DePIN has become a topic of current interest because of the emergence of blockchain technology and the increased interest in decentralized solutions. Although it is still in its infancy, DePIN is anticipated to upend the current infrastructure paradigms in a variety of fields.
DePIN is an example of the paradigm shift in which dApps employ tokens to encourage communities to construct and manage networks of physical infrastructure. Using the power of blockchain and decentralized principles, this novel method promises to completely transform how we think and manage physical infrastructure, from electricity grids to telecom.
Understanding DePIN Concepts and Technology
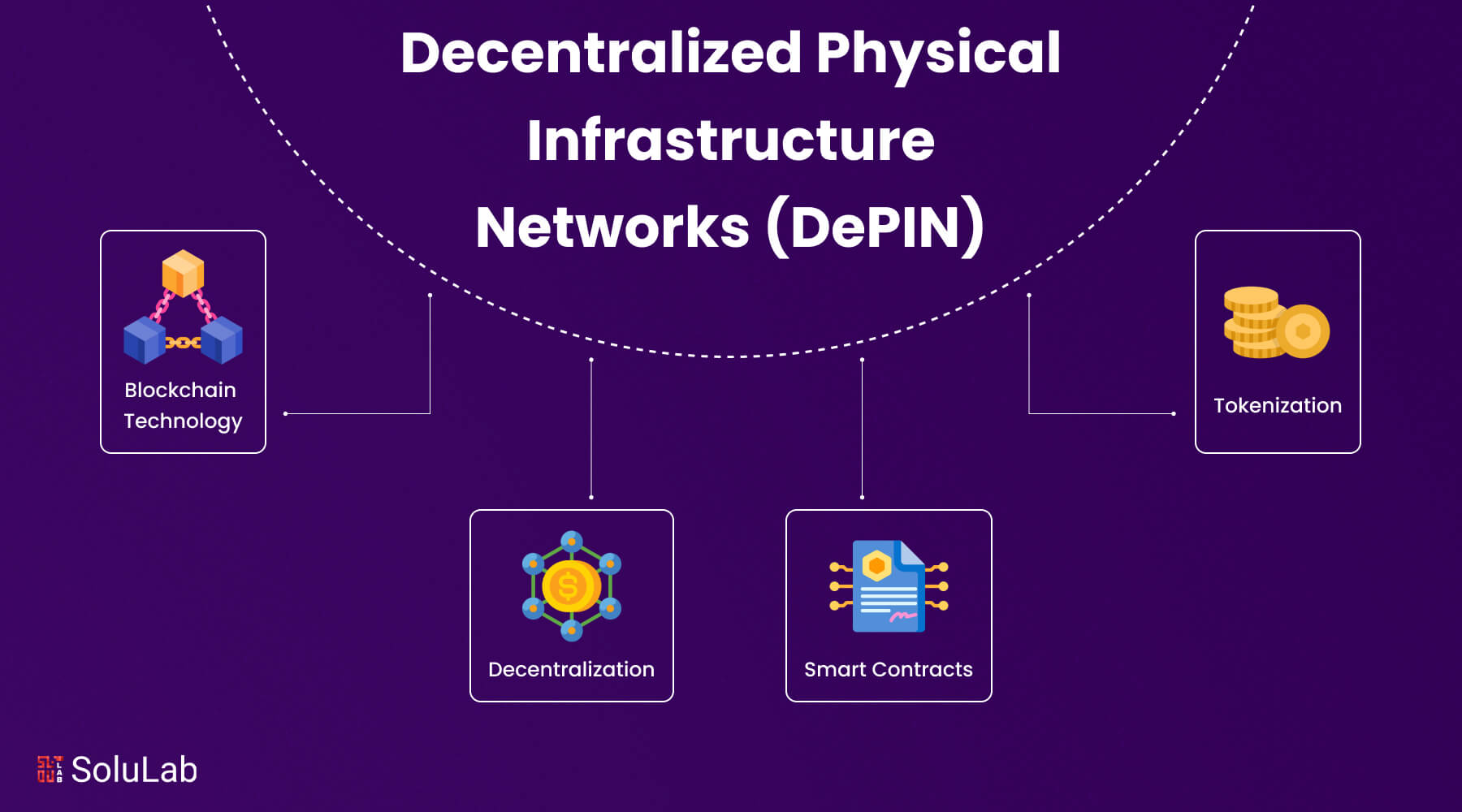
In the blockchain ecosystem, DePIN is an original idea that symbolizes a move away from centralized management and toward community-driven infrastructure development. Using smart contracts, tokens, and dApps, DePIN uses blockchain technology to encourage the development and upkeep of physical infrastructure. The concept of DePIN works on the fundamental tenet of decentralization, which holds that a network of participants shares accountability and benefits for constructing and maintaining infrastructure rather than being governed by a single entity. By removing any point of failure and promoting community ownership and engagement, this model creates a system that is more robust and effective.
