- AI Development
- AI App Development
- AI Consulting
- AI Software Development
- ChatBot Development
- Enterprise AI ChatBot
- AI Chatbot Development
- LLM Development
- Machine Learning Development
- AI Copilot Development
- MLOps Consulting Services
- AI Agent Development
- Deep Learning Development
- AI Deployment Services
- Deep Learning Consulting
- AI Token Development
- AI Development Company
- AI Development Company in Saudi Arabia
- AI Integration Services
- Hire Blockchain Developers
- Hire Full Stack Developers
- Hire Web3 Developers
- Hire NFT Developers
- Hire Metaverse Developers
- Hire Mobile App Developers
- Hire AI Developers
- Hire Generative AI Developers
- Hire ChatGPT Developers
- Hire Dedicated Developers
- Hire Solana Developer
- Hire OpenAI Developer
- Hire Offshore Developer
- About Us
- Networks+
- Smart Contracts +
- Crypto currency +
- NFT +
- Metaverse +
- Blockchain+
- Mobile Apps +
- WEB +
- Trending +
- Solutions +
- Hire Developers +
- Industries +
- Case Studies
- Blogs
Do you want to know how digital currencies can maintain a stable value in the highly volatile crypto market? Unlike Bitcoin or Ethereum, which experience wild price fluctuations, stablecoins are designed to offer the best of both worlds– cryptocurrency’s unmatchable efficiency with the stability of fiat money.
By pegging their value to assets like the U.S. dollar, gold, or other reserves, stablecoins have become essential for remittances, DeFi applications, and global transactions. As businesses, financial institutions, and blockchain developers recognize their potential, many are exploring how to create their stablecoin to facilitate secure and flawless digital payments. Solutions like Plasma stablecoin payment platform highlight how businesses can leverage digital assets for faster, borderless transactions.
Whether you’re a startup looking to launch a stable digital currency or a developer interested in tokenization, this guide will provide you with a clear roadmap to creating and deploying your stablecoin. Let’s get started!
What is Stablecoin?
Now let us understand in-depth what stablecoins are. A stablecoin is a type of cryptocurrency where its value is either fixed or linked to another form of currency, financial instrument, or commodity. Stablecoins are intended to provide a replacement to the extreme volatility of most cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, which makes crypto investments less suitable for everyday transactions.
Simply put, Stablecoin is a type of digital money that seeks to mimic traditional and stable currencies. A stablecoin is a cryptocurrency backed by the value of an underlying asset. Many stablecoins are pegged to certain fiat currencies, including the Euro or the US dollar, and may be exchanged on exchanges. Stablecoins may additionally be connected to other assets, such as gold or other cryptocurrencies.
Stablecoins, unlike other cryptocurrencies, are spared from excessive volatility. They make use of the characteristics of cryptocurrencies, such as immutability, transparency, security, quick transactions, digital wallets, privacy, and cheap costs, while maintaining the confidence and stability of fiat currency.
Let’s look at the different types of stablecoins.
What are Two Types of Stablecoins?
Stablecoins are primarily categorized into the following types:
1. Collateralized Stablecoins
Collateralized stablecoins are digital currencies whose values are supported by specific collateral. These can be further classified into:
-
Fiat-backed Stablecoins:
Fiat-backed stablecoins are pegged to the value of fiat currencies. Tether (USDT), the first of its type, popularized the idea of a cryptocurrency backed by reserves equal to the whole market capitalization and correlated with the US dollar. The stablecoin list also includes USD Coin and PAXOS Standard as further examples.
-
Asset-backed Stablecoins:
Asset-backed stablecoins are backed by assets other than cryptocurrency or fiat. The value of actual things such as gold, silver, diamonds, oil, real estate, and many more are linked to these tokens.
-
Crypto-backed Stablecoins:
Stablecoins backed by cryptocurrencies employ methods to maintain their value in the face of changes in the underlying cryptocurrency. An example is the DAI token, a stablecoin crypto backed by Ether and pegged to the US dollar. It maintains its price through the Maker Smart Contract, which creates and destroys MKR tokens in response to changes in ETH’s price.
