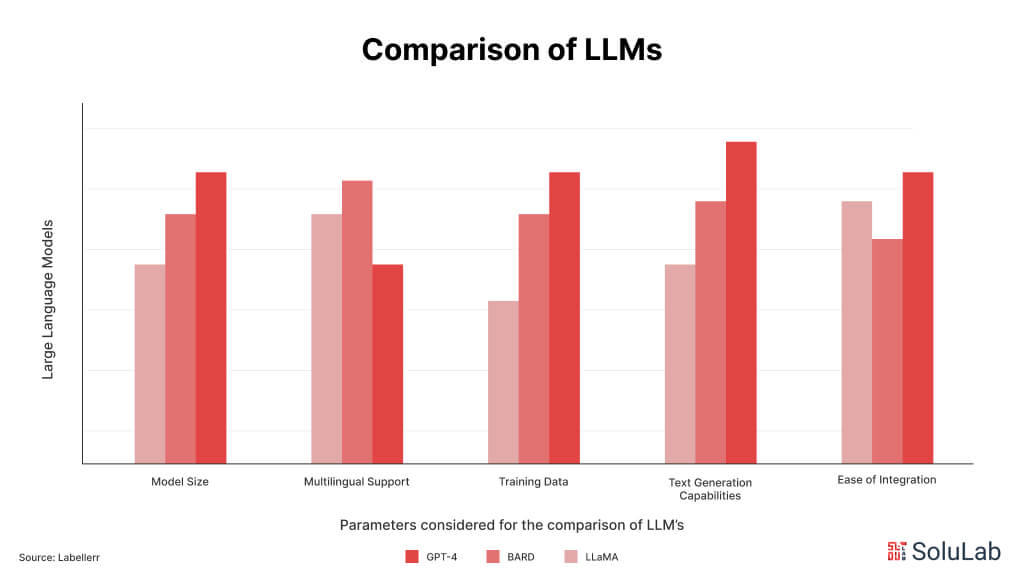
Generative AI chatbots have seen rapid growth in recent years, transforming industries from customer service to e-commerce with their ability to engage users in human-like conversations. By 2023, the global chatbot market was valued at approximately $5.7 billion and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.3% from 2023 to 2032. This surge in popularity is largely driven by advancements in large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4 and PaLM 2, which power these chatbots to provide more natural, context-aware responses.
As businesses increasingly adopt AI-driven customer interaction tools, generative AI chatbots are being deployed for everything from improving customer experience to automating sales and marketing. A recent report revealed that chatbot usage as a communication channel for brands surged by 92% between 2019 and 2020. In 2019, only about 11% of brands were using chatbots to engage with customers, but by 2020, this number had nearly doubled to 25%.
In this blog, we’ll explore the top 10 generative AI chatbots currently leading the market, highlighting their key features and applications across different sectors.
