- AI Development
- AI App Development
- AI Consulting
- AI Software Development
- ChatBot Development
- Enterprise AI ChatBot
- AI Chatbot Development
- LLM Development
- Machine Learning Development
- AI Copilot Development
- MLOps Consulting Services
- AI Agent Development
- Deep Learning Development
- AI Deployment Services
- Deep Learning Consulting
- AI Token Development
- AI Development Company
- AI Development Company in Saudi Arabia
- AI Integration Services
- Hire Blockchain Developers
- Hire Full Stack Developers
- Hire Web3 Developers
- Hire NFT Developers
- Hire Metaverse Developers
- Hire Mobile App Developers
- Hire AI Developers
- Hire Generative AI Developers
- Hire ChatGPT Developers
- Hire Dedicated Developers
- Hire Solana Developer
- Hire OpenAI Developer
- Hire Offshore Developer
- About Us
- Networks+
- Smart Contracts +
- Crypto currency +
- NFT +
- Metaverse +
- Blockchain+
- Mobile Apps +
- WEB +
- Trending +
- Solutions +
- Hire Developers +
- Industries +
- Case Studies
- Blogs
The combination of work and technology is growing, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence. As businesses and organizations seek to harness the power of AI to increase productivity and efficiency, the development of AI agent systems has become a crucial focus. With the potential to automate a significant portion of tasks—indeed, two-thirds of jobs could be partially automated by AI—these systems are set to transform industries. However, rather than completely replacing human roles, many of these jobs will be complemented by AI, allowing human workers to focus on more complex and creative aspects of their work.
In recent years, the AI industry has witnessed explosive growth. The global AI market size, which was close to $208 billion in 2023, is projected to surge to nearly $2 trillion by 2030. This expansion reflects the increasing integration of AI technologies across various sectors. This shift highlights the importance of developing AI agent systems that can seamlessly work alongside human teams, optimizing performance and driving innovation.
In this blog, we will learn the process of building an AI agent system, exploring key considerations that can help you experience this technology to its fullest potential.
What is an AI Agent?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents are software systems programmed to execute tasks autonomously. They make decisions based on their programming and the data they ingest. AI agents can be as simple as repetitive task-performing programs or as sophisticated as machine learning systems that learn and adapt over time through the application of machine learning algorithms.
AI agents find applications in various sectors. In customer service, they manage chat interfaces, providing automated responses. In healthcare, they assist in patient management by scheduling appointments and reminding patients about medication intake. In finance, AI agents monitor markets, execute trades at optimal times, and maximize profits.
In the corporate context, agents in AI are now considered the most reliable helping hand that businesses can use to perform mundane jobs that consume 62% of a workday.
Artificial agents offer businesses a valuable opportunity to optimize their workforce by handling tasks such as customer inquiries, data analysis, and standardized actions, thereby freeing up human employees for more complex and creative tasks.
The effectiveness of AI agents depends on their design, the quality of accessible data, and the efficiency of employed algorithms. Their versatility and value make them indispensable in different industries, enhancing efficiency and aiding in sound decision-making. A Twitter user named Patrick Dougherty has defined AI agents like:
It is equally important to highlight that an AI agent is not:
- Scripted: Agents do not follow a pre-defined sequence of steps or tool calls. Instead, they are responsible for choosing the right tool call to make next.
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): Agents are not AGI. An AGI would not need agents for specific types of work because it would be a single entity with access to all possible inputs, outputs, and tools. Current technology is far from reaching this level of intelligence.
- Black Box: Agents should demonstrate their work in a manner similar to how a human would if delegated tasks. Transparency and accountability are crucial in understanding and evaluating agents’ actions.
Types Of AI Agents
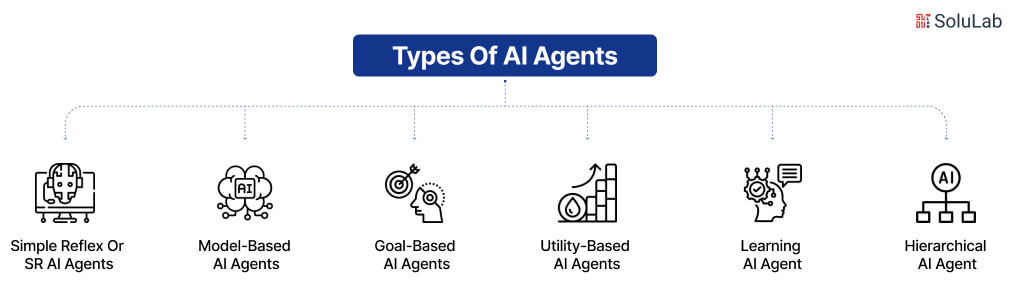
Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents have came up as game-changers in various industries, automating repetitive tasks, optimizing workforce efficiency, and enhancing decision-making. These software systems are designed to execute tasks autonomously based on their programming and data ingestion. AI agents can range from simple task-performing programs to sophisticated machine learning systems that learn and adapt over time.
1. Simple Reflex or SR AI Agents
Artificial intelligence (AI) agents are computer programs that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence. AI agents are becoming increasingly prevalent in various industries, including business, healthcare, and finance. Among the different types of AI agents, Simple Reflex (SR) agents are some of the most common and widely used.
