- AI Development
- AI App Development
- AI Consulting
- AI Software Development
- ChatBot Development
- Enterprise AI ChatBot
- AI Chatbot Development
- LLM Development
- Machine Learning Development
- AI Copilot Development
- MLOps Consulting Services
- AI Agent Development
- Deep Learning Development
- AI Deployment Services
- Deep Learning Consulting
- AI Token Development
- AI Development Company
- AI Development Company in Saudi Arabia
- AI Integration Services
- Hire Blockchain Developers
- Hire Full Stack Developers
- Hire Web3 Developers
- Hire NFT Developers
- Hire Metaverse Developers
- Hire Mobile App Developers
- Hire AI Developers
- Hire Generative AI Developers
- Hire ChatGPT Developers
- Hire Dedicated Developers
- Hire Solana Developer
- Hire OpenAI Developer
- Hire Offshore Developer
- About Us
- Networks+
- Smart Contracts +
- Crypto currency +
- NFT +
- Metaverse +
- Blockchain+
- Mobile Apps +
- WEB +
- Trending +
- Solutions +
- Hire Developers +
- Industries +
- Case Studies
- Blogs
You must have heard a lot about Large Language Models (LLMs) and the magic they work, but you may need to be made aware of what is a small language model. With the establishment of AI Agents in the industry LLMs’ progress seems to level off which has shifted the focus of developers on small language models. SLMs are packed in small sizes but are large vision models and can work over the phone as well, faster, more cheaply, and requiring less data and processing power for training. It is at this juncture that opportunities for innovative applications can be opened—the case of chatbots that give instant replies to your questions or AI assistants that continue to make your daily life easier.
But what exactly are small LLM models and how are they rewriting the rules of the game? We will further delve into the universe of features, benefits, and practical applications in the following blog post. We are going to break open the code on these little titans, one byte at a time, presenting to you how they are going to influence the future of AI and how to create a small language model.
What are Small Language Models?
You can spend a lot of time and energy learning every word and regulation in a huge textbook. As such, small language models could be effective language learners. These AI wizards do the inverse of this by using a more cunning approach: They just concentrate on the essential concepts so that they are ready to explain.
SLMs have fewer parameters than larger LLMs, much like a smaller grammar and vocabulary notebook. They are agile in this respect! AI small language models could even run on their phones, train faster, and eat less energy.
Now, imagine a virtual assistant that checks off your to-do list without you bleeding through all your battery life or pocket translation. These are examples of small language models working. Although they may not be memorizing every detail with a hold of basics, they achieve surprisingly complex tasks, hence making this an ideal tool for a future full of intelligent products and accessible artificial intelligence.
What Do Small in Small Language Models Indicate?
In the AI small language model, “small” refers to much more than physical dimensions. It encompasses some vital elements that set them apart from their rather imposing rivals: Large Language Models. The following contributes to what makes the SLM model both “small” and powerful:
- Accessibility and Affordability: More people and enterprises can access small language models because they are more efficient, hence making them a much more viable option for many more applications. This is because of lower development costs and the ability to run on less highly specified hardware. In this way, AI democratizes to the degree that it becomes possible for small businesses or even independent users to avail themselves of the power of language processing.
- Data Diet: The best small language models require less data for training, just like students do not need to learn everything to be proficient. They are perfect in situations where large vision model data may be restricted; they are perfect at learning from smaller datasets. This also increases their adaptability to particular tasks or domains in which well-targeted training on a well-chosen dataset may produce outstanding outcomes.
- Sleek design: Imagine a meta LLM as a multistory, complex building; now think of SLMs as even simpler than bungalows with fewer layers and connections. However, it makes use of almost all principles of deep learning learned from LLMs, including transformers and self-attention processes. Moreover, because of this simplification, can train the model faster and more effectively.
- Fewer Parameters: Imagine you are a student learning a language. LLMs memorize each word and every rule, just like carrying huge textbooks. In contrast, a small LLM model looks only at the core concepts. This would then imply fewer parameters—precise numbers that instruct or govern how the model comprehends and generates replies. While it is well known that LLMs have billions of parameters, the small models are normally reckoned to have less than 100 million, and occasionally even as little as 10 million.
Why are Small Language Models Required?
