The world of finance has seen a major upheaval since the emergence of the Decentralized Finance (DeFi) ecosystem in recent years. DeFi has emerged as an approach that is innovative, offering conventional financial institutions that are struggling with limitations and inefficiency a decentralized, transparent, and inclusive alternative. With blockchain technology and smart contracts, DeFi is increasing access to financial tools, changing the way financial services are delivered, and empowering individuals to take control of their assets like never before.
In this article we will explore the intricacies of the DeFi ecosystem, emphasizing its core principles, benefits, and range of applications that have driven the ecosystem’s rapid growth. We’ll go over DeFi’s main concepts, the problems they resolve, and how DeFi may alter global financial practices in this blog. You will also learn how DeFi is revolutionizing the finance sector and setting the stage for a more transparent and decentralized future.
What is a DeFi Ecosystem?
The DeFi Ecosystem, short for Decentralized Finance, is a network of financial applications built on blockchain technology. Unlike traditional financial systems, which rely on intermediaries like banks and brokerages, DeFi operates on decentralized networks where transactions are governed by smart contracts and peer-to-peer protocols.
Here’s a breakdown of the key components and features of the DeFi Ecosystem:
- Blockchain Technology: The foundation of DeFi is blockchain, which ensures transparency, security, and immutability of transactions. Ethereum is the most popular blockchain for DeFi projects due to its robust smart contract capabilities.
- Smart Contracts: The conditions of the agreement have been explicitly encoded into code in these self-executing contracts. Smart contracts eliminate the need for middlemen by automating and enforcing a contract’s requirements.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Platforms like Uniswap and Sushiswap allow users to trade cryptocurrencies directly with each other without a central authority. This reduces the risk of hacks and fraud associated with centralized exchanges.
- Decentralized Finance Applications: A diverse range of financial services built on blockchain, including lending protocols (like Compound and Aave), decentralized derivatives (like Synthetix), decentralized stablecoins (like MakerDAO), and yield farming protocols.
- Liquidity Pools: Pools of tokens locked in smart contracts provide liquidity for decentralized exchange trading, allowing users to trade assets seamlessly while earning fees or rewards.
- Governance Tokens: Tokens that grant holders voting rights and influence over the decision-making process of decentralized protocols, empowering the community to govern and evolve the ecosystem.
- Yield Farming: A strategy where users provide liquidity to DeFi protocols in exchange for rewards, typically in the form of additional tokens, governance rights, or a share of transaction fees.
- Flash Loans: Unsecured loans that are instantly borrowed and repaid within the same transaction, enabled by smart contracts, often used for arbitrage and other trading strategies without the need for collateral.
- Automated Market Makers (AMMs): Decentralized protocols that use algorithms and liquidity pools to facilitate token swaps, ensuring continuous liquidity and reducing price slippage for traders.
- Interoperability: The ability of different DeFi protocols and platforms to seamlessly interact and communicate with each other, enhancing the overall efficiency, usability, and composability of the ecosystem.
Understanding Basics of the DeFi Ecosystem
The DeFi ecosystem fundamentals are blockchain technology, smart contracts, and the ambition to replace traditional financial institutions. Building a decentralized, transparent, and open financial system devoid of middlemen is the primary goal of DeFi.
The blockchain technology is the foundation of the DeFi ecosystem. Transparency and immutability are ensured via a system called distributed ledgers, which uses a decentralized network of nodes to store data and transactions. Decentralization reduces the possibility of fraud and manipulation and does away with the necessity for centralized administration.
Smart contracts, the fundamental components of DeFi applications, allow for autonomous and self-executing agreements. The execution of many financial processes, such as borrowing, lending, trading, and yield farming, is made simpler by these programmable contracts. Because smart contracts only carry out transactions when specific conditions are met, they improve ecosystem security and trust.
Providing the user interface, Decentralized Applications (dApps) allow users to engage with DeFi protocols. Users of these blockchain-based applications can access a range of financial products and services. With the help of dApps, users may manage their assets, take part in decentralized exchanges, and apply for loans without the assistance of conventional financial middlemen.
Interoperability is another crucial element of the DeFi ecosystem. As the DeFi industry expands, projects are focusing on establishing cross-chain interoperability to enhance accessibility and liquidity across many blockchain networks.
Despite its great promise, the DeFi ecosystem has challenges related to scalability, security, and regulatory compliance. However, its fundamental principles of accessibility, openness, and decentralization have sparked a financial revolution that has upended traditional banking and laid the foundation for a future in finance that is more equitable and inclusive.
