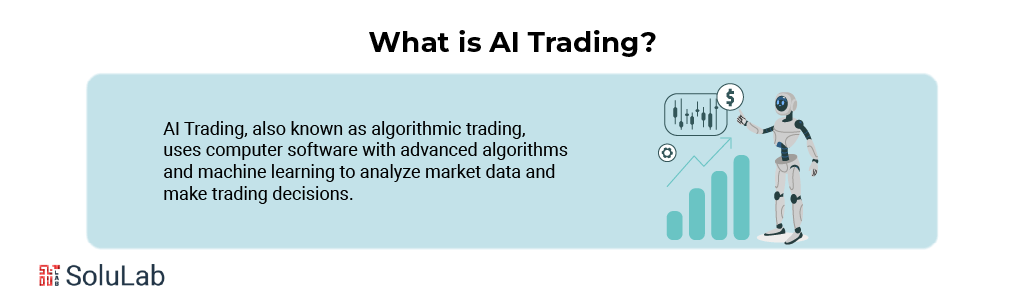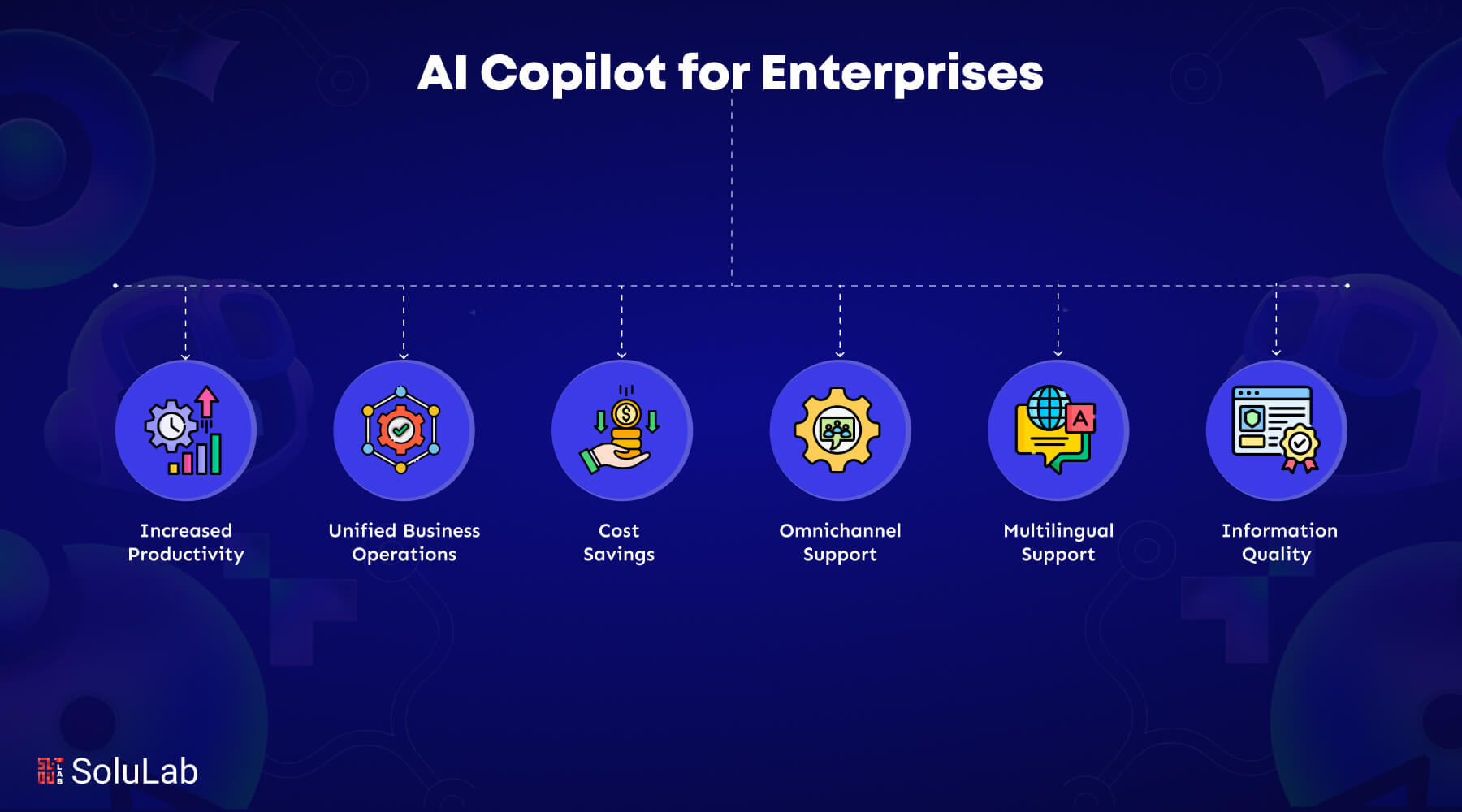
Gen AI was implemented on the work desks of almost every industry over the past year. The trend is expected to continue because 83% of organizations think AI is a high business priority. In 2023, financial services committed around $35 billion to AI. About $21 billion of this came from the banking sector.
