
Investing in real estate, art, or other high-value assets often feels out of reach for everyday investors. Traditional methods involve high costs, middlemen, and limited liquidity, making asset ownership complex and restrictive.
Wanting to invest in a luxury apartment or a rare painting, but being held back by high prices and red tape. However, asset owners find it difficult to generate capital or extract value from their holdings without completely liquidating them.
Asset tokenization is a game-changer that converts real-world assets into digital tokens on the blockchain. These tokens allow fractional ownership, increase liquidity, reduce transaction costs, and democratize access to previously illiquid markets. In this guide, we’ll break down what asset tokenization is, its benefits, use cases, and how you can get started.
Asset Tokenization (A Brief Introduction)
Tokenization is the transformative process of converting ownership and rights related to specific assets into a digital format. This method allows for the conversion of indivisible assets into tokenized representations.
To understand better, let’s take an example of an iconic painting, the Mona Lisa. To sell it traditionally, you’d need to find a buyer with the financial means to spend millions of dollars. This limits the pool of potential buyers significantly. However, through tokenization, we can fragment ownership of the painting, making it accessible to multiple individuals. Therefore, one person may own, for example, 1/25th of the painting or asset. This level of division is achievable only through tokenization, offering a modern solution compared to conventional methods.
Read Our Blog: Top 10 Asset Tokenization Platforms in 2025
Type of Tokenized Assets
The tokenized assets can further broadly be categorized into two types: Fungible Tokens and Non-Fungible Tokens
Fungible Tokens
Fungible tokens refer to an asset that can be exchanged for another identical asset of the same type. When a good or service is fungible, it means it can be substituted with another identical good or service without any distinction.
Non-Fungible Tokens
Non-fungible tokens signify that each token is unique and cannot be replaced by an identical token. These tokens possess distinct characteristics, making them individual and irreplaceable. This uniqueness imparts a higher intrinsic value to NFTs compared to fungible tokens.
What Real-World Assets Can Be Tokenized?
1. Commodities
Tokenization allows banks to trade commodities on the blockchain by generating digital tokens that represent ownership of the underlying commodity. These tokens can be traded on a blockchain network for faster, safer transactions.
The tokens can be exchanged for the underlying asset, usually stored commodities. Banks can improve commodities trading, lower transaction costs, and increase investor transparency.
2. Securities and Stocks
Digital tokens representing asset ownership allow banks to exchange stocks and securities on the blockchain. Tokens are usually backed by securities in custody and can be exchanged for the asset. Banks can speed securities trading, lower transaction costs, and increase investor transparency.
Fractional stock and private equity ownership allow new groups to pool resources for purchases, which is intriguing. Tokens allow banks to use present assets as collateral for future acquisitions, improving liquidity.
3. Currencies
Financial organizations create digital tokens backed by a reserve currency to represent real currency holdings. These “stablecoins” retain a stable value compared to their currency, such as the US dollar. Kaleido has built many institutional financial platforms.
The stablecoin’s one-to-one backing with the underlying currency is verified by third-party audits and verifications of the reserve currency. This makes fiat money transactions faster and more secure, and connects the regular banking system to cryptocurrencies.
4. Intellectual Property
Tokens can represent intellectual property like patents or copyrights. Trading these tokens on a blockchain platform makes intellectual property licensing and distribution more transparent and efficient.
Tokens with smart contract capability can automate royalty payments, licensing terms, and other contractual responsibilities. This helps financial institutions streamline intellectual property administration, save transaction costs, and increase owner liquidity.
5. Real Estate
Tokenizing real estate assets can boost liquidity for banks, as digital assets are easier to acquire, sell, and fractionalize. Buy smaller pieces of the property to lower entry barriers and make it more available to other investors. This allows banks to reach new consumers, including individuals who can’t afford or don’t want to acquire a whole property.
Eliminating intermediaries through real estate tokenization reduces transaction time and cost. These transactions can be audited or transparent. Digitizing physical places saves money. Management costs, including property maintenance, insurance, and legal fees, can be reduced.
6. Art & Collectibles
Tokenizing art entails digitizing it on a blockchain network. Like cryptocurrencies, this digital representation can be purchased, sold, or traded. The token can be used as loan collateral, increasing liquidity. Imagine all the new people who could possess a Picasso if they owned one millionth of it.
With art prices rising in some markets, this technology can generate a tamper-proof record of ownership and transaction history, prevent fraud, prohibit counterfeits, and confirm provenance.