Importance of AI Chatbots in Various Industries
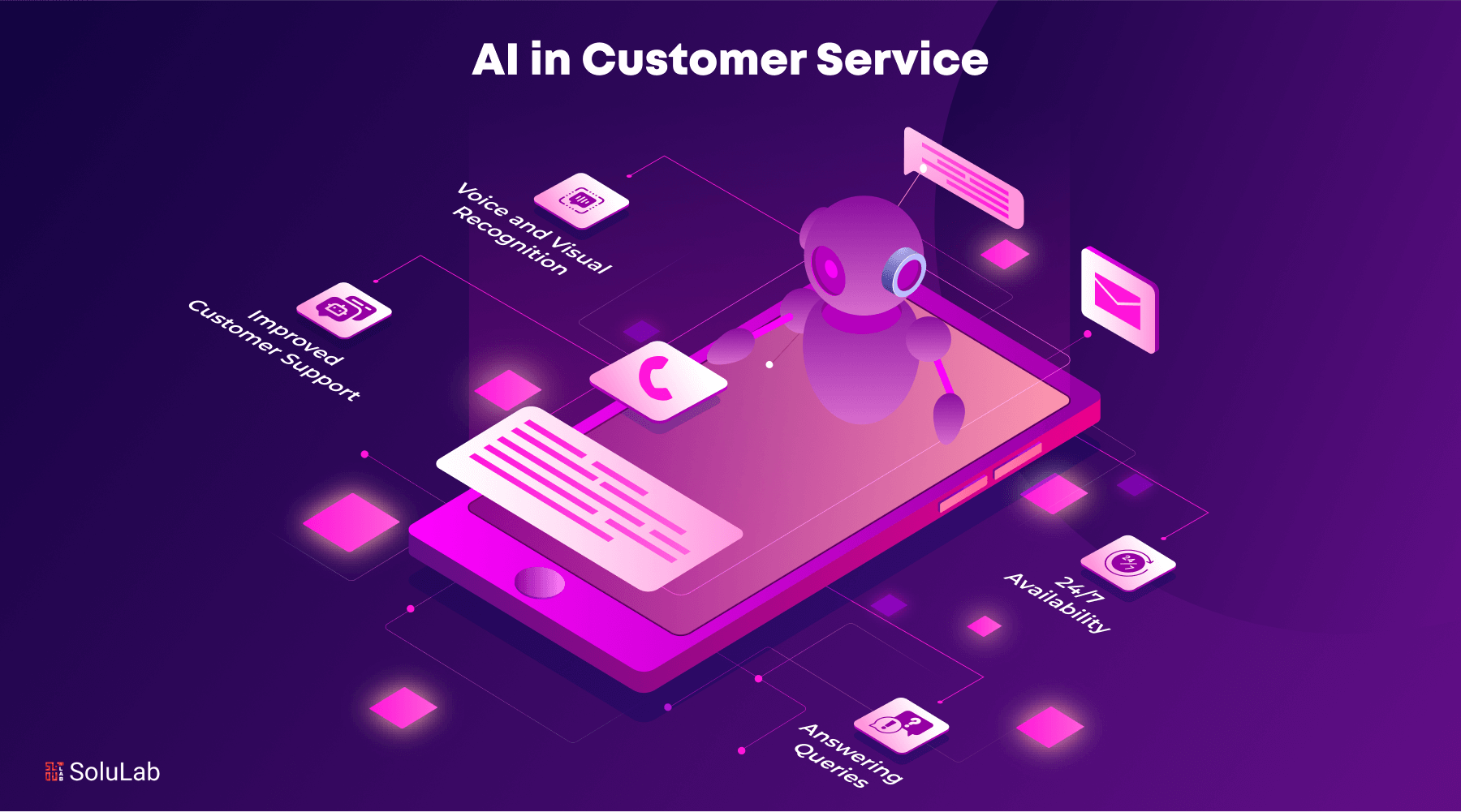
AI chatbots are revolutionizing how businesses interact with customers, providing faster, more efficient, and personalized experiences. In customer service, chatbots enable companies to respond to queries 24/7, significantly reducing response times and improving customer satisfaction. They handle routine tasks like answering FAQs, processing orders, or resolving common issues, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex interactions.
In e-commerce, chatbots guide users through product selection, offer personalized recommendations, and assist with checkout, leading to increased sales and reduced cart abandonment. Healthcare is another industry benefiting from AI chatbots, as they help patients schedule appointments, provide health advice, and even offer mental health support. The banking and finance sectors use chatbots for automating routine banking inquiries, managing transactions, and ensuring secure communication, enhancing customer experience and operational efficiency.
In education, AI chatbots facilitate personalized learning by offering study recommendations, answering course-related questions, and providing administrative support. Across these sectors and more, AI chatbots are transforming how businesses operate, increasing efficiency while enhancing customer engagement.
What is a Generative AI Chatbot?