Gen AI is an AI that produces data or content through the application of algorithms, which simulate human-generated content, and it is transforming the way we work. Generative Artificial Intelligence has transformed the accounting industry in ways that were unimaginable even a few years ago.
Advances in AI technology have become a significant tool for business operations, ranging from the automation of routine accounting duties to offering profound insights into financial data. Ultimately, AI can enhance financial transaction security and decision-making based on financial data analysis that highlights patterns, gives insights, and indicates possible fraudulent activity.
We will consider benefits and methods of overcoming and capitalizing on how and when to overcome and capitalize on obstacles that come through in the process of applying Generative AI in accounting.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a kind of artificial intelligence that learns the patterns from the extant information to generate new content, be it text, imagery, or data. This is not similar to the traditional AI that is meant to analyze or interpret data but instead creates new outputs that are very close to the input it was trained on. To mimic human creativity and problem-solving, this technology uses very sophisticated machine learning models, such as neural networks.
It utilizes generative AI to outsource activities related to financial forecasting, analysis of the tax code, and document generation. It transforms the workflows for accounting and finance. Generative AI will determine possible deductions, prepare comprehensive tax reports, and automate the compliance process in such a way that errors and unnecessary time spent will be reduced.
The impact of generative AI has transformed industries as it ensures efficiency and develops new solutions that can be customized to specific requirements. Hence, for organizations that strive to outshine others in an environment where the playing field is based on data, this is a very useful resource.
The Role of Generative AI in Accounting
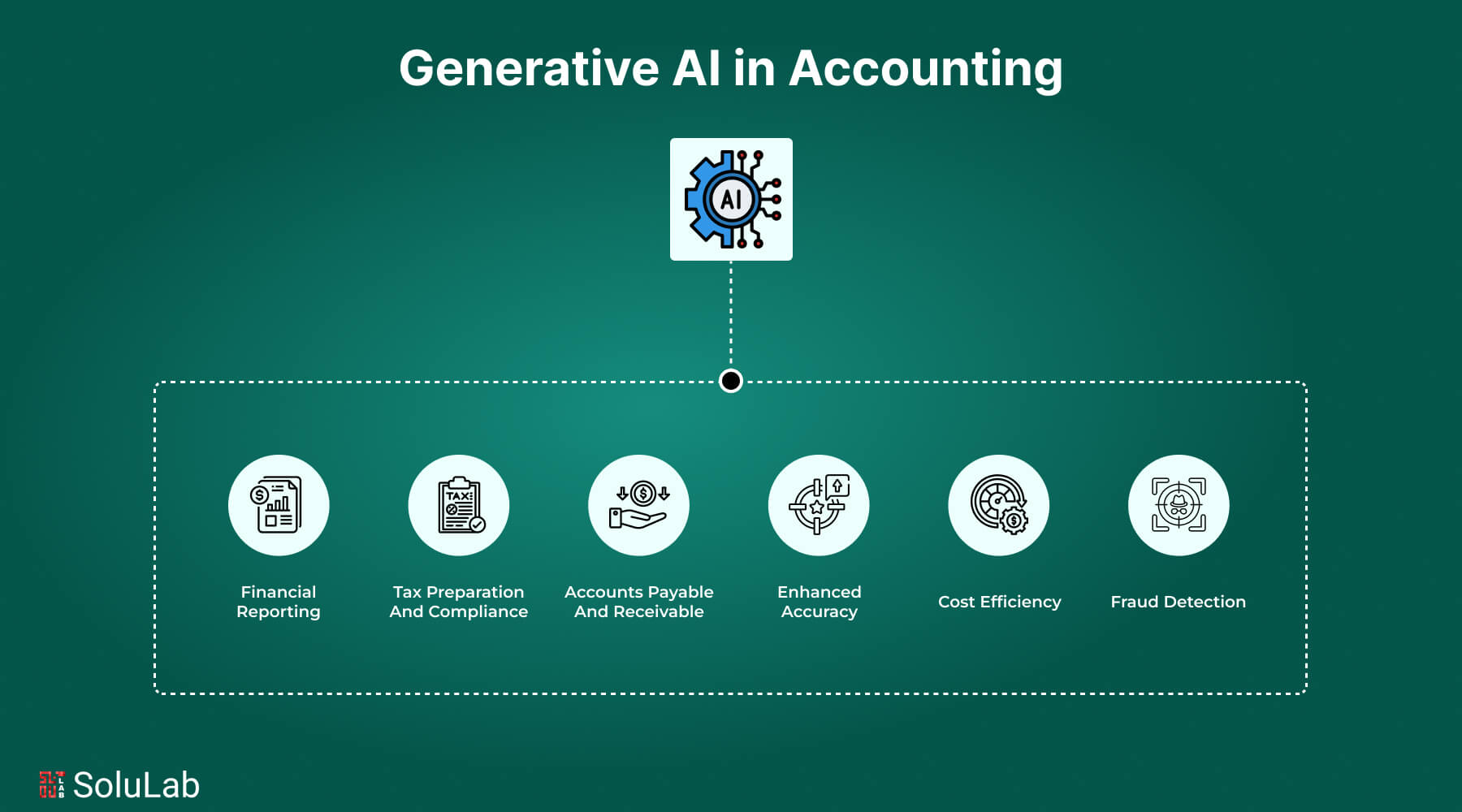
GenAI generally stands for generative AI, and it has changed almost every industry globally. Its impacts have also been felt in accounting, where it has reframed the way financial data processing, analysis, and reporting are handled. The technology leverages generative AI in payments and uses high-end machine-learning models for improved efficiency and accuracy. Some aspects of accounting such as financial reporting and audit compliance are being impacted by these factors.
1. GenAI Accounting for Streamlined Financial Reporting
The automation of data processing has revolutionized typical workflows with generative AI at the helm. Financial reporting could now be rendered faster and also less prone to errors, typically requiring extensive effort in preparing said reports. In this regard, GenAI creates comprehensive reports on specific needs on the part of the user as it picks out trends and extensively analyzes datasets. This feature is useful especially over month-end or year-end reporting as the accounts of the organizations can now be closed precisely and speedily.
