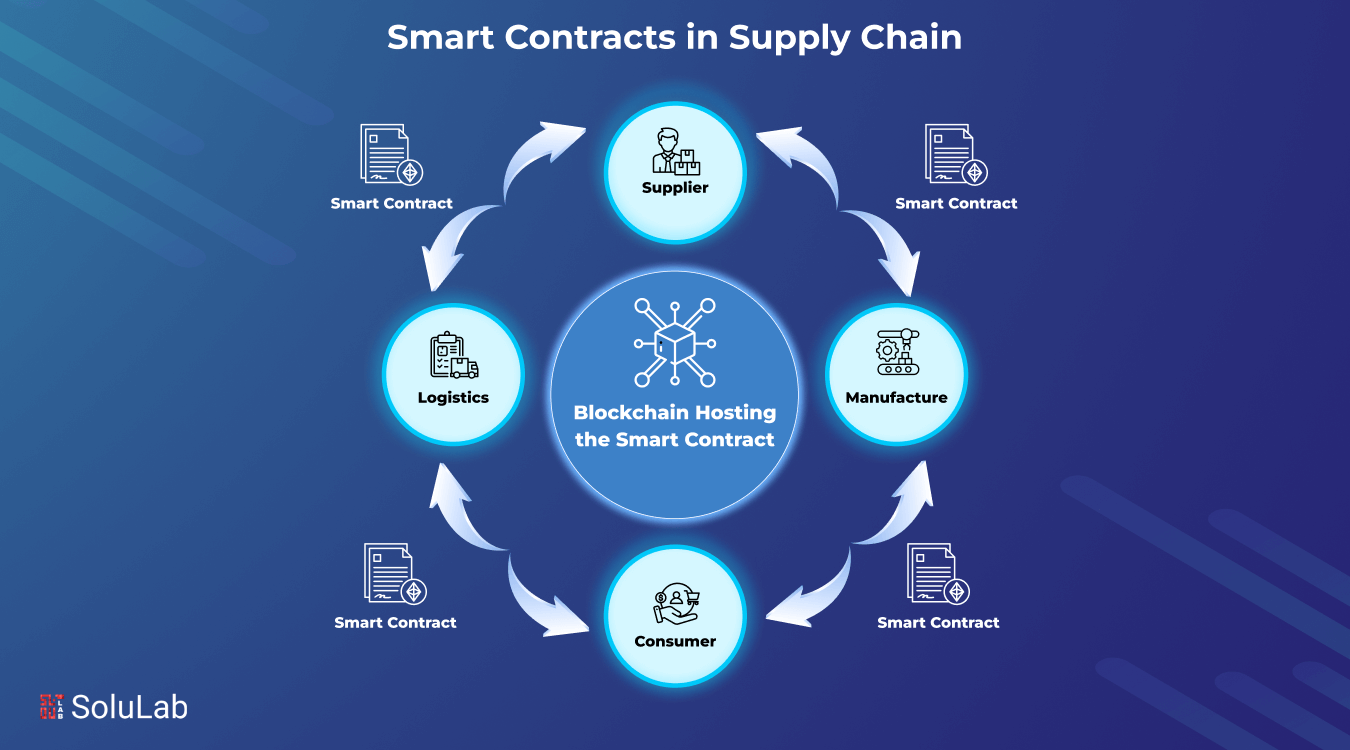
These days, supply chain networks cross continents, rely on several intermediaries, and frequently experience delays, inefficiency, or mistrust. This is where blockchain-powered smart contracts, self-executing digital agreements, are beginning to transform global business operations. Smart contracts bring in a new era of speed, security, and transparency in supply chain management.
| By 2034, the global smart contracts market is expected to have grown at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 82.21% to reach $815.86 billion. |
Industries including medicines, agriculture, and logistics, where timely delivery and compliance are quite vital, will experience multiple benefits. Smart contracts help to reduce human mistakes, automatically enforce contractual rules, and build confidence among people who may never cross paths directly. We will discuss how smart contracts operate within the supply chain ecosystem, explore the benefits of supply chain smart contracts, and their applications in changing world trade dynamics.
