What is the purpose of DeFi if we keep relying on centralized institutions to maintain the stability of our assets? This question is increasingly asked by builders and users, particularly while stablecoins such as USDC and USDT maintain their dominance, despite their reliance on conventional institutions. This is when algorithm-backed stablecoins are starting to stand out. They utilize smart contracts and mathematical models to maintain value stability, rather than depending on currency reserves.
Innovation continued even after TerraUSD’s collapse in 2022, which reduced trust in algorithmic models. The demand for decentralized, reliable solutions continues to increase. As of May 2025, DeFiLlama reports that the stablecoin market in DeFi possesses over $125 billion in total value, with emerging algorithmic models progressively capturing market share alongside established fiat-backed currencies.
In this blog, we will look at how algorithm-backed stablecoins work and explore how newer models are innovating to rebuild confidence. If you are interested in how stability without centralized governance may influence the coming generation of DeFi systems, this is worth a read.
What are Algorithmic Stablecoins?
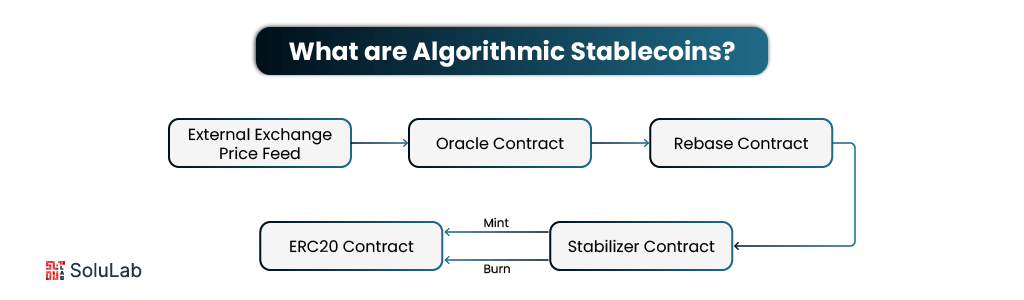
Most people are aware of stablecoins, such as USDC or USDT, which are digital currencies with values close to $1 that are backed by real-world assets such as bank dollars. However, algorithmic stablecoins function quite differently.
When demand for the coin rises, the system creates additional tokens to bring the price down. When demand falls, tokens are burned (or removed from circulation) to force the price back up. It’s essentially an automatic supply and demand balancer embedded right into the code. This allows for price stability without having to retain money or collateral in the background.
That is a significant thing in the world of DeFi. A stablecoin in DeFi that does not rely on centralized reserves allows platforms to run more autonomously, with no banks, no off-chain assets, and fewer trust difficulties.
For anybody trying to create next-gen financial products, selecting an appropriate stablecoin architecture is important. Working with a reputable stablecoin development company may ensure the underlying concept remains valid, especially if the objective is long-term sustainability and decentralization.
How Algorithmic Stablecoins Maintain Stability?
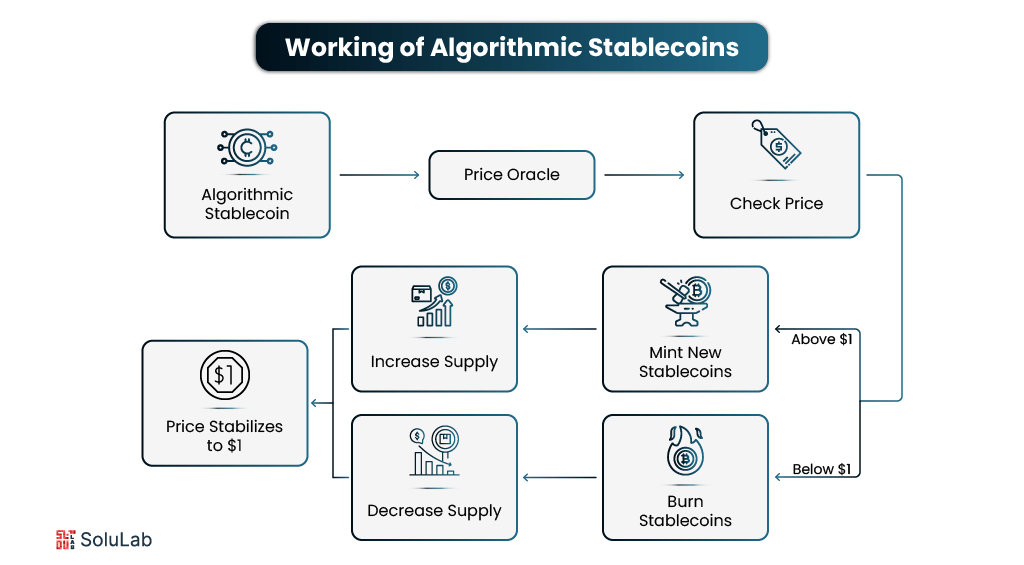
Unlike asset-backed stablecoins, which use fiat or crypto reserves to maintain value, algorithmic models use a carefully designed set of tools and strategies. If you’re developing an algorithmic stablecoin, here are the most critical factors you’ll need to consider to ensure stability and user trust.
