Adherence to regulatory norms has become more important than ever for organizations across all industries in today’s quickly expanding digital economy. Today, compliance involves more than just following the law; it also involves being flexible and sensitive to the current era. Serious consequences may arise from non-compliance, including heavy fines and reputational harm over time. According to recent research, the average cost of a data breach event is $4.24 million, the largest amount in 17 years. These breaches are frequently caused by compliance failures. In light of these difficulties, creative approaches are becoming more and more necessary to successfully manage compliance issues.
In response to this challenge, generative AI has shown itself to be a disruptive and timely answer. By automating labor-intensive processes like contract review, content moderation, and regulatory document analysis, this modern technology completely transforms how businesses approach compliance.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the impact of generative AI on compliance practices in various industries. We’ll explore how this innovative technology can be practically applied and the concrete benefits it can provide to businesses striving for compliance excellence.
An Overview of Compliance Frameworks
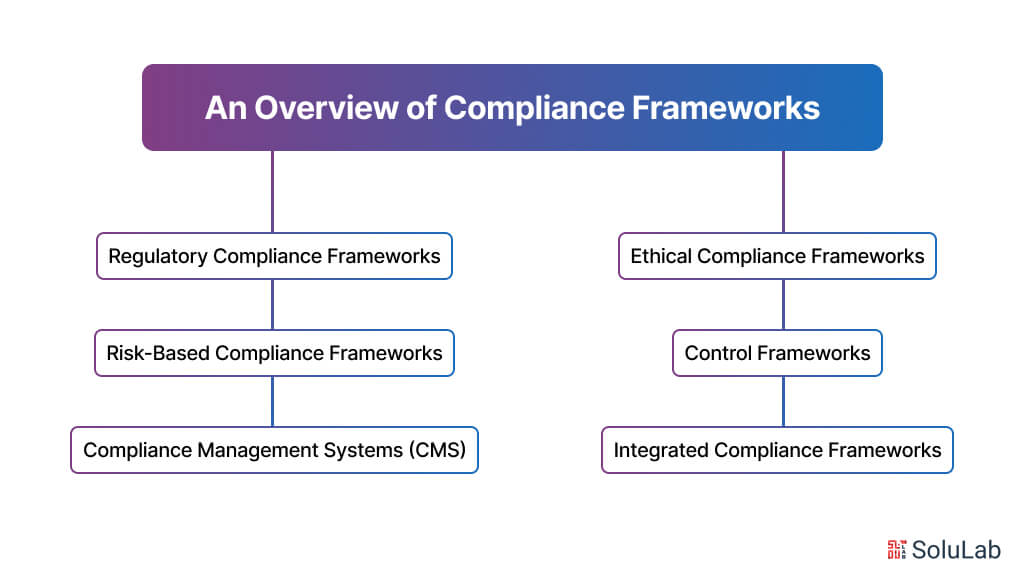
Compliance frameworks are structured sets of guidelines, policies, procedures, and controls designed to ensure that organizations adhere to relevant laws, regulations, industry standards, and ethical principles. Compliance automation software helps implement these frameworks efficiently by streamlining monitoring, enforcement, and reporting. These frameworks provide a systematic approach to managing compliance risks, fostering a culture of integrity, and promoting accountability within an organization. Here’s an overview of compliance frameworks:
1. Regulatory Compliance Frameworks
Regulatory compliance frameworks are tailored to specific industries or jurisdictions and outline the legal requirements that organizations must comply with. These frameworks typically include regulations, statutes, directives, and guidelines issued by regulatory authorities such as government agencies, industry associations, or international bodies. Examples include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for data privacy compliance, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) for financial reporting compliance, and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) for healthcare compliance.
2. Risk-Based Compliance Frameworks
Risk-based compliance frameworks focus on identifying, assessing, and managing compliance risks within an organization. These frameworks prioritize resources based on the level of risk posed by different compliance obligations, business activities, and external factors. Risk assessments, control assessments, and risk mitigation strategies are key components of risk-based compliance frameworks, enabling organizations to allocate resources effectively and address high-priority compliance risks.
3. Control Frameworks
Control frameworks define the internal controls and procedures that organizations implement to achieve compliance objectives. These frameworks provide a structured approach to designing, implementing, and monitoring controls to prevent, detect, and correct compliance failures. Examples of control frameworks include the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) Internal Control Framework and the Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology (COBIT) framework for IT governance and control.
