Today’s blockchain initiatives go beyond the boundaries of a single chain. Developers and teams are increasingly turning to multichain tokenization platforms to have access to more liquidity, reach new user bases, and ensure long-term scalability. These systems allow digital assets to operate fluidly across various blockchain networks, enabling use cases that were not viable in walled settings.
The stats speak for themselves. Over 35% of active Web3 developers contribute to multichain ecosystems, indicating a significant industry-wide effort for interoperability.
This blog breaks down how multichain tokens are designed, why they’re becoming essential infrastructure for modern Web3 initiatives, and what makes this approach so powerful for creating resilient, adaptable digital economies. Let’s delve in!
What are Multichain Tokenization Platforms?
It is quite similar to the concept of creating a digital token that isn’t limited to one blockchain but instead moves freely across many. That’s the promise of a multichain tokenization platform. It’s not just about flexibility, it’s about breaking down the invisible walls that divide ecosystems.
One of the biggest drawbacks of single-chain setups is isolation. Tokens and apps are confined to the features and flaws of one environment. In contrast, multichain platforms open the door to broader communities and let developers use the specific strengths of different networks. It’s a more resilient model that reduces dependency and opens up greater reach. This model plays a growing role in the broader rise of blockchain tokenization, where digital assets are built to move and evolve across systems.
Cross-Chain Functionality
The functionality of these platforms hinges on a few critical methods:
- Token wrapping works by locking the original asset on one chain and issuing a copy on another, for example, creating Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) from BTC to allow its use in Ethereum-based DeFi.
- Burn and mint models maintain balance during transfers. To ensure the overall supply remains constant, a token may be burned on the origin chain and minted on the destination chain.
- Dynamic liquidity routing enables tokens to travel through the most efficient and cost-effective cross-chain paths.
These technical processes are the core of multichain asset tokenization, allowing tokens to retain their value and functionality no matter which chain they traverse.
The Infrastructure Enabling Multichain Interoperability
To support seamless operation across chains, several foundational technologies work together:
- Cross-chain bridges serve as links that enable secure asset and data transfer between blockchains.
- Interoperability protocols, such as LayerZero and IBC, ensure that chains can communicate reliably, maintaining transactional accuracy across different environments.
- Smart contracts play a vital role by executing logic that allows one blockchain to trigger functions or responses on another.
In the debate of multi-chain vs. cross-chain, multichain solutions are often seen as more scalable since they enable native operation on multiple networks rather than simply bridging between them.
Key Features of Multichain Tokenization Platforms
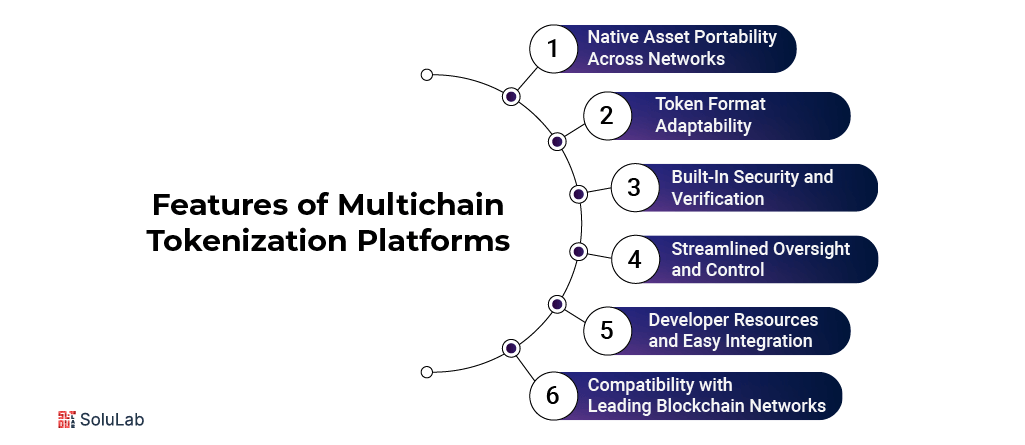
Multichain tokenization platforms are changing how digital assets are created and managed across blockchain ecosystems. This shift empowers projects to operate at a broader scale, unlocking utility and access that would otherwise be out of reach.
-
Native Asset Portability Across Networks
One of the most practical features is the ability to manage tokens across different chains without depending on manual swaps or third-party bridges. Assets created using these platforms can be moved across networks without losing their identity or functionality. This seamless movement encourages broader adoption and improves the user experience significantly.