These stablecoin types represent diverse approaches to ensuring stablecoin prices remain consistent, making them suitable for various stablecoin usage scenarios.
2. Non-collateralized Stablecoins
Also referred to as Seigniorage shares or algorithmic stablecoins, non-collateralized stablecoins embody the core principle of cryptocurrencies: decentralization. Many crypto enthusiasts believe that stablecoins should not be tied to an asset but instead derive their value through algorithms. This belief has led to the rise of non-collateralized stablecoins. The financial strength of non-collateralized stablecoins does not depend on a central authority but rather on a formula based on demand and supply. One example of these AI cryptocurrency coins is Basis, an algorithmic stablecoin that gained significant attention after raising $133 million from Bain Capital Ventures, Polychain Capital, and GV.
3. Algorithmic Stablecoins
Algorithmic stablecoins may hold reserve assets, but their key strategy for maintaining stablecoins prices is by controlling supply through an algorithm. This algorithm is essentially a computer program that follows a preset formula. This approach is somewhat similar to the way central banks operate, where the currency’s value is maintained without depending on a reserve asset. For instance, the U.S. Federal Reserve sets its monetary policy publicly, based on well-established parameters. The credibility of this policy is reinforced by the fact that the central bank is the issuer and holder of legal tender.
Now that we have covered the basics of stablecoins, including some of the best stablecoin options, we will move on to the next section: why are stablecoins essential?
Why are Stablecoins Essential?
Stablecoins are essential in the crypto ecosystem because they provide a stable store of value and a reliable medium of exchange. By mitigating the volatility of other cryptocurrencies, they enable seamless transactions, making them particularly valuable in decentralized finance (DeFi) and cross-border payments. Their integration with fiat currencies enhances accessibility, making them a crucial component of the digital financial space.
Stablecoins play a vital role in financial transactions within the crypto-verse for several reasons:
1. Best for Managing Market Volatility
Stablecoins are widely used on crypto exchanges as a low-volatility option for traders. They allow investors to move in and out of trades without relying on fiat, making them essential for risk management.
2. Simplifies Fiat-to-Crypto Conversion
Before trading on crypto exchanges, investors often convert fiat into stablecoins like USDT or USDC. These digital assets maintain a stable value, making them the preferred choice for seamless blockchain transactions.
Related: Stablecoin in DeFi
3. Preferred for Blockchain Transactions
Stablecoins, such as Tether (USDT), are the most traded assets on the blockchain. They facilitate cross-border payments and are commonly used in DeFi protocols to enable efficient transactions.
4. Essential for the DeFi Ecosystem
The DeFi ecosystem heavily relies on stablecoins for liquidity pools and lending services. DeFi lending protocols like Aave and Compound issue stablecoin-based loans, ensuring borrowers and lenders avoid the risks associated with volatile assets like Bitcoin.
What are Some Uses of the Stablecoins?