Technology Used By DePIN:
- Smart Contracts: By automating the implementation of agreements and procedures, smart contracts are essential to DePIN. When certain circumstances are met, contracts that self-execute are programmed to initiate certain actions, including payments or service supply. This improves the network’s dependability and efficiency while lowering the need for middlemen.
- Blockchain Technology: Offers a safe, transparent, and unchangeable ledger for documenting transactions and activity, which is the foundation of DePIN. This promotes confidence among the participants by guaranteeing that every contribution and reward are traceable and opaque.
- Tokens: Tokens are a type of reward that encourages users to make contributions to the network. By offering the network resources, infrastructure, or services these virtual assets are easily accessible.
How Cryptocurrency DePINs Work?
Within DePINs, cryptocurrency is essential to community growth. To encourage providers of decentralized physical infrastructure to join their networks, these networks use cryptocurrency tokens as rewards. Due to the influx of investor funds, a DePIN’s token value rises, enabling service providers to offer competitive pricing. This increases demand for and acceptance of DePIN’s services, which raises the token price even further. More consumers, service providers, and investors are drawn to the network by this beneficial cycle.
DePIN network platforms, which do not include traditional financial institutions, are based on blockchain technology and offer financial services including trading, borrowing, and lending. Tokenization, the technique of recording property like land or buildings on a permanent record for decentralized ownership and trade through tokens, might be used in one way or another by these platforms to connect with real-world assets.
Types of DePINS
DePINs, or Device Personal Identification Numbers, can take various forms depending on the device and its purpose. Here are some common types:
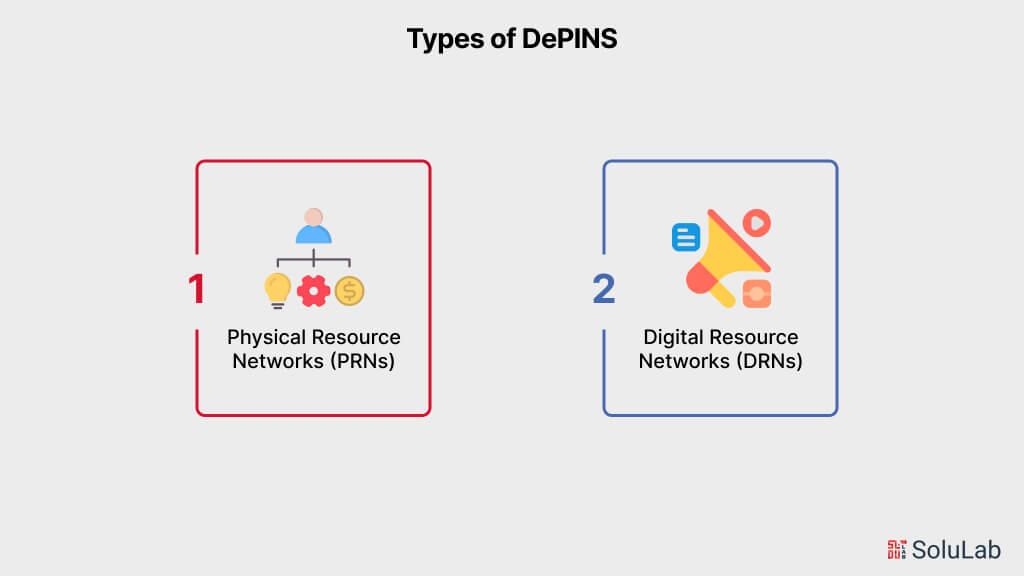
Physical Resource Networks (PRNs) and Digital Resource Networks (DRNs) are both frameworks used to manage and optimize resources, but they operate in different domains:
Physical Resource Networks (PRNs)
- PRNs deal with tangible, physical resources such as raw materials, equipment, transportation, and facilities.
- They focus on optimizing the flow of physical resources through supply chains, manufacturing processes, and distribution networks.
- PRNs may involve logistics management, inventory control, production planning, and transportation optimization to ensure efficient utilization of physical resources.
- Examples include traditional manufacturing industries, transportation and logistics companies, and supply chain management systems.
