- AI Development
- AI App Development
- AI Consulting
- AI Software Development
- ChatBot Development
- Enterprise AI ChatBot
- AI Chatbot Development
- LLM Development
- Machine Learning Development
- AI Copilot Development
- MLOps Consulting Services
- AI Agent Development
- Deep Learning Development
- AI Deployment Services
- Deep Learning Consulting
- AI Token Development
- AI Development Company
- AI Development Company in Saudi Arabia
- AI Integration Services
- Hire Blockchain Developers
- Hire Full Stack Developers
- Hire Web3 Developers
- Hire NFT Developers
- Hire Metaverse Developers
- Hire Mobile App Developers
- Hire AI Developers
- Hire Generative AI Developers
- Hire ChatGPT Developers
- Hire Dedicated Developers
- Hire Solana Developer
- Hire OpenAI Developer
- Hire Offshore Developer
- About Us
- Networks+
- Smart Contracts +
- Crypto currency +
- NFT +
- Metaverse +
- Blockchain+
- Mobile Apps +
- WEB +
- Trending +
- Solutions +
- Hire Developers +
- Industries +
- Case Studies
- Blogs
Modern manufacturers are going through numerous problems including the need to optimize production workflows, reduce downtime, uphold strict quality, and effectively manage costs. Conventional methods frequently require assistance to meet these expectations, which results in inefficiencies, higher expenses, and lost growth potential. This is where Artificial intelligence (AI) agents come in and provide an unprecedented solution that expands manufacturing processes.
Manufacturers can ensure excellent product quality, reach previously unheard-of levels of production, and react quickly to changes in the market by utilizing AI. AI agents in manufacturing integration are a strategic necessity in today’s competitive manufacturing dynamics, not just an option. The new era of effectiveness and imagination is ushered in by these sophisticated systems, enabling manufactures to manufacturers to meet changing industry demands and maintain their competitiveness.
Around 35% of manufacturers ought to adopt AI for performing tasks in the manufacturing industry in the coming 5 yeras. This article explores the main features of AI agents for manufacturing, including their types, benefits, top use cases, and major components.
What is an AI Agent and Its Types?
Business technology is evolving and AI agents are becoming the main component of this process. So let’s get to know what are AI agents. Artificial intelligence agents are electronic programs that can operate independently by making choices depending on their surroundings, inputs, and predetermined objectives. These agents are a significant advance above the typical automation because they are made to reason, adapt, and act on their own in addition to the following instructions.
Envision a digital entity that is constantly scanning its environment, gains knowledge via encounters, and makes decisions for accomplishing particular goals. This is what an AI agent is all about. It is similar to having a digital assistant who completes duties, recognizes context, modifies tactics, and even comes up with new ideas to accomplish goals. Manufacturers must comprehend these differences to choose the best AI agent for their unique requirements. Let’s examine AI agent types:
-
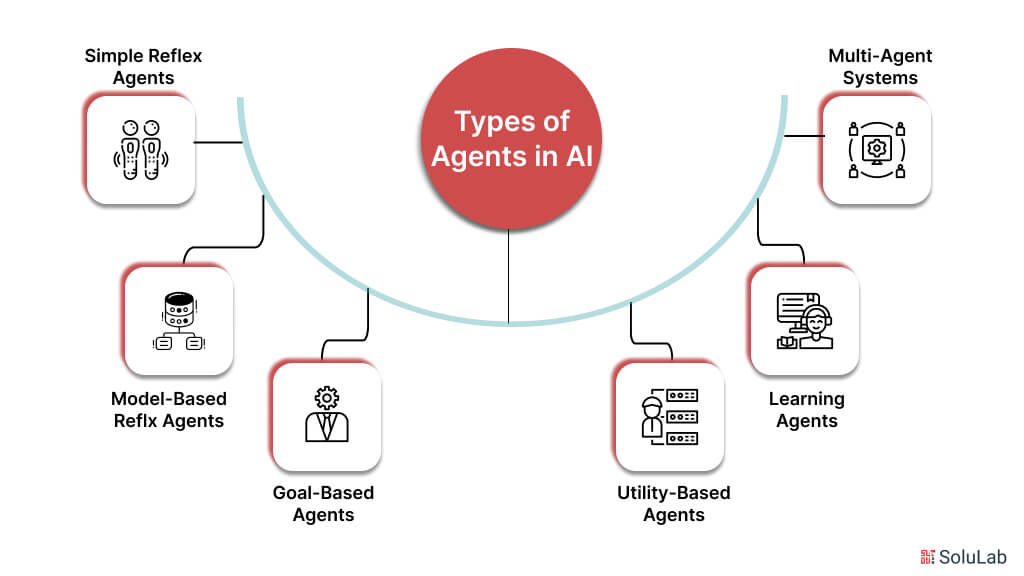
Simple Reflex Agents
The condition-action agent rules ideas underlie the operation of these agents. They do not have an internal representation of the world; instead, they react directly to their current perceptions. In circumstances where the agent’s next action is determined just by its current perception, simple reflex agents are easy to use and very effective.