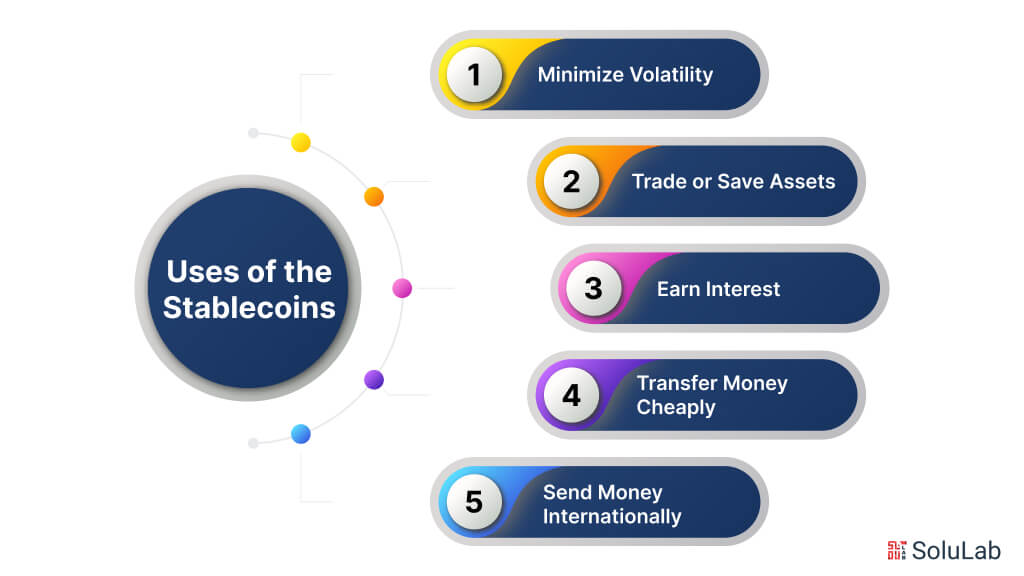
Stablecoins offer numerous benefits and versatile use cases, making them a valuable asset in the cryptocurrency space. Whether you’re looking to minimize risks or take advantage of specific financial opportunities, stablecoins provide practical solutions. Here are some key ways you can utilize stablecoins:
-
Minimize Volatility
The value of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ether can fluctuate dramatically, sometimes even within minutes. Stablecoins offer a more reliable alternative for buyers and sellers, ensuring that the value of their tokens remains stable and does not suddenly crash or surge in the future.
-
Trade or Save Assets
Stablecoins can be stored without needing a bank account and are easy to transfer. They can be easily sent across the globe, including to regions where accessing the U.S. Dollar or dealing with an unstable currency is challenging.
-
Earn Interest
Investing in stablecoins can yield interest, often at rates higher than those offered by traditional banks. This makes them an attractive option for those looking to grow their wealth with relatively low risk.
-
Transfer Money Cheaply
Stablecoins allow you to transfer any amount of money with minimal transfer fees, making them a cost-effective option for both small and large transactions.
-
Send Money Internationally
Stablecoins like USDC are an excellent choice for international money transfers due to their fast processing times and low transaction fees, making global financial transactions more accessible and affordable.
Stablecoins are a powerful tool for various financial activities, and their stable value opens up new possibilities for users in the digital economy. Combined with technologies like Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), they could further enhance how we interact with and utilize digital assets.
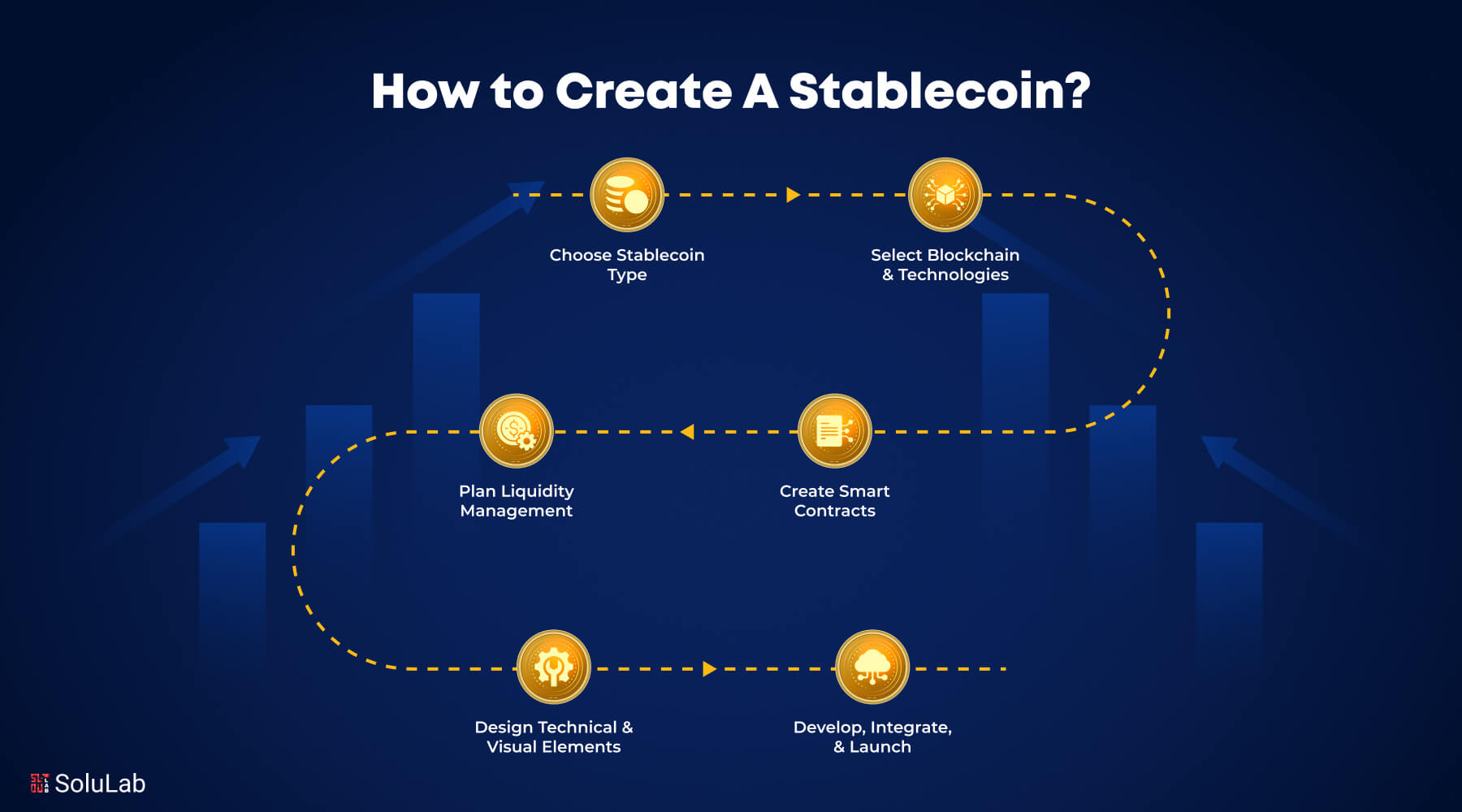
How are Stablecoins Created?
To create a stablecoin, you need to follow these essential steps:
1. Determine the Type of Stablecoin to Develop