Significance of Smart Contracts in Supply Chain
Supply networks are significantly more complicated now than they were a decade ago. Before goods reach their final destination, they pass through various borders and change ownership multiple times. In this context, even small errors or delays may create significant disruptions. Smart contracts are digital agreements that run automatically when specific circumstances are satisfied. They are kept on blockchain networks, thus, the terms cannot be amended without consensus. For supply chain professionals, that brings a new level of efficiency and trust.
Here are the core reasons why they are gaining momentum:
-
Faster Processing
When specific circumstances are satisfied, such as a package being scanned upon delivery, smart contract platforms might promptly release money or update inventory information. As a result, less back-and-forth is required between distributors, buyers, and suppliers.
-
Better Visibility
Smart contracts ensure that all parties have access to the same live data. Everyone involved understands where the items are, their condition, and when they will arrive. This builds trust and allows quick action if something goes off track.
-
Trusted Execution
The system handles compliance without any bias or misunderstanding because words are coded and applied automatically. This helps to decrease disputes among parties who are working together for the first time.
-
Cost Control
With fewer intermediaries involved and less room for disputes, companies save significantly on overhead. Legal fees, administrative work, and processing delays can all be reduced by using smart contracts effectively.
-
Transparent Compliance
Audit trails are very important in businesses that are regulated. Blockchain records every transaction with a time stamp that can’t be changed. This makes it easy to show compliance and product authenticity at every step.
For businesses ready to modernize, implementing smart contracts in supply chain management offers measurable benefits in accuracy, speed, and cost efficiency. It is best to work with a team that provides professional smart contract development services to create solutions that fit the needs of your business and the way it runs.

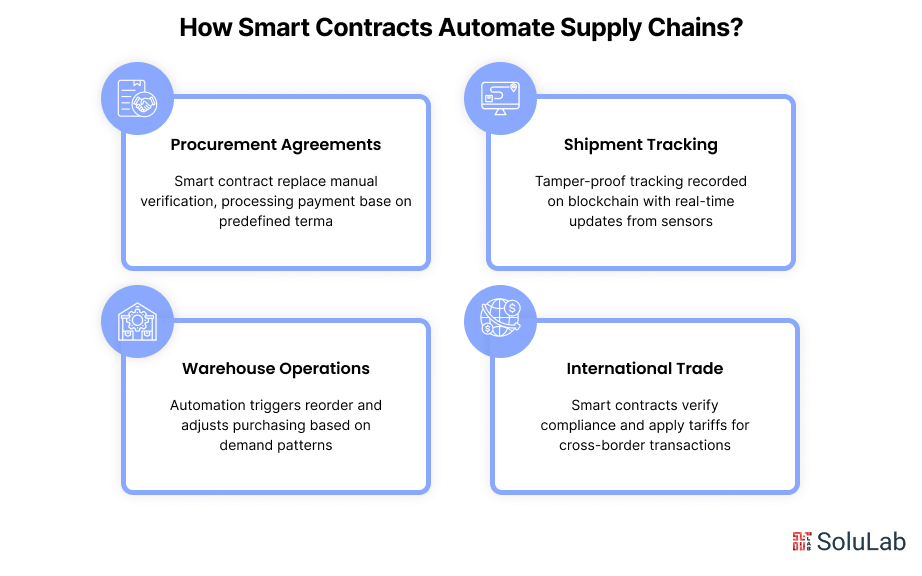
How Smart Contracts Automate Supply Chains?
The global supply chain encompasses many processes, from finding commodities and tracking warehouse inventory to scheduling delivery and deciding cross-border business practices. These steps are usually managed manually with paper records and trusted intermediaries. These tactics slow things down and increase errors, fraud, and miscommunications. Businesses can change supply chain stages with smart contracts and blockchain technology.
-
Procurement Agreements
Buying from wholesalers often involves a lot of paperwork and back-and-forth approvals. People are required in traditional purchasing processes to check orders, make payments, and keep track of outcomes. Unfortunately, this exposes the process to errors, delays, and even fraud.