Read Also: DeFi Vs. CeFi
Objectives of a DeFi Ecosystem
One of the key principles of DeFi is peer-to-peer (P2P) financial transactions, in which two people consent to trade cryptocurrency for products or services without the involvement of a third party.
Using DeFi permits you to do the following actions:
- Accessibility: Transactions on a DeFi platform take place anywhere there is an internet connection, thus anybody may use it.
- Low Fees and More Interest Rates: DeFi allows any two parties to communicate about interest rates and lend money or cryptocurrencies over DeFi networks, all with low costs and high interest rates.
- Security and Transparency: Records of completed transactions and smart contracts recorded on a blockchain are accessible to the public for examination, but they do not identify your name. Because they are immutable, blockchains cannot be changed.
- Autonomy: DeFi systems are not dependent on centralized financial institutions. Financial service management is not as necessary or as expensive because to the decentralized structure of DeFi protocols.
Examples of DeFi Ecosystem
Any application that provides financial services using blockchain and cryptocurrency technologies is referred to as DeFi. Certain applications have the ability to offer a wide range of services, from basic ones like savings accounts to more sophisticated ones like lending money to investors or corporations. Aave, a “decentralized non-custodial liquidity market protocol” that enables anybody to engage as a liquidity supplier or borrower, is one of the most well-known DeFi service providers.
With Aave, you may stake any cryptocurrency asset you own to generate interest revenue from potential loan recipients.
Use Cases of a DeFi Ecosystem
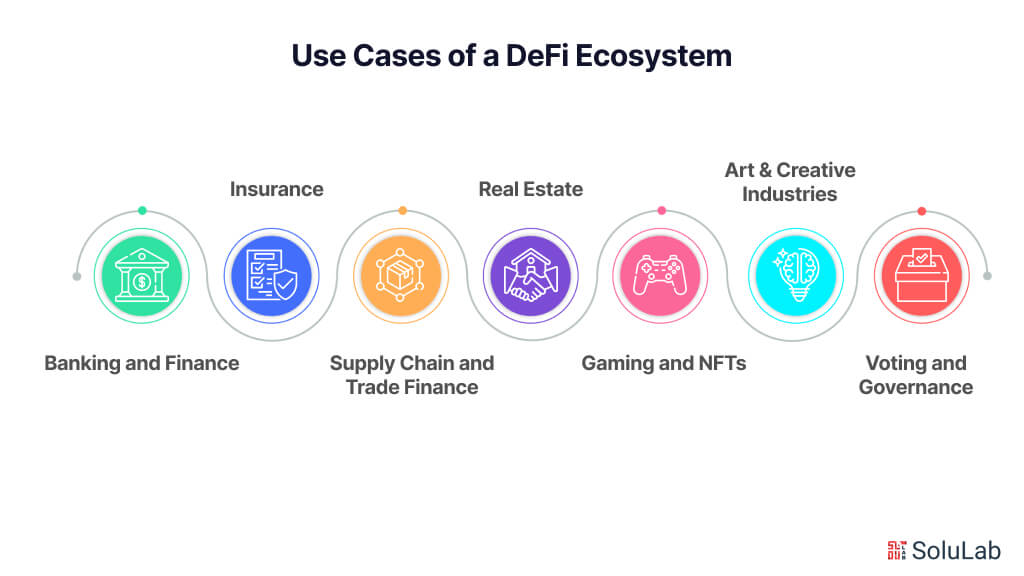
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has found great applications in a number of industries and has rapidly expanded its use. Its openness and transparency, together with the automation provided by smart contracts, have enabled creative uses. Here are a few well-known DeFi use cases across a range of industries:
- Banking and Finance: DeFi is disrupting traditional banking by offering decentralized platforms for lending and borrowing. The underbanked and unbanked populations today have easier access to financial services since loans may be obtained without a credit check or traditional collateral. DeFi provides an additional option to traditional savings accounts by enabling users to earn interest on their cryptocurrency holdings while taking part in yield farming protocols.
- Insurance: DeFi is revolutionizing the insurance industry by offering decentralized insurance protocols. Peer-to-peer insurance solutions eliminate the need for traditional insurance firms by enabling individuals to combine their resources to cover specific risks. This tactic reduces expenses, expedites the processing of claims, and fosters openness.
- Supply Chain and Trade Finance: DeFi is accelerating supply chain finance through the development of decentralized solutions that enable businesses to access working capital using smart contracts. By offering automated, trustless payment settlements, these systems reduce the likelihood of fraud and disputes in global trade.
- Real Estate: DeFi is revolutionizing the real estate industry by enabling tokenized fractional ownership of properties. By acquiring tokens that represent a share of a property, investors may bypass the typical entrance limitations and broaden their investment profile while gaining exposure to the real estate market.
