- AI Development
- AI App Development
- AI Consulting
- AI Software Development
- ChatBot Development
- Enterprise AI ChatBot
- AI Chatbot Development
- LLM Development
- Machine Learning Development
- AI Copilot Development
- MLOps Consulting Services
- AI Agent Development
- Deep Learning Development
- AI Deployment Services
- Deep Learning Consulting
- AI Token Development
- AI Development Company
- AI Development Company in Saudi Arabia
- AI Integration Services
- Hire Blockchain Developers
- Hire Full Stack Developers
- Hire Web3 Developers
- Hire NFT Developers
- Hire Metaverse Developers
- Hire Mobile App Developers
- Hire AI Developers
- Hire Generative AI Developers
- Hire ChatGPT Developers
- Hire Dedicated Developers
- Hire Solana Developer
- Hire OpenAI Developer
- Hire Offshore Developer
- About Us
- Networks+
- Smart Contracts +
- Crypto currency +
- NFT +
- Metaverse +
- Blockchain+
- Mobile Apps +
- WEB +
- Trending +
- Solutions +
- Hire Developers +
- Industries +
- Case Studies
- Blogs
Large Language Models (LLMs) have resulted in substantial improvements within the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP), allowing for the development and deployment of a wide range of applications that had been believed to be difficult or impossible to produce using traditional approaches. These powerful deep learning models, trained on enormous datasets, have a detailed comprehension of human language and can produce coherent, context-aware prose that matches human ability. From conversational artificial intelligence assistants and automated content production to sentiment analysis and language translation, LLMs have grown as the driving force underlying a plethora of innovative NLP solutions.
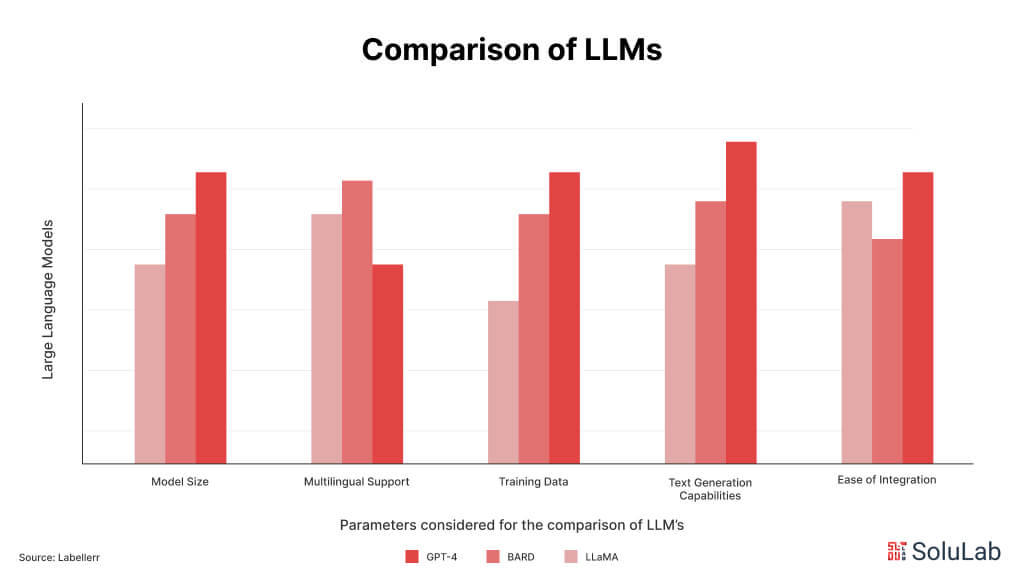
Choosing the correct LLM, however, might be difficult with so many options available, like GPT, LLaMa, Flan-UL2, Bard, and Bloom.
These models are excellent in language prediction, making them useful for tasks such as content creation and creative writing. Choosing between them, for example, whether to utilize ChatGPT for article refining or Notion AI for processing, can be difficult. In this blog, we hope to simplify the process by having a comparison of all LLMs and assisting you in selecting the best one to improve your career and daily life. Whether you’re a writer, developer, marketer, or anyone else looking for AI-powered help, this guide will serve as your compass as you navigate this constantly shifting technology.
