Traditional systems rely heavily on central authorities, making them vulnerable to corruption, fraud. This creates a major problem—how can we trust systems without giving up control?
Permissionless blockchains can help with that. Anyone can join, validate transactions, and keep the network running on open networks like Ethereum and Bitcoin without requiring permission from a central authority. However, the issue of guaranteeing security, integrity, and fairness accompanied total transparency.
Technologies like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) have made it possible. These consensus mechanisms ensure that permissionless blockchains remain decentralized, transparent, and tamper-proof.
In this blog, we’ll explore how permissionless blockchains work, the role of consensus mechanisms, and why they are considered a game-changer.
What are Permissionless Blockchains?
Ethereum and other permissionless blockchains are decentralized, trustless, and global public networks that anybody can access, participate in, and authenticate. Whenever a user wants to verify a previous transaction, they can fully replicate the current state of a permissionless blockchain.
Permissionless blockchains function without the need for an administrative control authority and are accessible to everyone. To enter the network, one does not need to finish any KYC (Know Your Customer) processes.
How do Permissionless Blockchains Work?
Permissionless blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum rely on consensus mechanisms to ensure decentralization, security, and data integrity.
The two most common consensus mechanisms are:
- Proof of Work (PoW)
- Proof of Stake (PoS)
1. PoW (used by Bitcoin):
- Miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles.
- The first to solve it gets to add a new block and earns a cryptocurrency reward.
- This process requires significant computational power.
- It ensures strong security and immutability, making it extremely hard to tamper with past transactions.
2. PoS (used by Ethereum and others):
- Validators stake cryptocurrency to become eligible for transaction validation.
- Validators are randomly chosen to add new blocks.
- The more they stake, the higher the chance of being selected.
- Honest behavior is encouraged, as malicious actions can lead to loss of the staked amount.
Both PoW and PoS:
- Provide a reliable framework for transaction validation.
- Help maintain decentralization, network integrity, and security in permissionless blockchains.
Related: Use Cases of Substrate Framework
Permissioned vs. Permissionless Blockchain
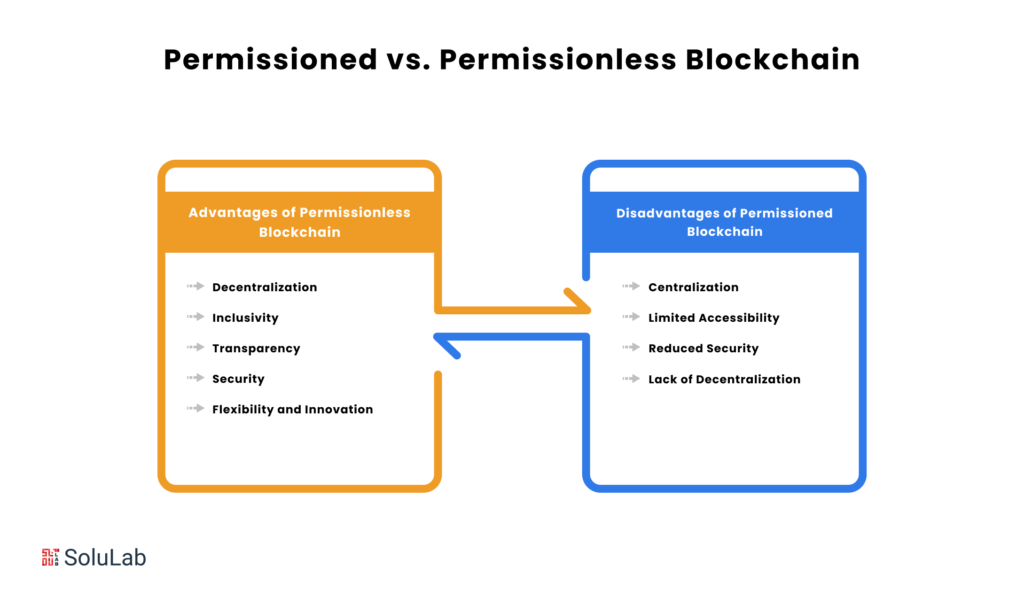
In this thought-provoking exploration, we will delve into the deep comparison between permissioned and permissionless blockchains, contrasting the dynamics of controlled access with unrestricted participation. By shedding light on the contrast, we gain invaluable insights into the key choices that shape the decentralized space.