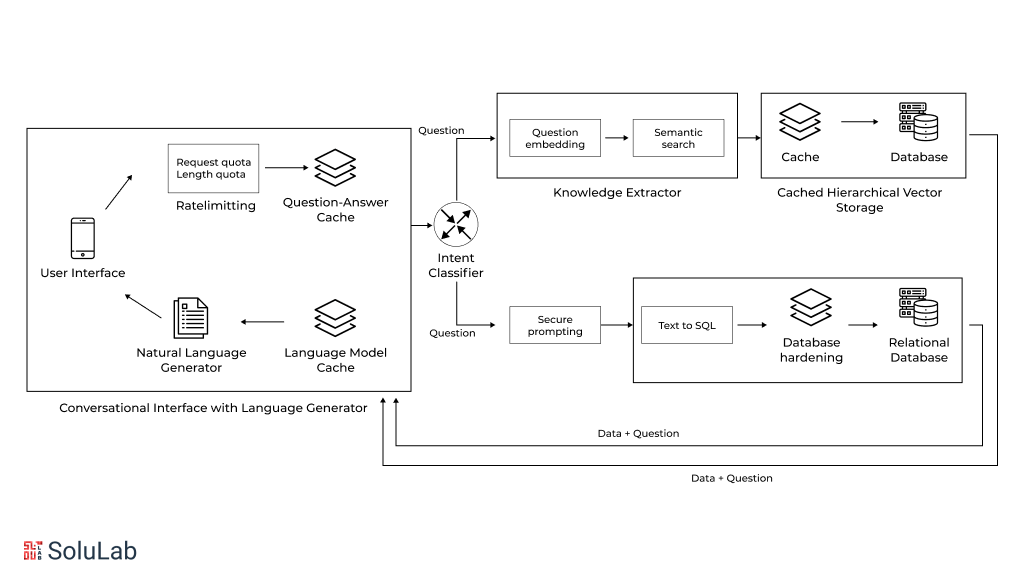
A generative AI chatbot is an advanced type of chatbot that uses artificial intelligence to generate human-like responses in real-time conversations. Unlike traditional chatbots, which rely on pre-programmed scripts and rule-based systems to provide responses, generative AI chatbots use large language models (LLMs) to understand and generate language dynamically. This allows them to engage in more natural, flexible conversations with users, responding to a wide variety of inputs in a meaningful way.
What sets top generative AI chatbots apart is their ability to generate context-aware, coherent responses without requiring predefined answers. They can handle more complex queries, offer personalized suggestions, and adapt their conversations based on the user’s intent. Traditional chatbots, on the other hand, are limited by a predefined set of responses, often leading to more robotic and less engaging interactions.
Generative AI chatbots, powered by LLMs such as GPT-4, PaLM 2, or LLaMA, leverage vast amounts of data to simulate human conversation. These models allow the best generative AI chatbots in 2026 to not only understand nuanced language but also predict and generate responses that feel more conversational and relevant. This makes them highly effective in customer service, sales, healthcare, and other industries that rely on efficient, human-like interactions.
Related: Customer Service Automation
Key Features of Generative AI Chatbot
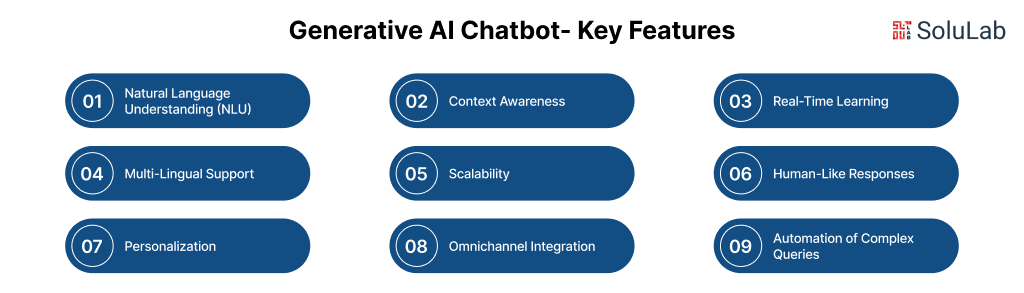
AI chatbots, particularly those powered by Generative AI, are transforming how businesses interact with customers by offering enhanced user experiences and operational efficiency. These chatbots go beyond traditional rule-based systems by utilizing advanced machine learning and large language models (LLMs) to generate human-like responses, providing more dynamic and personalized conversations.