What are Large Language Models?
So, you must be wondering what is LLM exactly. LLM meaning represents a category of foundational models that undergo training on extensive datasets. These models possess the capability to understand and generate natural language, enabling them to perform a wide range of tasks.
LLMs acquire these abilities through rigorous self-supervised and semi-supervised learning processes, in which they internalize statistical patterns from vast text datasets. A primary use case for LLMs is text generation, a form of generative AI where the models predict subsequent tokens or words based on the given input.
LLMs operate similarly to neural networks; by March 2024, the most advanced models will have a transformer-based design that solely uses decoders. Some of the latest versions also incorporate alternative architectures, such as recurrent neural networks or Mamba, a state space model. While numerous approaches have been tested for natural language processing tasks, LLM AI learning exclusively relies on deep learning techniques. These models are particularly adept at capturing complex relationships between entities within the text and can generate content by utilizing the semantic and syntactic subtleties of language. Additionally, they can be enhanced through techniques like Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to improve performance on specific tasks.
Read Also: How to Create an Open-Source AI Model like Llama?
How Do LLMs Work?
LLMs function using sophisticated deep learning methods, mainly utilizing transformer architectures like the Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT). Transformers are particularly effective for managing sequential data such as text input, as they can adeptly capture long-range dependencies and context within the data. LLM models are composed of multiple layers of neural networks, each with adjustable parameters optimized throughout the training process.
During training, LLM models learn to predict the next word in a sentence by analyzing the context provided by the preceding words. This prediction process involves assigning probability scores to tokenized words, which are portions of text segmented into smaller sequences of characters. These tokens are then converted into embeddings, numerical representations that encode contextual information about the text.
To ensure both accuracy and robustness, LLM models are trained on extensive text corpora, often consisting of billions of pages of data. This vast training corpus enables the model to learn grammar, semantics, and conceptual relationships through zero-shot and self-supervised learning methods. By processing large volumes of text data, LLM models become skilled at understanding and generating language patterns.
Once training is complete, LLM models can autonomously generate text by predicting the next word or sequence of words based on the input provided. The model leverages the patterns and knowledge acquired during training to produce coherent and contextually appropriate language. This ability allows LLM models to perform various tasks related to conversational AI and content generation.
The performance of LLM models can be further enhanced through various techniques such as prompt engineering, fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning with human feedback. These approaches help to refine the model’s outputs and address issues like biases or inaccuracies that may emerge from training on large, unstructured datasets. Continuous optimization of the model’s parameters and training processes allows LLM models to achieve higher accuracy and reliability.
Rigorous validation procedures are crucial to ensure that LLM models are ready for enterprise-level applications without introducing risks like liability or reputational harm. These processes include thorough testing, validation against diverse datasets, and adherence to ethical guidelines. LLM models may be successfully implemented in real-world settings, covering a range of language-related activities with high precision and effectiveness, by eliminating possible biases and guaranteeing resilient performance. In the comparison of Large Language Models, methods like LLMOPs play a key role in operationalizing these models for practical applications.