-
Token Format Adaptability
These platforms don’t restrict developers to a single technical format. They make it possible to issue tokens compatible with various blockchain standards such as ERC-20, BEP-20, and more. This versatility gives teams the freedom to build tokens that align with each chain’s technical requirements and community expectations.
-
Built-In Security and Verification
When assets move between blockchains, the risk of fraud or error increases. That’s why these platforms place a strong focus on verification. They include built-in mechanisms to validate each action, ensuring tokens aren’t duplicated and transactions reflect true ownership. This level of safety builds trust in both the platform and the assets it manages.
-
Streamlined Oversight and Control
Project owners often deal with multiple dashboards when managing tokens on different networks. Multichain platforms eliminate this hassle by providing a unified interface where developers can track movement, check supply levels, and monitor activity all from one place. It makes asset oversight much simpler and helps prevent critical errors.
-
Developer Resources and Easy Integration
Teams working on token creation and deployment often look for tools that speed up development. A well-designed multichain tokenization platform development suite includes everything from prebuilt code templates to detailed documentation and support. These resources reduce friction for builders and help projects go live faster.
-
Compatibility with Leading Blockchain Networks
Support for multiple blockchains expands reach. These platforms typically allow token deployment on Ethereum, Polygon, Solana, BNB Chain, and newer networks as they emerge. This level of reach gives projects the freedom to engage different communities and optimize for cost, speed, or decentralization, depending on what matters most to them.
Read Also: Entertainment Tokenization in Media & Film
How Does it Differ From Single-Chain Tokenization?
Unlike single-chain tokenization, which keeps digital assets locked within one blockchain, multichain tokenization allows tokens to operate across several networks simultaneously. This not only expands utility but also improves accessibility, flexibility, and ecosystem reach. Projects using multichain tokens can tap into different blockchain communities without duplicating effort or compromising user experience.
Compared to single-chain models, which are often limited by the performance and fees of one platform, multichain asset tokenization supports a more fluid, scalable approach. Many top blockchain platforms are already moving in this direction, helping creators and businesses build tokenized ecosystems that are future-ready and interoperable. Here are some of the key differences:
| Aspect | Single-Chain Tokenization | Multichain Tokenization |
| Blockchain Scope | Tokens are restricted to one blockchain network. | Tokens can operate across multiple blockchain ecosystems. |
| Flexibility | Limited adaptability due to reliance on one network’s features. | Greater flexibility to use the best tools and functions from different chains. |