Asset Tokenization on Blockchain: Potential Benefits
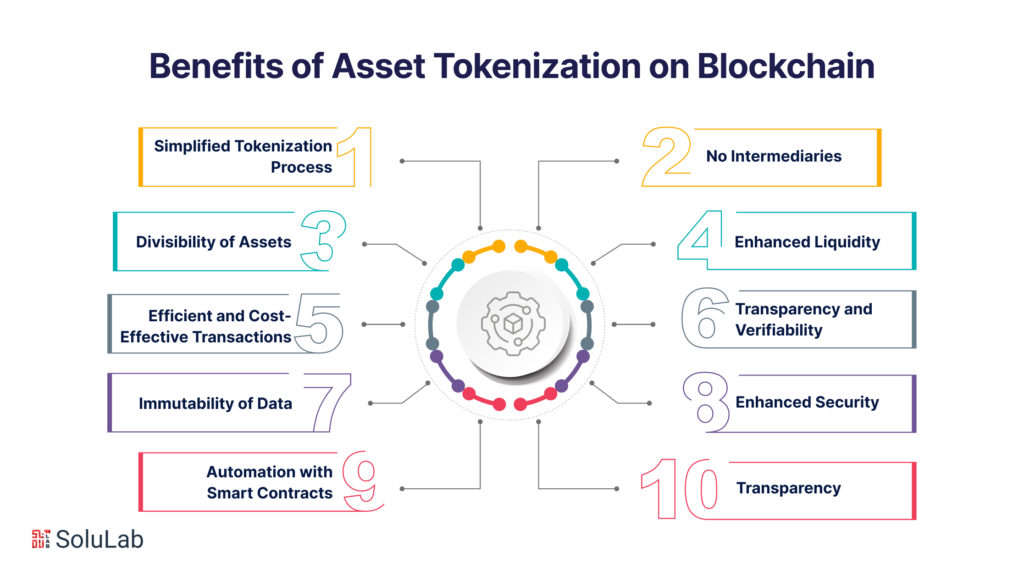
Tokenizing assets on the blockchain opens up significant growth and diversification opportunities in the market by bringing a plethora of new opportunities for businesses and individuals such as continuous operation, round-the-clock data accessibility, and immediate settlement possibilities.
-
Simplified Tokenization Process
In blockchain-based tokenization, the blockchain infrastructure replaces traditional banks, and cryptocurrency tokens replace digital dollars. While the mechanics change, the fundamental tokenization process remains similar to traditional banking, forex trading, or stock market tokenization.
-
No Intermediaries
Asset tokenization on the blockchain eliminates the intermediaries in the trading process. The distributed ledger system becomes a “source of truth” that ensures transaction integrity, securely stores digitized assets and facilitates transactions. Trust is primarily placed in the issuer and relevant regulatory bodies, simplifying and cost-reducing the process while enhancing security.
-
Divisibility of Assets
Tokenization can divide any asset into an unlimited number of virtual shares, each represented by a separate token. This feature enhances liquidity in markets where it was previously limited.
Consider real estate investments. Traditionally, buying or renting an entire building can be prohibitively expensive. However, using blockchain to divide a building into 100 tokens, each costing $2,500, reduces the investment threshold to $250.
Similar divisibility applies to intellectual property, pharmaceutical development, space research, and even entire countries, enabling greater citizen involvement in political processes.
-
Enhanced Liquidity
Tokenizing assets broadens their accessibility, amplifying market liquidity by removing the traditional obstacles associated with illiquid investments, such as fine art or real estate. Tokenized assets can be seamlessly exchanged online, enabling investors to acquire fractional ownership in the underlying asset. In addition to increasing the liquidity of existing markets, this double effect opens up a wider range of investment opportunities to a wider range of investors.
-
Efficient and Cost-Effective Transactions
Crypto tokens eliminate the need for intermediaries and intermediaries, prevalent in traditional asset management processes. As a result, the value transfer process becomes more efficient and cost-effective by a reduction in transaction costs and processing time. Moreover, crypto tokens, residing on blockchain technology, facilitate 24/7 global trading, providing uninterrupted accessibility and flexibility.
-
Transparency and Verifiability
Crypto tokens’ residence on the blockchain ensures transparent provenance and transaction histories, cryptographically verifiable by users. Blockchain automatically records transactions, and its immutable and transparent nature guarantees the authenticity of each token’s historical data. These attributes endow crypto tokens with a level of trustworthiness rarely matched by other digital assets.