What is Permissioned Blockchain?
In private or corporate networks with restricted membership, regulated access improves security and privacy. The authorized entities govern validation, enabling efficient and scalable consensus but centralizing and increasing weaknesses. They provide stability and direction but reduce autonomy and self-governance by actively managing the blockchain.
Permissioned blockchains exchange openness and decentralization for control, efficiency, and scalability, making them acceptable for certain applications but departing from permissionless blockchains.
Advantages of Permissionless Blockchains:
1. Decentralization: Permissionless blockchains operate on a decentralized network, where no single entity holds control. This eliminates a central point of failure and mitigates the risk of censorship or manipulation by any single party. It ensures that the blockchain remains resilient, secure, and resistant to attacks.
2. Inclusivity: Permissionless blockchains promote inclusivity by allowing anyone to participate in the network. There are no barriers to entry, and all individuals have equal rights to engage in transactions, contribute to the blockchain’s growth, and participate in its governance. This fosters a more democratic and accessible environment where everyone has a voice.
Related: What Are the Business Benefits of Blockchain-as-a-Service?
3. Transparency: All transactions on a permissionless blockchain are recorded on a public ledger, providing complete transparency. This ledger is immutable, meaning that once a transaction is added, it cannot be altered or deleted. This transparency enhances trust among participants, as they can verify the authenticity and integrity of every transaction, reducing the risk of fraud and corruption.
4. Security: Permissionless blockchains employ consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Work (PoW) or Proof-of-Stake (PoS) to validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the blockchain. These consensus mechanisms are designed to be resistant to attacks, making it extremely difficult for anyone to compromise the network. The decentralized nature of permissionless blockchains further enhances security by distributing the responsibility of maintaining the network among multiple independent nodes.
5. Flexibility and Innovation: Permissionless blockchains offer flexibility and adaptability due to their open-source nature. Developers can build various applications and protocols on top of these blockchains, leading to innovation and new use cases. This fosters a vibrant ecosystem where creativity and experimentation are encouraged, driving the blockchain technology forward.
Disadvantages of Permissioned Blockchains:
1. Centralization: Permissioned blockchains are inherently more centralized than permissionless blockchains. In a permissioned system, a central authority or a group of authorities controls who can participate in the network, which can lead to concerns about censorship, manipulation, and lack of transparency. This centralization can also make the blockchain vulnerable to attacks and single points of failure.
2. Limited Accessibility: Permissioned blockchains are not as accessible as permissionless blockchains. Participation in a permissioned blockchain is typically restricted to authorized entities, such as members of a consortium or organization. This limits the diversity of participants and can hinder global inclusivity. It also raises concerns about fairness and equal opportunities, as not everyone may have the same access to the blockchain.
3. Reduced Security: Permissioned blockchains may have reduced security compared to permissionless blockchains. In a permissioned system, the validators are known and trusted entities, which can make the blockchain vulnerable to collusion and insider attacks. Additionally, the limited number of validators can make it easier for malicious actors to gain control of the network and compromise its integrity.
4. Lack of Decentralization: Permissioned blockchains sacrifice decentralization for scalability and efficiency. In a permissioned system, the network is controlled by a select group of validators, rather than being open to anyone who wants to participate. This can lead to a lack of transparency and accountability, as the validators have more power and influence over the blockchain.
These disadvantages should be carefully considered when choosing the right blockchain model for a particular application. While permissioned blockchains offer certain benefits, they may not be suitable for all use cases, especially those that require a high degree of decentralization, transparency, and accessibility.
Characteristics of Permissionless Blockchain
Participants can only join a private blockchain network through an invitation. Their identity and other required details must be verified—either by the network operator or through a set protocol, often using smart contracts or automated approval methods.