Smart contracts replace much of that manual work. Once predefined terms are agreed upon, the contract automatically approves and processes payment. In cases where trust between parties is still building, funds can be securely held in a shared wallet that requires both sides to confirm before anything is released. To further streamline purchasing and ensure transparency, procurement management tools can integrate smart contracts, automate approvals, and track transactions, reducing errors and accelerating the entire procurement process
-
Shipment Tracking
Moving things from one area to another presents its own set of problems. Businesses have to deal with numerous risks such as delays, theft, and fake goods. Traditional transportation systems rely on barcode reading and third-party adjustments, which can be slow and unclear.
By choosing to implement smart contracts in logistics, companies can benefit from real-time, tamper-proof tracking. Containers equipped with smart sensors record and upload location, temperature, and other key data directly to the blockchain. This data becomes instantly accessible and verifiable by all parties involved.
In some systems, each shipment is given a unique digital identity, confirming authenticity and ownership from start to finish. If anything goes wrong, say the goods arrive damaged, the contract can immediately trigger a refund or initiate an insurance claim without human intervention.
-
Warehouse Operations
Inventory control is another area where errors are common. Many warehouses still depend on manual stock-taking, which can result in mismatched numbers and delayed restocking. This inefficiency increases holding costs and sometimes leads to lost sales.
Smart contracts bring automation to warehouse management. When stock runs low, the system can automatically reorder products without waiting for human approval. Over time, it also learns patterns in product movement and adjusts purchasing based on projected demand. In some forward-looking models, warehouse operations are governed by decentralized rules, reducing overhead and improving accuracy in how space and resources are managed.
-
International Trade
It’s even more difficult when you have to deal with taxes, customs clearing, and foreign rules. There are different rules for each area, and making sure that everything follows them can take weeks or even months.
Smart contracts help navigate these challenges with speed and accuracy. For example, they can confirm tariff rates and apply the correct taxes instantly when goods cross borders. Advanced cryptographic methods can also be used to confirm that a business meets certain compliance standards, without revealing sensitive financial or commercial information. With the help of blockchain interoperability protocols, smart contracts can work across multiple blockchain networks, making international trade seamless and reducing the friction that comes from incompatible systems.
Top Applications of Smart Contracts in the Supply Chain
Smart contracts are transforming how supply chains function by introducing automation, transparency, and trust into processes that have historically relied on intermediaries and manual coordination. Below are some of the most impactful smart contracts supply chain applications:
1. Automated Procurement and Payment Settlements
Smart contracts can trigger automatic payments once predefined conditions are met. For example, when goods are delivered and verified, the contract instantly initiates the payment process without requiring human intervention. This reduces disputes, streamlines accounting, and improves cash flow.
2. Real-Time Inventory Management
By integrating smart contracts with IoT sensors, businesses can track inventory levels in real-time. As stock depletes or is replenished, the smart contract updates the system, triggers reorders, or alerts stakeholders, ensuring optimal inventory without overstocking or shortages.
3. Transparent Supplier Compliance
Manufacturers and distributors can encode compliance requirements into smart contracts. If a supplier fails to meet quality standards, delivery timelines, or ethical sourcing policies, the smart contract can halt further transactions or flag the issue automatically. This ensures adherence to contracts and brand integrity.
4. Improved Shipment Tracking and Verification
Logistics providers can use blockchain-based smart contracts to log each checkpoint a shipment passes through. Once the final delivery is confirmed and the condition of the goods is verified (such as temperature for perishables), the contract is executed, releasing the shipment data to all involved parties.
5. Streamlined Customs and Cross-Border Trade
Smart contracts can pre-verify documents required for customs clearance, accelerating international shipments. Once the necessary paperwork is digitally verified, clearance can be granted without delays, reducing wait times at borders.
6. Dispute Resolution and Auditability
In case of disagreements, all transactions recorded via smart contracts provide an immutable audit trail. This simplifies resolution and removes the need for third-party arbitration, saving both time and legal costs.