As previously mentioned, stablecoins fall into two major categories: collateralized and non-collateralized. Deciding which type to create can be challenging, as no single kind of stablecoin is inherently superior to the others. If your objective is long-term stability, you may want to consider algorithmic stablecoins. On the other hand, if you’re aiming for short-term stability with a reliable underlying asset, collateralized stablecoins could be the better choice. To identify the type of stablecoin you need, ask yourself the following questions:
- How much liquidity do I need from my stablecoins?
- What level of decentralization or independence do I desire?
- How many audits can I afford to enhance trust and mitigate risks in my stablecoins?
- How simple or complex should the overall architecture be?
Once you have answers to these questions, you’ll be better equipped to decide which type of stablecoin to build.
2. Select the Blockchain Platform and Technologies for Development
After determining the type of stablecoin you wish to develop, the next step is to choose the appropriate platform to build your stablecoin. Initially, Ethereum was the primary platform for stablecoin development, but this has changed.
Before 2018, the majority of stablecoins operated on Ethereum, but new blockchain platforms have since emerged. Platforms like Tron and EOS are now being utilized for building stablecoins. In 2019, several EOS-based stablecoin projects, such as Carbon (CUSD), Tether, EUSD, and EOSDT, were launched. Many developers opted for EOS over Ethereum due to its benefits:
- Greater interoperability
- High scalability and transaction bandwidth
By weighing the pros and cons of each available platform, you can make an informed decision about which one to use. Once you’ve selected the platform and technologies for your stablecoin development, the next step involves maintaining liquidity.
3. Consider Liquidity Maintenance
Without adequate liquidity, the entire stablecoin project could fail. To ensure good liquidity, consider the following steps:
- Evaluating Inflation and Value: Integrate an automated monitoring system to provide daily currency rates and index rates from the Consumer Price Index and Personal Consumption Expenditures.