Digital Resource Networks (DRNs)
- DRNs, on the other hand, deal with intangible, digital resources such as data, information, software, and digital services.
- They focus on managing the flow of digital resources across digital platforms, networks, and systems.
- DRNs involve processes such as data management, information sharing, digital collaboration, and software development.
- Examples include digital platforms like social media networks, cloud computing services, digital marketplaces, and online collaboration tools.
While both PRNs and DRNs involve resource management and optimization, their focus and the nature of the resources they deal with differ significantly. PRNs are concerned with physical assets and logistics, whereas DRNs are concerned with digital assets and information flow in the digital world.
Related: Why are Startups, Businesses, and Governments Looking for DePIN Development?
Core Principles of Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks
Innovative infrastructure systems known as DePINs (Decentralized Public Infrastructure Networks) are reshaping traditional models of resource management. Embracing principles of decentralization, blockchain technology, tokenization, and smart contracts, DePINs represent how infrastructure is conceived, governed, and sustained. Let’s look into the core principles driving the evolution of DePINs:
- Decentralization: Departing from centralized control structures, DePINs distribute authority across diverse stakeholders, fostering resilience and inclusivity. This approach empowers local communities, investors, and end-users, ensuring equitable decision-making and reducing dependency on singular entities.
- Blockchain Technology: Central to DePINs is the integration of blockchain, a distributed ledger system renowned for its transparency and security. By leveraging blockchain, DePINs establish immutable records of transactions, enhancing trust and accountability among participants. This foundational technology underpins the integrity of collaborative endeavors within DePIN ecosystems.
- Tokenization: Incentivizing participation lies at the heart of DePINs, often realized through token economies. Tokens, serving as digital assets, incentivize contributions to infrastructure projects and grant stakeholders access to network resources. Whether representing ownership stakes or facilitating service provision, tokens foster engagement and alignment of interests within DePIN ecosystems.
- Smart Contracts: Automating governance and operational processes, smart contracts streamline interactions within DePIN networks. These self-executing agreements encode terms and conditions into executable code, facilitating seamless coordination and reducing reliance on intermediaries. Smart contracts optimize resource allocation and operational efficiency, driving the sustainable development of DePIN infrastructure.
How Does DePIN Make Use of Blockchain Technology?
DePIN uses blockchain technology to guarantee the highest level of security and immutability for any data that is sent over its network. A more trustworthy and efficient network is produced by this configuration, which enables devices to communicate directly without depending on middlemen or centralized servers. The blockchain serves as a safe and open ledger to decentralized infrastructure networks, permanently documenting all network transactions and data transfers and promoting openness and trust.
DePIN applications in a number of industries like energy, supply chains, data storage, telecommunications, transportation, and real estate, utilize blockchain technology to decentralize authority across networks. Caldera and Eclipse are two examples of layer-two systems that are efficient and scalable, meeting the changing requirements of DePIN projects.
The strategic alignment of DePIN initiatives with certain blockchains is essential to their successful deployment and future scaling.
Use Cases of DePINs in Different Sectors
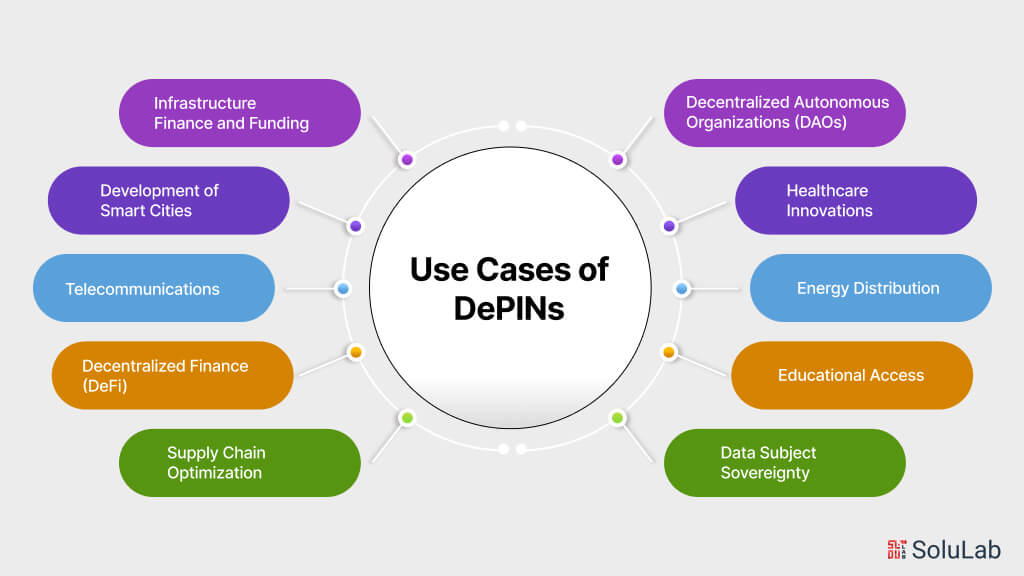
The top applications of decentralized physical infrastructure across a range of sectors are listed below.