This means private blockchains have strict control over who can access the network. The owner or operator also has the authority to override, edit, or delete blockchain entries when needed or to make changes to the system’s programming.
Use Cases of Permissionless Blockchain
Here are some key use cases of permissionless blockchain:
- Cryptocurrencies: Enables decentralized digital currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, allowing peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, ensuring transparency, security, and resistance to censorship.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Offers financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading without traditional banks, using smart contracts to automate and secure transactions.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Facilitates ownership and trading of unique digital assets such as art, music, and collectibles on the blockchain with proof of authenticity and scarcity.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Tracks the movement of goods from origin to delivery, improving traceability, reducing fraud, and ensuring product authenticity through an immutable record.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): Enables community-led governance for projects or funds where decisions are made through voting, increasing transparency and reducing centralized control.
- Gaming and Virtual Worlds: Allows players to own in-game assets and currencies, trade them freely, and earn real value through play-to-earn models on decentralized platforms.
Benefits of Permissionless Blockchain
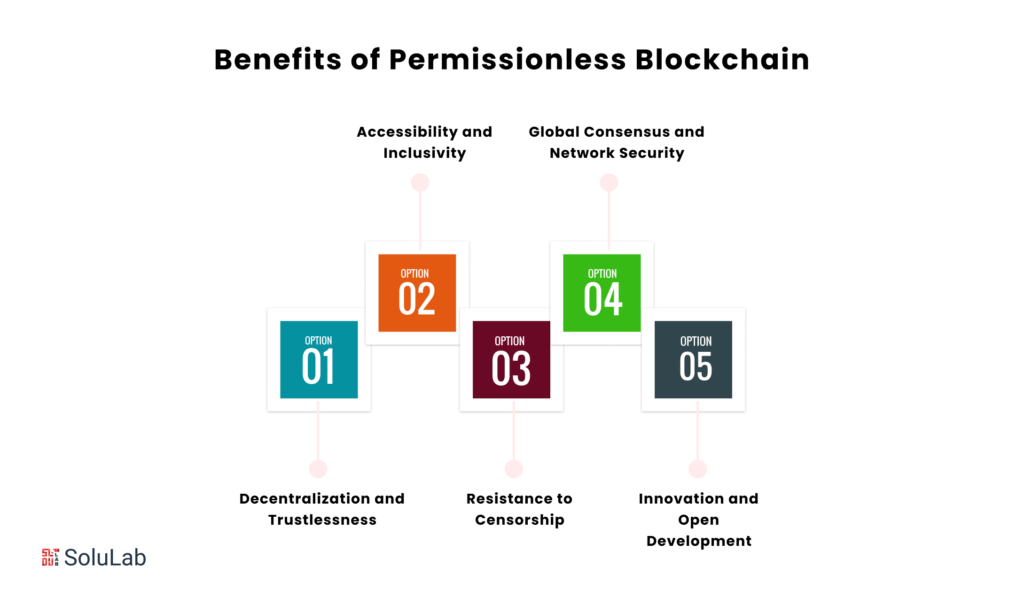
Permissionless blockchains stand out as decentralized and trustless systems, providing enhanced security through collective key ownership. They promote accessibility and inclusivity, allowing anyone to participate and contribute, fostering innovation. Moreover, their transparent nature enables the tracing of every transaction, building trust and ensuring integrity. Permissionless blockchains revolutionize the digital landscape by transforming security, innovation, and interaction.
1. Decentralization and Trustlessness:
The transparent nature of permissionless blockchains further enhances trust. All transactions and data on the blockchain are publicly accessible and verifiable, allowing participants to validate the authenticity and accuracy of the information. This transparency fosters a sense of trust and confidence among users, as they can rely on the immutability and security of the blockchain.
Trustlessness provides several advantages in permissionless blockchains:
- Security: The elimination of trust reduces the attack surface for malicious actors. Without a central authority to target, it becomes significantly more difficult for attackers to compromise the entire network.