1. Elastic Supply Mechanism
The supply of tokens is automatically adjusted based on price movement. If the coin is trading above its target (like $1), more tokens are minted and released into circulation. If it’s trading below, tokens are burned or removed from the system. This supply adjustment helps pull the price back toward equilibrium.
2. Market Oracles
Oracles are trusted sources of off-chain data that the smart contracts rely on. They track the real-time price of the stablecoin across various exchanges. This price input is essential for triggering supply changes at the right moment. If oracles fail or get manipulated, the entire system can become unstable.
3. Incentive Structures
Stability isn’t just managed by code, it also depends on how users interact with the system. Many algorithmic stablecoins offer rewards (like profit shares or new tokens) for actions that help restore the peg, such as burning tokens when the price drops or buying bonds during contraction phases.
4. Dual-Token or Multi-Token Models
A common approach involves creating two (or more) tokens: one stablecoin and one “share” token. The share token absorbs system gains and losses, and holders are rewarded when stability is maintained. This separation helps reduce pressure on the stablecoin itself while distributing financial risk more evenly.
5. Rebase or Seigniorage Model
In a rebase model, the number of coins in your wallet changes dynamically to maintain the price. In a seigniorage system, instead of changing balances, the protocol uses market mechanisms to expand or contract supply. Both models aim to maintain the peg but do so in different ways.
6. Protocol Governance
Some advanced systems include decentralized governance, where token holders vote on changes to supply mechanisms, reserve ratios, or incentive policies. This flexibility allows the system to evolve as market conditions change and gives users a voice in maintaining long-term stability.
7. Emergency Controls (Circuit Breakers)
When the market behaves unpredictably, like during a flash crash, smart contracts can temporarily pause supply adjustments or shut down part of the protocol. These circuit breakers act as a fail-safe to prevent the system from spiraling out of control during extreme volatility.
Read Also: Tokenizing TradFi: Real-World Assets & Smart Bonds
Types of Algorithmic Stablecoins
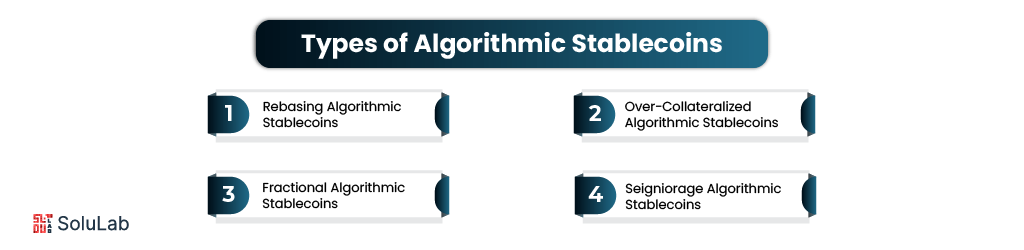
To understand the world of algorithmic stablecoins, you should first look at their main groups. Each type has its own structure and set of rules, which means they can be used for different things in autonomous banking. The main types of algorithmic stablecoins are broken down below:
-
Rebasing Algorithmic Stablecoins
Rebasing algorithmic stablecoins manages the value by changing the number of available tokens. When the price falls below the goal, the algorithm cuts back on the stock that is in circulation. If, on the other hand, the price goes above the targeted amount, the system raises the supply.