SR agents operate based on condition-action rules, which means they take a specific action when a certain condition is met. These rules are typically defined by human experts or derived from data. SR agents are relatively easy to develop and implement, making them accessible to businesses of all sizes.
An SR agent consists of several components:
- Agents: These are the responsible AI entities for making decisions and taking actions.
- Actuators: These are the components that allow the agent to interact with its environment, such as motors, wheels, or speakers.
- Sensors: These are the components that allow the agent to perceive its environment, such as cameras, microphones, or temperature sensors.
- Environment: This is the physical or virtual world in which the agent operates.
One of the key advantages of SR agents is their ability to discard historic precepts while making decisions. This means that they can make decisions based solely on the current situation, without being influenced by past events. This can be particularly useful in dynamic environments where the conditions can change rapidly.
Here are some examples of how SR agents are being used in businesses today:
- Customer service chatbots: These chatbots can answer customer questions, provide product recommendations, and resolve complaints. They are typically trained on a large dataset of customer interactions.
- Fraud detection systems: These systems can identify potentially fraudulent transactions by analyzing purchase patterns and other data. They are often used by banks and credit card companies.
- Inventory management systems: These systems can track inventory levels and reorder products when necessary. They are used by businesses of all sizes to ensure they have the products their customers want in stock.
Read Also: AI Agent Development on Azure
2. Model-Based AI Agents
Model-based AI agents are a type of AI agent that is known for making quick, rules-driven decisions by incorporating a deeper understanding of the surroundings. These agents are able to do this because they maintain a model of the world in their memory, which they use to reason about the best course of action. One of the key advantages of model-based AI agents is that they are able to learn from their experiences. As they encounter new situations, they update their model of the world to reflect the new information. This allows them to make better decisions in the future, as they are able to take into account the lessons they have learned from the past.
Another advantage of model-based AI agents is that they are able to handle complex tasks. This is because they are able to use their model of the world to reason about the different ways that a task can be completed. This allows them to choose the best course of action, even when the task is complex or unfamiliar. However, One disadvantage is that they can be computationally expensive to run. This is because they need to maintain a model of the world in their memory, which can be a large and complex data structure. Another disadvantage is that model-based AI agents can be brittle. This means that they can make poor decisions if their model of the world is inaccurate.
Here are some specific examples of how model-based AI agents can be used:
- Self-driving cars: Model-based AI agents can be used to help self-driving cars navigate their environment. The agents can use their model of the world to identify obstacles, such as other cars, pedestrians, and traffic signs. They can then use this information to make decisions about how to navigate around the obstacles safely.
- Robotics: Model-based AI agents can be used to help robots perform complex tasks, such as assembling products or cleaning up a room. The agents can use their model of the world to understand the environment and the task that needs to be completed. They can then use this information to plan and execute a sequence of actions that will complete the task.
- Healthcare: Model-based AI agents can be used to help doctors diagnose diseases and develop treatment plans. The agents can use their model of the human body to understand the symptoms of a disease and the different ways that it can be treated. They can then use this information to make recommendations about the best course of treatment for a patient.
3. Goal-Based AI Agents
Goal-based agents are a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that businesses can develop to meet specific objectives. These agents use decision-making algorithms to understand the best course of action based on the information they have learned from their surroundings. One of the best use cases for goal-based agents is to predict future trends. These agents can analyze large amounts of data to identify patterns and relationships that may indicate future events. This information can be used to make informed decisions about product development, marketing, and other business strategies.
Another use case for goal-based agents is to promote optimized resource allocation. These agents can help businesses identify the most efficient way to use their resources, such as time, money, and personnel. This can lead to significant cost savings and improved productivity.
Goal-based agents can also be used for automated designing. These agents can generate creative and innovative designs based on the input they receive. This can save businesses time and money by eliminating the need for human designers. Goal-based agents can be used for personalized marketing. These agents can track individual customer behavior and preferences to create targeted marketing campaigns. This can lead to increased sales and improved customer satisfaction.
Examples of Goal-based agents:
- Virtual Personal Assistant: A virtual personal assistant, like Amazon’s Alexa or Google Assistant, is a goal-based agent that aims to assist users with their daily tasks. Its goals include; Answering user queries, Setting reminders and calendar events, Controlling smart home devices, Playing music or videos
- Autonomous Vehicle: An autonomous vehicle, like Waymo or Tesla’s Autopilot, is a goal-based agent that aims to transport passengers safely and efficiently. Its goals include; Reaching the destination, Avoiding obstacles and collisions, Following traffic rules and regulations, Optimizing route planning
- Customer Service Chatbot: A customer service chatbot, like those used in e-commerce or banking, is a goal-based agent that aims to resolve customer inquiries and issues. Its goals include; Answering customer questions, Resolving customer complaints, Providing product recommendations, Routing complex issues to human representatives
4. Utility-based AI Agents
Utility-based AI agents are highly sophisticated artificial intelligence agents capable of making decisions based on a specific value or utility function. They are designed to make the most advantageous choices for predefined tasks or utilities, such as resource allocation and strategic planning. Their unique ability to ensure optimal decision-making at each repeated step sets them apart from other AI agents. One of the key strengths of utility-based AI agents is their ability to handle a wide range of problems. They can be applied to various domains, including finance, healthcare, and manufacturing. In each of these domains, utility-based AI agents can provide valuable insights and recommendations to help humans make better decisions.