- Transparency: The transparent nature of permissionless blockchains ensures that all transactions and data are open for anyone to review. This transparency helps prevent fraud and corruption, as any irregularities can be easily identified and addressed.
- Inclusivity: Trustlessness allows anyone with an internet connection to participate in permissionless blockchains. There are no barriers to entry, and users do not need to seek permission from any central authority.
- Efficiency: The absence of intermediaries in permissionless blockchains streamlines transactions and reduces processing times. This efficiency is crucial for applications that require fast and reliable transactions.
2. Accessibility and Inclusivity:
The permissionless nature of blockchains promotes financial inclusion and empowerment by providing equal access to financial services for individuals worldwide, irrespective of their socioeconomic status or location. This inclusivity enables the unbanked and underbanked to engage in financial transactions, store and transfer funds, and access a diverse range of financial products. Beyond mere access, financial inclusion through permissionless blockchains fosters economic growth, reduces poverty, and enhances overall well-being, particularly in underserved regions.
Moreover, the transparency and immutability of blockchain technology instill trust and confidence, encouraging economic activities, investments, and innovation. Permissionless blockchains represent a transformative approach in the financial landscape, empowering individuals to transcend boundaries and actively participate in the global economy, thus shaping a more equitable and inclusive financial future for all.
Related: What Are The Applications And Use Cases of Blockchains?
3. Resistance to Censorship:
Censorship in Traditional Systems: Traditional systems, such as centralized governments and financial institutions, often face issues of censorship. In these systems, authorities have the power to control or restrict the flow of information, often based on political, economic, or social considerations. This can lead to the suppression of dissent, the dissemination of propaganda, and the manipulation of public opinion.
How Permissionless Blockchains Resist Censorship: Permissionless blockchains, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, are designed to resist censorship. They operate on a decentralized network of computers, with no central authority controlling the flow of information. This decentralized nature makes it extremely difficult for any single entity to censor or manipulate the data on the blockchain.
Key Features of Permissionless Blockchains that Resist Censorship:
- Immutability: Transactions on a permissionless blockchain are recorded on a public ledger that is immutable. This means that once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted.
- Decentralization: Permissionless blockchains are not controlled by any central authority. Instead, they are maintained by a network of independent computers, or nodes. This decentralization makes it difficult for any single entity to censor or control the blockchain.
- Transparency: All transactions on a permissionless blockchain are publicly visible. This transparency makes it difficult for anyone to hide or manipulate information.
Examples of Permissionless Blockchains Resisting Censorship:
- Bitcoin: Bitcoin has been used to facilitate financial transactions in countries with strict capital controls, such as China and Venezuela.
- Ethereum: Ethereum has been used to create decentralized applications (dApps) that are resistant to censorship, such as censorship-resistant news platforms and social media networks.
Permissionless blockchains offer a powerful tool for resisting censorship. Their decentralized nature and immutable records make them difficult for any single entity to control or manipulate. This makes them a valuable tool for promoting freedom of speech, transparency, and accountability.
4. Global Consensus and Network Security:
Permissionless blockchains utilize global consensus mechanisms involving participants worldwide, enhancing network security and resilience. The decentralized structure distributes trust, preventing any single entity from controlling the network. This setup resists censorship and attacks, making permissionless blockchains highly secure and reliable. The decentralized nature and global consensus of permissionless blockchains offer several security advantages over centralized systems. They reduce vulnerability to single points of failure and make it incredibly challenging for attackers to compromise the entire network.
The global consensus mechanism ensures that blocks are added to the blockchain only after a majority of nodes agree, minimizing the chances of fraudulent transactions. The enhanced security and resilience provided by global consensus mechanisms in permissionless blockchains have significant implications for the future of blockchain technology. These mechanisms are essential for applications requiring high security and trust, such as finance, supply chain management, and secure voting systems. Permissionless blockchains with global consensus will play a crucial role in shaping a secure and trustworthy future as blockchain technology advances.