4. Ethical Compliance Frameworks
Ethical compliance frameworks focus on promoting ethical behavior, integrity, and corporate social responsibility within an organization. These frameworks articulate the ethical principles, values, and standards of conduct that guide decision-making and behavior at all levels of the organization. Ethical compliance frameworks often include codes of conduct, ethics training programs, whistleblower policies, and mechanisms for reporting and addressing ethical concerns.
5. Integrated Compliance Frameworks
Integrated compliance frameworks encompass multiple dimensions of compliance, including regulatory, risk-based, control, and ethical considerations. These frameworks aim to align compliance efforts with broader organizational goals and objectives, fostering a holistic approach to compliance management. Integrated compliance frameworks promote collaboration across functions and departments, enabling organizations to address compliance requirements in a coordinated and efficient manner.
6. Compliance Management Systems (CMS)
Compliance management systems provide the infrastructure and processes for implementing and maintaining compliance frameworks within an organization. These systems typically include components such as compliance policies and procedures, compliance training and awareness programs, compliance monitoring and reporting mechanisms, and compliance audit and review processes. Compliance management systems facilitate the systematic management of compliance activities, documentation, and evidence, supporting accountability and continuous improvement in compliance performance.
What is Generative AI Compliance?
Generative AI compliance refers to the use of generative artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to facilitate and enhance compliance-related tasks within organizations. Generative AI, a subset of AI, involves systems that can generate new content, such as text, images, or even entire applications, based on patterns learned from existing data.
In the context of compliance, generative AI can be applied in various ways:
- Regulatory Document Analysis: Generative AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of regulatory documents, such as laws, regulations, and compliance guidelines. By understanding and summarizing these documents, generative AI can help compliance professionals stay informed about regulatory changes and requirements.
- Contract Review: Generative AI can assist in reviewing contracts and agreements to ensure compliance with legal and regulatory standards. As part of a broader AI contract management strategy, it analyzes contract language, flags potential risks or discrepancies, and streamlines the review process to minimize errors. By analyzing contract language and identifying potential risks or discrepancies, generative AI can streamline the contract review process and minimize errors.
- Content Moderation: In industries where content moderation is crucial for compliance, such as social media platforms or online marketplaces, Generative AI can help identify and remove inappropriate or harmful content. By analyzing text, images, and videos, generative AI algorithms can flag content that violates regulatory guidelines or community standards.
- Compliance Training: Generative AI can be used to develop interactive training materials for compliance education and training programs. By generating realistic scenarios and simulations, generative AI can enhance the effectiveness of compliance training and ensure that employees understand and adhere to regulatory requirements.
- Risk Assessment: Generative AI algorithms can analyze data from various sources to identify potential compliance risks and vulnerabilities within an organization. By detecting patterns and anomalies in data, generative AI can help compliance officers proactively address compliance issues before they escalate.
Overall, generative AI compliance solutions offer organizations a powerful tool for improving efficiency, accuracy, and effectiveness in meeting regulatory requirements. By harnessing the capabilities of generative AI, organizations can enhance their compliance processes and mitigate the risks associated with non-compliance.
The Significance of Regulatory Compliance for Businesses
For a number of reasons, compliance is essential to many different businesses as it serves to guarantee the reliability, safety, and integrity of operations. The following are some salient features that highlight how crucial compliance is in many industries:
1. The cornerstone of legal and ethical integrity is compliance, which directs businesses to respect moral principles and stay within the law while promoting a culture of lawfulness and ethics throughout all industries.
2. Organizations may protect their interests and stability by identifying and mitigating legal, financial, reputational, and operational risks with the assistance of strict compliance adherence.
3. Strong compliance obligations are the foundation of credibility and trust. Gaining the trust of stakeholders including partners, consumers, investors, and the general public leads to long-term success and a positive reputation.
4. Complying with legal requirements for data privacy and security guarantees the safe management of financial records, proprietary data, and sensitive information.
5. By demanding complete documentation and examination of choices, activities, and financial transactions, compliance encourages accountability and transparency by encouraging moral conduct and discouraging unethical activity.
6. Strong compliance pledges guarantee health and safety in consumer products, healthcare, and general workplaces, with the goal of preserving a safe environment for all parties involved.
7. In order to reduce an organization’s ecological footprint, environmental compliance is essential. This calls for ethical resource management, proper waste disposal, and pollution control across all industries.
8. Universal compliance standards frequently contain specifications for upholding high-quality goods and services that guarantee dependability and consumer satisfaction.