-
Model-Based Reflx Agents
As these agents have an internal representation of the world, they can easily monitor aspects of it that are not immediately apparent. By assuming incomplete data, this approach assists the agent in navigating partially visible settings. Compared to basic reflex agents, they are more flexible since they make decisions about what to do depending on their internal model and present perception.
-
Goal-Based Agents
Agents with gaols take things, a step further by thinking about how their actions will affect the future. They make decisions based on the likelihood that certain will lead to the achievement of their goals. They can plan to select actions that result in desired outcomes because of their foresight, which qualifies them for difficult decision-making duties.
-
Utility-Based Agents
These agents use a utility function function to determine how desirable stats are. Based on specified utility measures, they aim to maximize their performance and accomplish a goal. This method works well in situations where there are several possible courses of action or results and the agent must choose the best one based on desire.
-
Learning Agents
With time, these agents become more proficient because of their experience. They are especially in changing situations where they can modify and advance their tactics. For example, to maximize ad placements, a learning agent could constantly, improve its comprehension of consumer preferences.
-
Multi-Agent Systems
Several agents collaborate and cooperate for shared personal objectives in MAS. When coordination is essential for complicated activities requiring numerous agents to work together, MAS is utilized. Supply chain management is one use of these systems, where numerous agents represent different supply chain components and collaborate to optimize the process as a whole.
How Does AI Agents Work?
Techniques and information inputs are combined to power AI Agents. To understand and respond to their surroundings, they process information using machine learning models. Here is the breakdown of how AI agents work:
1. AI agents use data intake mechanisms or sensors for obtaining data. All processes that come after this data are built on it.
2. The agents look through the data and extract insights by using artificial intelligence and machine learning models for processing and analysis.
3. They base their decisions on analysis, which may include the use of sophisticated algorithms, logic based on rules, or predictive models.
Following a choice, the agent carries out an action, which may involve anything from manipulating a physical robot to updating a database.
Read Blog: Top 15 Use Cases Of AI Agents 2024
How do AI agents work if often organized as:
1. Receiving data: Getting new information from the sources or receiving data from the user
2. Assess Data: Use AI models to contextualize and evaluate data.
3. Decision-Making: Choosing the best action.
4. Act: Execute the decision by a response or some change in the environment.
Major Components of AI Agents in Manufacturing
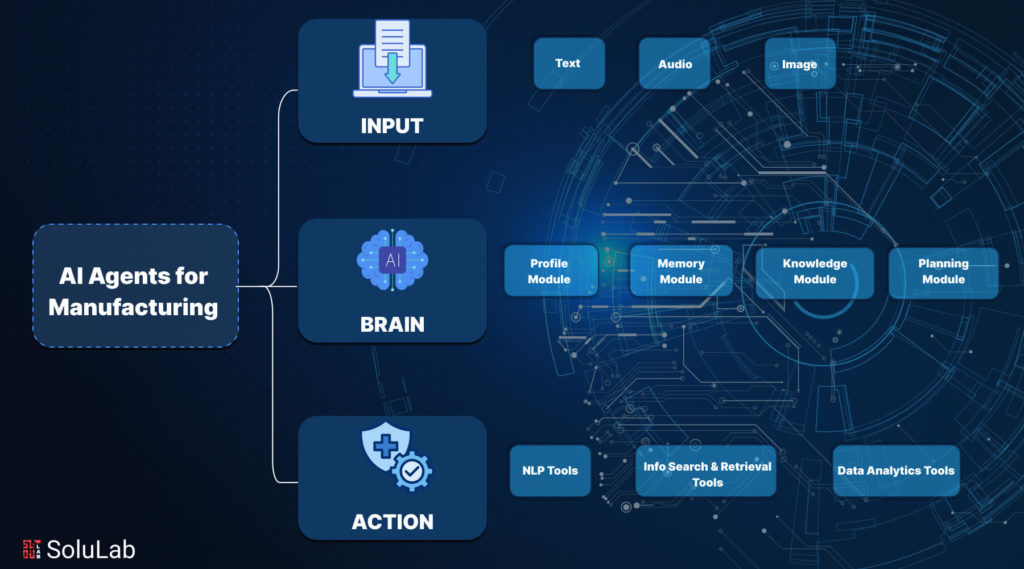
Input
The component is responsible for retrieving and managing several types of inputs into machines, sensors, and operators. This would include data but not limited to operational logs, production metrics, and sensor readings. These inputs drive the decisions and actions of the agent and provide real-time insights into the manufacturing process. The input can be anything such as:
- Text
- Audio
- Image
Brain
The brain is composed of many modules and is highly essential in the cognitive functions of manufacturing operations.