Generative AI in accounting and AI agents for finance examples include systems that can bring up data from external databases, CRM platforms, and ERP systems into a single standardized and consistent report. The GenAI systems can also be coded to align with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or international financial reporting standards (IFRS) to conform to regulatory demands over the outputs.
2. Improved Audit and Compliance Processes
Generative AI in sales and accounting is also being developed in the auditing field. Due to the voluminous nature of data, sampling has been used by auditors to assess financial transactions. Generative AI can identify anomalies or patterns that may indicate fraud or errors, analyzing 100% of transactions. This approach not only eliminates the risk of monitoring but promises a higher degree of compliance with regulatory standards.
It would also be beneficial in producing audit traces that have plain, concise narratives over flagged transactions. That would be useful for internal auditing as well as external regulatory analysis.
3. Predictive Analytics and Personalized Insights
GenAI enables financial analysts and accountants to have predictive and prescriptive information that goes beyond compliance and reporting. Generative AI systems predict financial outcomes and suggest strategies that can improve the performance of firms by analyzing historical data and market trends. This is one of the key benefits for SMEs, who need data-driven advice without spending money on extensive financial consulting services.
Generative AI in accounting demonstrates a few tools to create personalized accounting dashboard templates that offer real-time metrics on financial health and revenue as well as monitoring of expenses. These instruments facilitate the rapid adjustment of businesses to market changes and enable the formation of informed decisions.
4. Enhanced Accuracy and Reduction of Human Mistakes
Human mistakes in accounting can lead to significant financial losses and immense reputational damage. GenAI is minimizing this risk because it automates mundane and error-prone tasks like data entry and reconciliation. It increases the overall reliability of financial data by ensuring consistency in processes.
5. Future Implications of Generative AI in Accountancy
Integration of GenAI in accounting is going to grow more profound with its evolution. Some of the emerging applications of the integration include real-time tax optimization, automated budgeting, and conversational AI-powered financial assistants that can answer complex inquiries. Generative AI in accounting is no longer merely a matter of efficiency but represents the shift of accountants from routine responsibilities towards strategic roles focused on business expansion and financial planning.
Thus, GenAI accounting has provided significant improvements in the financial realm sector. Generative AI in payments is transforming the field: it improves financial reporting’s credibility; it makes it easier to operate in compliance while providing actionable information. Businesses would be able to gain a sustainable competitive advantage because they would, through this kind of technology, be able to administer their finance operations efficiently, and with foresight.