Below are some key features that set Generative AI-powered chatbots apart:
-
Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
AI chatbots powered by Generative AI excel at understanding complex, nuanced language inputs. This allows them to provide accurate and relevant responses, making conversations more fluid and natural.
-
Context Awareness
These chatbots retain information from previous interactions, enabling them to provide contextually appropriate responses. This leads to more personalized and meaningful conversations with users.
-
Real-Time Learning
Generative AI chatbots learn and adapt from each user interaction in real-time. Over time, this allows them to improve their accuracy and relevance in responses, enhancing user satisfaction.
-
Multi-Lingual Support
With the ability to seamlessly switch between languages, AI chatbots can communicate with users in their preferred language. This makes them accessible to a global audience, broadening their application.
-
Scalability
Generative AI chatbots can handle multiple conversations simultaneously, maintaining high-quality interactions. This feature makes them ideal for businesses with large customer bases or high volumes of inquiries.
-
Human-Like Responses
By leveraging large language models, these chatbots generate responses that closely mimic human conversation. This leads to more engaging and relatable interactions with users.
-
Personalization
AI chatbots can tailor responses based on individual user preferences and past interactions. This personalized approach enhances user engagement and builds stronger relationships.
-
Omnichannel Integration
AI chatbots can seamlessly integrate with multiple platforms, including websites, messaging apps, and CRM systems. This allows businesses to provide a consistent communication experience across all channels.
-
Automation of Complex Queries
Generative AI chatbots are capable of handling complex queries without human intervention. This reduces the workload on human agents while improving response speed and accuracy for users.
Criteria for Choosing the Top Generative AI Chatbots
When selecting the best generative AI chatbots, there are several key factors to consider to ensure that the solution aligns with your business needs and delivers a seamless user experience. Here are the most important criteria for choosing the top generative AI chatbots:
-
Accuracy and Language Understanding
A top priority when choosing an AI chatbot is its ability to understand and respond accurately. The best generative AI chatbots are built on advanced language models that ensure context-aware conversations and high-quality responses, minimizing errors and misinterpretations.
-
Customization and Flexibility
The ability to customize the chatbot to fit specific business workflows and user requirements is essential. The top generative AI chatbots offer extensive customization options, allowing you to tailor responses, integrate with existing systems, and modify behaviors based on user interactions.
-
Integration Capabilities
Seamless integration with existing platforms and tools is critical for optimizing business processes. Look for chatbots that can easily integrate with CRM systems, websites, messaging apps, and customer support channels, enhancing the overall efficiency of your operations.
-
Natural and Conversational Flow
A smooth, human-like conversation flow is a hallmark of the best generative AI chatbots. The chatbot should be able to maintain engaging, context-aware conversations without appearing robotic, ensuring a positive user experience.
-
Scalability
Businesses often require chatbots that can scale as their customer base grows. The top generative AI chatbots are highly scalable and capable of handling increasing volumes of interactions without compromising performance or quality.
-
Security and Data Privacy
Protecting user data and maintaining privacy is non-negotiable. Ensure that the chatbot complies with industry security standards and data privacy regulations, especially when dealing with sensitive customer information.
-
Cost-Effectiveness
While high-quality AI chatbots can require significant investment, it’s essential to consider their long-term return on investment (ROI). The best generative AI chatbots deliver strong performance at competitive pricing, providing value while minimizing operational costs.