Another advantage of utility-based AI agents is that they offer an objective framework for decision-making. Unlike human decision-makers, utility-based AI agents are not influenced by personal biases or emotions. This objectivity can lead to more rational and consistent decisions. However, it’s important to note that utility-based AI agents are not without limitations. One of the main challenges with utility-based AI agents is that they require additional oversight. This is because utility-based AI agents can only make decisions based on the information they are given. If the information is incomplete or inaccurate, the agent’s decisions may not be optimal. Additionally, utility-based AI agents can be computationally expensive. This is because they often require a large amount of data and processing power to make decisions. This can make them impractical for use in real-time applications.
Here are examples of utility-based agents:
- Recommendation System: A recommendation system, like Netflix or Amazon’s product recommendations, is a utility-based agent that aims to suggest items that maximize the user’s satisfaction. Its utility function includes; User preferences and ratings, Item attributes and features, and Contextual information (e.g., time of day, location).
- Resource Allocation Agent: A resource allocation agent, like a cloud computing resource manager, is a utility-based agent that aims to allocate resources to maximize efficiency and minimize costs. Its utility function includes; Resource availability and demand, Task priorities and deadlines, and Cost and performance metrics.
- Portfolio Optimization Agent: A portfolio optimization agent, like a financial investment manager, is a utility-based agent that aims to optimize investment portfolios to maximize returns and minimize risk. Its utility function includes; Asset prices and returns, Risk tolerance and constraints, Diversification, and portfolio metrics
5. Learning AI Agent
In artificial intelligence (AI), learning AI agents have emerged as powerful tools for knowledge acquisition and feedback provision. Equipped with sensors that enable them to observe their surroundings, these agents employ advanced algorithms to analyze collected data and make informed decisions. The four fundamental components of a learning agent in AI are:
- Learning: This component is responsible for acquiring new knowledge and updating the agent’s existing knowledge base. It enables the agent to continuously improve its performance over time.
- Critic: The critic component evaluates the agent’s performance and provides feedback. This feedback helps the agent identify areas for improvement and refine its strategies.
- Performance: The performance component is responsible for executing actions based on the knowledge acquired by the learning component and the feedback provided by the critic component.
- Problem Generator: This component generates new problems or challenges for the agent to solve. This helps the agent develop a more robust and versatile knowledge base.
Learning artificial intelligence agents offer significant benefits to businesses. As they can evolve with time and effortlessly convert ideas into actions, they can be leveraged to gain valuable insights into customers’ past experiences and evaluate past performance. This information can be instrumental in making informed decisions and developing effective strategies. However, developing and maintaining learning AI agents can be a resource-intensive endeavor. It requires specialized expertise, advanced infrastructure, and significant investment. To mitigate these challenges, businesses can seek the assistance of AI agents consulting services. These services offer a range of expertise, from software development to deployment and maintenance, enabling businesses to optimize their AI agent development costs.
Here are examples of intelligent agents:
- AlphaGo: A computer program that learned to play the game of Go at a world-class level by using a combination of machine learning and tree search algorithms. AlphaGo learned from a large dataset of human games and improved its performance through self-play and reinforcement learning.
- Netflix Recommendation System: A learning agent that uses collaborative filtering and machine learning algorithms to recommend movies and TV shows to users based on their viewing history and preferences. The system learns from user behavior and adapts its recommendations over time.
- Autonomous Vehicle: A self-driving car that uses a combination of sensors, mapping data, and machine learning algorithms to navigate roads and avoid obstacles. The vehicle learns from experience and adapts to new situations through reinforcement learning and deep learning techniques.
Read Also: How Businesses in Every Industry Are Benefiting from AI Agents?
6. Hierarchical AI Agent
Hierarchical agents in AI represent a sophisticated approach to creating intelligent systems capable of handling complex tasks and making informed decisions. These agents are not merely individual AI entities but rather a structured network of multiple AI agents working together in a hierarchical manner. At the core of hierarchical agents is the concept of a top-level AI agent. This agent serves as the central authority, overseeing the operations of other AI agents within the hierarchy. Its primary responsibility is to coordinate and manage the overall workflow, ensuring that all subtasks are executed efficiently and effectively. The lower-level AI agents, on the other hand, are specialized in specific tasks or domains. They operate under the guidance of the top-level agent, carrying out assigned tasks and reporting their progress.
This division of labor allows hierarchical agents to handle complex problems by breaking them down into smaller, manageable subtasks. One of the key benefits of hierarchical agents is their ability to coordinate between different interlinked departments or modules within a system. Each department or module can be represented by an AI agent, and the top-level agent acts as a central hub for communication and coordination. This enables seamless information exchange and decision-making across various functional areas. Additionally, hierarchical agents are equipped with the ability to identify and address operational bottlenecks. By analyzing data and monitoring the performance of lower-level agents, the top-level agent can detect potential issues that could hinder the overall efficiency of the system. It can then take appropriate actions, such as reallocating tasks or adjusting resource allocation, to mitigate these bottlenecks.