- Transaction Fees: Split transaction fee revenues, with a portion going to the stablecoin partner and the remainder into a liquidity reserve to enhance liquidity.
- Protection from High Supply: Users should be able to redeem or sell their stablecoins at the current face value minus transaction fees. This prevents sellers from offering their stablecoins at discounted rates in secondary markets.
Related: RWA-Backed Stablecoins
4. Develop a Smart Contract
Creating a smart contract is a crucial step in stablecoin development and a key factor in the success of any crypto business. Smart contracts provide security through digital agreements. To ensure the reliability and authenticity of your stablecoin on a decentralized platform, you must choose the right protocols for smart contract development. Developers will create, test, and launch these smart contracts on the test network using virtual wallets.
5. Design the System’s Visual and Technical Aspects
At this stage, it’s time to design the necessary token. Designing a stablecoin involves understanding how transactions will flow and how the entire system will function. You may also need to design a system that enables users to interact with your token, which could involve creating a website or mobile app. This step requires the design of web or mobile app screens. Our stablecoin experts can also provide technical designs that represent the entire workflow of a stablecoin.
6. Develop, Integrate with a Blockchain Platform, and Launch on the Mainnet
Once the designs are complete, the next step is system development. During this phase, you’ll write the smart contracts required to interact with the stablecoin and launch nodes on the selected blockchain platform. After developing the stablecoin’s features and connecting them to the blockchain backend, you can launch it on the test net. If you’re using Ethereum, there are various test nets available. Have different groups test your product on the test net and provide feedback for improvement. Address any issues identified during testing, and once resolved, you can launch your stablecoin on the mainnet.
To better understand the process of creating a stablecoin, let’s explore an example in detail, considering factors such as Asset-Backed Securities (ABS) vs. Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) in the context of collateralized stablecoins.
Example of Creating a Stablecoin
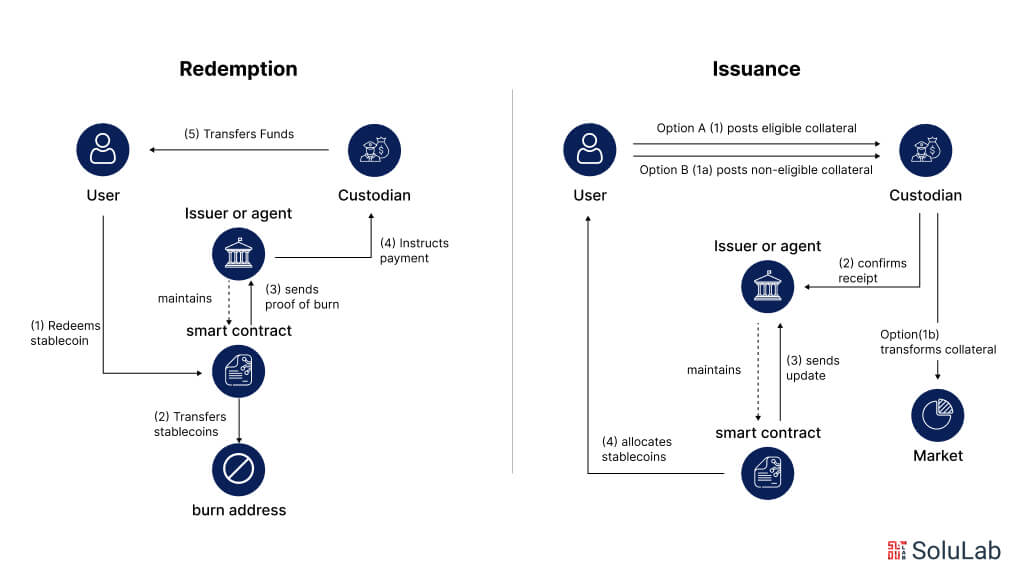
Imagine you need to develop a gold-backed stablecoin on the Ethereum platform, supported by verified physical gold holdings. The gold-backed token would represent the value equivalent to 1 gram of gold. Each token should provide the benefits of physical gold—being liquid, tradable, transferable, and fully backed by verifiable gold assets.