| User Reach | Access is limited to the user base of one chain. | Wider access across different communities and user groups. |
| Scalability | Bound by the scalability and transaction limits of a single platform. | Easier to scale using parallel networks with different performance strengths. |
| Risk Mitigation | Heavily dependent on the health of one chain. | Reduces dependency by distributing asset presence across chains. |
| Ecosystem Integration | Less adaptable when integrating with diverse DeFi, NFT, or dApp ecosystems. | Seamless integration with varied ecosystems supporting multichain tokens. |
| Development Strategy | Requires redeployment on new chains to expand. | Simplifies expansion using multichain asset tokenization methods. |
| Platform Examples | Runs on one chain like Ethereum or BNB Chain. | Often supported by top blockchain platforms like Polkadot, Avalanche, and Cosmos. |
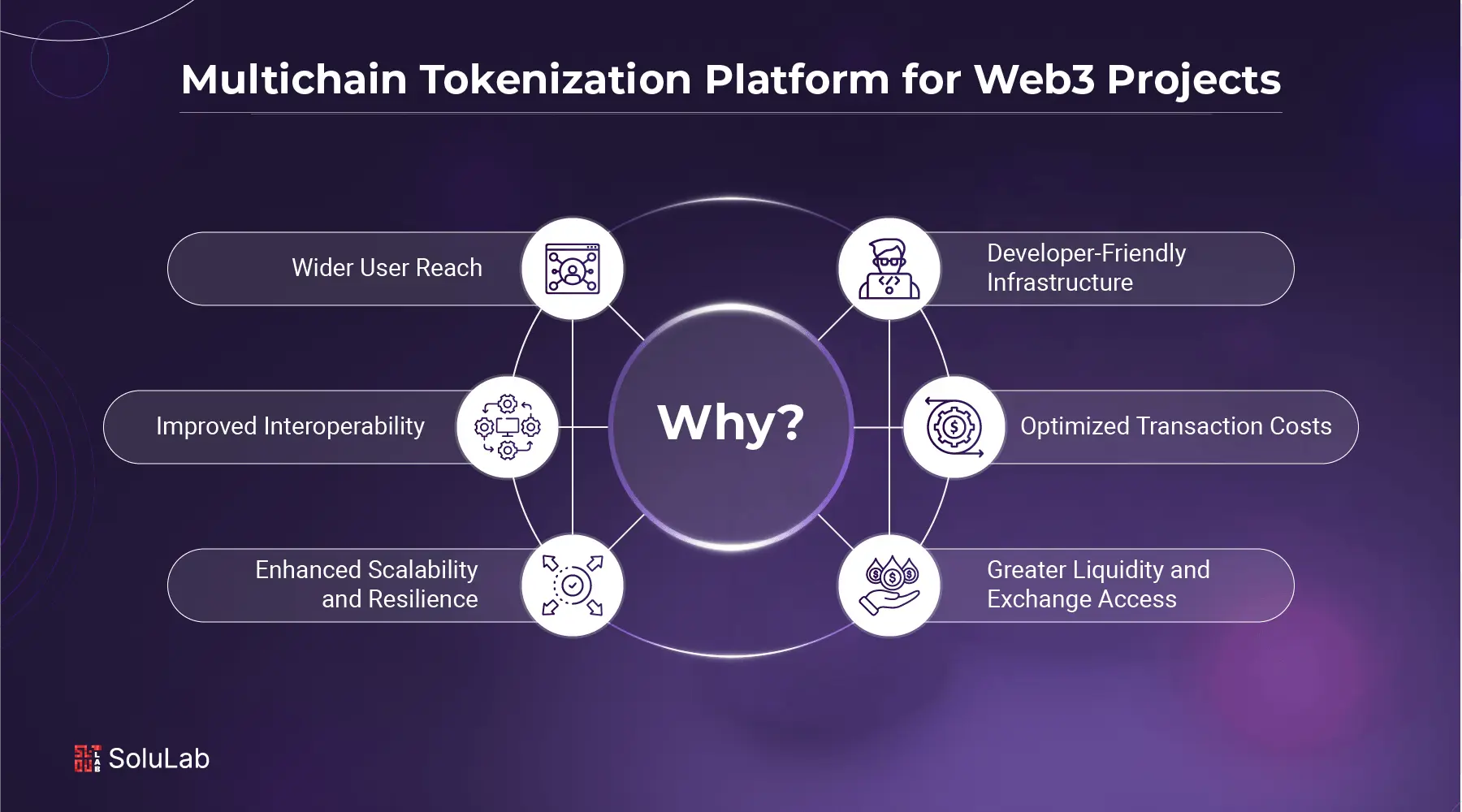
Benefits of Multichain Tokenization for Web3 Projects
Multichain tokenization gives Web3 projects the flexibility to operate beyond the limits of a single blockchain, opening up new possibilities for growth, efficiency, and user engagement. By using a reliable multichain tokenization platform, developers can create tokens that function across multiple ecosystems, improving reach and reducing operational risks, all while streamlining development and integration processes. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Wider User Reach
Multichain tokenization allows projects to connect with users across different blockchain communities, expanding visibility and adoption without being tied to one ecosystem.
2. Improved Interoperability
Tokens can seamlessly interact with DeFi protocols, NFT marketplaces, and dApps on various chains like Ethereum, BNB Chain, Solana, and Avalanche, enhancing overall utility.
3. Enhanced Scalability and Resilience
Distributing token operations across multiple blockchains reduces pressure on any one network and ensures the project stays functional even if one chain faces congestion or downtime.
4. Optimized Transaction Costs
By using lower-fee chains for certain activities (e.g., minting NFTs or microtransactions), projects can reduce gas expenses and improve the user experience.
5. Greater Liquidity and Exchange Access
Multichain tokens can be listed and traded on a wider range of exchanges, giving users more options and driving increased token flow across platforms.
6. Developer-Friendly Infrastructure
A robust multichain tokenization platform provides APIs, SDKs, and prebuilt smart contracts that simplify cross-chain deployment, saving development time and reducing risk.
Who Can Use the Multichain Tokenization Platform?
Multichain tokenization platforms are built for a wide spectrum of users aiming to create, manage, or scale digital assets across several blockchain environments. By offering chain abstraction, these platforms handle the complex background processes while giving users a straightforward way to build for multiple networks. This opens up valuable opportunities for creators, developers, businesses, and communities alike.