- Autonomous Robot: A robot that uses a hierarchical control system to perform tasks such as assembly, navigation, and manipulation. The hierarchy consists of; Low-level control: sensorimotor control, and motor control, Mid-level control: task planning, and motion planning, High-level control: goal planning, decision-making
- Smart Home System: A smart home system that uses a hierarchical AI agent to control and optimize various subsystems such as; Low-level control: temperature control, lighting control, Mid-level control: energy management, security monitoring, High-level control: user preference learning, smart automation
- Drones for Search and Rescue: A drone that uses a hierarchical artificial intelligence agent to perform search and rescue operations in disaster scenarios. The hierarchy consists of; Low-level control: sensor processing, flight control, Mid-level control: obstacle avoidance, path planning, High-level control: mission planning, decision-making
Forms of AI Agents
In this section, we will discuss the three primary categories of AI agents:
- Single AI Agent: Designed to handle specific task scenarios tailored to user needs.
- Multi-AI Agents: Collaborate with other AI agents, making decisions and taking actions based on mutual communication.
- Hybrid AI Agent: A high-end category that combines human and computer interaction for decision-making. These agents are capable of performing complex professional activities.
How Does An Agent Work?
To create autonomous agents, it’s essential to imitate human cognitive functions and plan task execution strategically. LLM agents can break down complex and intricate tasks into smaller, more manageable parts during this phase. Additionally, these agents can reflect on themselves and learn from previous actions and errors, leading to improved future performance and outcomes.
Let’s start by defining an agent as a software program that carries out tasks on behalf of a user. The ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to emulate human-like cognitive processes opens up new possibilities for tasks that were previously difficult or impossible.
At its core, an LLM-based agent is a program that combines ChatGPT with a text interface capable of executing tasks like document summarization.
The concept of “agent orchestration” introduces a higher level of complexity. For example, two specialized agents could work together on your code—one focusing on code generation and the other on code review. Alternatively, you could enhance an agent with a tool like an API that provides access to internet search. Or you could improve an agent’s intelligence and reliability by providing additional context through techniques like Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG).
The most advanced agents are called “autonomous.” These are programs capable of handling sequential tasks, iterating, or pursuing objectives with minimal or no human intervention. Consider fraud detection—an autonomous agent can adapt its behavior to identify intricate and evolving patterns of fraud, significantly reducing false positives and ensuring legitimate transactions are not mistakenly flagged as fraudulent. It can also detect and prevent fraud in real time by determining the appropriate actions to take, thereby saving both time and resources.
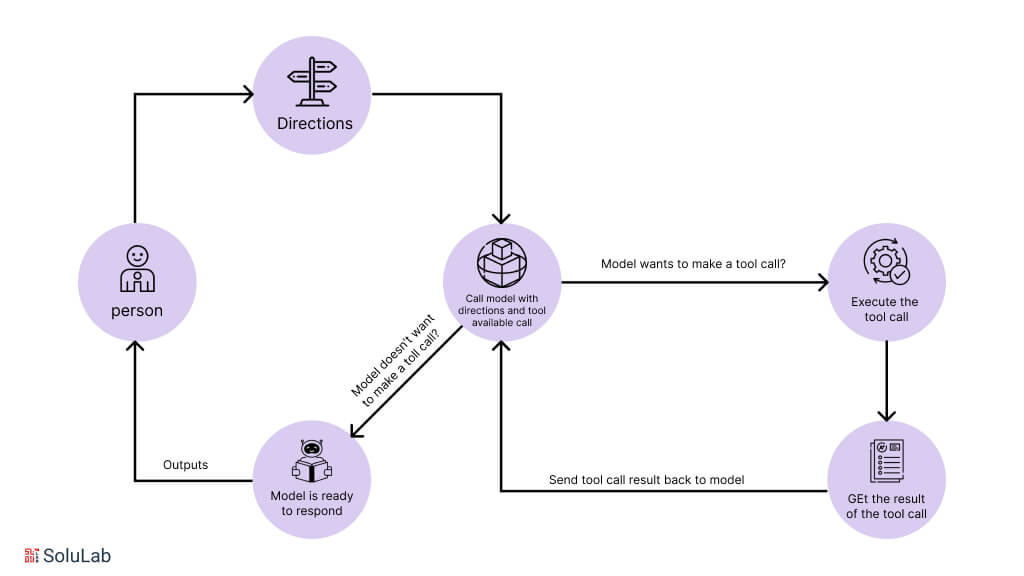
The included diagram illustrates a basic framework of an autonomous agent that processes inputs from users or triggers from applications.
The autonomous agent consists of specialized agents that work together. The observer agent assesses incoming information, adds context, and stores it in memory or adds it to a task queue. A task to investigate potential fraud is created when a second transaction within a short time frame and across different continents occurs. The prioritization agent evaluates and ranks the task, and the execution agent carries out the tasks. The execution agent can access additional context and utilize tools to access external services and interact with the customer.