9. Following ethical compliance encourages companies to embrace ethical compliance as a key value for societal impact by highlighting ethical corporate conduct and social responsibility.
10. Organizations can broaden their worldwide reach through partnerships and international trade made possible by adhering to international standards.
11. Compliance measures protect enterprises from fraud detection, corruption, and unethical behavior, maintaining integrity, fairness, and trust in all sectors of the economy.
Related: Effective Generative AI Strategy For Your Enterprise
Challenges Organizations Encounter in Attaining Compliance
Organizations encounter various hurdles when striving for compliance, irrespective of their sector or the specific regulations they must meet. These challenges can be intricate and multifaceted. Below are some common obstacles faced by organizations in their pursuit of compliance:
- Dynamic Regulatory Landscape: Compliance requirements are prone to change as laws, regulations, and industry standards evolve. Staying abreast of these changes can pose a significant challenge for organizations.
- Interpretation Complexity: Many compliance regulations are complex and subject to interpretation. Organizations need to invest time and resources to grasp the intricacies of these regulations accurately.
- Cross-Industry and Regional Compliance: Organizations operating across multiple regions or industries may need to adhere to a broad array of regulations. Harmonizing compliance efforts across diverse requirements can be daunting.
- Resource Allocation: Achieving compliance demands dedicated resources, including personnel, technology, and financial investments. Smaller organizations may struggle to allocate these resources effectively.
- Data Management and Security: Compliance often involves handling sensitive data, necessitating robust data management and security measures to safeguard against breaches and unauthorized access.
- Legacy System Integration: Legacy systems and disparate software solutions can impede compliance efforts. Integrating these systems to ensure data accuracy and consistency can be challenging.
- Supply Chain Compliance: Organizations with extensive supply chains must ensure that suppliers and partners comply with relevant regulations. Monitoring and verifying compliance throughout the supply chain can be complex.
Read Our Blog: Generative AI in Supply Chain
- Awareness and Training: Employees and stakeholders must be aware of compliance requirements and how to adhere to them. Insufficient training and awareness programs can lead to unintentional compliance breaches.
- Ambiguity in Regulations: Some regulations may lack clear guidance on compliance measures, leaving organizations uncertain about how to meet the requirements.
- Cultural Shift for Compliance: Implementing compliance initiatives often necessitates changes in processes and organizational culture. The reluctance to adapt to change can pose a substantial obstacle to compliance.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Continuous monitoring of compliance and timely reporting of violations or issues is crucial. Establishing effective monitoring and reporting mechanisms can be challenging.
- Global Regulatory Environment: Organizations with a global presence must navigate diverse regulatory environments. Achieving consistency in compliance practices across borders can be challenging.
- Audit Preparedness: Being prepared for compliance audits or inspections is crucial. Preparing documentation and evidence to demonstrate compliance can be time-consuming and stressful.
- Financial Costs: Achieving and maintaining compliance often entails financial costs, including legal fees, technology investments, and staff training. Organizations must manage these costs effectively.
- Ethical Compliance: Ensuring that employees and stakeholders adhere to ethical standards and conduct can be challenging, often requiring a cultural shift within the organization.
What is the Role of Generative AI in Compliance?
Generative AI plays a crucial role in compliance across various industries by automating and streamlining several processes. Here’s a breakdown of its roles:
1. Risk Assessment and Monitoring: Generative AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate potential compliance risks. By continuously monitoring transactions, communications, and other activities, generative AI helps organizations stay ahead of regulatory issues.
2. Policy Development and Implementation: Generative AI can assist in developing and updating compliance policies by analyzing regulatory requirements, industry standards, and internal guidelines. It can generate policy documents tailored to specific organizational needs, ensuring alignment with relevant laws and regulations.
3. Training and Education: Generative AI-powered platforms can create interactive training modules and simulations to educate employees on compliance procedures, ethical guidelines, and regulatory obligations. These AI-driven training tools can adapt to the learner’s progress and provide personalized feedback to enhance comprehension and retention.
4. Compliance Reporting and Documentation: Generative AI can automate the generation of compliance reports, audit trails, and documentation required for regulatory purposes. By extracting relevant information from structured and unstructured data sources, AI algorithms streamline the reporting process, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors.
5. Transaction Monitoring and Surveillance: Generative AI can analyze transactional data in real-time to detect suspicious activities, such as money laundering, fraud, or insider trading. By applying advanced machine learning techniques, AI-powered surveillance systems can identify complex patterns indicative of illicit behavior and alert compliance teams for further investigation.