- Profiling: This would define the role and objectives of the agent and its position within the production environment.
- Memory: The ability to learn from previous production cycles and operation settings through stored history and interactions.
- Knowledge: Domain-specific information for planning and decision-making comprising information on production processes, quality standards, equipment, and tool specifications.
- Planning: Considering demand and stock on hand, the system should, based on current demand and stock level, come up with an optimum production schedule, resource investment, and process investment at the best time.
Action
To that note, this section implements planned activities by applying the modules of the brain in the automation and optimization of manufacturing processes. This ensures efficiency in the manufacturing functions since complex tasks will be subdivided into feasible stages.
With a sophisticated set of capabilities for analysis and decision-making, AI agents can help optimize production line results, prevent production line downtime, or enhance operational efficiency in the manufacturing industry. This step makes use of various tools that include:
- NLP Tools
- Info Search and Retrieval Tools
- Data Analytics Tools
Role of AI Agents in Manufacturing
AI agents are bound to assume a very important role in contemporary manufacturing as competitiveness boosters, efficiency enhancers, and innovation promoters. AI agents can serve potential transformative roles in manufacturing processes, right from supply chain optimization to predictive maintenance.
1. Improving Predictive Upkeep
Equipped with proper advanced predictive analytics onboard, AI agents provide proactive maintenance solutions to manufacturers. AI agents can predict the problems in equipment in advance by analyzing the records of its maintenance and current data from sensors in real time. The predictive ability of AI agents enables optimized operational efficiency and lowered costs for maintenance by reducing wear and tear of machinery and minimizing unscheduled downtime.
2. Transforming Quality Assurance
Manufacturing gives a lot of importance to quality control, while AI agents raise this bar even higher by automating tasks and doing them with precision. AI agents for manufacturing use machine vision combined with deep learning algorithms to identify product flaws with unparalleled accuracy, while only top-notch products are forwarded to the market. The detection skills of AI agents are enhanced continuously through learning from inspection data.
3. Supply Chain Management Optimization
AI agents will not hesitate to optimize supply chain operations, making improvements in the sphere of resilience and efficiency with data-driven insights. That would imply assessing the efficiency of suppliers, levels of stock, and projections of market demand with the aim of logistics and inventory optimization. Lower lead times, stock-outs, and, in general, supply chain agility will permit changing market trends and consumer needs.
4. Energy Efficiency Promotion
Since energy consumption is one of the major components of costs, AI agents become necessary for improving energy utilization within manufacturing processes. It becomes quite easy for AI agents to detect areas where production operations can save energy, considering that it assists in real-time monitoring and predictive analytics. By optimizing equipment scheduling and utilization, Artificial Intelligence agents lower energy costs and environmental effects, coordinating industrial processes with sustainability objectives and legal requirements.
Key Benefits of AI Agents in Manufacturing
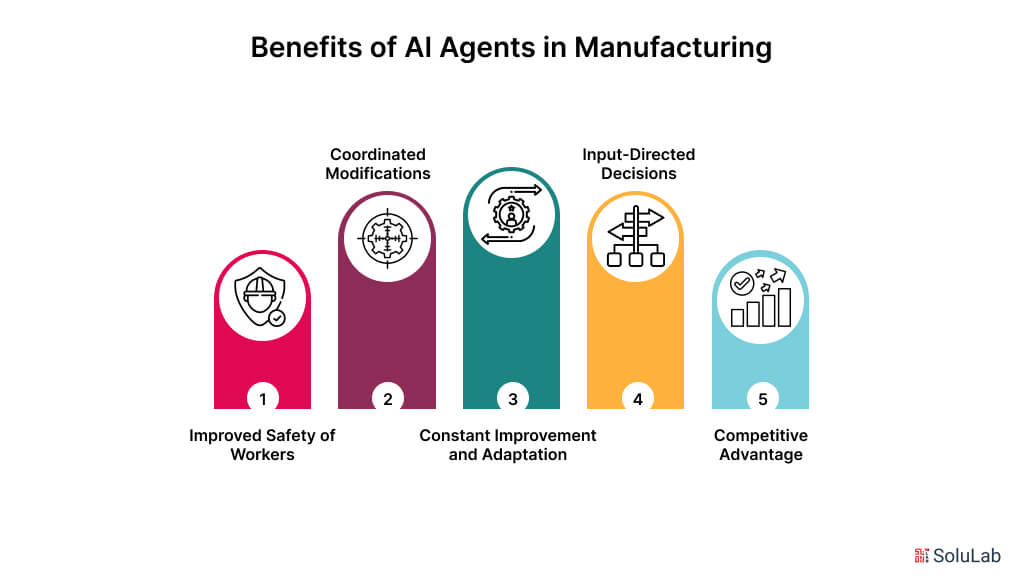
AI agents are bringing a revolution to every field, and manufacturing is an exception. The advantages of the AI applications in manufacturing are as follows:
-
Improved Safety of Workers
It would be with proper analysis of past safety data, spotting patterns in hazards, and compilation of knowledge strictly based on best practices. Agents of the language learning model assist initiatives in making workplaces even safer and more ergonomic through insightful analyses and dialogues about safety-related issues.