-
Over-Collateralized Algorithmic Stablecoins
For over-collateralized algorithmic stablecoins to work, they need to hold a lot more cryptocurrency assets than stablecoins are released. This extra reserve works as a safety net, letting the system handle changes in the market and keeping the token’s peg. Some of the main features of backed stablecoin examples are included in this model.
-
Fractional Algorithmic Stablecoins
Fractional algorithmic stablecoins are a mix of computational methods and partial asset backing, making them a hybrid solution. Cryptographic methods and a tiny, controlled stock of collateral help these stablecoins stay stable. Their design aims to make the best use of capital while still providing some security from the base assets.
-
Seigniorage Algorithmic Stablecoins
A dual-token method is used by seigniorage-based algorithmic stablecoins, which is different from the rebasing model. One token is the stablecoin with an adjustable amount, and the other is an investment part in the system. Shareholders can get rewards during growth times and take a hit when the price of the stablecoin goes down.
Comparison with Fiat-Backed and Crypto-Backed Stablecoins
When comparing stablecoin models, it’s clear that each type brings its own strengths and weaknesses to the table. Whether you prioritize decentralization, stability, or transparency, understanding the trade-offs between algorithmic vs. traditional stablecoins helps you decide which model fits your project or use case best.
| Feature | Fiat-Backed Stablecoins | Crypto-Backed Stablecoins | Algorithmic Stablecoins |
| Backing | Real-world currency (e.g., USD) | Over-collateralized crypto (e.g., ETH) | No physical or crypto backing |
| Stability Mechanism | Maintained via fiat reserves | Managed through the collateral ratio | Supply adjusts based on price triggers |
| Decentralization | Low (centralized issuers) | Medium (uses on-chain assets) | High (fully protocol-driven) |
| Regulatory Risk | High | Medium | Low to moderate |
| Exposure to Volatility | Low | High | Varies by model; often high |
| Transparency | Varies (depends on issuer) | High (fully on-chain) | Very high (open-source smart contracts) |
Key Benefits of Algorithmic Stablecoins in DeFi