Environments Where AI Agents Can Work Seamlessly
Prior to hire AI developer and entrusting them with the task of constructing fully customized AI-powered agents, it’s crucial to gain an understanding of the operational environments in which these agents can excel.
1. AI agents can seamlessly operate in virtual environments that mimic real-world scenarios, making them ideal for training and testing tasks.
2. Equipped with sensors, microphones, lidar, and actuators, AI agents excel in physical settings like warehouses, hospitals, airports, and factories.
3. In the retail sector, AI agents can monitor sales, adjust product prices, personalize promotions, notify customers, and analyze customer purchasing patterns.
4. AI agents in the travel industry can assist with trip planning, suggest destinations, optimize itineraries based on budget, and interact with customers in virtual and text-based environments.
5. Advanced AI development techniques enable businesses to create AI agents that perform accurately in various in-game environments, including video games, casino games, and mobile games. They can design game rules, assess player performance, and create diverse game objectives.
6. Social media platforms, such as dating apps, online communities, Facebook, and Twitter, can utilize AI agents to interact and collaborate with humans and other agents.
The finance industry can use autonomous AI agents to analyze stock prices, customer transactions, market risks, and investments, and identify potential threats.
How To Build An AI Agent System?
In artificial intelligence, agents are software entities designed to perceive their surroundings and make decisions and actions based on defined rules or algorithms. These agents encompass a spectrum of complexity, from simple reflex agents that respond to immediate inputs to goal-based agents that plan and act toward future outcomes. The most advanced, learning agents, possess the ability to adapt their behavior based on past experiences, akin to how humans learn from mistakes.
The power of agents lies in their capability to automate intricate tasks, make intelligent choices, and interact with their environment in a manner that mirrors human intelligence. The remarkable aspect is that anyone has the potential to create these agents. By harnessing AI agents, a world of possibilities unfolds, allowing for the development of systems that are not only efficient and effective but also capable of continuous learning, adaptation, and evolution.
While creating complex agents might require specialized knowledge, starting on the journey with simple agents provides an excellent opportunity to grasp and progress in this captivating field. The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has significantly propelled the development of autonomous agents, leading to the introduction of numerous technologies and frameworks based on this concept. Among these advancements, We hope you’ve gained a solid understanding of the capabilities and potential of artificial agents in AI. As you progress on your journey, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamentals of creating an AI agent tailored to your specific tasks and requirements. Here is a quick overview of building an AI agent:
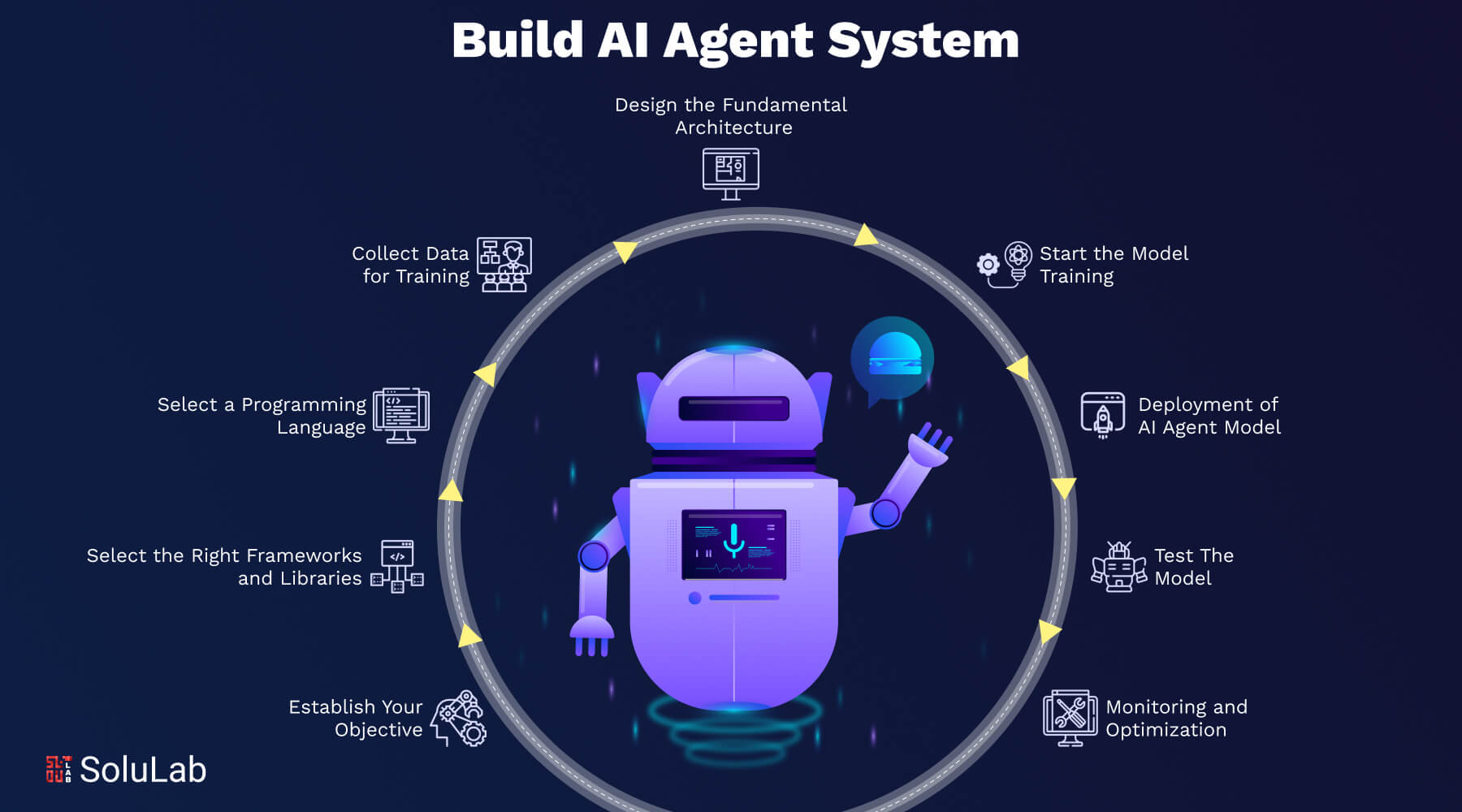
1. Establish Your Objective
To commence the development of AI agents, it is crucial for businesses to have a clear understanding of the purpose and objectives behind their implementation. Before embarking on the journey, it is essential to determine the specific needs and requirements of the AI agent.