-
Coordinated Modifications
AI systems monitor the tastes of customers and make changes to the production process to efficiently place personalized requests. Considering such potential, the producers can offer customized items without compromising productivity and reasonable prices.
-
Constant Improvement and Adaptation
The agents undergo constant improvements over time as their algorithms are fine-tuned with new insights from continuous data feeds. Due to constant improvements, despite fluctuating market conditions and technological breakthroughs, truly effective and efficient processes for production can be achieved.
-
Input-Directed Decisions
These frequent data inputs are like learning and evolving the AI automation continuously, which helps in enhancing the algorithms and overall performance over some time. With continuous improvement in technologies and changing market conditions, manufacturing processes remain effective and efficient.
-
Competitive Advantage
With the integration of AI agents in manufacturing, manufacturers can realize greater operational efficiencies and quality of the product. A faster growth cycle and better market accountability result from this, which provides the company with a greater advantage against the competition.
How Do AI Agents Improve Customer Experiences?
1. Tailored Customer Experiences
This is a one-to-one marketing tactic that not only provides each unique customer with highly relevant but also customized experiences by utilizing machine learning and intelligent artificial intelligence. Customers want manufacturers to be aware of their needs and preferences and the latest market trends.
AI can analyze customer data both past and present to produce a comprehensive picture of each individual, including social media activity browsing patterns, and past purchases.
For example, Netflix uses AI to adjust its suggestions as per each user depending on their past watch.
2. 24/7 Customer Support
Chatbots are now a necessary tool for companies trying to offer at all times, immediate customer service. These chatbots can respond to standard inquiries, offer pertinent responses, and point users in the direction of the right resources. They can also help by pointing clients in the direction of live agents for more complicated issues and queries Client queries are handled in much better ways when you leverage chatbots.
Various customer inquiries even on the product, order status, and troubleshooting can all be handled quite easily by these AI-powered chatbots.
For example, H&M uses chatbots to answer questions about order monitoring and other relevant details of the order or products.
3. Anticipate the Needs of the Customers
Predictive analysis is used to improve customer satisfaction by anticipating the needs of the customers and boosting customer retention by providing meaningful insights into customer behavior, preferences, and purchasing patterns. Additionally, you can use this for spotting possible customer attrition.
For instance, telecom firms use predictive analysis for the identification of clients who are more likely to discontinue the service and provide them with special offers to keep them hooked.
4. Understanding Customer Feedback
Sentiment analysis is the practice of analyzing customer evaluations and feedback with AI algorithms to learn about the attitudes, feelings, and opinions of the customers. This AI-driven feature can be used to examine consumer input from a variety of sources such as social media, online reviews, and customer surveys. You can find areas for development and take appropriate action to resolve consumer problems by examining this feedback.
Top 5 Use Cases of AI Agents in Manufacturing
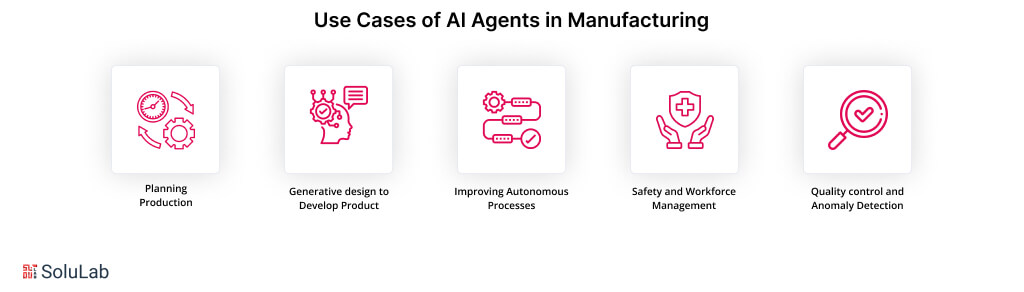
Artificial intelligence (AI) agents are transforming with GenAI in manufacturing by improving productivity, precision, and creativity in a range of production-related areas. The following are the top 5 use cases of AI agents in manufacturing:
-
Planning Production
Large volumes of production data like demand projects, level of stocks, and availability of machines are analyzed by LLM agents to find patterns and offer insightful analysis that helps with production planning decisions.