1. Energy Distribution
Energy distribution companies employ Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePINs), where participants provide energy grids to the network in exchange for tokens. Using an example, let’s examine how DePIN is used in the energy distribution industry. With the DePIN system, solar-powered households may sell their extra energy to nearby neighbors directly.
They receive tokens in exchange, which have real-world and virtual monetary worth. This decentralized method lowers transmission losses, does away with the need for centralized facilities and service providers, and effectively distributes energy. Additionally, offering immediate rewards in the form of tokens encourages more donors to provide extra services and assist in overall infrastructure growth.
2. Healthcare Innovations
Another area that stands to gain from utilizing decentralized physical infrastructure networks (DePINs) is the healthcare sector. In addition to enabling remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, record sharing, and other features, DePIN provides a decentralized healthcare infrastructure.
For example, everyone in the world can donate resources to a decentralized network of physical infrastructure for healthcare and receive benefits in the form of tokens. Additionally, users can utilize the same network for obtaining these facilities or services, including remote patient monitoring or telemedicine consultations. These networks enable people to safely keep sensitive data and communicate their medical history with physicians around the world.
3. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
DePINs are essential to the growth of decentralized autonomous organizations, or DAOs. The network gives users access to a number of vital physical and digital resources and services, including computer networks, communication systems, and data storage, which are necessary for the DAOs to operate smoothly and preserve their decentralized governance.
DePINs, for example, offer distributed computing resources that let DAOs do complicated tasks on their own. Additionally, donors provide decentralized data storage, which DAOs use to safely store data. In this way, DePIN infrastructures provide access to additional physical and digital resources that support DAO operations in a variety of sectors, including banking, government, entertainment, and more, in a safe, transparent, and efficient manner.
4. Educational Access
Through the support of decentralized educational initiatives, Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks, or DePINs, contribute to the transformation of the education sector. With these networks, students in impoverished places may access educational materials including e-books, online learning environments, and communication technologies that improve remote learning chances.
Students may participate in virtual classroom discussions, access top-notch educational resources, and even work together with world-class professors by utilizing the DePIN infrastructure. In addition to supporting lifelong learning, DePIN in education transforms conventional educational methods and encourages information sharing.
5. Data Subject Sovereignty
DePIN guarantees privacy and sovereignty by enabling people to be the owners of their personal information. An illustration of how patients safely save and manage their medical information on DeFi platforms will help you comprehend this.
Patients do not need to rely on centralized databases when they save their data on DePIN systems. They have complete control over their data and may authorize healthcare professionals to access it as needed. Furthermore, by giving their permission to be used for targeted advertising, studies, or medical research with full transparency and payment, people may monetize their health data through DePIN networks.
6. Supply Chain Optimization
Transparent and decentralized supply chain networks are also made possible by decentralized physical infrastructure networks. These solutions enable supply chain and logistics managers to safely complete transactions, effectively manage logistics, and track delivery in real-time.
For instance, logistic businesses such as FedEx and DHL can use the real-time tracking services offered by the DePIN to follow the movement of a package in real-time. Furthermore, they may carry out safe transactions with the use of smart contracts in the DePIN infrastructure, which simultaneously lowers fraud and guarantees just compensation.
7. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
By enabling lending and borrowing through decentralized collateralized loans, DePIN networks also transform Decentralized Finance (DeFi). Without depending on centralized middlemen, users may get loans by holding digital assets from contributors in the DePIN, such as virtual real estate, Non-Fungible Tokens, and more.
For instance, a user can utilize NFTs, virtual property, or any other digital token as collateral to request loans from donors in the DePIN. The lending procedure is straightforward and automated because of smart contracts. Furthermore, the collateral security automatically passes to the lender (contributor) if the user fails on the loan arrangement.
8. Infrastructure Finance and Funding
Tokenization and funding for infrastructure are also made possible by decentralized infrastructure solutions. Investors can contribute to projects and receive incentives based on the amount they provide.
