- AI Development
- AI App Development
- AI Consulting
- AI Software Development
- ChatBot Development
- Enterprise AI ChatBot
- AI Chatbot Development
- LLM Development
- Machine Learning Development
- AI Copilot Development
- MLOps Consulting Services
- AI Agent Development
- Deep Learning Development
- AI Deployment Services
- Deep Learning Consulting
- AI Token Development
- AI Development Company
- AI Development Company in Saudi Arabia
- AI Integration Services
- Hire Blockchain Developers
- Hire Full Stack Developers
- Hire Web3 Developers
- Hire NFT Developers
- Hire Metaverse Developers
- Hire Mobile App Developers
- Hire AI Developers
- Hire Generative AI Developers
- Hire ChatGPT Developers
- Hire Dedicated Developers
- Hire Solana Developer
- Hire OpenAI Developer
- Hire Offshore Developer
- About Us
- Networks+
- Smart Contracts +
- Crypto currency +
- NFT +
- Metaverse +
- Blockchain+
- Mobile Apps +
- WEB +
- Trending +
- Solutions +
- Hire Developers +
- Industries +
- Case Studies
- Blogs
AI is transforming the way companies operate, the way individuals operate technology, and the way decisions are made daily. From small startups to big international businesses, AI is now integrated into the routine business processes in different industries.
The global AI market outlook growth will be better than ever between 2026 and 2030. AI development solutions will be used by more companies to save time, reduce cost and enhance customer experiences. Meanwhile, investors are investing increasingly in AI-based products and services to automate repetitive tasks and spend more time strategising and growing their business.
This blog examines the future of AI market trends in the next few years. We will deconstruct major growth patterns where investment is growing.
Key Takeaways
- AI services that are hosted on the cloud will reduce barriers to entry for startups.
- The sectors that are going to make the most investments in AI are the industries of healthcare, finance, manufacturing, retail, and marketing.
- Generative AI, AI agents, and industry-specific AI models will generate new sources of revenue.
- The most rapid AI expansion will happen in the Asia-Pacific, whereas the largest market will be North America in terms of AI innovation and investment.
Global AI Market: Overview
The AI market is expected to experience strong growth due to the adoption of cloud platforms, machine learning, generative AI, and enterprise automation. The Global AI market size is projected to reach USD 3823 .49 billion by 2034.
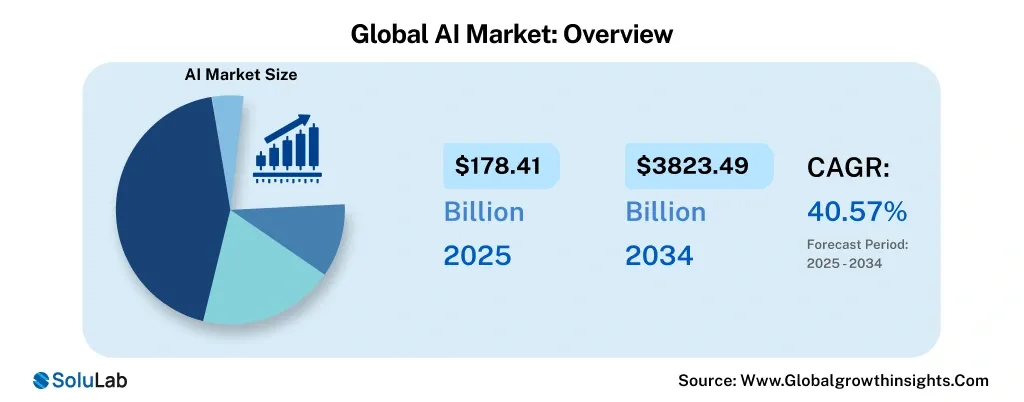
The most important factors are the increased demand for AI-driven efficiency, data-driven decision-making, routine tasks automation, and the growing availability of AI cloud services, which creates fewer adoption barriers.
North America is currently the market share leader, and Asia-Pacific has the highest growth rate. Talent issues and ethical issues are some of the critical market constraints regardless of the rapid growth.
Read More: Top 10 AI Trends in 2026
Global AI Market Outlook 2026 – 2030: Key Growth Projections
The AI market worldwide in 2026-2030 will expand at a wholly new pace due to smarter systems, greater enterprise usage, and solid cloud, automation, and emerging digital ecosystem convergence.
- Cloud and AI Convergence: Cloud platforms are emerging as the foundation of AI expansion due to their ability to provide scalable computing, reduced model deployment speed, and reduced infrastructure costs. Such convergence enables companies to test, educate, and implement generative AI tools without making significant initial investments.
- Assistive AI to Agentic AI: AI is evolving away towards agentic systems capable of planning, making decisions and taking actions on their own. Such agents of AI will oversee the working processes, streamline operations, and deal with sophisticated tasks with minimal human intervention in the industries.
- Growth of AI + Web3 Ecosystem: AI + Web3 is the concept of decentralized intelligence, smarter smart contracts and AI-driven blockchain applications. The combination brings in transparency, security and automation in areas such as finance, identity management and digital ownership.
- AI in Automation and Advanced Analytics: AI-associated automation is transforming the decision-making process involving real-time insights and predictive analytics. Enterprises are applying AI to work to examine big volumes of data, lower the number of individuals working, improve accuracy and facilitate faster and more information-oriented strategic choices.