Generative AI in Accounting Pros and Cons
With the advent of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) in accounting, considerable change has occurred, which has improved the efficiency and accuracy of financial work. Nevertheless, as is the case with any technological advancement, it will come with its own benefits and drawbacks. The following is a balanced discussion of the advantages and disadvantages of using GenAI in accounting.
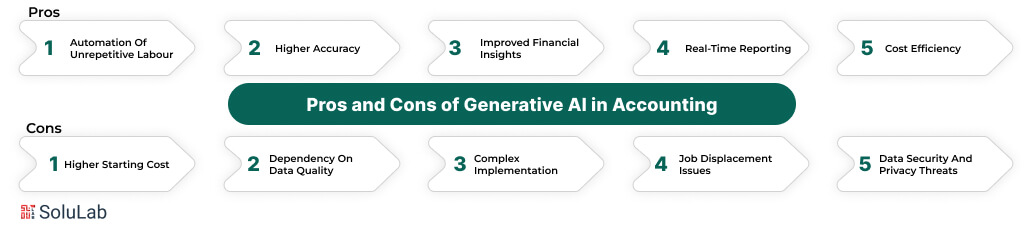
Pros of Generative AI in Accounting
- Automation of Unrepetitive Labour: GenAI automates tedious tasks (e.g., data entry, reconciliation, report generation). Through management of these routine processes, it liberates accountants to embrace more strategic functions, including financial planning and analysis.
- Higher Accuracy: Human error in financial operations, such as in ledger maintenance or tax processing, is greatly diminished by using GenAI. The accuracy of these systems guarantees cleaner audit trails and reliable financial reporting.
- Improved Financial Insights: Generative AI agents sift through massive data sets to discover patterns, trends, and anomalies that would be missed routinely. This capability gives companies actionable information, which enables swift decision-making.
- Real-time Reporting: GenAI can, for example, produce real-time financial reports. This functionality is very useful, especially for decision-makers who need real-time updates to act on market dynamism and/or operational requirements.
- Cost Efficiency: By automating redundant tasks and minimizing manual activities, GenAI leads to lower operational costs. It also reduces the risk of expensive mistakes, helping meet regulatory requirements.
- Customizable Solutions: Generative AI systems can be tailored to meet specific organizational needs, such as compliance with industry regulations or alignment with unique internal processes.
Cons of Generative AI in Accounting
- Higher Starting Cost: GenAI necessitates a substantial investment in software, hardware, and training. Small businesses may find it challenging to allocate resources for these upfront costs.
- Dependency of Data Quality: Dependent on the quality of data processed by GenAI, the usability is high. Malfunctioning or erroneous datasets can result in erroneous outputs, which negate its advantages.
- Complex Implementation: The labor-intensive integration of generative AI into existing accounting systems is possible. It can take expertise to provide both smooth integration and how it relates to organizational goals.
- Job Displacement Issues: Automation of routine work has created a concern about job suppressions for accountants. Although GenAI offers a platform for introducing some strategic work, these changes may prove difficult for some of the workforce.
- Data Security and Privacy Threats: Generative AI models may involve sensitive financial data. If no strong security controls are available, they can be susceptible to cyber-attacks and threaten data privacy and compliance.
- Approaches with Limited Contextual Understanding: Whereas GenAI is powerful at the formalization of data, it can be lacking in the interpretation of complex, nuanced financial contexts or policy alterations, where human supervision is needed.