-
Immutability of Data
Data recorded on the blockchain cannot be altered, deleted, or tampered with by bribing officials or hacking systems. This inherent feature is due to blockchain architecture, which records information in blocks.
This immutability makes blockchains suitable for state registries, online banking systems, and corporate databases where data accuracy is paramount. It ensures the ability to trace the history of tokens or assets, deterring fraud, theft, errors, or corruption.
-
Enhanced Security
Blockchain Tokenization relies on cryptography and distributed registries. Cryptography safeguards open data by encrypting it with secret algorithms and keys. This enables secure storage of confidential or financial information while maintaining transparency.
These security measures enhance the safety of stored information in Token, including owner details and billing information.
-
Automation with Smart Contracts
Blockchain enables the automation of most workflow and bureaucratic procedures through smart contracts—autonomous algorithms that facilitate the exchange of assets like money, stocks, tokens, or real estate.
Smart contracts automate processes, eliminate intermediaries, accelerate transactions, reduce costs, and combat corruption. They operate based on predefined conditions, executing actions when certain criteria are met.
-
Transparency
Most blockchains are open-source software, allowing users and developers to inspect the code for vulnerabilities and functionality. This transparency ensures compliance with regulations, reduces fraud risk, and instills confidence in issuers and their assets.
How Does Asset Tokenization Profit the Asset Owners?
Asset tokenization brings real financial and operational benefits to asset owners. Here’s how:
- Increased Liquidity: Owners can sell fractional shares of high-value assets, making it easier to access cash without selling the entire asset.
- Wider Investor Reach: Digital tokens allow global investors to participate, expanding the potential buyer pool.
- Lower Transaction Costs: Blockchain reduces the need for intermediaries, cutting fees and speeding up transactions.
- Improved Transparency: Smart contracts ensure automated, secure, and traceable transactions, building trust with investors.
- Enhanced Asset Utilization: Previously illiquid assets (like art or real estate) become monetizable, unlocking hidden value.
How Does Asset Tokenization Profit the Investors?
- Investors can easily diversify their portfolios by investing small amounts in tokenized assets, enhancing liquidity, and reducing paperwork hassles.
- Tokenization enables quicker asset liquidity, eliminating long lock-up periods and allowing investors to access profits or make adjustments sooner.
- Blockchain-based asset history ensures transparency, enabling investors to make informed decisions based on an asset’s true background.
- Decentralized identity and blockchain technology provide secure, verifiable ownership and identity verification, meeting KYC/AML requirements and ensuring trust across various platforms.
Additional Features
In addition to the above benefits, tokenization offers a wide range of possibilities, including trading, storage, collateral usage, payment for goods and services, participation in loyalty programs, voting, and access to blockchain platforms.
How Does Asset Tokenization Work?
The working of tokenization on the Blockchain network involves replacing sensitive information with an equivalent, non-sensitive placeholder known as a “token.” These tokens can be generated through several methods:
- Using a mathematically reversible cryptographic function with a specific key.
- Employing non-reversible functions, such as a hash function.
- With indexing functions or generating a random number.
As a result, the token takes the place of sensitive information, while the actual sensitive data it represents is securely stored in a server referred to as a “token vault.” The token vault serves as the sole location where the original information can be mapped back to its corresponding token, ensuring the safeguarding of sensitive data.
