Can digital tokens make carbon credits more trustworthy and easier to trade? Germany seems to do so. As one of the world’s leading industrial economies, Germany is taking bold steps to merge technology with sustainability. A new blockchain-based carbon credit trading platform is making headlines, but that’s not all. Behind the scenes, a serious clean-up effort is underway to fix past carbon fraud and build a market that actually works.
Let’s explore how Germany is leading the Carbon credits tokenization transformation, from launch to clear regulations. It is chasing down carbon credit fraud, and why this matters for businesses, traders, and the planet.
Germany Backs Blockchain Technology for Climate Innovation
Germany has committed to achieving climate neutrality by 2045. This bold goal needs more than just policy; it demands innovation. That’s why tech firm Neutral and regulated brokerage DLT Finance teamed up to build a new kind of carbon credit tokenization trading platform. This isn’t just another crypto experiment. It’s a regulated, buttoned-up exchange designed for serious commodity traders. The goal? Bring real liquidity, trust, and compliance into a market that’s been missing all three.
Neutral provides the technology while DLT Finance offers the regulatory setup. Traders don’t need crypto wallets, blockchain knowledge, or token jargon. They just get a professional platform that lets them trade verified carbon credits smoothly.
Inside the First Regulated Tokenized Carbon Exchange
The new platform aims to solve the biggest problem in carbon markets access and trust. Traditional traders often avoid decentralized exchanges due to a lack of oversight and poor liquidity. This exchange changes that.
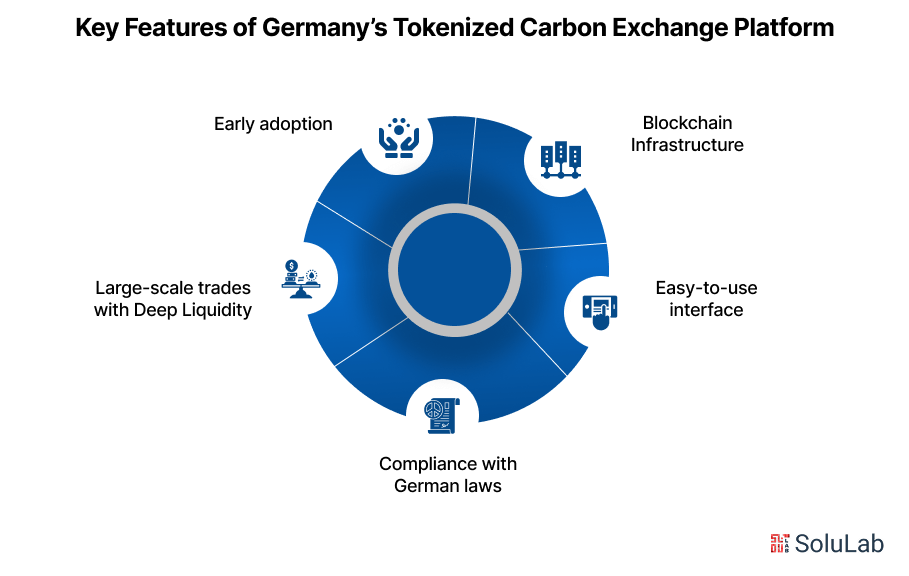
Key Features of the Platform
- The platform uses blockchain infrastructure, but it stays hidden from the user to offer a smooth, easy-to-use interface.
- Built under full regulatory compliance with German financial laws, ensuring legal clarity and trust for institutional traders and participants.
- Specifically designed to handle large-scale trades with deep liquidity, making it more reliable than most decentralized exchanges in operation.
- Ten major commodity trading houses are currently being onboarded, reflecting strong early adoption and institutional interest in regulated tokenized assets.
Ghandour, the CEO of Neutral, made it clear that they designed the platform to feel like any other high-end commodities exchange. The only difference? It’s backed by real-world tokenized assets, making it efficient and verifiable.
Germany’s Political Push for Market Legitimacy in Tokenization of Carbon Credits
The tech is only part of the story. Germany’s upcoming coalition government is aligning regulation with innovation. A new treaty presented by party leaders pledges to support carbon credits tokenization, even foreign-based ones, as a legitimate way to meet climate targets.
Key Political Commitments
- Germany will meet its legally set 88% carbon reduction target for 2040 without burdening industries with unrealistic expectations.
- Companies can use up to 3% high-quality, certified foreign carbon credits to offset residual emissions under strict verification guidelines.
- The government supports expanding EU-wide carbon pricing systems and aligning laws with broader climate neutrality goals for all members.
- New policies will enable carbon capture, transport, and offshore storage to manage unavoidable emissions from critical industrial sectors efficiently.
This political backing shows Germany isn’t just testing new tech, it’s building policy guardrails to make tokenized carbon credits work for real.
Germany’s Investigation Revealed the Carbon Credit Fraud
While this new exchange offers hope, Germany also had to deal with a harsh truth: carbon credit fraud has been real and widespread. The Federal Environmental Agency (UBA) found several German companies using fake or inflated carbon credits. These credits were supposed to represent real CO2 reductions through environmental projects. Many didn’t exist or didn’t deliver the impact they promised.

How the Investigation Unfolded
In multiple cases, companies claimed credits for projects that were either non-existent or misreported. The result?