Large Language Models are the rage in artificial intelligence. Their powers in generating text, translating languages, and writing other forms of creative content are remarkable and extremely well-documented. Small Language Models come in as a new class of AI models that are subtly sweeping the waves. Although SLMs are not as powerful as other models in their leading categories, the type comes with a set of very special benefits that make them of value to a huge array of applications. To understand more deeply the role of SLMs within the dynamic field of AI, read on:
1. Low-Resource Effectiveness
If you build private LLMs they will become your data hoarders; training them requires huge amounts of data and a lot of processing power. This can be quite a barrier to many companies and individuals who don’t have the means to use such models. SLMs come to the rescue in this regard. Enabling them to learn with small llm datasets and run on less powerful hardware due to their small size and focus on core functionality makes them good at learning. This will result in more cost-effective AI solutions, thereby opening up possibilities for integrating intelligent features, even where resources are limited.
2. Faster Deployment and Training for Faster Development
Everything today is all about speed. Depending on the model’s complexity, training an LLM might take weeks or months. This, in turn, could reduce the pace of development cycles for apps that should, otherwise be developed and deployed at a much faster rate. Such cases call for the best small language models. They can be trained much faster compared to LLM use cases due to their slimmed architecture and focus on key features. This means developers can get AI-powered features up and running more quickly, accelerating time to market and time to innovation.
3. Taking Intelligence to New Heights
AI is not only going to reside in the cloud but at the periphery of everyday devices, we use because they are so large and resource-intensive, LLMs are not very suitable for running on wearables or even smartphones. That is where small language models shine: because they are small in size and less resource-intensive, they become perfect on-device applications of artificial intelligence. This allows a whole new level of interesting possibilities. Imagine a virtual assistant that can answer your questions without an internet connection or a language translator that’s not only real-time but works right from your phone. It’s that sort of future technology—intelligence baked right into our devices—that SLMs are making possible.
Examples of Small Language Models
AI small large language models are among the most significant breakthroughs in AI. With small footprints, the range of applications of SLMs is immense. These models exhibit both prowess and efficiency. Some of the examples of small language models are as follows:
- DistilBERT: This is a distilled version of one of the most popular large vs small language models, BERT, created by Google AI. The important characteristics are thus retained while the size is decreased in tasks like text categorization and sentiment analysis. The application developers can additionally prosper by integrating such characteristics into those specific applications without the simultaneous expenditure on computing power. DistilBERT is the favored one when one has a scarcity of resources because its training time is less while it is compared to BERT. This is a distilled version of BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) that retains 95% of BERT’s performance while being 40% smaller and 60% faster. DistilBERT has around 66 million parameters.
- Microsoft Phi-2: Phi-2 is a versatile small language model known for being efficient and well-capable with handling several applications. It can incorporate text production, summarization, and some question-answering tasks. This Microsoft project focused on building an appraisal engine to realize low-resource language processing; this comes in handy for applications with several hard linguistic demands. This means that Phi-2 may work fine even if trained on a small subset of data in some specific language.
- MobileBERT by Google AI: This is a distilled version of BERT that targets running on cell phones and other devices that have constrained computing power. In particular, it was designed to work on mobile devices. It is, therefore, possible for developers to implement question-answering and text-summary features on mobile applications without affecting the user experience. This will now be possible with intelligent features on the move because MobileBERT is efficient in doing so.
- Gemma 2b: Google Gemma 2b is a 9B and 27B strong, very effective SLM making an entry into the market. Compared with open-source models available, Gemma 2b is top-of-class performance and was also designed with some safety enhancements in mind. More will be able to use it since these small language models will run on a desktop or laptop computer directly used for development. With a context length of 8192 tokens, Gemma models are suitable for deployment in resource-limited environments like laptops, desktops, or cloud infrastructures.
How Small Language Models Work?