- Web3 Startups: New blockchain-based ventures can launch tokens that function across several chains, helping them reach wider audiences and avoid being locked into one ecosystem.
- DeFi Protocol Developers: Builders of decentralized finance solutions can design tokens that interact with lending pools, DEXs, and liquidity hubs on different chains without needing to duplicate code.
- NFT Artists and Collectible Platforms: Creators and platforms can mint NFTs compatible with different blockchain marketplaces, offering users more choices while minimizing gas fees and platform limitations.
- Enterprises Exploring Tokenized Assets: Businesses that want to tokenize ownership of real-world assets such as real estate, inventory, or intellectual property can benefit from secure and compliant multichain deployment.
- DAOs With Growing Communities: Decentralized communities can distribute governance tokens and manage cross-chain treasuries with ease, allowing for more transparent and flexible participation.
- Cross-Border Payment Solutions: Projects working in international finance or remittances can issue interoperable stablecoins and digital assets that function smoothly across regions and blockchain infrastructures.
- Token Launchpads and Crypto Incubators: These platforms can empower new projects by simplifying token launches with ready-made multichain deployment tools that speed up go-to-market timelines.
Essential Components for Building Effective Tokenization Platforms

To develop a multichain tokenization platform that actually delivers performance and scales over time, there’s no room for shortcuts. It demands a reliable core backed by the right mix of protocols, frameworks, and development tools. Here’s a closer look at what it takes:
1. Asset Tokenization Engines
Tokenization engines function as the gateway between real-world assets and digital ecosystems. They’re the foundation that enables tangible or intangible items like property, patents, art, or contracts to be turned into tradeable blockchain tokens.
Today’s tokenization engines go far beyond simple minting. They support an entire asset lifecycle, including:
- Creating and registering tokens across various blockchain networks
- Embedding governance features such as dividend sharing or voting rights
- Providing real-time oversight, audits, and proof of asset backing
2. Smart Contract Frameworks
If tokenization engines give a token its form, smart contracts define its function. These frameworks act as the rulesets that automate how tokens operate across apps, wallets, users, and different chains.
Strong smart contract frameworks typically offer:
- A modular structure, so updates or feature enhancements don’t require starting over
- Built-in multichain compatibility, allowing seamless interaction across networks
- High security standards with pre-integrated testing, audits, and permission systems
3. Compliance-First Infrastructure
Moving forward, regulation isn’t optional, it’s a built-in requirement. Platforms must be designed to comply with financial and legal frameworks across borders from the start.
Key features of a regulation-ready platform include:
- KYC and AML verification tools that streamline onboarding
- Region-based access controls to filter out restricted jurisdictions
- Ongoing audit mechanisms for monitoring suspicious activity or unusual behavior
4. Token Lifecycle Management
The lifecycle of a token doesn’t stop at creation. It includes ongoing operations, updates, and at times, removal. Lifecycle tools help platforms manage this journey responsibly and flexibly.
These tools include:
- Multi-chain minting and issuance workflows
- Smooth migration processes to shift tokens to updated networks or standards
- Burn and freeze functions for asset control or regulatory enforcement
- Upgrade paths that allow tokens to evolve without losing value or continuity
Read Also: What is Cross-Chain Compatibility?
5. Developer and User Experience
Even the most technically advanced platform won’t succeed if it’s too hard to use. For any solution to thrive, it must balance backend sophistication with frontend simplicity, both for developers and end users.
Key elements include:
- SDKs that make it easy for developers to embed token features in existing tools and products
- Intuitive APIs that simplify integration and abstract away complex blockchain logic
- User dashboards that enable non-technical users, such as asset managers or IP holders, to tokenize, manage, and track assets with ease
Bringing all these components together is the foundation of effective multichain tokenization platform development. It’s about building more than just technology, it’s about creating trust, usability, and longevity for tokenized assets in a multichain world.
Real-World Use Cases of Multichain Tokenization
Multichain tokenization is not just a technical breakthrough, it’s already reshaping how businesses, creators, and institutions operate in the digital world. Here are some of the real-world use cases of multichain tokenization:
1. Fractional Real Estate Ownership: Real estate developers are tokenizing high-value properties and distributing fractional ownership across chains. This approach improves liquidity, allows smaller investors to participate, and enables seamless global trading.
2. Tokenized Financial Instruments: Banks and fintech firms are issuing digital bonds, securities, and equity tokens using blockchain-as-a-service platforms. These assets are managed across compliant networks, reducing intermediaries and enabling faster settlements.