Key Technical Features of Large Language Models (LLMs)
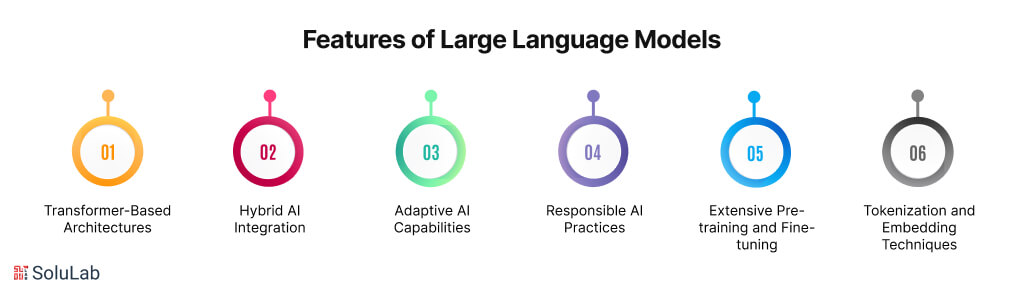
Large Language Models (LLMs) are at the forefront of AI innovation, boasting a range of technical features that make them powerful tools for natural language processing. Here are some of the key technical features that define LLM development:
1. Transformer-Based Architectures
LLMs primarily utilize transformer architectures, known for their ability to handle sequential data efficiently. These architectures allow LLMs to capture long-range dependencies and context within text, making them highly effective in understanding and generating human language.
2. Hybrid AI Integration
LLMs often incorporate hybrid AI approaches, combining traditional rule-based systems with advanced deep learning models. This integration enhances the models’ versatility, enabling them to perform a broader range of tasks with improved accuracy. Hybrid AI also allows LLMs to benefit from the strengths of both symbolic and neural approaches, resulting in more robust and adaptable systems.
3. Adaptive AI Capabilities
One of the standout features of modern LLMs is their adaptive AI capabilities. LLMs can dynamically adjust their responses based on new data and context, allowing them to provide more relevant and accurate outputs. This adaptability is crucial in applications where the environment or user inputs are constantly changing, ensuring that the LLM remains effective over time.
4. Responsible AI Practices
LLM development increasingly emphasizes responsible AI practices. This includes building models with mechanisms to minimize biases, ensure fairness, and maintain transparency. Responsible AI also involves implementing ethical guidelines and validation processes to prevent harmful outputs and ensure that LLMs are aligned with societal values and norms.
5. Extensive Pre-training and Fine-tuning
LLMs undergo extensive pre-training on large-scale datasets, followed by fine-tuning on specific tasks. This two-phase training process enables LLMs to generalize well across different domains while also being specialized for particular applications. Fine-tuning allows for the customization of LLMs, tailoring them to meet specific industry requirements or user needs.
6. Tokenization and Embedding Techniques
LLMs utilize advanced tokenization and embedding techniques to process text data. Tokenization breaks down text into smaller units, which are then transformed into embeddings—numerical representations that encode semantic and contextual information. These techniques are fundamental to how LLMs understand and generate language, ensuring that the models capture the nuances of human communication.
These key technical features make LLMs powerful and flexible tools, capable of addressing a wide range of natural language processing challenges. Whether it’s through hybrid AI, adaptive AI, or responsible AI practices, LLM development continues to push the boundaries of what AI can achieve in understanding and generating human language.
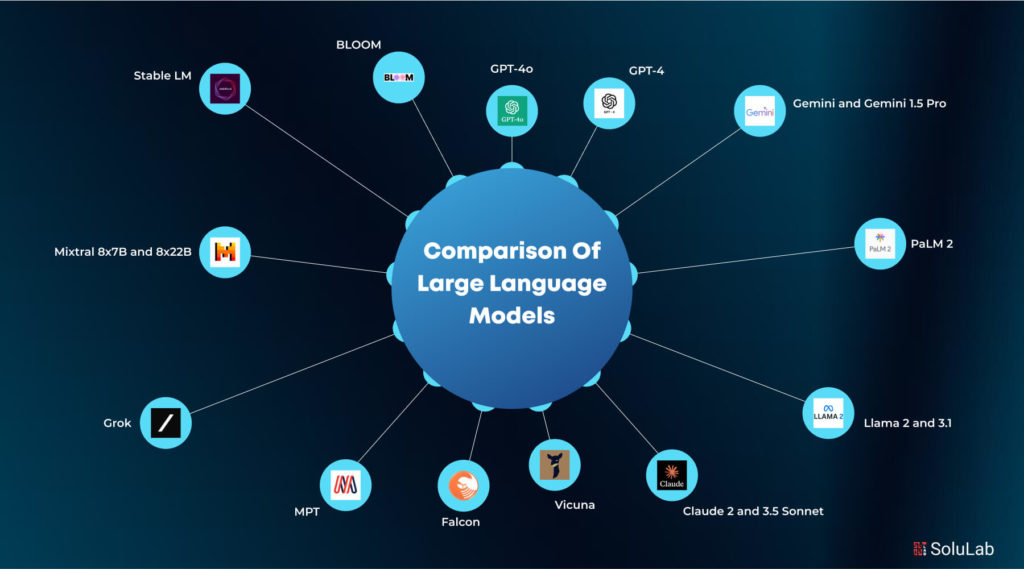
Detailed Insights into Top LLMs
Large Language Models (LLMs) have evolved rapidly, leading to a diverse landscape of powerful models. Below is a detailed analysis of some of the most prominent LLMs, highlighting their features and applications.