- Vertical-Specific AIs and Domain Intelligence: Vertical-specific AIs are no longer companies relying on generic models, but rather industry-specific AI, which is trained on industry data. These solutions are more accurate, more compliant, and give viable results in these sectors of healthcare, manufacturing, finance, and retail.

Industry-Wise AI Adoption Outlook from 2026 to 2030
In 2026, investing in AI consulting services is the only way to be competitive. Businesses across industries will start using AI use cases to grow their businesses further.
1. AI in Healthcare
The early detection of disease, drug discovery, and personalised treatment plans will be automated by AI for healthcare between 2026 and 2030. Hospitals will use AI to diagnose and monitor patients and improve their working performance, and life sciences companies will reduce the time of the R&D process by a significant margin.
2. AI in Finance and Banking and Fintech
The fields of fraud detection, credit scoring, risk assessment and individualized financial products will be dominated by AI in BFSI sector. AI-driven automation in banks and fintech companies will enable cost reduction, enhance compliance, and provide more secure and faster customer experiences at scale.
3. AI in Retail, eCommerce and Supply Chain
AI for businesses will be applied by retailers in demand predictions, dynamic prices, optimal inventory and customized shopping experiences. AI predictions of the disruption, optimization of logistics, and management of vendors and warehouses will make supply chains more robust.
4. AI in the Factories
Since the year 2026, predictive maintenance, quality control, and real-time optimization of production will be a driver of AI. The AI-based robotics and analytics will be used to decrease downtime, enhance safety, and increase the general efficiency of manufacturing in smart factories.
5. Artificial Intelligence in Marketing
AI in marketing services will automate the content production, segmentation of customers, lead scoring and sales forecasting. Companies will provide hyper-personalized experiences on channels, and autonomous chatbots and assistants will respond to customer inquiries faster and more precisely.
AI Startup Ecosystem and Funding Trends
The AI startup ecosystem is accelerating fast, fundraising is increasing, novel business models, corporate strategies, and policy provisions are defining how innovation is growing and influencing global sectors nowadays.
According to the new Hypergrowth Startup Index report from HubSpot for Startups, data indicate that 34 of the 100 fastest-growing companies are AI-driven.
Here are the latest AI trends you’ll see in the next few years:
1. AI Startup Funding Patterns & Ecosystem
Major investments are being made in AI startups globally, and investments are no longer limited to the conventional tech hubs. The generative AI enterprise solutions and deep-tech innovators experience capital inflow that propels the valuation and deal activity continues to boom despite large-scale market changes.
2. AI SaaS Business Model Growth
Revenue-based software is changing because of AI-enhanced SaaS. Ventures combining machine learning with cloud services are raising substantial capital, and in regions such as India, AI-first companies are already surpassing legacy SaaS in terms of investment focus with scalable intelligent offerings.
Read Also: How to Develop an AI SaaS Product That Solves Real Business Problems?
3. Enterprise-AI Startup Corporate Partnerships
Big tech and old businesses are collaborating with AI startups via investments and integrations. Such partnerships speed up the use of artificial intelligence technology to scale startups in fields such as cloud, analytics, and automation and improve enterprise competitiveness.
4. Programs supported by the government on AI innovation
The governments actively fund, build infrastructure and talent programs in support of AI innovation. Efforts such as the IndiaAI Mission in India, where it invests billions in AI research and development and startups, and regional AI roadmaps and skilling initiatives to develop founders and technologies.
5. The Vertical and Domain-Specific AI Companies
In addition to horizontal, industry-specific AI startups (healthcare, fintech, language tech, robotics) are increasingly becoming popular. Such niche players are targeted investments because they can be used to address specific challenges of business through custom AI applications.
6. International Growth and Foreign Investment
AI startups are raising more funds and are growing in size and globalization. Massive investment rounds and cross-country capital movements are an indicator of international trust in AI innovativeness, and startups in various areas are becoming unicorns.

Conclusion
AI will cease to be a nice-to-have, and it will become part of the daily activities of businesses. The companies will spend more on AI to save time and cost, and make improved decisions.
This growth will involve start-ups, big businesses, and governments. The greatest opportunity for businesses is to apply AI in real-life applications and not to pursue the hype. Individuals who prioritize resolving evident issues, establishing robust alliances, and embracing changes will be better placed to achieve success in the next few years.
SoluLab is an AI development company that can assist companies in automating their workflows in different industries. Book a free discovery call today!
FAQs
Simple AI tools can be used in marketing, customer support, content creation, and analysis without requiring heavy investments or technical expertise.
The greatest beneficiaries will be in healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, and marketing because AI will save time, allow cost reduction, make more accurate decisions, and enable more fast-decision-making.
Yes. AI can assist companies to achieve quicker workflows, reduce human input, enhance consumer experience, and remain competitive, and as such, it is an intelligent long-term investment in most sectors.
The main risks are poor data quality, high cost of setup, lack of skilled talent, privacy of data, and the use of AI without objectives or a business strategy.
AI will not replace all jobs. It will be robots do repetitive jobs, and human beings can concentrate on creative thinking, decision making, problem solving and relationship based jobs.