3. Cross-Chain NFT Marketplaces: Digital artists and game studios are launching NFTs that live on multiple chains, letting users trade them on different platforms without friction. This widens the collector base and increases long-term token utility.
4. Decentralized Identity and Records: Governments and enterprises are building digital ID systems and registries that use multichain in blockchain structures. These allow identity credentials to be verified and stored across secure, sovereign networks.
5. Supply Chain Transparency: Manufacturers are tokenizing inventory and logistics data to track goods in real time. Multichain setups allow parties across different chains, like Ethereum for compliance and Avalanche for speed, to access unified records.
6. Loyalty and Rewards Programs: Brands are issuing multichain-compatible loyalty tokens that can be used across ecosystems. Customers can earn, redeem, and trade these rewards on various networks without being tied to a single platform.
7. Tokenized Carbon Credits: Environmental projects are creating carbon offset tokens that can be verified and traded across blockchains. This supports transparency, traceability, and easier integration with global ESG reporting systems.
Future Trends in Multi-Chain Tokenization
Nowadays, multichain tokenization platforms are entering a new phase of innovation, driven by user demands, regulatory complexity, and emerging technologies. These upcoming shifts will shape how digital assets are created, governed, and exchanged across multiple networks. Here are some of the future trends in multi-chain tokenization:
-
Universal Interoperability Protocols
Instead of relying on custom-built bridges for each pair of blockchains, future platforms will adopt standardized interoperability protocols. This shift will allow digital assets to move effortlessly between different chains, enabling smoother integration across ecosystems without the need for tailor-made solutions every time.
-
Automated Compliance Engines
Regulatory expectations are growing, and tokenization platforms will begin incorporating smart compliance layers that update in real time. These systems will help projects stay aligned with local laws automatically, adjusting KYC (Know Your Customer), access rights, and reporting processes as rules change, making legal adaptation far less burdensome.
-
Bridging Traditional and Decentralized Finance
The line between traditional finance and Web3 will continue to blur. Tokenized platforms will increasingly connect to established banking systems, custody services, and investment infrastructure, enabling institutions to benefit from blockchain functionality while retaining regulatory oversight and user familiarity.
-
AI-Powered Platform Optimization
Artificial intelligence will soon play a central role in managing and improving multichain platforms. From auto-detecting compliance red flags to optimizing liquidity across chains and predicting market shifts, AI will help automate decisions that previously required manual oversight.
These trends are not just speculation, they’re already taking shape. Many of the top blockchain development companies are exploring these innovations to make tokenization smarter, safer, and more scalable. As the technology matures, multichain tokenization is set to become not only more powerful but also more user-centric and adaptable to the needs of a global financial system.
The Final Words
Multichain tokenization is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s already reshaping how digital assets are created, managed, and exchanged. By enabling tokens to operate across different blockchains, this approach opens the door to greater flexibility, broader access, and a more connected user experience.
SoluLab has been at the forefront of this transformation, working with forward-thinking clients to bring real-world utility to tokenized ecosystems. As a trusted asset tokenization development company, we helped develop Borrowland, a decentralized crypto lending and borrowing platform. Designed to make digital asset management easier and more rewarding, Borrowland allows users to lend, borrow, swap, and earn interest in a secure and transparent environment powered by blockchain.
FAQs
1. Why choose multichain tokenization instead of a single blockchain?
Single-chain launches can limit audience reach and ecosystem access. Multichain tokenization allows assets to function across several networks, helping projects tap into broader user bases and diverse blockchain utilities.
2. Can multichain tokenization help reduce gas fees for users?
Absolutely. By shifting token interactions to chains with lower transaction costs, like Polygon or Optimism, projects can offer more affordable user experiences without sacrificing overall utility.
3. Is multichain tokenization suitable for non-crypto industries?
Yes. Sectors like real estate, supply chain, and intellectual property are using tokenization to digitize assets. Multichain support ensures these tokens interact with more platforms and reach a wider set of stakeholders.
4. How does token liquidity improve with multichain deployment?
When a token exists on multiple chains, it can be listed and traded on more exchanges and integrated into various DeFi protocols. This broad presence typically results in higher liquidity, more consistent pricing, and easier access for users.
5. What tools are required to implement multichain tokenization?
You’ll typically need cross-chain smart contracts, secure bridges, asset tracking dashboards, and a well-structured backend to ensure token consistency and performance.