1. GPT-4o
An improved version of GPT-4, known as GPT-4o, aims to provide better performance while using less processing power. It maintains the same architecture as GPT-4 but is streamlined for faster processing, making it more suitable for applications where speed and efficiency are critical. NLP vs. LLM discussions often highlight GPT-4o’s efficiency in NLP tasks compared to traditional models, offering high accuracy without the need for extensive resources.
2. GPT-4
GPT-4 is one of the most advanced LLMs developed by OpenAI, known for its extensive capabilities in natural language understanding and generation. GPT-4 builds on the success of its predecessors with even larger datasets and more sophisticated training techniques. It excels in generating human-like text, answering questions, translating languages, and more. The comparison of LLM vs. generative AI is evident in GPT-4’s ability to create coherent, contextually relevant content across various domains, showcasing the power of generative AI.
3. Gemini
Gemini is an advanced LLM designed for versatility and performance across diverse NLP tasks. It integrates advanced transformer architectures with hybrid AI approaches, enabling it to handle complex language processing tasks with precision. Gemini LLM stands out for its adaptability, making it suitable for applications ranging from conversational AI to specialized industry use cases. Its hybrid AI capabilities allow it to combine rule-based logic with deep learning, enhancing its overall performance.
4. Gemini 1.5 Pro
Gemini 1.5 Pro is an enhanced version of the Gemini LLM, offering superior processing power and advanced features tailored for enterprise-level applications. It includes improvements in context awareness, real-time adaptability, and multi-modal processing, making it a top choice for businesses requiring robust language processing solutions. LLM vs. LAM comparisons often highlight the Gemini 1.5 Pro’s scalability and complexity, surpassing traditional language models in handling large-scale, multi-domain tasks.
5. PaLM 2
PaLM 2 (Pathways Language Model) is an advanced LLM developed by Google, designed to handle multi-modal inputs and outputs. It excels in tasks that require understanding and generating language across different formats, such as text, images, and even video. LLM vs. generative AI comparisons often place PaLM 2 in the context of its multi-modal capabilities, which extend beyond traditional text-based generative AI, making it a versatile tool for various applications.
6. Llama 2
Llama 2 is the next iteration in the Llama series, building on the foundation of its predecessor with enhancements in scalability and performance. It is optimized for efficient training and inference, making it suitable for applications where resource constraints are a concern. LLM vs. LAM discussions frequently highlight Llama 2’s ability to handle larger datasets and more complex tasks compared to earlier, smaller language models.
7. Llama 3.1
Llama 3.1 pushes the boundaries of what is possible with LLMs, offering even greater scalability and adaptability than Llama 2. It is designed for high-performance NLP tasks and excels in environments where accuracy and speed are paramount. Llama 3.1’s architecture allows it to process massive datasets with minimal latency, making it a leading choice for enterprise applications.
8. Vicuna
Vicuna is an open-source LLM known for its community-driven development and emphasis on transparency and accessibility. It offers a balance between performance and openness, allowing researchers and developers to explore and adapt its architecture for various applications. LLM vs. generative AI comparisons often highlight Vicuna’s flexibility in generating language, thanks to its open-source nature, which encourages innovation and customization.