- German authorities rejected 215,000 tonnes worth of carbon credits after discovering false claims about emission reductions in certified projects.
- Eight more projects were flagged for serious violations, including missed deadlines and failure to follow operational and reporting requirements properly.
- Berlin prosecutors conducted raids on environmental auditing firms suspected of approving fake carbon credits and colluding with project developers.
Germany’s response was swift and aggressive. UBA suspended credits and flagged 40 out of 69 projects for further review.
The Cost of False Credits
The companies under investigation may have avoided up to €4.5 billion in penalties by padding their climate records with fake credits. That’s not just fraud, it’s a serious blow to public trust in climate action.
A closer look at how Germany assessed the carbon fraud cases and the scale of ongoing investigations.
| Project Category | Total Reviewed | Flagged for Irregularities | Estimated Avoided Fines (€) |
| Renewable Projects | 25 | 12 | 1.2 billion |
| Forestry Offsets | 18 | 10 | 950 million |
| International Projects | 26 | 18 | 2.35 billion |
| Total | 69 | 40 | 4.5 billion |
Germany’s Response to Carbon Credit Fraud
Germany took real steps to prevent this from happening again. Here’s how they’re fixing the cracks and rebuilding market integrity:
- New verification rules now require full project audits by independent international bodies, reviewed locally before approval.
- Environmental auditing firms must meet strict compliance standards and pass annual oversight by government climate watchdogs.
- Only certified projects with geolocation and timestamp verification will qualify for credits on regulated exchanges.
Restoring Trust Among Carbon Credit Investors
Regulators didn’t stop with corporate offenders. They also targeted the auditing firms involved in certifying these fake credits. In July, German prosecutors raided their offices, alleging collusion and negligence.
Germany rolled out urgent reforms to ensure carbon credits are valid, trackable, and impactful.
| Reform Area | Description |
| Certification Process | Independent audits, project geo-verification, and timestamped tracking |
| Legal Action | Raids and investigations into auditing firms and corporate offenders |
| Regulatory Oversight | Annual compliance checks by the Federal Environmental Agency (UBA) |
| Public Transparency | Open data access for all certified credits on government-backed portals |
These actions show that Germany wants to build a model system, one that other countries can learn from.
Why Germany Leads the Way in Carbon Credit Reform
Germany combines strong tech and law, building a carbon credit market that balances innovation with strict regulation. Regulators act quickly, punishing fraud and reforming broken systems with clear public messaging and new enforcement rules. Germany promotes blockchain-backed projects while keeping user experience clean, simple, and familiar for traditional traders.
What This Means for the Global Market
Germany’s moves go far beyond its borders. Other countries struggling with carbon fraud now have a clear roadmap. Start with strict and transparent verification reform to ensure every carbon credit represents real, measurable, and scientifically backed emission reductions. Enforce clear climate regulations with strong legal power to hold companies and verification partners accountable for fraud or misreporting practices. Introduce blockchain-based tools that improve credit traceability and data transparency without confusing users or requiring deep technical knowledge or crypto tools.
By enforcing these steps, Germany proves that tokenizing carbon credits can be both effective and ethical.
The Path Ahead: Merging Tokenization and Trust
The launch of Neutral’s regulated platform shows how blockchain can support, not replace, climate systems. When backed by law, transparency, and simple access, tokenized carbon credits become far more than a niche tech solution. They become a core financial tool in the fight against climate change. And Germany, with its tech-driven approach and regulatory courage, may just lead the way.
SoluLab, a tokenization platform development company, builds end-to-end blockchain solutions for climate impact, from credit design to DeFi integration. With expertise across Ethereum and Polygon, their team ensures secure, transparent, and scalable carbon credit tokenization. SoluLab helps organizations create smart contracts and integrate with DeFi for better liquidity and trust. Unlock the full potential of blockchain for sustainability with a trusted partner. Contact SoluLab today to get started.
FAQs
1. What is carbon credit tokenization, and why is Germany focusing on it?
Carbon credit tokenization turns emission reductions into secure digital tokens. Germany is focusing on it to improve transparency, stop fraud, and make carbon markets more efficient for both companies and climate-focused investors.
2. How is Germany making tokenized carbon credits more trustworthy?
Germany enforces strong regulations, requires independent project audits, and uses blockchain technology to track and verify each credit. This approach builds real trust and accountability in a market that previously lacked clear oversight.
3. Why are traditional traders choosing this new platform over decentralized exchanges?
This regulated platform feels familiar, works without crypto wallets, and offers better liquidity. It’s simple for traders to use, without needing to understand blockchain, just the benefits of verified, tradable, and secure carbon credits.
4. What steps has Germany taken against carbon credit fraud?
Germany suspended fraudulent credits, raided auditing firms, and introduced stricter verification rules. These steps ensure only genuine, impactful carbon projects get tokenized and traded, protecting the environment and restoring market confidence.
5. How does blockchain make carbon credit trading better?
Blockchain helps by tracking every credit transparently from origin to trade. It prevents double-counting, fraud, or lost data, giving both businesses and regulators a clear view of the carbon impact and ownership trail.
6. What other countries are backing carbon credit tokenization like Germany
Singapore, Switzerland, and the UAE are also exploring or supporting tokenized carbon credit projects. Like Germany, they aim to combine blockchain’s efficiency with strong oversight to build global trust in climate-focused finance.