- Gaming and Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): DeFi and the gaming industry have joined to enable players to purchase, trade, and sell in-game items using non-fungible tokens. These unique digital assets might provide gamers with extra revenue streams by acting as virtual property, collectibles, or rare products.
- Art & Creative Industries: DeFi has transformed the art sector by enabling artists to tokenize their creations as NFTs. Because of this, artists may now advertise their digital artwork to collectors instead of going via traditional galleries or auction houses. Artists may also get royalties if their NFTs are resold on the secondary market.
- Voting and Governance: DeFi is a pioneer in decentralized governance techniques, enabling token owners to participate in choices that impact the expansion and enhancement of the platform. This democratic approach allows users to have a say in how the DeFi project they are involved in develops in the future.
These are just a few examples of how DeFi is introducing more efficient, accessible, and transparent financial systems and revolutionizing several industries. As technology advances, more industries are anticipated to embrace DeFi solutions, expanding the possibilities for global prosperity and innovation.
Benefits of a DeFi Ecosystem
DeFi platform provides consumers with a number of benefits such as better cost-effectiveness, more transparency, and easier access to financial services.
1. Availability
One of the significant benefits of DeFi is that it gives those who may otherwise be shut out of the regular financial system more access to financial services. This covers those who don’t fulfill the credit standards for conventional loans or who reside in places without access to regular banks.
2. Reduced Prices
DeFi lowers the cost of financial services by doing away with middlemen like banks. Users may benefit from reduced costs and improved interest rates as a consequence. DeFi also does away with the need for middlemen, which lowers transaction costs and improves transaction speed and efficiency.
3. Transparency
DeFi leverages blockchain technology to provide a transparent and secure ledger of all transactions. This level of transparency allows users to clearly understand the terms and conditions of various DeFi financial products, such as DeFi lending platforms, and to monitor the performance of their investments in real-time.
4. Security
The foundation of DeFi on blockchain technology ensures a secure and tamper-proof environment for transactions. This high level of security significantly reduces the risk of fraud and hacking, making DeFi platforms, including DeFi lending platforms, a safer alternative to traditional financial systems.
5. Innovation
DeFi fosters the development of innovative financial products and services. For instance, DeFi lending platforms and borrowing protocols offer users fresh investment opportunities, while decentralized investment platforms grant access to a broader spectrum of assets, driving innovation within the financial sector.
6. Decentralization
DeFi operates on a decentralized blockchain network, eliminating the need for a central authority. This decentralization empowers users with greater control over their financial transactions and minimizes the risk associated with a single point of failure.
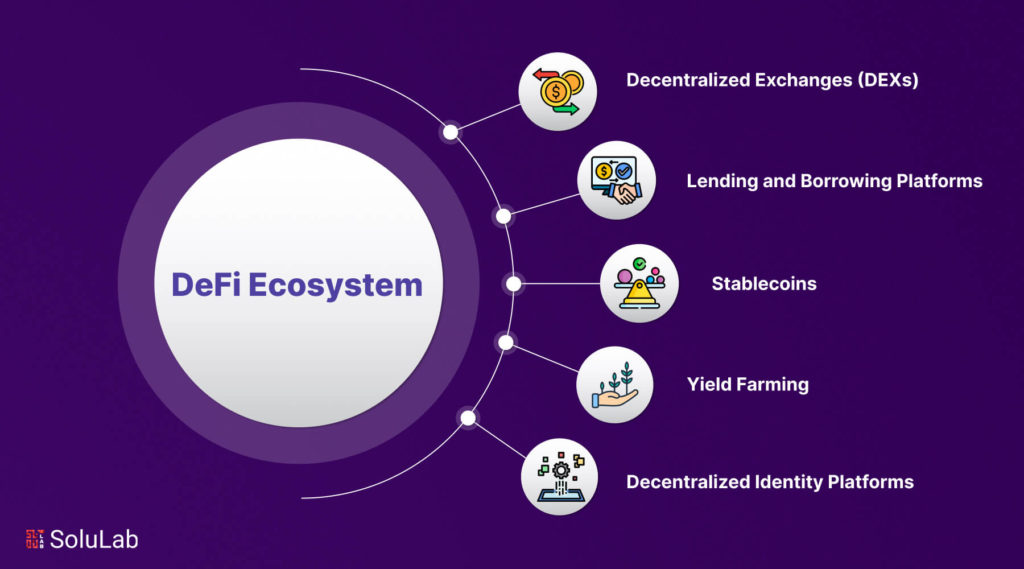
Different Types of Decentralized Finance Platforms
The DeFi ecosystem has expanded swiftly and now encompasses a variety of applications and platforms. This section will cover the different types of DeFi applications and platforms, highlighting their unique features and advantages over traditional, centralized finance.
1. Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Decentralized exchanges are platforms that facilitate cryptocurrency trading without intermediaries. By leveraging smart contract technology, DEXs offer a secure, transparent, and swift trading process. Users benefit from greater control over their funds and the ability to trade anonymously, distinguishing DEXs from centralized exchanges.
2. Lending and Borrowing Platforms
Lending and borrowing platforms allow users to directly lend and borrow funds without the need for intermediaries. These platforms utilize smart contracts to manage loans, ensuring security and transparency. Typically, loans are collateralized with assets such as cryptocurrencies or stablecoins, mitigating default risks, and showcasing a key difference between centralized vs. decentralized finance.
3. Stablecoins
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged to stable assets like the US dollar. Designed to maintain a consistent value, stablecoins are ideal for transactions and payments. They offer users stability in the otherwise volatile cryptocurrency market, providing a reliable alternative to traditional finance options.
4. Yield Farming
Yield farming involves lending cryptocurrencies to earn interest or rewards. Participants can deposit their assets into liquidity pools, which are used for trading on decentralized exchanges. The trading activities generate rewards that are distributed to the depositors, illustrating a unique investment opportunity within decentralized finance compared to centralized finance systems.
Related: Guide to DeFi Yield Farming
5. Decentralized Identity Platforms
Decentralized identity platforms give users control over their personal data and digital identity. Using blockchain technology, these platforms store data securely and in a decentralized manner, ensuring users have full control over their information. Additionally, decentralized identity platforms allow users to share their data securely and privately, offering enhanced privacy compared to centralized identity management systems.
Predicting the Role of DeFi in the Future
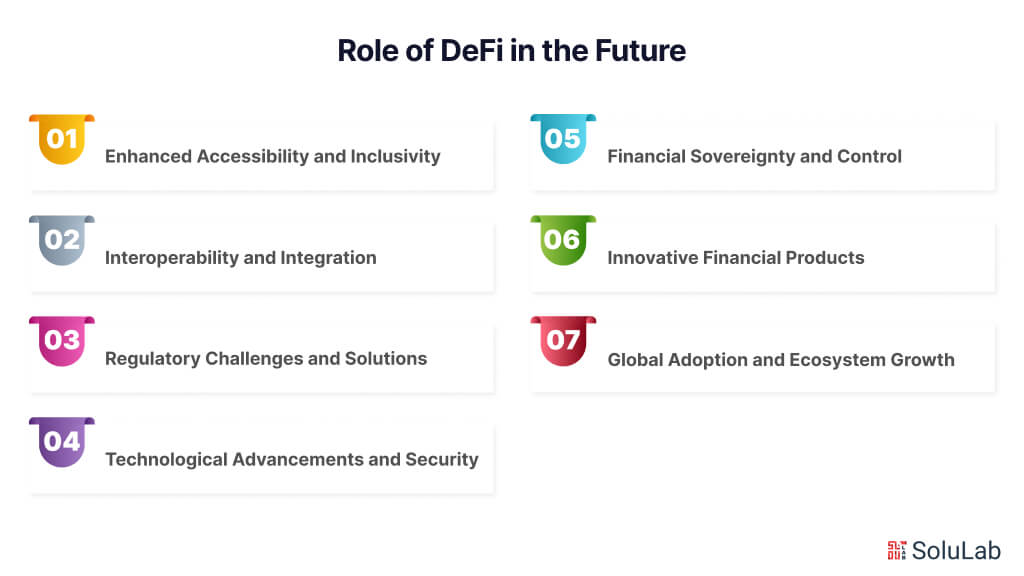
The future of DeFi (Decentralized Finance) promises a transformative shift in the financial era, to challenge traditional centralized finance (CeFi) models. DeFi development, driven by blockchain technology, aims to create a more inclusive, transparent, and efficient financial ecosystem. As DeFi platforms continue to evolve, several key trends and predictions can be outlined.
-
Enhanced Accessibility and Inclusivity
DeFi has the potential to democratize access to financial services. Unlike traditional finance, which often requires intermediaries and imposes barriers to entry, DeFi platforms enable users to engage directly with financial products. This inclusivity can bridge gaps for the unbanked and underbanked populations worldwide, providing them with access to lending, borrowing, and investment opportunities.