9. Claude 2
Claude 2 is an LLM developed by Anthropic, designed with a focus on safety and alignment. It incorporates advanced techniques for responsible AI, ensuring that its outputs are both accurate and ethical. Claude 2 excels in conversational AI tasks, providing coherent and context-aware responses. NLP vs. LLM comparisons often emphasize Claude 2’s advancements in alignment, making it a safer choice for applications involving sensitive or complex topics.
10. Claude 3.5 Sonnet
Claude 3.5 Sonnet is an upgrade from Claude 2, offering enhanced processing power and more sophisticated alignment techniques. It is particularly effective in maintaining context over extended conversations, making it ideal for long-form dialogue and customer support applications. LLM vs. LAM discussions frequently underscore Claude 3.5 Sonnet’s ability to handle complex conversational flows better than traditional language models.
11. Falcon
Falcon is a high-performance LLM designed for speed and efficiency. It is optimized for real-time applications where latency is a critical factor, such as voice assistants and interactive AI systems. LLM vs. generative AI comparisons often highlight Falcon’s ability to generate content rapidly without sacrificing accuracy, making it a top choice for applications requiring quick, reliable responses.
12. MPT (Multi-Path Transformer)
MPT is an advanced LLM that utilizes a multi-path transformer architecture to enhance its processing capabilities. This architecture allows MPT to handle multiple input paths simultaneously, improving its ability to manage complex tasks that require parallel processing. NLP vs. LLM comparisons often focus on MPT’s efficiency in handling diverse data streams, making it a versatile tool for complex language processing tasks.
13. Mixtral 8x7B
Mixtral 8x7B is part of the Mixtral series, known for its balanced performance across a range of NLP tasks. With 7 billion parameters, it offers a strong combination of speed and accuracy, making it suitable for mid-sized applications that require efficient language processing. LLM vs. LAM comparisons often highlight Mixtral 8x7B’s ability to outperform smaller language models while remaining resource-efficient.
14. Mixtral 8x22B
Mixtral 8x22B is a larger and more powerful version of the Mixtral series, with 22 billion parameters. It is designed for high-demand applications where large-scale data processing and high accuracy are essential. LLM vs. generative AI discussions often emphasize Mixtral 8x22B’s capacity to generate more sophisticated and nuanced language, making it ideal for advanced NLP tasks.
15. Grok
Grok is an LLM focused on deep understanding and reasoning. It is designed to excel in tasks that require comprehension of complex concepts and the ability to generate insightful responses. LLM vs. generative AI comparisons often position Grok as a model that goes beyond surface-level text generation, offering deeper analysis and context-aware content creation. If you’re building with Grok, you can start quickly using a Grok API gateway with code examples for common use cases.
16. StableLM
StableLM is an open-access LLM developed by Stability AI, known for its robustness and stability across a variety of applications. It is particularly well-suited for research and development, offering a stable platform for experimentation with LLM capabilities. NLP vs. LLM comparisons often highlight StableLM’s reliability in maintaining performance across different tasks, making it a valuable tool for researchers and developers.
17. BLOOM (BigScience Large Open-Science Open-access Multilingual Language Model)
BLOOM is a multilingual LLM developed by the BigScience project, designed to support a wide range of languages and cultural contexts. It is open-access and developed with a strong focus on inclusivity and global accessibility. LLM vs. generative AI comparisons often emphasize BLOOM’s ability to generate text across multiple languages, making it a unique and valuable resource in global AI technology.
LLMs and Their Applications and Use Cases
Large Language Models (LLMs) have transformed the AI industry, powering a wide array of applications across industries. By leveraging advanced natural language processing (NLP) capabilities, these models enable businesses to automate tasks, enhance customer experiences, and gain insights from vast amounts of data. Below, we explore the several leading LLM use cases and applications.