-
Generative design to Develop Product
Based on generative design algorithms that employ AI, generative design produces numerous design propositions in line with certain specifications like cost, dimensions, weight, materials, and fabrication methods among others. This makes product innovation easier in terms of design and shortens the time taken in product development, especially when combined with access to a 3D printing service for fabricating complex shapes and structures.
-
Improving Autonomous Processes
Industrial processes are studied by artificial intelligence (AI) bots who look for the aspects that can be improved. It requires the use of machine learning algorithms to adjust temperature, pressure, and speed so that production is optimized, cost is reduced and the quality of the product is enhanced.
-
Safety and Workforce Management
Mobile technologies and computer vision monitor workers’ movement and activities as well as allow the identification of risky behaviors and triggering of alarms together with indicating the necessary preventive actions. The use of AI in this area can be helpful to manufacturers in assessing the workload needed and avoid overloading the employees, and the duties to be assigned to specific employees for better performance and efficiency.
-
Quality control and Anomaly Detection
Automated inspection systems powered by artificial intelligence (AI) technology analyze sensor data and visual inspection results in real-time mode to detect defective part features, anomalies, and other quality issues in the manufacturing process. Thus, producers can reduce wastages, detect faults at the initial stage, and ensure quality products are produced.
Future Trends in AI Agents
| Trends | Impact |
| Ethics-Based and Reliable | With the increase in the strengths of AI agents, more focus will be given to establishing these AI agents in an ethical, open, and reliable way. There are plans to ensure that AI agents would not encroach on the privacy of human beings, they do not have any bias and act rightly like human beings. |
| Increased Physical Abilities | There will be more and more instances of artificial intelligence agents being embodied as robots, drones, self-driving cars, and such other forms. This will allow people to further work within and interact with the real-world environment along with the virtual environments. |
| More Autonomy and Sophistication | AI agents in the future will be capable of understanding language, reasoning ability as well as decision-making tendencies. However, with more autonomy the level of automation increases they will be capable of handling more complex tasks more practical and general, and less human intercession. |
| Seamless Integration Within Systems | Each of, the bots, and software programs will have close ties with AI agents to be well-informed about our existence and more importantly, provide real value. It will be possible to switch from our telephones, automobiles, smart homes, and workplaces without any hitch. |
How Can SoluLab Help in Building Customer Experience Using AI Agents?
SoluLab specializes in AI Agent development service provision and sets itself apart by implementing AI agents that bring impressive transformations in customer experience. SoluLab is a team of experts that gathers professionals in the field of AI and offers applicative solutions that are tailored to companies’ specifics of various industries. As AI is bound with the most up-to-date machine learning algorithms thus AI agents will be providing interaction as well as progressive learning that is likely to improve service standards at some point.
This is why working with SoluLab can become the beginning of new opportunities for growth and customer relations amid the growth of competition in the digital space. Why lose the chance to revolutionize the way your clients engage with your business; contact SoluLab today to learn how we can assist your business.
FAQs
1. How do AI Agents work?
AI agents work on various complex algorithms and constantly learn from the data provided within sources for making informed decisions and providing users with up-to-the-mark outcomes to their inputs.
2. How can I use AI agents for my business?
Be the business in any field AI agents have the potential to perform several time-consuming tasks for you which include monitoring your sales, automating your processes, and even tailoring the outreach according to customer preferences and needs.
3. What is the most common real-life AI agent example?
The most common and majorly equipped by businesses of all kinds by now real-life examples of AI agents are chatbots and voice assistance. Every business requires a 24/7 approach to solve customer inquiries which in turn improves their satisfaction.
4. What is the manufacturing industry using AI agents for?
The major benefits AI agents are providing to the manufacturing industry are proactive monitoring of production, predicting possible failures of the equipment, and automation of repetitive tasks.
5. Can SoluLab help with the integration of AI agents?
Yes, SoluLab can help with the integration of AI agents by thorough optimization of data flow making use of tactics such as API architecture. This integration will help you with your task automation, customer service, and complex workflows.