6. Regulatory Compliance Audits: Generative AI can assist in conducting compliance audits by systematically reviewing organizational processes, documentation, and controls against regulatory requirements. AI algorithms can identify discrepancies, inconsistencies, and areas of non-compliance, facilitating corrective actions and mitigating regulatory risks.
7. Predictive Analytics for Compliance Trends: Generative AI algorithms can analyze historical compliance data to identify trends, predict potential compliance issues, and recommend proactive measures to mitigate risks. By leveraging predictive analytics, organizations can anticipate regulatory changes, market trends, and emerging risks, enabling more informed decision-making and strategic planning.
8. Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Regulatory Analysis: Generative AI-powered NLP tools can analyze regulatory texts, legal documents, and compliance guidelines to extract relevant information, interpret complex language, and provide actionable insights. Natural Language Processing algorithms can assist compliance professionals in understanding and interpreting regulatory requirements, facilitating compliance management and adherence.
Overall, generative AI enhances compliance efforts by providing advanced analytics, automation, and decision support capabilities, enabling organizations to proactively manage regulatory risks, ensure adherence to legal requirements, and maintain ethical standards.
Benefits of Using Generative AI for Regulatory Compliance
For enterprises in a variety of sectors, using generative AI to compliance has several benefits:
- Efficiency and Automation: Compliance benefits of Generative AI minimize the time and effort needed for compliance management by automating several regulatory compliance processes, such as document preparation and monitoring.
- Accuracy and Consistency: AI-driven procedures ensure that compliance-related papers and procedures are very accurate and consistent, reducing mistakes and inconsistencies.
Read Our Blog: Generative AI and Automation
- Real-time Monitoring and Cautionary Notes: Generative AI can continually monitor data and transactions, sending real-time notifications for any compliance violations and allowing for quick remedial measures.
- Predictive Analytics for Risk Mitigation: AI has the capacity to study historical data, allowing for the prediction of compliance risks and supporting companies in taking proactive steps to resolve potential concerns before they become major problems.
Generative AI Applications in Compliance
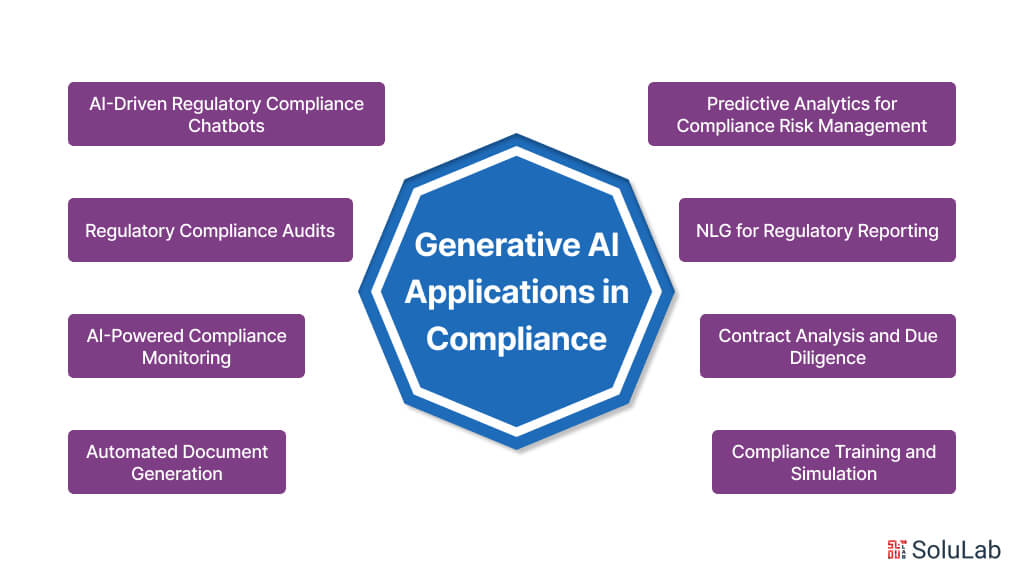
Generative AI, with its ability to create and synthesize new content based on patterns and data inputs, offers several applications in compliance across various industries. Here are some notable examples:
1. Automated Document Generation: Generative AI can create compliance documents such as policies, procedures, contracts, and regulatory reports. By analyzing existing templates, regulations, and organizational data, AI algorithms can generate customized documents tailored to specific compliance requirements, saving time and reducing manual effort.