By evaluating these criteria, businesses can confidently choose the top generative AI chatbots that not only meet their needs but also deliver enhanced customer engagement and operational efficiency.
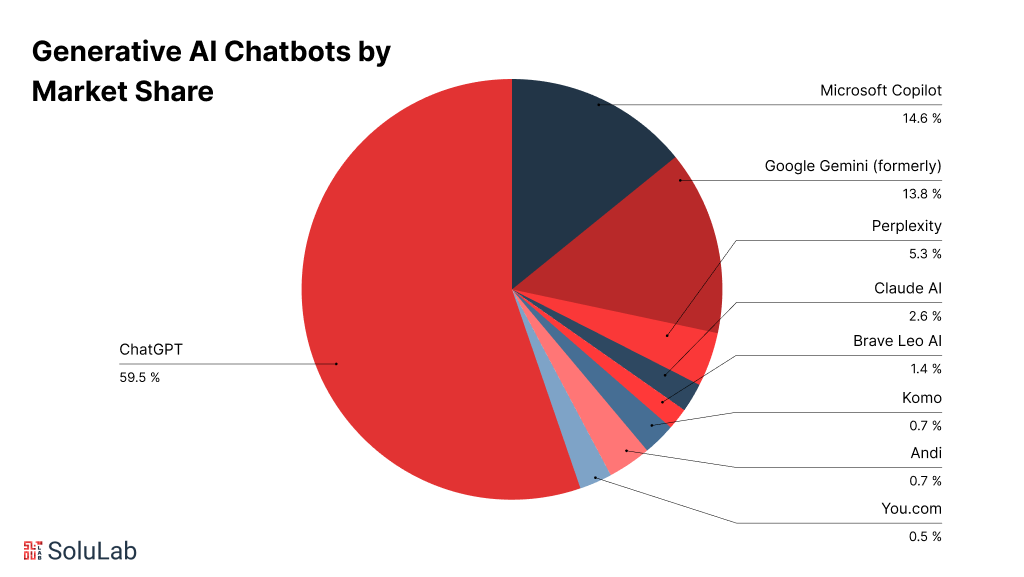
Interested? Here are the top 10 generative AI chatbots in 2026:
1. ChatGPT by OpenAI
One of the best generative AI chatbots in 2026, ChatGPT continues to be a dominant player in the industry, powered by OpenAI’s GPT-4 architecture. Known for its versatile language model, ChatGPT offers a wide range of applications from customer service to content generation. Its ability to generate context-aware, high-quality responses makes it a go-to solution for businesses looking for an intelligent and adaptable chatbot solution. With its extensive customization options and API support, ChatGPT has remained a leader in the top generative AI chatbot software landscape.
As a generative AI-powered chatbot, ChatGPT excels in conversation flow, maintaining human-like dialogues while understanding user inputs with precision. Its integration with business platforms and its ability to scale across various use cases make it highly efficient for enterprises. With continuous updates and enhancements, ChatGPT remains a prime example of the latest generative AI technology in chatbot development.
2. Bard by Google
Google’s Bard is a strong contender among the best generative AI chatbots in 2026. Leveraging Google’s extensive language models, Bard is designed to provide accurate, engaging, and informative responses, making it an ideal choice for businesses and consumers alike. Its intuitive interface and seamless integration with Google services allow for easy deployment and adaptation across multiple industries. Bard’s advanced AI capabilities ensure it can handle complex conversations, making it one of the top generative AI chatbot software options.
In addition to its strong natural language processing (NLP) capabilities, Bard excels in enhancing user experience through personalized interactions. Businesses using Bard can benefit from its smooth integration into customer service platforms, automating routine queries and improving response times. Bard’s continuous learning and language comprehension abilities are excellent examples of what generative AI chatbots can achieve.
3. Claude by Anthropic
Claude, developed by Anthropic, is another top-performing generative AI-powered chatbot making waves in 2026. It is specifically designed to handle safe and accurate conversations, focusing on reducing harmful outputs in chatbot interactions. Claude’s advanced model ensures robust comprehension of user input and a high level of accuracy in generating responses. It stands out as one of the top generative AI chatbot software for businesses focused on security and ethical AI use.