-
Interoperability and Integration
A significant development in the future of DeFi will likely involve greater interoperability with centralized finance. Hybrid models that leverage the strengths of both systems could emerge, offering seamless integration between DeFi protocols and traditional financial institutions. Such synergy could enhance liquidity, reduce transaction costs, and improve the overall user experience.
-
Regulatory Challenges and Solutions
The rapid growth of DeFi will inevitably attract increased regulatory scrutiny. Policymakers worldwide are grappling with how to oversee decentralized platforms that operate beyond traditional jurisdictions. The future of DeFi will depend heavily on finding a balance between innovation and regulation, ensuring consumer protection without stifling technological advancement. Developing robust regulatory frameworks that address concerns such as security, fraud, and compliance will be crucial for the sustainable growth of DeFi.
-
Technological Advancements and Security
As DeFi development progresses, technological advancements will play a pivotal role in its maturation. Innovations in smart contract security, scalability solutions like layer 2 protocols, and improvements in user interfaces will make DeFi platforms more secure, efficient, and user-friendly. These enhancements will help mitigate current risks such as hacks and vulnerabilities, fostering greater trust and adoption among users.
-
Financial Sovereignty and Control
One of the core philosophies driving DeFi is the notion of financial sovereignty—giving individuals full control over their assets without reliance on intermediaries. This decentralization trend is expected to continue, empowering users to manage their financial portfolios with greater autonomy. The ability to participate in decentralized governance and staking can further reinforce user engagement and investment in the DeFi ecosystem.
-
Innovative Financial Products
The future of DeFi is likely to witness the creation of more sophisticated and diverse financial products. From decentralized insurance and prediction markets to synthetic assets and decentralized exchanges, DeFi is poised to offer a wide array of financial instruments that cater to various user needs. These innovative products can provide new avenues for wealth generation and risk management, attracting a broader audience to the DeFi space.
-
Global Adoption and Ecosystem Growth
As awareness and understanding of DeFi increase, its adoption is expected to spread globally. Emerging markets, in particular, stand to benefit significantly from DeFi solutions that can bypass inefficient traditional banking systems. The continuous development of the DeFi ecosystem, supported by venture capital and institutional investments, will further accelerate its growth and adoption worldwide.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the DeFi ecosystem brings up a new change in the financial industry, challenging centralized vs decentralized finance with its transparent, and inclusive approach. By using blockchain technology, DeFi platforms eliminate intermediaries, reduce costs, and provide users with direct access to a wide range of financial services. From lending and borrowing to trading and staking, the opportunities within the DeFi space are vast and continually expanding, making it an exciting frontier for innovation and financial empowerment.
However, the DeFi ecosystem faces several challenges, including security vulnerabilities, regulatory uncertainties, and scalability issues. These challenges can hinder the widespread adoption and trust in DeFi solutions. SoluLab, as a leading DeFi development company, is well-equipped to address these issues by providing robust security measures, compliance with regulatory standards, and scalable blockchain solutions. With expertise in developing secure and user-friendly DeFi platforms, SoluLab can help businesses and individuals navigate the complexities of decentralized finance. To learn more about how SoluLab can support your DeFi development, contact us today!
FAQs
1. What is DeFi and how does it differ from traditional finance?
DeFi, or Decentralized Finance, refers to financial services built on blockchain technology that operate without intermediaries like banks. Unlike traditional centralized finance (CeFi), DeFi platforms enable direct peer-to-peer transactions, offering greater transparency, reduced costs, and increased accessibility.
2. How secure is the DeFi ecosystem?
While DeFi offers many benefits, it also faces security challenges, including smart contract vulnerabilities and potential hacks. However, ongoing advancements in blockchain technology and security measures, such as code audits and improved smart contract protocols, are continually enhancing the security of DeFi platforms.
3. What are the main advantages of using DeFi?
The main advantages of DeFi include increased accessibility to financial services, lower transaction costs, faster and more transparent transactions, and greater financial autonomy for users. DeFi platforms also offer innovative financial products like decentralized lending, borrowing, and yield farming.
4. What are the regulatory challenges facing DeFi?
DeFi operates in a relatively nascent regulatory environment, leading to uncertainties and challenges. Key regulatory concerns include compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements, as well as ensuring consumer protection and financial stability. Finding a balance between regulation and innovation is crucial for the sustainable growth of DeFi.
5. How can SoluLab help in DeFi development?
SoluLab, as a leading DeFi development company, addresses key challenges in the DeFi ecosystem by providing robust security measures, ensuring regulatory compliance, and offering scalable blockchain solutions. With expertise in developing secure and user-friendly DeFi platforms, SoluLab helps businesses and individuals navigate the complexities of decentralized finance.