If you’ve spent any time exploring DeFi, you’ll know that stablecoins play a huge role in making it all work. But not all stablecoins are built the same. Some rely on banks to hold real dollars, others lock up volatile crypto. Then you’ve got algorithmic stablecoins, which try something different; they manage everything through code. This approach isn’t perfect, but it comes with some real advantages. Here are a few pros of algorithmic stablecoins that make them stand out in the DeFi world:
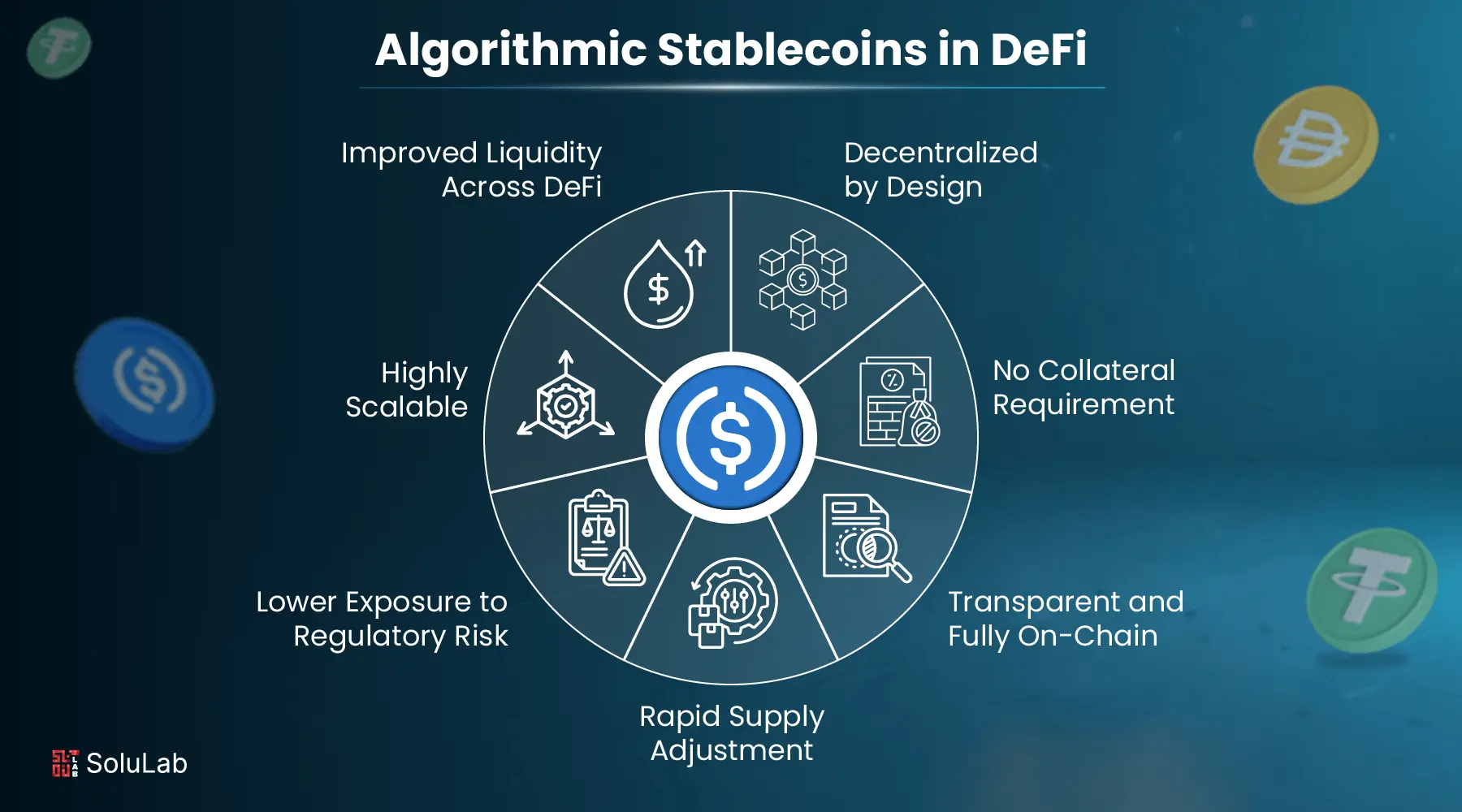
1. Decentralized by Design
These stablecoins are governed entirely by smart contracts, not corporations or banks. This removes the need to trust a central authority, which aligns perfectly with DeFi’s goal of trustless infrastructure.
2. No Collateral Requirement
Unlike crypto- or fiat-backed models, algorithmic stablecoins don’t need to hold reserves. This reduces the barrier to entry for launching or scaling a project, freeing up capital for other uses within the ecosystem.
3. Transparent and Fully On-Chain
Since the logic and mechanics are open-source and executed on public blockchains, users can audit the system at any time. This kind of transparency helps build trust and avoids the opacity of traditional stablecoins.
4. Rapid and Autonomous Supply Adjustment
The coin’s supply can expand or contract automatically in response to price shifts, without needing human intervention. This automation allows for quicker reactions to market volatility compared to centralized models.
5. Lower Exposure to Regulatory Risk
Because they aren’t tied to real-world assets or centralized banking systems, algorithmic stablecoins face fewer legal uncertainties in most jurisdictions, at least for now.
6. Highly Scalable
With no need to manage or safeguard physical assets, these coins can scale more quickly and be deployed across various DeFi platforms without operational overhead.
7. Improved Liquidity Across DeFi
Their compatibility with lending protocols, DEXs, and yield platforms makes algorithmic stablecoins a versatile building block, promoting liquidity and utility across decentralized ecosystems.
Read Also: Hong Kong Stablecoin Regulation
Use Cases of Algorithmic Stablecoins in the DeFi Ecosystem
Algorithmic stablecoins have evolved from an experimental concept to a practical tool within the DeFi space. Unlike traditional stablecoins, they rely on code and real-time market data to adjust supply, allowing them to maintain stability without holding collateral. Understanding how algorithmic stablecoins work gives better insight into why they’re gaining traction across various decentralized applications.