Use Cases of Generative AI in Accounting
New solutions are offered to the accounting industry through generative AI to streamline operations, enhance accuracy, and improve decision-making. Among the most significant use cases of GenAI making an impact in accounting are as follows:
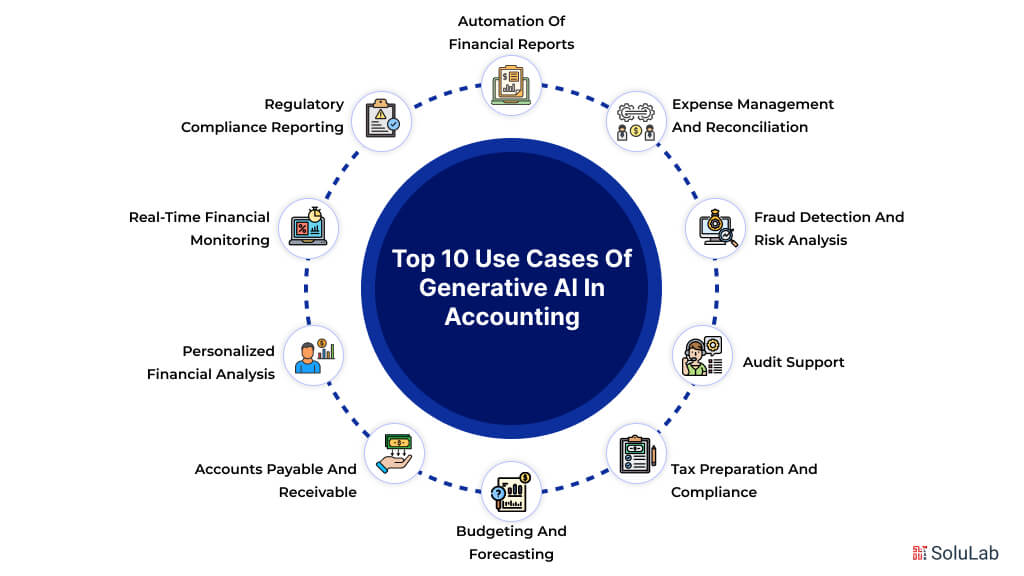
1. Automation of Financial Reports
One of the most well-known applications of GenAI in accounting is generating a financial report. Given the enormous amounts of financial data, GenAI can generate a highly precise and accurate report of statements of income, balance sheets, and cash flows. This saves time and reduces errors while also agreeing with accounting standards.
2. Expense Management and Reconciliation
Tracking and reconciling costs is easy because of generative AI. Generative AI may automatically categorize an expense, raise flags on odd transactions, and reconcile bank statements with accounting records. This relieves the burden of accountants and reduces the chances of misaligned financial information.
3. Fraud Detection and Risk Analysis
GenAI has strong fraud detection due to its ability to identify patterns and anomalies over large data sets. It would scan suspicious transactions such as unauthorized payment or invoice discrepancies based on transaction history. It also helps in risk assessment in terms of financial trends and vulnerabilities.
4. Audit Support
In auditing, GenAI enables the auditor to examine 100% of the transactions instead of sampling. This way, the audit process is more precise and reliable. GenAI also produces audit trails and summaries, thus making the review process easier while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
5. Tax Preparation and Compliance
Tax laws are complex and always changing. In the UK, Generative AI for tax preparation and Making Tax Digital software assist in keeping companies compliant by determining taxes, eligible deductions, and filing taxes without errors. In the United States, similar AI-driven tax platforms support compliance with IRS regulations by automating filings, identifying potential deductions, and ensuring accurate reporting. These systems further help in the preparation of necessary documents in case of audit or tax review to avoid penalties.
6. Budgeting and Forecasting
Generative AI enhances financial planning with a dynamic budget and forecasts. Historical data and market trends are essential in developing insights to be used during the decision-making process. Such valuable insights are of great importance to businesses that are looking to optimize resources and meet financial goals.
7. Accounts Payable and Receivable
Another area where GenAI proves helpful is in managing accounts payable and receivable. It can automatically process invoices, remind recipients to make payments, and initiate the collection process. This way, cash flows occur without any hitch, thus further enhancing the health of the entire financial system.
8. Personalized Financial Analysis
GenAI also provides personalized financial advice for organizations and individuals. Based on spending patterns and financial goals, it formulates customized strategies for cost-cutting, investment opportunities, and the use of resources.
9. Real-Time Financial Monitoring
With generative AI, companies now get real-time insights into their financial performance. This is through dashboards and analytics tools for decision-makers to monitor revenue, expenses, and KPIs in real time. This now makes possible immediate proactive adjustments and better control of finances.
10. Regulatory Compliance Reporting
Compliance in accounting is also a must and generative AI in compliance will make it easy by producing error-free compliance reports according to the latest standards in the industry. It will prevent errors and guarantee that the company will promptly comply with the legal requirements.
Steps to Integrate Generative AI in Accounting
The application of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) in accounting has the potential to automate most aspects of financial operations, facilitate better decisions, and achieve compliance with minimal human effort. Yet implementation of this technology is necessary and demands a structured approach so that it is successful. Below are the key steps to integrate generative AI in accounting processes.
- Assess Business Needs and Objectives: Before the incorporation of GenAI, it is important to identify the accounting problems or inefficiencies the technology could solve. Whatever the application, from automating financial reporting, identifying fraud, or improving the tax compliance process, the ability to set clear objectives will ensure that the integration process is aligned with business requirements.
- Evaluate Data Readiness: Generative AI is deeply sensitive to the quality of its data inputs. Start by verifying the quality of your financial datasets, i.e., they have the correct values, are not missing information, and are current. Data is cleaned and preprocessed whenever needed to feed it to GenAI models. This step is critical to prevent mistakes and to obtain consistent outputs.