To create such a stablecoin, the owner must possess the underlying assets. For a gold-backed stablecoin, this means you must have physical gold, which can be stored with a custodian. After submitting the gold to the custodian, you must record timestamped details such as the gold’s serial number, custody events, purchase receipt, and the custodian’s digital signatures on a distributed ledger. This process creates proof of ownership for the gold asset.
Gold-backed tokens can only be minted once the gold is submitted to the custodian. As soon as the timestamped custody events are recorded on the blockchain, smart contracts are triggered to mint tokens. These minted tokens are then added to your organization’s holdings and can be issued to users.
To ensure your token is compliant, you can integrate third-party AML/KYC APIs to onboard reliable and authentic users.
Developing the entire stablecoin infrastructure requires both front-end and back-end components. The front end could be native iOS/Android apps or web apps, while the back end would be built on a blockchain platform. One platform used for tokenizing, minting, and burning tokens is the Alphapoint Blockchain Network.
Here are some third-party integrations that can be incorporated into the system:
- Coinbase Wallet:
You can use Coinbase Wallet or another third-party wallet to store and transfer stablecoins. - Stock Exchange API:
A specific stock exchange API can fetch real-time gold values from an exchange where your physical gold assets are stored. This allows users to access the current value of their assets. - Bank Merchant Account APIs:
Bank merchant account APIs can be integrated to enable various payment methods for purchasing gold-backed tokens.
It’s crucial to highlight that our team has the expertise required to build a fully compliant and tradable stablecoin. This process showcases how you can create a stablecoin, specifically a gold-backed one, within the list of stablecoins available today. Understanding the ICO working and the stablecoin price dynamics is also essential when planning such a project.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, creating a stablecoin involves a series of strategic steps, from choosing the right type of stablecoin and blockchain platform to developing smart contracts and ensuring liquidity. Whether you are aiming to create a gold-backed stablecoin or another asset-backed cryptocurrency, the process requires careful planning and execution to ensure stability, security, and compliance. This guide has outlined the essential aspects you need to consider to successfully develop a stablecoin that can meet market demands and offer value to users.
However, building a stablecoin comes with challenges such as maintaining liquidity, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, and integrating secure third-party services like wallets and payment gateways. SoluLab, as a leading Stablecoin development company, has the expertise to navigate these complexities. We offer end-to-end solutions tailored to your stablecoin development needs, from conceptualization to deployment on the blockchain Technology. To discuss how we can help you bring your stablecoin project to life, contact us today.
FAQs
1. How are stablecoins different from bitcoins?
The supply and demand in the market influence the value of bitcoin, which causes significant volatility. Stablecoins, on the other hand, are designed to minimize price fluctuation by maintaining a constant value, usually linked to a fiat currency and various assets that are stable.
2. Which currency is backed by gold?
With the advantages of the blockchain, investors can acquire investment-grade real gold at a reasonable price with PXAG. One solid ounce of gold is backing for each Pax Gold (PAXG) token, and it is kept in London’s LBMA vaults.
3. What is the price of creating a stablecoin?
The sort of stablecoin that is built has a significant impact on the cost of manufacturing. In general, creating asset-backed collateralized stablecoins is easier and less costly, the approximate cost ranges from $10,000 to $12,000 USD.
4. Why should I buy a stablecoin?
They happen to provide security as well as worth that other cryptocurrencies do not, stablecoins are essential to the cryptocurrency ecosystem. Stablecoins use a variety of techniques, including decentralized governance, collateralization, and algorithms to maintain a constant value.
5. How does SoluLab provide solutions for the challenges associated with stablecoin development?
Developing stablecoins has several difficulties, including integrating safe third-party services, keeping liquidity, and guaranteeing regulatory compliance. As a crypto development company, SoluLab is providing all-inclusive solutions to tackle these issues, from creating safe smart contracts to complying with all legal regulations.