The Steps Involved in the Tokenization Process
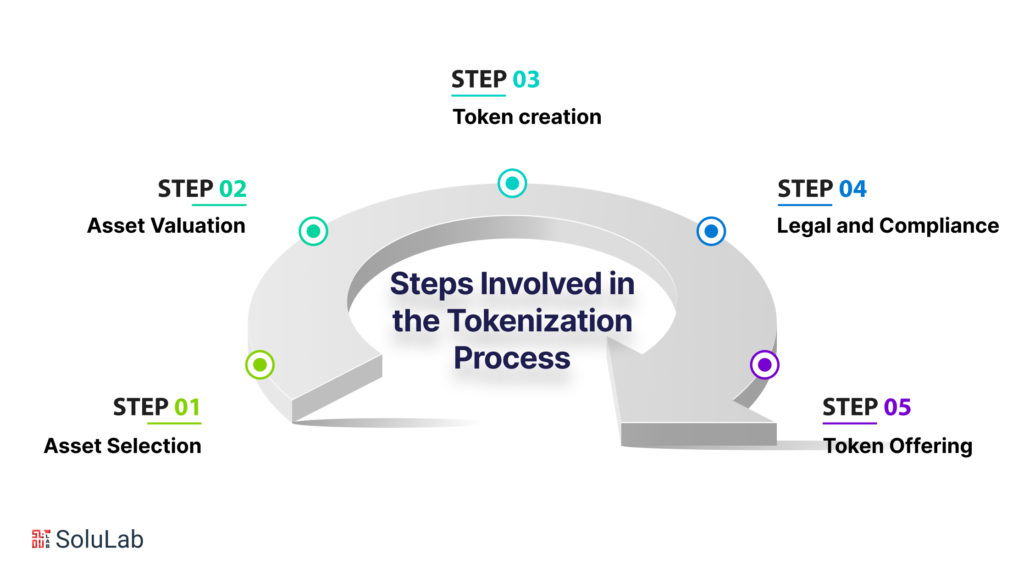
1. Asset Selection- Select an asset, for example- a piece of art, intellectual property right, or house to tokenize.
2. Asset Valuation- In this step, asset evaluation is done to determine its value, and parameters are set to understand the worth of the digital token
3. Token Creation: After determining the value, the token is created using Blockchain technology. The token contains information related to the asset it represents such as ownership information, benefits, and rights.
4. Legal and Compliance– As per the jurisdiction, a token must fulfill the regulatory requirements and legal agreements. The process ensures that created tokens adhere to the applicable laws and regulations.
5. Token Offering – The token created now can be made available for sale. The interested party who purchases the token will become the owner of the faction and the entire token as per the purchase agreement.
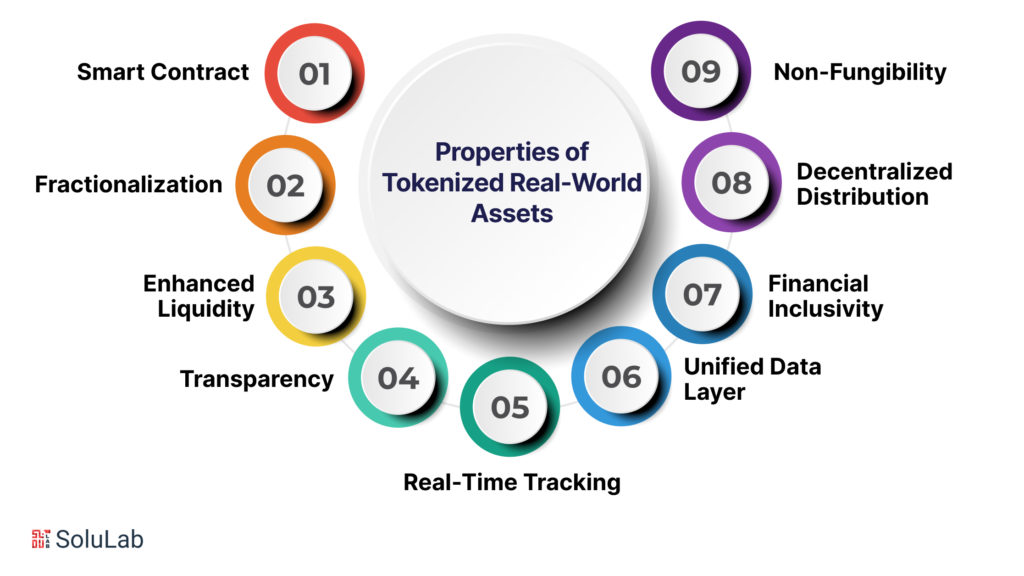
Properties of Tokenized Real-World Assets
-
Smart Contract
The tokenization of real-world assets is achieved through the deployment of smart contracts. These self-executing contracts contain predefined instructions and automatically execute when specified conditions are met. This innovative approach promotes decentralization and eliminates the necessity for third-party intermediaries in transaction processes.
-
Fractionalization
Real-world assets can be subdivided into numerous digital tokens within the blockchain ecosystem. This fractionalization enhances liquidity and fosters financial inclusivity. For instance, a $1 million commercial building can be fragmented into one million digital tokens, each valued at just $1, thereby significantly reducing the investment threshold.
-
Enhanced Liquidity
Asset tokenization enhances liquidity by simplifying asset trading and transfers within a unified platform. Digital tokens can be freely and instantaneously exchanged in a peer-to-peer manner, obviating the need for intermediary financial institutions.