- Decentralized Lending & Borrowing: These stablecoins act as neutral collateral and a reliable unit of value, making them ideal for lending platforms without central dependencies.
- Liquidity Pools on DEXs: Their predictable pricing helps users and protocols manage slippage and maintain deeper liquidity on decentralized exchanges.
- Yield Farming & Incentive Distribution: Minting algorithmic stablecoins as rewards allows DeFi platforms to grow sustainably without locking in external assets.
- Cross-Border Peer-to-Peer Payments: With no middlemen involved, they offer fast, cheap, and borderless transactions, especially valuable in emerging markets.
- DAO Contributor Payments: DAOs use these stablecoins for payroll, enabling fully on-chain compensation without the need for traditional banks.
- Synthetic Asset Collateralization: Algorithmic models are often used to support synthetic versions of real-world assets, ensuring scalability and decentralization.
- Innovation in Automation: Many teams working on AI stablecoin development are integrating advanced algorithms and machine learning for smarter, more resilient supply management.
Future Outlook for Algorithmic Stablecoins in DeFi
The road for algorithmic stablecoins hasn’t been easy, but it’s far from over. While early failures like Terra shook user confidence, they also pushed the community to rethink how these systems are built. Today, developers are approaching the concept with more caution, better risk controls, and smarter designs. The lessons learned are now shaping a new generation of algorithmic models that are more transparent, better governed, and better equipped to handle extreme market conditions.
Looking ahead, algorithmic stablecoins have the potential to become a core layer of the DeFi stack, not just as a tool for trading, but for lending, payroll, DAOs, and even cross-border settlements. Their on-chain, rule-based nature makes them an ideal fit for a decentralized world where trust in intermediaries continues to erode.
For teams building in this space, working with a reliable stablecoin development company will be key. It’s not just about writing smart contracts, it’s about designing for resilience, scale, and long-term adoption.
The Bottom Line
Algorithmic stablecoins have opened up a new chapter in how we think about digital money, especially in decentralized finance. Instead of relying on traditional banks or crypto reserves, they use smart contracts to keep value steady, giving DeFi platforms a more flexible and autonomous option. While they’re still evolving, the potential is clear: for anyone looking to create a stablecoin that’s scalable, transparent, and free from centralized control, algorithmic models are worth serious consideration.
At SoluLab, we’ve had the opportunity to work on several forward-thinking projects in this space. As a trusted stablecoin development company, we helped build a complete blockchain ecosystem for DLCC, a platform aiming to transform regulated crypto and digital asset lending. Our work included a decentralized wallet, an exchange platform, and backend solutions that make digital asset financing simple, secure, and compliant with financial regulations.
If you’re exploring stablecoin solutions, whether for lending platforms, DeFi apps, or next-gen financial tools, our team is here to help!
FAQs
1. Are algorithmic stablecoins safe to use in DeFi protocols?
They can be, but it depends on the design. Like any financial tool, they carry risks, especially if the underlying code or economic model hasn’t been thoroughly tested. Newer versions are more cautious, often with built-in safeguards, but users should always do their research before using them in high-risk strategies.
2. Can algorithmic stablecoins completely replace fiat-backed stablecoins?
Not yet. Fiat-backed coins like USDC still dominate because they offer predictable, low-risk stability. Algorithmic stablecoins are better suited for projects focused on decentralization, but most ecosystems use a mix of both for now.
3. What happens when an algorithmic stablecoin loses its peg?
If the system isn’t well-designed, it can spiral—either printing too many tokens or collapsing in value. That’s why well-audited code, strong incentive mechanisms, and clear emergency responses are critical parts of any good algorithmic stablecoin system.
4. How are these coins different from regular crypto tokens?
Unlike typical tokens that fluctuate based on supply and demand alone, algorithmic stablecoins are built to adjust their own supply to hold a steady value. It’s more like a self-correcting system than a regular investment token.
5. Who should consider using or building with algorithmic stablecoins?
They’re great for DeFi builders who want to maintain full decentralization without relying on banks or custodians. If you’re building a lending platform, DAO, or cross-border payment solution, algorithmic stablecoins can be a powerful, flexible fit.