5. Innovation and Open Development:
Permissionless blockchains have emerged as catalysts for innovation and collaboration, fostering an environment that encourages contributions from developers, researchers, and entrepreneurs. They shine in decentralized applications (DApps) development, leveraging blockchain’s transparency and immutability for trustless transactions without intermediaries. Smart contracts automate processes and reduce disputes, proving potential in areas like supply chain management and finance. Interoperability solutions connect different blockchain networks, enhancing the ecosystem’s interconnectedness and utility.
Scalability advancements address the increasing usage and popularity of blockchain networks, with solutions such as sharding and layer 2 scaling. These advancements and innovations drive the growth and evolution of blockchain technology, creating a vibrant ecosystem where new ideas and technologies are constantly being developed. Permissionless blockchains have the potential to reshape industries, revolutionize systems, and create a more decentralized, transparent, and efficient future.
6. Transparency
Transparency is another characteristic that sets permissionless blockchains apart. Users can view and access the same data on the blockchain network thanks to public blockchains. Peer-to-peer networks facilitate the traceability of data flow and network transactions.
In permissionless blockchains, each participant keeps an identical copy of comparable data in the distributed ledger. As a result, any unwelcome change to the ledger would be noticed right away by other members, who would then reject the change.
7. Immutability
Another key response to “What is permissionless blockchain?” is immutability. Permissionless blockchain networks provide strong security through decentralization and data immutability through hashing.
Hashing encrypts data with a unique hash value. Hashing turns any size of data into a fixed number that must match the original text. Any tampering in the original text would completely change the hash value.
Conclusion:
Permissionless blockchains enable open participation without the need for a central authority. Platforms like Bitcoin and Ethereum use consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work and Proof of Stake to ensure transparency, security, and trust in a trustless environment.
These blockchains empower users by giving them equal access to validate, verify, and contribute to the network. While they come with challenges like scalability and energy consumption, their benefits lie in terms of transparency and decentralization. As innovation continues, permissionless blockchains will play a key role in shaping the future.
Partner with SoluLab, a top blockchain development company in the USA, to build secure, scalable dApps on permissionless blockchains like Ethereum and Solana.
FAQs
1. What sets permissionless blockchains apart from permissioned ones?
Permissionless blockchains are characterized by their open participation, allowing anyone to join the network and validate transactions. In contrast, permissioned blockchains restrict access to designated entities or organizations, emphasizing control.
2. How does SoluLab contribute to the development of permissionless blockchains?
SoluLab, as a leading Blockchain Development Company, excels in crafting and implementing cutting-edge solutions for permissionless blockchains. Their team of Blockchain Developers leverages expertise to create decentralized systems, fostering innovation and security.
3. Can private permissionless blockchains ensure data confidentiality while maintaining openness?
Yes, private permissionless blockchains strike a balance between openness and privacy. They cater to industries requiring transparency while safeguarding sensitive data. SoluLab specializes in developing such hybrid solutions tailored to enterprise needs.
4. What benefits do permissionless blockchains offer in terms of security?
Permissionless blockchains enhance security through decentralization and global consensus. The distributed nature of the network reduces vulnerabilities associated with centralization, making it more resistant to attacks.
5. How does SoluLab stay ahead in the competitive landscape of Blockchain Development Services?
SoluLab stays ahead by continually innovating and adapting to emerging trends in blockchain technology. Their team of skilled Blockchain Developers is committed to delivering services that align with the evolving needs of businesses.
6. Are there any notable industries leveraging private permissionless blockchains developed by SoluLab?
Yes, industries such as supply chain management, healthcare, and finance have found value in private permissionless blockchains developed by SoluLab. These solutions offer transparency where needed while upholding data confidentiality.
7. How can businesses benefit from SoluLab’s Blockchain Development Services for permissionless blockchains?
SoluLab empowers businesses by providing tailored Blockchain Development Services. From enhancing security to fostering innovation and inclusivity, their expertise in permissionless blockchains ensures that businesses can navigate the decentralized landscape with confidence.