-
Transparency
Tokenized real-world assets are the real-world tokens present on a blockchain, which inherently offers transparency. Blockchain users can check the transaction records, trace the asset’s origins, scrutinize its complete history, and validate ownership.
-
Real-Time Tracking
As blockchains are transparent, they enable real-time tracking of tokenized assets, effectively deterring fraudulent activities. Central banks worldwide are adopting fiat currency in tokenized form, known as CBDC – “Central Bank Digital Currency”, that users can continuously monitor.
-
Unified Data Layer
Blockchain technology streamlines data management by providing a unified data layer. This facilitates more efficient data sharing and collaboration among multiple parties involved in asset management.
-
Financial Inclusivity
Digital tokens can be issued by a wide range of entities, from small-sized businesses to big-scale industries, individuals, private companies, and non-governmental organizations, without the need for approval from traditional financial institutions. However, if these tokens are classified as securities, registration with regulatory bodies like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission may be required. Additionally, asset fractionalization lowers the entry barrier, promoting financial inclusivity.
-
Decentralized Distribution
Digital tokens can be easily distributed without reliance on third-party intermediaries. Token issuers have the flexibility to list their tokens on DEXs or can sell them autonomously.
-
Non-Fungibility
Non-fungible digital tokens (NFTs), which are unique and irreplaceable. Unlike fungible tokens like ETH, each NFT is distinct and non-replicable.
Industries Leveraging the Concept of Tokenization of Assets
1. Finance: Blockchain technology, specifically payment tokenization, has changed finance operations. Tokenization has altered asset management by improving exchange services and data security, eliminating the need to store credit card data. In 2020, decentralized finance (DeFi) emerged, disrupting traditional institutional frameworks by offering a variety of financial goods and services. Decentralized Finance (DeFi), with lending protocols and yield-farming tokens, can alter global banking and lending regardless of local financial conditions.
2. Real Estate: Blockchain technology has enabled asset tokenization in the real estate business, reducing middlemen and enabling cost-effective buyer-seller platforms. Tokenization promotes diverse markets and prevents fraud. Tokenization includes describing properties as blockchain tokens. This strategy allows fractional ownership by dividing ownership into smaller fractions. Thus, tokenization facilitates secondary market property share transactions. This method increases liquidity and democratizes real estate investments, making them more accessible.
Read Also: 9 Blockchain Real Estate Companies to Watch in 2025
3. Healthcare: The healthcare industry is considering asset tokenization to solve data security and supply chain management issues. Healthcare blockchain solutions use tokenization to replace sensitive patient data with non-sensitive representations. This empowers individuals and healthcare organizations by giving them personal data ownership. Pharmaceutical tokens are unique units of medication that use tamper-proof QR codes for authentication. This strategy increases supply chain transparency and reliability, reducing counterfeit pharmaceutical items. Thus, this step is vital to patient safety.
4. Retail: Tokenization has become a popular strategy in retail, enhancing user experiences and security. Businesses may offer safer, more convenient payment options with blockchain tokenization. Payment tokenization lets users trade without sharing credit card information, reducing data breaches and fraud. Businesses can transform consumer loyalty points and prizes into tokens, making them more transferable across stores and platforms. This strategy boosts customer loyalty and simplifies store loyalty program
5. Supply Chain: Tokenization has improved supply chain transparency, traceability, and operational efficiency. Blockchain technology lets companies tokenize commodities, transportation, and inventories. This lets stakeholders track these assets along the supply chain. Transparency helps prevent counterfeiting, theft, and fraud and ensures product authenticity. Tokenization streamlines payments and documentation, reducing paperwork and administrative overhead. Thus, supply chains are more agile and responsive, speeding delivery and lowering costs for businesses.
6. Entertainment: Blockchain tokenization is changing entertainment content development, distribution, and monetization. Music, film, and art producers can tokenize their digital assets. This empowers individuals by increasing their control over intellectual property and royalties. Blockchain technology might automate licensing, copyright, and revenue-sharing arrangements, ensuring artists fair compensation. Tokenization also allows fans and investors to support their favorite musicians and invest in their projects. Democratizing the entertainment industry may empower content creators and consumers.
Real-World Use Cases of Asset Tokenization
Tokenization is revolutionizing various industries by leveraging blockchain technology to transform real-world assets into digital tokens, thereby enhancing liquidity and accessibility. Here are some real-life use cases where tokenization is making a significant impact.