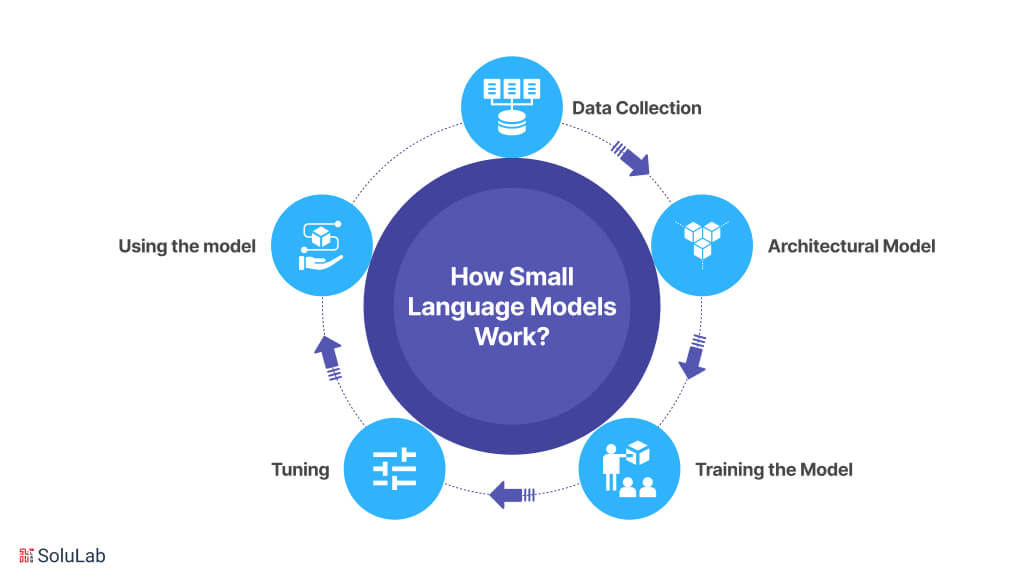
Now that you are aware of what is a small language model, know about how it works. The phases of Small Language Models’ creation can be decomposed as follows:
1. Data Collection
- The very first step to developing an SLM is to generate and collect a large dataset containing textual information. This data may be obtained from various places like source code repositories, online forums, books, new articles, etc.
- The data is pre-processed to ensure it is quality and consistent. This may involve cleaning the content of such extraneous information as formatting codes or punctuation.
2. Architectural Model
- Deep learning architecture, normally a neural network, is what forms the backbone for an SLM. This network shall process the data through the layers of artificial neurons interconnected with each other.
- SLMs are simpler models with fewer layers and parameters, which makes them learn faster and more efficiently.
Read Blog: AI in Architecture: Transforming Design & Construction
3. Training the Model
- Training is a process where the prepared text data is fed into the SLM. During its training process, the model learns the relationships and patterns in the data.
- The methodology the model uses is what might be called “statistical language modeling.” It guesses the next word in a sequence based on that which has come before.
- The model sees how good it is at these predictions as it keeps training. This feedback makes it easier for it to adjust its internal parameters and improve its accuracy over time.
4. Tuning (Optional)
- Although they can initially be trained to acquire broad language competence, SLMs can later be fine-tuned for specialized tasks.
- Fine-tuning is when a previously trained model is trained on a domain-specific dataset—in other words, data from an area like health care or finance. Because it focuses on this domain-specific knowledge, the SLM has a chance to master that particular domain.
5. Using the model
- This way, the SLM is functional after it has been trained or calibrated. In interacting with it, users can input text into the model, such as a question, a sentence that has to be translated, or a passage of text that has to be summarized.
- The SLM evaluates such input against its learned experience and returns an appropriate response.
Benefits of Small Language Models
Although small language models look pretty tiny compared to their bigger counterparts, they have many advantages. Here are the reasons that make SLMs increasingly popular in the AI space:
1. Efficiency
Small Language Models are much more efficient when it comes to computational resources and memory usage than large models. They do not require much processing power, storage, or energy to run which makes them a more suitable choice for deployment on devices that are resources-constrained like smartphones.
2. Speed
With the small size and simple designs, small large language models can perform tasks at a much faster pace than large language models. This speed is specifically beneficial in applications where real-time responses are essential like chatbots.
3. Privacy
It is easier to train small language models than large vision models and deploy them locally on devices, which reduces the need to send sensitive data to remote servers. This approach not only enhances privacy by keeping users’ data under control but also minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
4. Customization
These small models are more prone to customization for specific domains and use cases than LLMs. Their smaller size makes it possible to fine-tune fast for specific data and enables the creation of tailored models for the needs of individual industries and uses.