- Choose the Right GenAI Tools: Select GenAI tools or platforms that cater to your accounting needs. Identify descriptors, including features related to report generation, anomaly detection, and projection features, e.g. Approaches shall also be considered whether these tools meet industry standards and whether integrations are available with current accounting systems.
- Develop a Pilot Program: Before rolling out GenAI across the organization, start with a pilot program. Select a particular accounting specialty, such as accounts payable, financial reporting, etc., for the pilot effort. Watch the tool’s performance, detect problems, and collect feedback from the team to optimize the process.
- Train Your Team: Introducing generative AI requires a shift in skill sets. Demonstrate how generative AI can be used in accounting, using concrete examples of how it can be beneficial. They are familiar with the tools and understand how to use AI outputs to support decision-making.
- Integrate GenAI with Existing Systems: Seamless integration with current accounting software (e.g., ERP or financial management) is highly desirable to maintain maximum operational efficiency. Partner with the IT trade to guarantee that systems built upon GenAI can talk and exchange information across your existing plumbing without downtime.
- Monitor Performance and Outputs: Once integrated, continuously monitor the performance of GenAI systems. Continuously scrutinize the reliability of generated reports, the effectiveness of automated procedures, and the quality of produced insights. Employing this feedback fine-tuns the system and resolves the new problems.
- Ensure Compliance and Security: Financial information is confidential and usually regulated severely. Implementing strong security measures to ensure data integrity and confidentiality. Make sure your GenAI tools meet relevant industry regulations e.g., GDPR or SOX) to avoid legal or financial penalties.
- Scale and Optimize: Extend the application of generative AI to other accounting tasks, once applied successfully to particular applications. Continuously learn to optimize its application through updating algorithms, the use of new datasets, and the introduction of new features, to respond to ever-changing market requirements.
- Measure ROI and Impact: Assess the return on investment (ROI) and the general effect of generative AI on your accounting activities. Assess improvements in efficiency, cost savings, and decision-making accuracy. Once upon a time, these metrics will be used to make a case for continued funding of AI technologies.
Knowing how to use generative AI in accounting must be managed deliberately, and phased to exploit its capabilities best. Through needs analysis, data preparation, and, most importantly, the appropriate training and compliance mechanisms, businesses can successfully deploy GenAI and realize its value. The strategic use of generative AI by accounting firms will enable them to improve their financial processes and results.
Benefits of Generative AI in Accounting
By bringing tools and methods that improve productivity, accuracy, and decision-making, generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) has transformed accounting. GenAI provides several significant advantages that impact how accounting operations are carried out by automating intricate processes and offering sophisticated insights.
By bringing tools and methods that improve productivity, accuracy, and decision-making, generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) has transformed accounting. GenAI provides several significant advantages that are revolutionizing the way accounting operations are carried out by automating intricate processes and offering sophisticated insights.
-
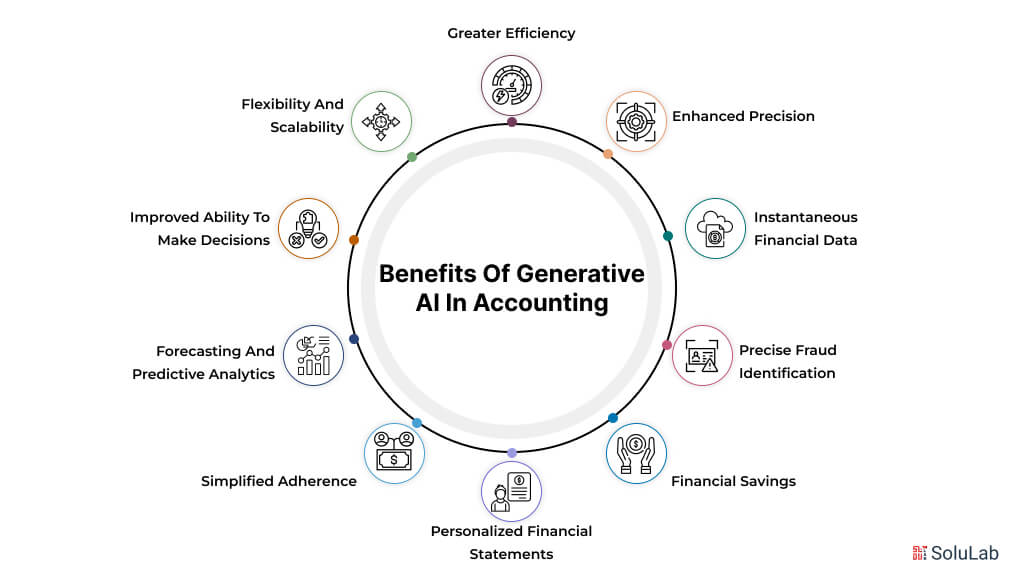
Greater Efficiency
Consuming processes like data input, conciliation, and report preparation are simplified using generative AI. Businesses may save a lot of time by optimizing these procedures, freeing up accountants to concentrate on deeper analysis and strategic tasks. Things that used to take hours or days can now be finished in minutes.