As an example of generative AI chatbots focused on responsible AI usage, Claude integrates well into business processes that prioritize data safety and trustworthy AI interactions. Its ethical design and strong performance make it a reliable choice for companies looking to deploy AI chatbots in sensitive industries such as healthcare, finance, and legal services.
4. Gemini by Google DeepMind
Google DeepMind’s Gemini is a powerful example of a generative AI-powered chatbot that excels in understanding and responding to complex user queries. Known for its multi-turn conversation handling, Gemini provides coherent, intelligent responses, making it suitable for customer support and other interaction-heavy use cases. It seamlessly integrates with Google’s ecosystem, which adds to its value for businesses using Google’s suite of products.
In 2026, Gemini has cemented its place as one of the best generative AI chatbots by offering exceptional language comprehension and the ability to generate creative content. It provides businesses with an adaptable and intelligent solution that’s easy to scale. Gemini’s strong integration options make it one of the most versatile chatbots available today.
5. Midu by Baidu
Baidu’s Midu is another top-tier chatbot among the best generative AI chatbots in 2026. Developed for both English and Chinese-speaking audiences, Midu is widely adopted in the Asian markets. It offers high-level language understanding and is designed to handle both simple and complex inquiries, providing accurate and concise responses. Its advanced machine-learning capabilities allow Midu to improve its interactions over time, which makes it an appealing choice for businesses looking for top generative AI chatbot software.
Midu’s standout feature is its capability to process multilingual conversations seamlessly, making it one of the most advanced generative AI chatbots available. With its strong focus on localization and multilingual capabilities, Midu is an excellent choice for global businesses seeking to improve customer interactions across different regions.
6. Mistral by Meta
Meta’s Mistral is a versatile generative AI-powered chatbot with a focus on enhanced contextual understanding and creative language generation. It’s well-suited for social media platforms and real-time interaction use cases, thanks to its ability to generate personalized and engaging conversations. As one of the best generative AI chatbots in 2026, Mistral is known for its efficiency in handling high volumes of data, making it a great fit for large-scale enterprise use.
What sets Mistral apart from other top generative AI chatbots is its ability to learn and adapt quickly to new trends and conversational nuances, particularly in dynamic environments such as e-commerce and social media. With continuous improvements and updates from Meta, Mistral is a reliable and future-proof solution for businesses looking for advanced chatbot technology.
7. Vivoka AI Assistant
Vivoka’s AI Assistant is a notable generative AI chatbot designed primarily for voice interaction. Its speech-to-text and natural language understanding features are highly advanced, making it a favorite for businesses requiring voice-activated customer service solutions. As one of the top generative AI chatbot software in 2026, Vivoka excels in voice-based applications, offering a smooth, human-like interaction experience.
Its integration with IoT devices and smart assistants is another strong point, allowing businesses to implement generative AI-powered chatbots across a range of platforms and technologies. Vivoka is ideal for businesses in the automotive, home automation, and hospitality sectors, where voice-driven interfaces are becoming the standard.
8. Replika
Replika is a unique generative AI chatbot designed to provide users with emotional and mental health support through conversations. As one of the best generative AI chatbots for personal use, Replika focuses on building long-term relationships with users through empathetic interactions. Its conversational abilities are not just limited to answering queries but also involve engaging users in deeper, more personalized conversations.
Replika stands out from other generative AI chatbot examples by focusing on well-being and emotional intelligence. It’s increasingly being used in industries like mental health and wellness, where conversational AI can support individuals in a non-judgmental, human-like manner. With its ability to understand emotional cues, Replika exemplifies the evolving potential of AI in providing emotional support.