2. Natural Language Generation (NLG) for Regulatory Reporting: Generative AI-powered NLG systems can convert structured data into human-readable narratives for compliance reporting. These systems can generate detailed reports summarizing key metrics, regulatory compliance status, and risk assessments, facilitating communication with stakeholders and regulatory authorities.
3. Compliance Training and Simulation: Generative AI can develop interactive training modules and simulations to educate employees on compliance policies, procedures, and ethical standards. AI-generated scenarios can simulate real-world compliance challenges, allowing learners to practice decision-making in a risk-free environment and improve their understanding of regulatory requirements.
4. AI-Powered Compliance Monitoring: Generative AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to monitor compliance with regulations, policies, and internal controls. By detecting patterns, anomalies, and deviations from expected behavior, AI-powered monitoring systems can identify potential compliance risks in areas such as fraud, insider trading, and data privacy breaches.
5. Regulatory Compliance Audits: Generative AI can assist in conducting compliance audits by analyzing documents, transactions, and operational data for adherence to regulatory requirements. AI algorithms can automatically identify discrepancies, inconsistencies, and areas of non-compliance, streamlining the audit process and reducing the risk of oversight.
6. Contract Analysis and Due Diligence: Generative AI-powered natural language processing (NLP) tools can analyze legal contracts, agreements, and regulatory documents to identify relevant clauses, obligations, and compliance risks. AI algorithms can extract key information, flag potential issues, and provide insights to support due diligence and contract management processes.
7. Predictive Analytics for Compliance Risk Management: Generative AI can analyze historical compliance data to identify trends, patterns, and emerging risks. By applying predictive analytics techniques, AI algorithms can forecast future compliance issues, enabling organizations to proactively mitigate risks, allocate resources effectively, and improve decision-making.
8. AI-Driven Regulatory Compliance Chatbots: Generative AI-powered chatbots can provide real-time assistance and guidance on compliance-related queries and issues. These chatbots can interpret natural language queries, access relevant compliance information, and provide personalized responses to employees, customers, and other stakeholders, enhancing accessibility and responsiveness in compliance support.
Final Thoughts
Rules, norms, and ethical principles must be followed without exception. It is the cornerstone of legal integrity, ethical behavior, and responsible business practices across sectors. As we’ve looked at the diverse functions of regulatory compliance in numerous industries, it’s clear that its effect goes far beyond legal checks. With an ever-expanding number of compliance rules, generative AI emerges as a formidable partner capable of automating complicated processes, producing correct documentation, and negotiating the complexity of regulatory systems. It allows compliance experts to concentrate on strategy, interpretation, and ethical issues rather than being bogged down in heaps of compliance paperwork.
SoluLab, as an AI development company, specializes in using Generative AI for compliance, ensuring businesses meet regulatory standards efficiently. With modern technology, SoluLab provides tailored solutions that automate compliance processes, minimizing manual effort and reducing the risk of errors. With our expertise, businesses can streamline compliance tasks, enhance accuracy, and adapt to regulatory changes seamlessly. Connect with SoluLab today to revolutionize your compliance approach with advanced Generative AI solutions.
FAQs
1. What is Generative AI, and how does it relate to compliance?
Generative AI is a branch of artificial intelligence that focuses on creating new data or content. In the context of compliance, Generative AI can be utilized to generate synthetic data sets that mimic real-world scenarios, allowing companies to train and test their compliance systems without risking sensitive information.
2. How can Generative AI enhance compliance processes?
Generative AI can enhance compliance processes by generating large volumes of realistic data for training machine learning models used in compliance monitoring and detection systems. It can also simulate various compliance scenarios, helping organizations identify and address potential risks more effectively.
3. What are the key challenges in implementing Generative AI for compliance?
Some key challenges in implementing Generative AI for compliance include ensuring the synthetic data accurately represents real-world data, addressing ethical concerns related to data generation and usage, and integrating Generative AI solutions with existing compliance frameworks and systems.
4. How can businesses ensure the ethical use of Generative AI in compliance?
Businesses can ensure the ethical use of Generative AI in compliance by establishing clear guidelines for data generation and usage, prioritizing data privacy and security, and regularly auditing Generative AI systems to identify and mitigate any biases or ethical concerns.
5. What are some real-world applications of Generative AI in compliance?
Real-world applications of Generative AI in compliance include generating synthetic financial transaction data for anti-money laundering (AML) monitoring, creating simulated healthcare records for compliance with healthcare regulations, and generating synthetic customer data for privacy and data protection compliance testing.