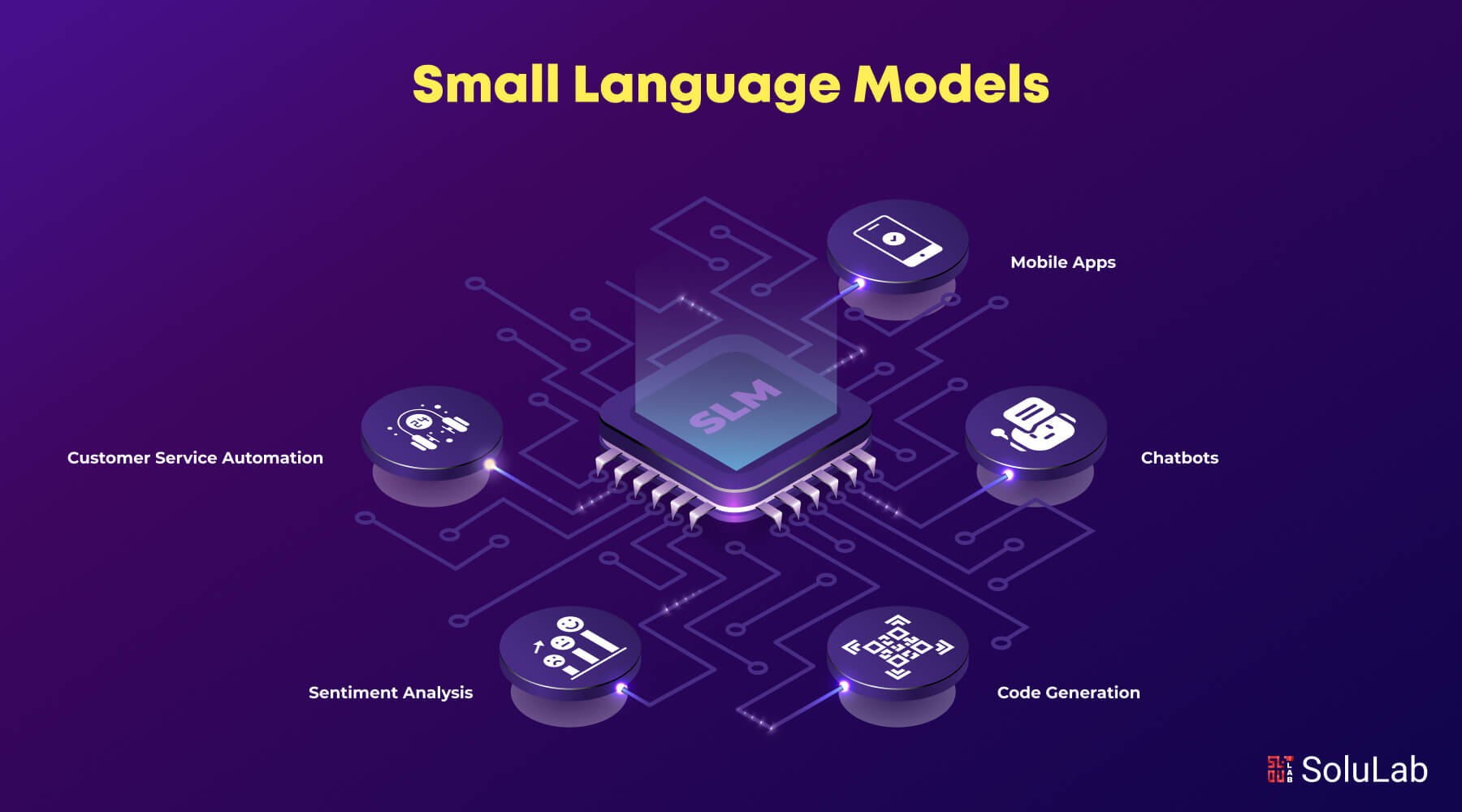
Use Cases of Small Language Models
Here is a breakdown of some notable small language model use cases:
1. Mobile Apps
Models like MobileBert assist developers with integrating natural language processing features like text summarization and answering questions directly from mobile apps. This also allows more efficient real-time interactions without compromising user experiences.