GPT-4 and GPT-4o
- Applications: GPT-4 and its optimized variant, GPT-4o, are at the forefront of AI-powered content creation, code generation, and conversational AI. They are used in developing chatbots, virtual assistants, and AI agents that can perform complex tasks, such as drafting documents, summarizing content, and generating creative ideas.
- Use Cases: In the legal industry, GPT-4 can assist with contract analysis by generating summaries and identifying potential risks. In healthcare, it supports diagnostic assistance by providing detailed explanations of medical conditions based on patient records.
Gemini and Gemini 1.5 Pro
- Applications: The Gemini models excel in multilingual translation, sentiment analysis, and personalized content generation. They are particularly useful in global marketing campaigns, where accurate language translation and culturally relevant content are crucial.
- Use Cases: E-commerce companies utilize Gemini for personalized product recommendations based on customer preferences and behavior. In social media, these models analyze user sentiments to optimize content strategies.
PaLM 2
- Applications: PaLM 2 is designed for tasks requiring high-level reasoning and contextual understanding, such as complex question-answering, scientific research, and technical documentation.
- Use Cases: In education, PaLM 2 aids in creating intelligent tutoring systems that provide personalized learning experiences. In finance, it helps analyze market trends and generate investment strategies based on large datasets.
Llama 2 and Llama 3.1
- Applications: Llama models are known for their efficiency in knowledge extraction, data synthesis, and domain-specific language modeling. They are used in industries requiring rapid processing of specialized information, such as legal, healthcare, and academic research.
- Use Cases: Law firms use Llama 2 for legal research, automating the extraction of relevant case law and statutes. Llama 3.1 is employed in scientific research for summarizing complex research papers and generating hypotheses.
Vicuna
- Applications: Vicuna specializes in creative writing, storytelling, and generating dialogue in interactive applications like video games and virtual reality experiences.
- Use Cases: Game developers use Vicuna to create dynamic, interactive dialogues for NPCs (non-playable characters) in RPGs (role-playing games). In marketing, it is used to generate engaging copy for brand storytelling.
Claude 2 and Claude 3.5
- Applications: Claude models are designed for high-stakes decision-making processes, ethical AI, and scenarios requiring deep contextual understanding and empathy, such as mental health support and conflict resolution.
- Use Cases: In customer service, Claude 2 enhances AI agents’ ability to handle complex queries and resolve issues empathetically. Claude 3.5 is used in teletherapy platforms to provide emotionally intelligent responses during counseling sessions.
Falcon
- Applications: Falcon is tailored for high-speed data processing and real-time decision-making, making it ideal for financial trading, supply chain optimization, and autonomous systems.
- Use Cases: In finance, Falcon is used to develop high-frequency trading algorithms that make split-second decisions based on market data. In logistics, it optimizes delivery routes in real time to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
MPT (Multi-Purpose Transformer)
- Applications: MPT is a versatile LLM that adapts to various tasks, including natural language understanding, text classification, and anomaly detection.
- Use Cases: In cybersecurity, MPT detects and responds to unusual patterns in network traffic, preventing potential breaches. In customer support, it classifies and prioritizes incoming queries, improving response times.
Mixtral 7×8 B and Mixtral 8X22B
- Applications: The Mixtral models are engineered for large-scale data analysis and model integration, supporting applications in AI-driven decision-making, predictive analytics, and automated reporting.
- Use Cases: Manufacturing companies use Mixtral models to predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance proactively. In retail, these models analyze consumer trends to forecast demand and optimize inventory management.
Grok
- Applications: Grok focuses on enhancing AI-powered insights in business intelligence, predictive analytics, and customer relationship management (CRM).
- Use Cases: In CRM, Grok helps businesses predict customer needs and personalize interactions, improving retention rates. It also aids in market research by identifying emerging trends from unstructured data sources.
Stable LM
- Applications: Stable LM is optimized for stability and reliability in mission-critical applications, such as healthcare diagnostics, legal analysis, and automated content moderation.