9. Xiaoice by Microsoft
Xiaoice, developed by Microsoft, is another standout example among the top generative AI chatbots in 2026. Popular in China and Japan, Xiaoice specializes in creating emotionally engaging conversations with users, offering both text and voice interaction. It’s widely used in entertainment, customer engagement, and companionship applications. Xiaoice’s ability to handle multiple languages, including dialects, adds to its appeal in diverse markets.
As one of the most conversationally advanced generative AI chatbots, Xiaoice provides businesses with a tool that can significantly enhance user engagement. It’s particularly useful in industries such as entertainment and social media, where maintaining ongoing, meaningful dialogues with users is key to long-term engagement.
10. Dialogflow by Google Cloud
Dialogflow is one of the most flexible and customizable generative AI-powered chatbots in the market. Widely used in contact centers, e-commerce, and enterprise customer support, Dialogflow offers powerful NLP applications, and capabilities and supports multiple languages. It allows businesses to design highly personalized and efficient conversation flows, making it one of the best generative AI chatbots for large-scale operations.
With its strong integration capabilities within Google Cloud and other third-party services, Dialogflow is a comprehensive solution for businesses looking for top-tier AI chatbot software. It’s adaptable, scalable, and designed to handle complex user interactions, ensuring that enterprises can maintain high-quality customer support while automating routine processes.
How to Choose the Right AI Chatbot for Your Needs?
Selecting the best generative AI chatbot for your business requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure the solution aligns with your goals and enhances customer engagement. With so many options in the market, identifying the top generative AI chatbot software that suits your needs can be challenging. Here are some essential steps to guide you through the decision-making process:
-
Identify Your Use Case
Start by defining the purpose of the AI chatbot in your organization. Whether you need it for customer service, lead generation, or content creation, each use case may require different capabilities. For instance, if you need a chatbot for customer support, a solution with strong natural language processing (NLP) and multi-turn conversation abilities would be ideal. Identifying your goals will help you focus on the best generative AI chatbots that are tailored to those specific tasks.
-
Evaluate Language and Conversational Abilities
One of the most important criteria is the chatbot’s language understanding and generation capabilities. The top generative AI chatbot software excels at creating coherent, context-aware, and human-like conversations. Look for a chatbot with advanced NLP that can handle diverse queries and adapt to different conversational tones. This will ensure smooth, engaging interactions with users, enhancing the overall experience.
-
Customization and Integration
Choose a chatbot that can be easily customized to suit your business processes and branding. The ability to modify conversation flows, and responses, and integrate the chatbot into your existing systems is critical for ensuring it fits seamlessly within your organization. The best generative AI chatbots offer strong API support and can integrate with CRM systems, websites, social media platforms, and other business tools to streamline operations.
-
Scalability and Performance
As your business grows, so will the demand for your AI chatbot. The top generative AI chatbots are designed to scale effortlessly, managing large volumes of interactions without sacrificing performance. Ensure that the chatbot you choose can handle increased demand, offering quick response times and high reliability, especially during peak usage.
-
Security and Compliance
Data privacy and security are essential when deploying AI chatbots, especially in industries like finance, healthcare, and legal services. Ensure the chatbot adheres to industry standards and compliance regulations such as GDPR. The best generative AI chatbot software prioritizes data security, offering encryption and secure storage of user information to protect sensitive data.
-
Cost and ROI
While price should not be the only factor in your decision, it’s important to consider the long-term return on investment (ROI). Compare the features and pricing of different chatbots, and evaluate how well the solution will meet your business needs while keeping operational costs in check. The best generative AI chatbots deliver both high performance and cost-effectiveness, ensuring you get value from your investment over time.
By following these steps, you can choose the right AI chatbot that not only meets your business needs but also enhances productivity and user experience.
How SoluLab Can Help in Generative AI Technology?