Consider the following questions:
a. What are the key tasks that you need the AI agent to perform?
Do you need it to sort and categorize documents, handle customer queries, generate insights from data, or perform other specific functions? Identifying the core responsibilities of the AI agent will help guide the development process.
b. What is the desired outcome or goal of using an AI agent?
Do you aim to enhance efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, automate repetitive tasks, or achieve other specific objectives? Clearly defining the desired outcome will help measure the success of the AI agent.
c. What data sources will the AI agent leverage?
Identify the sources of data that the AI agent will use to learn and make decisions. This could include structured data from databases, unstructured data from emails and documents, or real-time data from sensors and IoT devices.
d. What level of autonomy is required?
Determine the extent to which the AI agent should operate independently. Will it make decisions and take actions on its own, or will it require human oversight and approval?
e. What are the ethical considerations and regulatory requirements?
Consider the ethical implications and regulatory requirements associated with the use of AI agents. Ensure that the AI agent is designed and developed in a responsible and compliant manner.
If you are having difficulty clarifying the purpose and objectives of the AI agent, it is advisable to seek the assistance of an AI consulting company. These services can provide valuable guidance and expertise, helping you define the scope, identify potential challenges, and develop a comprehensive strategy for the successful implementation of your AI agent.
2. Select the Right Frameworks and Libraries
Training a fundamental AI model to process data and make decisions is a complex task that requires careful consideration of the framework and libraries used. The right tools can streamline the development process, enable faster prototyping, and improve the overall efficiency of the AI model. One of the leading technologies for AI development is TensorFlow. TensorFlow is an open-source machine learning framework developed by Google Brain. It is widely used for a variety of AI tasks, including natural language processing, computer vision, and reinforcement learning. TensorFlow provides a comprehensive set of tools and features that make it easy to build and train AI models.
Another popular technology for AI development is PyTorch. PyTorch is an open-source machine learning framework developed by Facebook AI Research. PyTorch is known for its flexibility and ease of use. It is often used for research and prototyping AI models. PyTorch provides a dynamic computational graph that allows for easy experimentation and debugging. Keras is a high-level neural networks API, written in Python, that can run on top of TensorFlow or Theano. It is designed to make building and training deep learning models easier and faster. Keras provides a user-friendly interface and a wide range of features for building and evaluating neural networks. These tools and frameworks are essential for developing different types of AI agents, including reactive agents, goal-based agents, and learning agents, each suited for various AI applications.
3. Select a Programming Language
Programming languages play a vital role in the development of artificial intelligence (AI) agents. They provide the means to implement complex algorithms and leverage specialized libraries and frameworks that facilitate the creation of AI models. One of the most popular programming languages for AI development is Python. Python’s popularity can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, it is a high-level language, which means that it is easy to read and write, making it accessible to developers of all skill levels. Secondly, Python is highly versatile and can be used for a wide range of AI applications, including natural language processing, machine learning, and computer vision.
Python has a large and active community, which contributes to its extensive library of open-source tools and frameworks. This makes it easier for AI developers to find and use pre-built components, saving time and effort. Additionally, Python is compatible with popular AI libraries such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Keras, enabling seamless integration and collaboration with these frameworks. The simplicity and ease of use of Python make it an ideal choice for rapid prototyping and experimentation. This allows AI developers to quickly test and validate their ideas and iterate on them efficiently. Additionally, Python’s extensive documentation and tutorials make it easy for developers to learn and apply the language effectively. When exploring AI agents use cases, Python’s versatility becomes even more evident, as it supports various applications, from chatbots to autonomous systems, highlighting its crucial role in AI development.