- Use Cases: In healthcare, Stable LM supports AI-driven diagnostic tools that ensure consistent and accurate analysis of medical data. In legal tech, it is used to maintain consistency in legal document drafting and review processes.
BLOOM
- Applications: BLOOM is designed for biodiversity research, environmental monitoring, and sustainability efforts, leveraging its capabilities in processing scientific texts and large datasets.
- Use Cases: Environmental agencies use BLOOM to monitor climate data and predict ecological impacts. In agriculture, it helps in optimizing crop management by analyzing weather patterns and soil conditions.
These many LLM applications and use cases promote effectiveness and inventiveness in a variety of sectors. From enhancing AI agents to powering complex decision-making processes, the potential of these models continues to expand, paving the way for new AI use cases and transformative applications.
How SoluLab Can Help Transform Your Business Through LLMs?
At SoluLab, as an LLM development company, we specialize in leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) to drive innovation and efficiency across industries. Our expertise in LLM development and integration enables businesses to harness the power of AI for various applications, from automating routine tasks to enhancing customer engagement. By collaborating with SoluLab, you can unlock the potential of LLMs to streamline operations, gain actionable insights, and build intelligent systems tailored to your specific needs. Our services have been developed to be safe, scalable, and compatible with your company’s goals.
Recently, we launched a project named InfuseNet that empowers your team to design intricate business logic effortlessly. With its intuitive drag-and-drop Flow interface, InfuseNet allows you to seamlessly link multiple LLMs, templates, and media models with extraction tools, simplifying the creation of robust intelligent applications. In just minutes, you can craft a personalized ChatGPT-like app using proprietary data, register, establish a knowledge base, and integrate it into workflows for heightened operational efficiency. InfuseNet streamlines data import from databases, cloud storage, and APIs, preparing it for fine-tuning with LLMs, while ensuring data confidentiality in self-hosted deployments. Seamlessly interface with services like MySQL, Google Cloud, and CRMs to create secure, high-performance AI solutions that drive your business forward. Ready to transform your business with advanced LLM solutions? Contact us today to get started on your AI journey!
FAQs
1. What are Large Language Models (LLMs) and why do we need them?
Large Language Models (LLMs) are advanced AI systems designed to understand, generate, and interpret human language. They are essential in many applications, including content production, translation, chatbots, etc. Their ability to process large datasets and generate coherent, context-aware text makes them invaluable for automating tasks, enhancing customer experiences, and driving innovation across industries.
2. How do LLMs like GPT-4, PaLM 2, and Llama 2 differ from each other?
LLMs differ in their architecture, training data, and specific use cases. For example, GPT-4 is known for its versatility in content creation and conversational AI, while PaLM 2 excels in complex reasoning and contextual understanding. Llama 2 is optimized for domain-specific tasks, making it ideal for industries like legal and healthcare. The differences in design and capabilities make each LLM suitable for distinct applications.
3. Which industries benefit the most from using Large Language Models?
Industries such as finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and customer service benefit significantly from LLMs. In finance, LLMs help in analyzing market trends and generating investment strategies. Healthcare uses LLMs for diagnostic assistance and personalized patient care. E-commerce leverages LLMs for product recommendations and sentiment analysis, while customer service improves response accuracy and speed through AI-powered agents.
4. What aspects of an LLM should firms take into account?
When choosing an LLM, businesses should consider factors such as the specific use case, the model’s ability to handle the required language or domain, scalability, integration capabilities, and data privacy. It’s also important to assess the LLM’s performance in terms of accuracy, speed, and its ability to be fine-tuned to meet industry-specific needs.
5. How does fine-tuning improve the performance of LLMs?
Fine-tuning an LLM involves adjusting the model’s parameters using specific datasets relevant to a particular task or industry. This process enhances the model’s accuracy and relevance, allowing it to generate more precise and contextually appropriate responses. Fine-tuning is essential for businesses looking to customize LLMs to their unique requirements, ensuring that the AI delivers optimal performance in real-world applications.