SoluLab offers comprehensive solutions in generative AI technology that empowers businesses to innovate and automate complex processes. Whether it’s building intelligent chatbots, automating content creation, or generating personalized experiences, our team of experts specializes in developing tailored generative AI-powered solutions that align with your unique business needs. Leveraging the latest advancements in AI, we ensure that your systems are equipped to handle high-level tasks, offering seamless integration, scalability, and top-tier performance.
With a proven track record in delivering AI-driven innovations across industries, SoluLab provides end-to-end support from consulting and strategy to implementation and post-launch maintenance. By collaborating with us, you’ll gain access to the latest technology that enhances productivity and transforms customer engagement. Ready to unlock the full potential of generative AI technology? Contact us today to discuss how we can drive your business forward.
FAQs
1. How do generative chatbots work?
Generative chatbots use large language models (LLMs) like GPT to generate human-like responses based on user input. They utilize natural language processing (NLP) to understand context, predict the next words, and provide relevant answers. These chatbots learn from vast datasets, allowing them to handle diverse conversations without predefined scripts.
2. What is the most powerful AI chatbot right now?
As of 2024, ChatGPT-4 by OpenAI and Claude 3 by Anthropic are considered the most powerful AI chatbots, known for their advanced conversational abilities, contextual understanding, and adaptability across various applications like customer service and content generation.
3. What is the market share of generative AI in 2024?
The generative AI market in 2024 is valued at around $40 billion, driven by growing adoption across industries like healthcare, finance, and e-commerce. Its rapid expansion is attributed to the increasing demand for AI-driven automation and personalized experiences.
4. Which AI is better than ChatGPT?
Claude 3 by Anthropic is considered a strong competitor to ChatGPT, offering improved safety, alignment with user goals, and nuanced conversational abilities. Other contenders include Google’s Gemini and Meta’s LLaMA 2, which also excel in various applications.
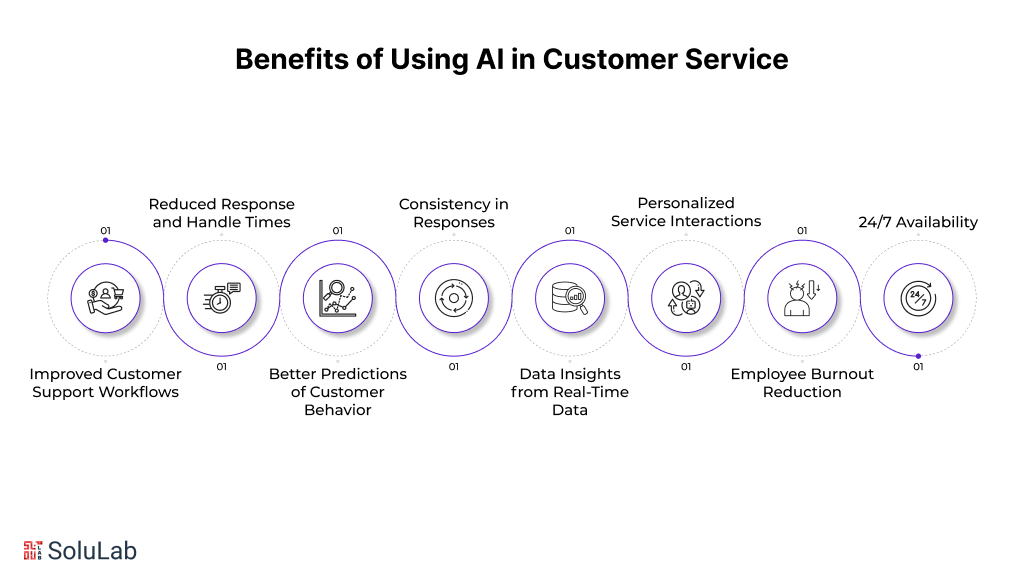
5. What are the benefits of using AI chatbots?
AI chatbots enhance customer service by providing 24/7 support, reducing response times, and automating repetitive tasks. They improve user engagement, cut operational costs, and deliver personalized experiences, boosting overall business efficiency.