4. Collect Data for Training
In artificial intelligence (AI), your agents rely heavily on data for processing and analysis. The quality of this data plays a pivotal role in effectively training machine learning models, ultimately determining the accuracy and dependability of your AI agents. Therefore, collecting high-quality data is of paramount importance. There are various methods you can employ to gather suitable data. Crowdsourcing, for instance, involves obtaining data from a large group of people, often through online platforms. This approach can yield a diverse and extensive dataset but may come with challenges related to data consistency and reliability. Alternatively, you can utilize off-the-shelf datasets, which are readily available and often well-curated. However, it’s crucial to assess the quality and relevance of such datasets to your specific AI application. AI agents use cases highlight how these data-driven systems excel in tasks such as fraud detection, personalized recommendations, and autonomous vehicle navigation, all of which depend on high-quality data inputs.
Regardless of the data collection method, ensuring the data’s quality is paramount. Here are some key characteristics of high-quality data:
- High Quality: The data should be accurate, complete, and consistent. This means it should be free from errors, missing values, and inconsistencies. High-quality data leads to more accurate and reliable AI models.
- Unbiased: The data should not be biased towards any particular outcome or group. Unbiased data ensures that your AI models are fair and equitable.
- Error-free and Well-cleaned: The data should be cleaned and processed to remove any errors or inconsistencies. This process involves identifying and correcting data entry mistakes, removing duplicate data points, and handling missing values. Clean and error-free data leads to more efficient and effective AI models.
Achieving high-quality data can be a tedious and highly skill-demanding task. If you lack the resources or expertise to handle this process effectively, consider outsourcing to professional data science services. These service providers specialize in collecting, cleaning, and preparing data for AI and machine learning applications.
5. Design the Fundamental Architecture
Designing a powerful AI Agent Architecture involves key considerations such as scalability, modularity, performance optimization, openness for integration, resilience, security, privacy, and ethical considerations. Scalability enables handling increasing data and computational demands. Modularity allows for easy maintenance and updates. Performance optimization involves leveraging parallel processing and specialized hardware. Openness for integration ensures seamless communication between components. Resilience protects against failures and errors. Security safeguards against unauthorized access and data breaches. Privacy mechanisms protect sensitive data and user information. Ethical considerations ensure responsible and transparent AI operations. For better understanding, AI agents examples include autonomous drones, intelligent virtual assistants, and predictive analytics tools, all designed to operate efficiently within robust architectures that account for these considerations.
6. Start the Model Training
Once adequate data is collected and the basic architecture of the AI agent application is ready, the next crucial step is to train the model. This training process is where the AI agent learns to make decisions and perform tasks. AI developers engage in various activities during this stage to ensure the model’s effectiveness. One key task is data feeding, where the model is provided with labeled data from which to learn. The data should be carefully curated and preprocessed to ensure its quality and relevance. The AI agent’s environment is also created, which defines the context in which the model will operate. This environment can be simulated or real-world, depending on the application. Implementing the learning experience involves selecting appropriate algorithms and techniques to train the model. Common methods include supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. The model’s decision-making abilities are optimized by adjusting hyperparameters and fine-tuning the model’s architecture. For more clarity, AI agents examples can include virtual assistants, autonomous systems, and recommendation engines across industries like finance, healthcare, and retail.
To achieve perfection at this stage, several considerations are essential:
1. Model Selection: Choosing the right model architecture is crucial. Options such as random forests, neural networks, and decision trees have different strengths and weaknesses. Factors like data type, problem complexity, and desired accuracy influence the selection.
2. Model Validation: Once the model is trained, its performance is evaluated using validation data. This data is distinct from the training data and helps identify any overfitting or underfitting issues. The model’s accuracy, precision, recall, and other metrics are analyzed to assess its effectiveness.
3. Continuous Learning: Ensuring the model can learn continuously is vital for adapting to changing environments and improving performance over time. Techniques like transfer learning and online learning allow the model to incorporate new data and knowledge as they become available. This is especially important for AI agents in Healthcare, where evolving data and medical advancements require the system to adapt continuously to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment plans.
7. Deployment of AI Agent Model
After successfully training an AI model, the next step is to deploy it into production so that it can be used by end-users. There are several tools and platforms available for deploying AI models, including serverless platforms, Docker, WebAssembly, and Kubernetes. The choice of deployment ecosystem depends on factors such as the scale of the application, the required level of security, and the desired level of control. One of the key steps in deploying an AI model is containerization. Containerization involves packaging the model and its associated components into a container, which is a lightweight and portable execution environment. Containers make it easier to deploy and manage AI models across different environments, such as on-premises servers, cloud platforms, and edge devices. This is particularly beneficial for AI agents in supply chain applications, where real-time data processing and scalability are crucial for optimizing operations and improving efficiency.
In addition to containerization, AI developers need to perform several other tasks to prepare a model for deployment. These tasks include refining and optimizing the model to improve its performance and efficiency, creating APIs to facilitate communication between the model and other components of the application, and ensuring that the deployment environment is secure and compliant with privacy regulations. AI developers also need to set up the user interfaces and interaction mechanisms that will allow users to interact with the deployed model. This may involve creating web applications, mobile apps, or other interfaces that are tailored to the specific use case, including what are AI agents to help streamline user interaction.