-
Enhanced Precision
Costly errors in accounting can result from human error. By guaranteeing accuracy in computations, reporting, and data analysis, generative AI reduces this risk. Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies reduce inconsistencies by producing accurate and consistent findings, whether they are used to generate financial statements or calculate taxes.
-
Instantaneous Financial Data
Businesses may obtain real-time financial analytics using GenAI. AI offers decision-makers the latest and most current measurements and trends by assessing data as it is created, enabling them to take prompt action. This feature is beneficial for risk assessment, evaluation of investments, and cash flow management.
-
Precise Fraud Identification
Generative AI is very good at spotting trends and irregularities that might point to fraud. It can identify anomalies that manual assessments might miss by examining transaction histories and cross-referencing financial data. This enhances security and shields businesses from monetary losses.
-
Financial Savings
GenAI lowers the need for intensive manual intervention by automating repetitive processes and increasing accuracy, which results in considerable cost savings. To further improve the bottom line, it also aids in preventing monetary losses brought on by mistakes or fraud.
-
Personalized Financial Statements
Customized financial reports that meet certain company requirements can be produced via generative AI. These reports may provide stakeholders with comprehensive insights, summaries, and visualizations that make difficult financial data easier to understand and use.
-
Simplified Adherence
It might be difficult to navigate regulatory requirements, but GenAI makes it easier by guaranteeing compliance with financial reporting standards, tax laws, and other regulations. It minimizes the possibility of fines by simplifying compliance reporting and producing audit-ready paperwork.
-
Forecasting and Predictive Analytics
Generative AI forecasts future financial results by analyzing market patterns and past data. Businesses may use these projections for resource allocation, budgeting, and strategic planning. Organizations may maintain their competitive edge in marketplaces by using predictive insights.
-
Improved Ability to Make Decisions
GenAI gives financial executives and accountants useful insights by processing and analyzing enormous volumes of data. These insights enhance overall financial strategy and planning by assisting in data-driven decision-making.
-
Flexibility and Scalability
Businesses’ financial data and procedures get increasingly complicated as they expand. Because of their great scalability, generative AI systems facilitate integrating new methods and managing bigger datasets without requiring a substantial increase in resources.
Challenges of Using Generative AI in Accounting
Although generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) has several benefits for accounting, there are drawbacks to its use. Comprehending these challenges is essential for companies hoping to use this technology successfully. Here are a few of the most notable dangers and difficulties associated with generative AI in accounting.
- High Costs of Implementation: Generative AI adoption requires a large infrastructure, software, and training investment. Small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) could find these upfront expenses unaffordable, particularly if the ROI is uncertain.
- Dependency of Data Quality: The completeness and quality of the data processed by GenAI are critical factors in determining its efficacy in accounting. The dependability of the system’s insights may be compromised by inaccurate, out-of-date, or inconsistent data, which can provide erroneous results.
- Limited Knowledge of Context: Although it is quite good at organized tasks, generative AI often has trouble deciphering intricate, subtle accounting situations that call for human judgment. Manual intervention may still be necessary in situations involving extraordinary transactions or unclear restrictions.
- Issues with Privacy and Security: Since managing sensitive financial data is a part of accounting, data security is an important consideration. Without strong security measures, generative AI systems might be subject to data breaches or cyberattacks, putting businesses at risk for financial loss and damage to their brand.
- Difficulties in Regulatory Compliance: Strict data protection and financial laws, such as SOX or GDPR, must be followed by generative AI. As rules change, ensuring AI systems adhere to these requirements may be a difficult and continuous effort.
- Worries About Job Displacement: There are worries that ordinary procedures being automated may cause accounting experts to lose their jobs. Although GenAI opens up prospects for more strategic positions, people who can’t adjust to new technology may find the move difficult.
- A Lack of Transparency: Generative AI models, and intense learning systems, often function as “black boxes,” with difficult-to-understand reasoning behind their choices. This lack of openness may be problematic when accountability is essential, such as audits and compliance.