-
Tokenization of Real Estate Assets
In the realm of real estate tokenization entails breaking down traditionally illiquid property assets into fungible blockchain tokens.
Elevated Returns, an asset management firm based in New York, demonstrated the potential of this approach by tokenizing the St. Regis Resort in Aspen, Colorado, worth $18 million on the Ethereum blockchain in 2018.
-
Tokenization of Artwork
Tokenization extends its influence to the world of art. Consider the scenario where a company holds ownership of a limited number of prints of an artwork by a renowned artist. These prints can be tokenized, allowing the public to redeem tokens for physical copies. If the value of tokens redeemed falls short of a certain threshold, token holders can retain fractional ownership based on the assessed value.
TheArtToken (TAT) offers tokens representing partial ownership of Contemporary and post-war art, securely stored by the Swiss government. This approach simplifies the buying and selling of art fractions.
- Monetary Gold Tokenization by Perth Mint
The Perth Mint (Australia) launched GoldPass, a digital platform that lets users buy, sell, and transfer digital gold certificates backed by physical gold stored in their vaults. Each digital certificate is fully backed by real gold, offering a modern way to trade the metal securely and efficiently.
This highlights how a gold tokenization development company can enable financial institutions and mints to digitize gold assets, making them accessible to everyday investors without physical handling.
Read Also: Gold Tokenization and How Does It Work?
-
Tokenization of Physical Commodities
Even in the realm of physical commodities, tokenization is making strides. Take the example of gold stored in a vault owned by ABC. ABC can tokenize ownership of a portion of the gold, maintaining an ownership registry with the vault owner, XYZ. Each token sold represents ownership of a corresponding amount of gold. Token holders can redeem their gold by proving ownership via a digital signature or certificate.
JP Morgan, a financial services giant, has revealed plans to tokenize gold bars on their Quorum blockchain network. This showcases the potential for tokenization in the world of physical assets.
-
Tokenization in Cargo
In the logistics sector, tokenization addresses the inefficiencies associated with traditional proof of ownership, such as Bill of Lading (B/L) documents.
CargoX introduces a solution through tokenization called Smart B/L, built on Ethereum. The Smart B/L system operates akin to tokenization. Carriers create a Smart B/L using their app and send it to exporters. Upon receiving payment from importers, exporters transfer ownership of the Smart B/L token. Importers, in turn, can claim ownership of the goods by presenting the Smart B/L token to the carrier. This innovative approach streamlines cargo logistics, reducing delays and simplifying ownership verification.
These real-world examples vividly illustrate how tokenization is enhancing liquidity, accessibility, and efficiency across various sectors.
Conclusion
Asset tokenization is changing how we view ownership, trade, and investment. By converting real-world assets into digital tokens on the blockchain, it offers greater transparency, liquidity, and accessibility to investors across the globe.
Whether it’s real estate, art, or commodities, tokenization breaks down traditional barriers and opens up new opportunities for fractional ownership. As regulations evolve and technology matures, more businesses and individuals are likely to adopt this model.
For anyone looking to future-proof their investment strategy or business model, understanding asset tokenization isn’t just smart, it’s essential.
SoluLab, a top asset tokenization development company in the USA, provides the best services as per your business needs. Contact us today to discuss further.
FAQ
1. What is the future of asset tokenization?
Asset tokenization is set to revolutionize global finance by boosting liquidity, enabling fractional ownership, and making investments more accessible, transparent, and efficient.
2. What distinguishes cryptocurrencies from tokens?
While tokens seek to facilitate the creation of decentralized applications (dApps), and other blockchain-based platforms, coins serve as the cornerstone for safe and decentralized networks.
3. Which is the best cryptocurrency for tokenization?
The mantra OM in the realm of real-world asset tokenization arena is a layer 1 blockchain platform the other cryptocurrencies for tokenization are such as OriginTrail (TRAC), Pendle (PENDLE), Polymesh (POLYX), and TokenFi (TOKEN).
4. What should businesses look for when choosing an asset tokenization development company?
Businesses should prioritize expertise in blockchain, regulatory compliance, security, and industry-specific solutions to ensure scalable, secure, and legally sound tokenization platforms.
5. How can asset tokenization be aided by SoluLab?
Consultation, creation, and deployment of tokenization of assets customized according to your company’s needs and preferences all come under SoluLab’s extensive services offered.