For instance, a city plans to build a new bridge. To avoid relying solely on funding from the government or big investors, the bridge project’s creator has tokenized it. Tokens that reflect ownership of the bridge’s revenue stream are available for purchase by citizens. In addition, token holders earn dividends as a return on their investment when the bridge makes money.
9. Telecommunications
Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePINs) in telecommunications facilitate in the establishment of communication channels apart from conventional centralized service providers.
Let’s use an example to better grasp this. Let’s say there is no conventional telecommunications infrastructure in a rural community. Residents may now use peer-to-peer connections and DePIN infrastructure to access various communications services, such as sending messages and making calls, without depending on centralized suppliers. In this sense, DePIN improves self-sufficiency and connection in a rural community with little access to conventional telecommunications services.
10. Development of Smart Cities
By decentralizing the control of essential systems like electricity and water supplies, waste management, transportation, and more, DePIN also plays a critical part in the development of smart city infrastructure.
Take the example of a city managing its trash, water, electricity, and transportation systems via a DePIN network. It will make use of decentralized sensors that track real-time resource use. These sensors help cut down on waste and maximize resource allocation. Furthermore, smart contracts can automate the billing process. DePIN systems can quickly react to situations, such as natural disasters or war, without interfering with the city’s vital services and operations. This is another advantage of DePIN in the development of smart cities.
Related: DePIN in Web3 Space
The Future of Decentralized Physical Networks
Business executives now have a novel approach to enter the Web3 space: via DePINs. Consider pursuing the traditional route of becoming a power grid provider through the use of renewable energy sources. In this case, you normally look to a centralized, well-established organization for funding. This path necessitates large upfront expenditures for personnel, real estate, and infrastructure in addition to protracted bureaucratic procedures, all in exchange for giving up a sizable percentage of your earnings to your financier. With this old strategy, you are frequently left to start from scratch and receive minimal pay for your labor.
Discover the constantly changing domain of DePINs, where service delivery and infrastructure development are approached radically differently. You may bootstrap your project by asking interested people to join your network and contribute using blockchain technology and crowdsourcing. This strategy guarantees advantages to all parties engaged in addition to decentralizing ownership. The network’s service providers are in charge of setting up, deploying, and maintaining their gear. This lowers your overhead substantially.
In essence, you’re building an autonomous ecosystem—a utopian village—where everyone collaborates and is free from the centralized powerhouses’ tyranny. This concept’s fundamental strength can upend monopolies and alter the competitive environment in several industries. 
How is SoluLab assisting with crypto trends?
Mainstream acceptance of the cryptocurrency industry and the ability to fit infrastructure into DePIN will predictably be a key trend in the industry in 2025. DePIN is designed to facilitate decentralized control of actual assets through blockchain technology, which, thereby, enhances their protection, productivity, and accountability. Besides people and communities, this innovative approach also holds new opportunities for companies to move to a more environmentally friendly setting as well.
NovaPay Nexus development by SoluLab is a clear example of how technologies based on decentralization can change the scale of e-commerce. With the help of this platform, corporations can create and maintain several stores. Merchants might provide different currencies and wallets to satisfy their needs to enhance the customer experience and usability. Also, the NovaPay Nexus helps in the development of applications such as payment buttons as well as point-of-sale applications in a way that payment can be accepted easily without integrating with third parties or even getting technical support.
With SoluLab, bring the future into your company and reap the benefits of its strong functions for your business. Join us today to reshape your company’s payment processes’ evolution and risk management opportunities! Contact us today to know how you can benefit from these unique services.
FAQs
1. What is Decentralized Infrastructure?
DePINs employ blockchain technology to build distributed systems, as opposed to conventional networks that are managed by a single organization. This implies that a small number of people can manage infrastructure.
2. Is decentralization beneficial or detrimental?
According to the conventional opinion, centralization is considered detrimental while decentralization is known as beneficial, but in reality, both are beneficial and essential only when they are balanced well.
3. Which network is called a decentralized network?
A network design that has several authorities acting as a centralized point for participants is known as a decentralized network. Instead of depending on a single central server, this network divides workloads among multiple computers.
4. What makes decentralized a better choice?
An agile ecosystem is made possible by decentralization, which permits a dispread and independent approach to management and decision-making, this strategy can also encourage a collaborative and creative culture.
5. Can SoluLab assist with Blockchain Development?
SoluLab is one of the leading blockchain development companies, our expertise lies in developing smart contracts, decentralized apps (dApps), and various blockchain solutions that help improve security and transparency for the involved organizations.