- Integration Difficulties: Integrating GenAI with current accounting software and processes may be difficult and time-consuming. Organizations may need to customize systems and ensure compatibility, which might delay installation and raise expenses.
- Excessive Automation Dependence: One of generative AI’s main benefits is automation, but human supervision may be compromised if used excessively. If AI systems are too trusted, critical mistakes or abnormalities that need human intervention can go unreported.
- Issues of Ethics and Bias: When trained on biased datasets, generative AI models may unintentionally inject biases into financial operations. This might result in unjust consequences or inaccurate decision-making, which presents corporations with moral conundrums.
Future of Accounting With Generative AI
With the emergence of Generative AI (GenAI), accounting is going through a significant transition. This technology has the potential to transform conventional accounting procedures by providing real-time insights, automating repetitive chores, and facilitating more strategic decision-making. Increased accuracy and efficiency will assist the accounting sector as AI capabilities develop, allowing experts to concentrate on higher-value tasks like financial planning and consulting work.
Generative AI is anticipated to improve risk management and fraud detection significantly. AI technologies may proactively detect possible fraud and lower financial risks by examining transaction patterns and spotting irregularities. Additionally, by combining AI with other technologies like blockchain and the Internet of Things, financial records will become more transparent and traceable, increasing the dependability and credibility of accounting procedures.
Additionally, the technology will transform financial forecasting and compliance management. Generative AI can automatically update systems to guarantee compliance with legal standards and track regulation changes in real time. In addition to lowering the possibility of fines, this will streamline intricate compliance procedures. AI-powered predictive analytics will also help businesses anticipate revenue patterns, manage budgets, and plan expenditures with never-before-seen precision.
These technological developments are expected to change the job of accountants. Accountants will become strategic consultants, analyzing AI-generated insights and assisting companies in navigating complex financial environments as generative AI takes over monotonous duties. As modern accounting technologies become more widely available, even small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) will benefit from comprehensive financial management, guaranteeing development and inclusion throughout the company spectrum.
The use of generative AI in accounting portends a creative and exciting future. Companies that adopt this change will have an advantage over their rivals as AI may improve decision-making, expedite procedures, and create a more sustainable financial plan.
The Bottom Line
The accounting industry is changing because of generative AI, which makes jobs quicker, more accurate, and more intelligent. It is assisting firms in being more efficient and concentrating on what matters—growth and strategy—by automating time-consuming procedures and revealing insightful financial data. Whether it’s generating financial reports in real-time or identifying fraud early on, this technology creates intriguing opportunities for accounting’s future.
We at SoluLab – as a Generative AI development company have been delving deeply into AI’s possibilities. Our most recent project, Gradient, demonstrates the full potential of generative AI. Gradient creates beautiful pictures and in-depth text explanations by combining steady diffusion with GPT-3. It illustrates how cutting-edge AI technologies, including accountancy, can be imaginatively used in any industry.
Want to explore how generative AI might improve your accounting systems? Contact SoluLab; we can help you realize your goals!
FAQs
1. What is Generative AI, and how does it apply to accounting?
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that creates content, such as text, images, or data, using advanced algorithms like GPT-3. In accounting, it automates tasks such as financial reporting, data reconciliation, and fraud detection, while also providing real-time insights and predictive analytics to improve decision-making.
2. What are the main benefits of using Generative AI in accounting?
Generative AI streamlines repetitive tasks, enhances accuracy, and provides actionable insights. It helps businesses generate real-time reports, detect anomalies for fraud prevention, ensure compliance with regulations, and forecast financial trends, saving both time and costs.
3. Are there risks associated with Generative AI in accounting?
Yes, there are risks, including data security concerns, high initial implementation costs, dependency on data quality, and the potential for over-reliance on automation. Ensuring proper oversight, secure systems, and high-quality data can mitigate these challenges effectively.
4. Can small businesses benefit from Generative AI in accounting?
Absolutely. Generative AI can help small businesses automate their financial processes, reduce manual errors, and access insights that were previously only available to larger companies. Many AI tools are scalable and offer cost-effective solutions tailored to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
5. How is SoluLab contributing to the advancement of Generative AI solutions?
SoluLab specializes in developing customized AI solutions to meet unique business needs. From automating financial processes to enhancing fraud detection and compliance, our team works closely with clients to integrate Generative AI into their accounting systems, ensuring seamless implementation and measurable results.









![AI Copilot for Sales and Marketing: A Comprehensive Guide [2025]](https://www.solulab.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/AI-Copilot-for-Sales.png)