Real-Life Examples of Smart Contracts in the Supply Chain
Smart Contracts in SCM are no longer experimental—they’re reshaping global logistics through automation, real-time data exchange, and trustless coordination. By combining blockchain technology and smart contracts, companies across sectors are solving long-standing inefficiencies. Below are real-world examples of how this technology is driving measurable change.
-
Maersk & IBM – TradeLens for Global Shipping
TradeLens, a blockchain initiative by Maersk and IBM, exemplifies how smart contracts in SCM reduce friction in international shipping. By automating customs clearance, shipment tracking, and document verification, the platform enhanced visibility across over 90 organizations in the logistics chain.
-
Walmart – Blockchain for Food Traceability
Walmart adopted blockchain technology and smart contracts to ensure food safety. Using a blockchain-based system, the company tracked fresh produce from farm to shelf. The ability to trace contamination in under three seconds revolutionized their recall response process.
-
De Beers – Tracr for Ethical Diamond Sourcing
De Beers launched Tracr, a blockchain-powered platform that leverages smart contracts in SCM to certify the origin of diamonds. Each transaction—from mining to retail—is recorded immutably, ensuring that only ethically sourced stones reach the customer.
-
BHP – Mineral Sample Tracking with Blockchain
Mining giant BHP uses blockchain technology and smart contracts to manage the custody of mineral samples. With each handoff recorded securely, the company eliminated paperwork delays and gained real-time oversight across the supply lifecycle.
-
Provenance – Transparency in Ethical Fashion and Food
Provenance uses smart contracts in SCM to provide end-to-end transparency for fashion and food brands. Customers can scan a product tag and verify claims related to sustainability, fair trade, and carbon footprint, backed by data stored immutably on blockchain.
Conclusion
Supply chains have always depended on trust between suppliers, logistics partners, and buyers. But trust alone is not enough in a fast-moving and globalized world. That is where smart contracts come in. They help simplify complex processes, remove unnecessary steps, and ensure that agreements are enforced automatically without delays or confusion. It is not just about technology, but about making day-to-day operations more reliable and easier to manage.
At SoluLab, we have seen the real impact this can make as a smart contract development company. In our project called Snackhack, we built a smart contract-powered platform to track packaged food items from the production facility to retail shelves. The system verifies product quality, processes payments once delivery is confirmed, and gives everyone involved real-time visibility. It is a clear example of how purposeful technology can solve everyday supply chain challenges cleanly and efficiently.
For any supply chain looking to grow while staying in control, adopting this technology is not just useful, it is becoming essential. SoluLab can be your partner to success. Connect now!
FAQs
1. Are smart contracts legally binding in the supply chain industry?
Smart contracts can be legally enforceable if they meet the standard requirements of a traditional contract: offer, acceptance, intent, and consideration. However, the enforceability can vary depending on jurisdiction. Many companies pair smart contracts with traditional legal agreements to cover both technical and legal bases.
2. Can smart contracts work without blockchain in supply chain use cases?
No. Smart contracts rely on blockchain as their underlying infrastructure. Blockchain smart contracts provide a decentralized, immutable ledger that ensures smart contracts execute securely and transparently. Without blockchain, they lose the trustless and tamper-proof nature that makes them valuable.
3. How do smart contracts handle exceptions or unexpected events?
Smart contracts operate based on predefined logic, so handling unexpected changes like shipment delays or supplier errors requires thoughtful design. Many systems use oracles—external data sources—to feed real-time updates into the contract, allowing it to respond to changes or trigger manual overrides when necessary.
4. What industries beyond logistics are using smart contracts in their supply chains?
Industries such as pharmaceuticals, luxury goods, agriculture, and aerospace are actively exploring smart contracts. For example, pharmaceutical companies use them to track drug authenticity, while agricultural firms use them for farm-to-fork traceability and fair-trade verification.
5. What are the biggest risks in adopting smart contracts in supply chain operations?
The main risks include coding errors, reliance on external data sources, lack of regulatory clarity, and challenges with system integration. To mitigate these, companies should conduct rigorous smart contract audits, use trusted oracle services, and work with experienced development teams to ensure reliability.