2. ChatBot
SLM models are used to power virtual assistants by providing quick and accurate responses to user queries. Their efficiency and speed make them suitable for handling tasks like customer support to enhance user engagement.
Check Out Our Blog: AI use cases and Applications in Key Industries
3. Code Generation
Small Language Models can help developers generate code snippets that are based on natural language descriptions. This ability to streamline the coding process allows programmers to rapidly prototype features and automate repetitive tasks to increase productivity.
4. Sentiment Analysis
The small LLM model is effective for the analysis of sentiments on social media monitoring customer feedback. They can quickly analyze text data to determine public sentiments, aiding businesses in making informed decisions on user opinions.
5. Customer Service Automation
The small LLM models are effective for automating customer service interactions, which enables businesses to handle inquiries and support requests without human intervention. By giving accurate results and outcomes these models also improve response time for customer satisfaction.
LLM vs SLM: Key Differences
The field of Artificial Intelligence is dominated by two popular language models: Large Language Models and Small Language Models. While they are both concerned with language processing, they do so differently:
-
Computational Requirements
Champions of the resource! Since SLMs are smaller, they run and require less data and less processing power. Thereby, it makes them quite perfect for resource-constrained settings. On the other hand, LLMs are very famished for data and processing power; large-scale training datasets and costly hardware are frequently called for.
-
Dimension Count
Model Size and Training Speed: Because SLMs have fewer parameters to tune, model size is smaller, and train times are faster. Because of their size, LLMs need more substantial amounts of data and greater processing power, translating to longer training times.
-
Real-World Applications
Observe what is being done! SLMs’ efficiency makes them excellent at on-device AI. Consider AI-powered chatbots that could answer simple queries or real-time translation on your phone. Because they are narrow in their scope of knowledge, LLMs excel at tasks such as generating new forms of text or complex analysis, which typically is handled in the cloud.
-
Performance Trade-Off
While SLMs are fast and efficient, they may not offer the same level of accuracy or degree of fine-grained understanding achieved by LLMs. Although resource-intensive, LLMs can still provide very good performance due to their broad coverage.
Conclusion
SLMs and LLMs each occupy a special niche in this very exciting area of language models. ExPEC both these models should become more sophisticated as AI grows further in the future. SLMs may continue to become more efficient, leading to seamless on-device AI experiences and even more deeply integrated into our daily lives. On the other hand, LLMs would keep pushing beyond the limits posed in language generation and comprehension with improved training methodologies, finding new applications across a wide array of domains has been made possible with LLM Development Company.
The choice between SLM vs LLM lies in the specific needs of the project. SLMs provide results that work in activities that need on-device processing and are power-efficient. If the crucial aspects are depth analysis and complexity, then it would be recommended to approach with LLMs.
At SoluLab, we are dedicated to helping enterprises tap into the power of artificial intelligence. Whether you need SLMs to enhance your processes or want to benefit from LLMs for a myriad of cutting-edge applications, our experts are here to help you choose the most appropriate language model for your needs. Contact now and discover more about how AI can revolutionize your business!
FAQs
1. SMLs or LLMs: which one is more accurate?
Due to their complex architecture and greater knowledge base, LLMs are usually more accurate. Conversely, an SML with sufficient training may be more effective and turn out results comparable for some jobs.
2. Can I run an SML on my phone?
SMLs are indeed perfect for on-device processing because they are small and less resource-intensive. Indeed, they would be very suitable for text summary functions on smartphones, simple chatbots, and language translation.
3. What are some real-world applications of SML?
SLMs already find their place in several applications: from text summarization functions on smartphones to basic question-answering chatbots, and on-device language translation.
4. Is the bigger model always better?
Well, not necessarily! Where LLMs master the complex tasks, at times their resource requirements might become a barrier. SLMs are suited to a large number of use cases that need on-device processing or faster development cycles—striking a balance between efficiency and capability.
5. How can I take advantage of SoluLab to get the most out of language models?
SoluLab is your one-stop marketplace for all AI needs! Whether it is an efficient SML or a powerful LLM, our experts are there to guide you through the world of language models, evaluate your requirements, and advise you accordingly on the best course of action. We even develop and implement to ensure you can harness the full potential of AI for your business. Discuss your AI journey with SoluLab now.