8. Test The Model
To achieve optimal performance and decision-making capabilities in your AI agents, it’s imperative to ensure the functional model is flawless and operates as intended. This involves rigorous testing to identify and eliminate any bugs, errors, or inappropriate behaviors that could compromise the model’s integrity. One crucial step in this process is unit testing, where individual components of the model are tested in isolation to verify their functionality and adherence to specifications. This helps to pinpoint specific issues early on and enables prompt resolution. Additionally, integration testing is essential to assess how different components interact and work together as a cohesive system. This ensures that the model’s overall behavior aligns with its intended design and that there are no unintended consequences or conflicts arising from the integration of various components.
Conducting system testing is vital to evaluate the model’s performance under real-world conditions. This involves simulating user interactions and scenarios to assess how the model responds and makes decisions in different contexts. System testing helps to identify potential issues that may not be apparent during unit or integration testing. To ensure that the model meets user needs and expectations, user acceptance testing is crucial. This involves involving actual users or user representatives in the testing process to gather feedback on the model’s usability, functionality, and overall satisfaction. This step helps to validate that the model aligns with user requirements and that it delivers a positive user experience. you can build confidence in the functional model’s reliability, accuracy, and appropriateness, laying the foundation for successful AI agent performance and decision-making.
9. Monitoring and Optimization
After deploying your artificial intelligence (AI) agents, it is crucial to continuously monitor their performance to ensure they operate optimally. Regular observation allows you to identify any potential issues or areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments. One way to enhance the performance of your AI agents is by feeding them new data. This data can come from various sources such as sensors, user interactions, or external databases. By incorporating new data, you can help your agents learn and adapt to changing environments, making them more effective in their tasks. Additionally, creating extra user interaction points can provide valuable feedback for your AI agents. This feedback can help them understand user needs and preferences better, leading to more personalized and efficient interactions. For example, you could incorporate chatbots, voice assistants, or other interactive elements to facilitate communication between users and what are AI agents.
Regularly updating the underlying structure of your AI agents is essential. AI technology is constantly evolving, and new advancements can significantly impact your agents’ performance. By staying up-to-date with the latest developments, you can ensure that your agents leverage the most advanced techniques and algorithms. Scaling your AI agents according to your business needs is also crucial. As your business grows and changes, the demands on your AI agents may also evolve. By scaling your agents, you can ensure they have the resources to handle increased workloads and maintain optimal performance. Following these steps will help you establish a smooth AI agent development process and create fully customized AI agents tailored to your specific business requirements. These agents can support your operations on multiple fronts, enhancing efficiency, productivity, and customer satisfaction. By continually observing, updating, and scaling your AI agents, you can ensure that they remain effective and valuable assets to your organization.
Start Your AI Agent Development Journey With SoluLab
Building an AI agent application requires a strategic approach, from integrating the right AI models to ensuring data security and seamless workflows. Recently, we published a case study on InfuseNet, which uses AI for data-driven decision-making and operational efficiency. It utilizes advanced AI models like GPT-4 and FLAN, enabling real-time data processing from multiple sources while ensuring data security. Businesses can fine-tune AI models with their own data, driving innovation and process optimization. InfuseNet demonstrates how AI can transform industries.SoluLab is the perfect partner to help you kickstart your AI agent development journey.
With years of experience in AI and machine learning, SoluLab offers solutions that guide you through the entire AI agent development process, from ideation to deployment. AI Agent Development Company has a team of experts who utilize tools and platforms like Microsoft Azure, GPT models, and custom machine learning frameworks to design AI agents for your needs. You Should Hire AI Developers because SoluLab focuses on delivering scalable, secure, and efficient AI solutions that integrate seamlessly with your existing systems. SoluLab aligns AI agents with strategic objectives to provide a competitive advantage. With a client-centric approach and success across various industries, they harness the full potential of AI and automation for businesses.
FAQs
1. What is an AI agent system?
An AI agent system is a combination of algorithms and data-driven models that enable machines to perform tasks autonomously, making decisions based on the data they process.
2. How do AI agents work in different industries?
AI agents can be applied across various sectors, such as healthcare, retail, and manufacturing, to automate tasks, improve efficiency, and enhance decision-making.
3. How can AI agents improve business operations?
AI agents help businesses streamline operations, from optimizing supply chain processes to improving customer service interactions and automating HR tasks.
4. What are the benefits of using AI agents?
AI agents improve accuracy, reduce human error, and provide valuable insights in industries like healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing by analyzing large volumes of data in real time.
5. How can AI agents be used in customer service?
AI agents for customer service can handle repetitive tasks, answer common queries, and provide personalized recommendations, improving response times and customer satisfaction.
6. How do AI agents help in industries like sales and marketing?
AI agents in sales and marketing can analyze customer behavior, predict trends, and assist with lead generation, helping businesses create targeted campaigns and close deals more efficiently.
7. What is the future of AI agents in enterprises?
AI agents will continue to transform enterprises by automating processes in areas like finance, HR, and supply chain management, driving innovation and operational efficiency.



