 The world of finance is experiencing a deep digital shift. Banking systems are changing fast, fueled by advances in blockchain, mobile payments, and digital finance infrastructure. From contactless payment to artificial intelligence-based financial services, economies are shifting toward quicker, safer, and more accessible financial systems.
The world of finance is experiencing a deep digital shift. Banking systems are changing fast, fueled by advances in blockchain, mobile payments, and digital finance infrastructure. From contactless payment to artificial intelligence-based financial services, economies are shifting toward quicker, safer, and more accessible financial systems.
At the heart of this shift is the emergence of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)—official digital forms of national fiat currencies. In contrast to cryptocurrencies, CBDCs marry central banks’ trust with blockchain technology’s efficiency and transparency.
If you are looking for in depth information on the concept of CBDCs, the article is for you!
What is a Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)?
A CBDC is a digital version of the national currency of a nation, issued and controlled by the central bank. In contrast to cryptocurrencies, CBDCs are legal tender, providing the confidence of fiat money with the efficiency of blockchain.
Key Features:
- Issued by central banks
- Supported by national fiat reserves
- Works digitally but with regulation
- Secure, programmable, and traceable
| Feature | Physical Currency | CBDC |
| Form | Paper/coins | Digital-only |
| Storage | Wallets/safes | Digital wallets |
| Issuer | Central bank | Central bank |
| Traceability | Low | High |
| Programmability | No | Yes |
Function of Central Banks:
Central banks are both the issuer and regulator, promoting monetary stability and control over policy through the utilization of CBDCs.
How CBDCs Differ from Cryptocurrencies?
Though both Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) and cryptocurrencies are in digital format and utilize distributed ledger or blockchain technology, there are major differences between them with regard to control, objective, and trust framework.
1. Issuing Authority
Central Bank Digital Currencies are issued and supported by a nation’s monetary or central bank authority, thereby being legal tender. It ensures they are accepted and recognized nationwide, just like physical currency.
Conversely, digital currencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum are developed by decentralized groups or networks. They do not have a central issuer, implying there’s no government or institution assuring their use or value.
2. Legal Status and Regulation
CBDCs are considered legal tender within a country. This implies that citizens and businesses are bound by law to accept them as payment. They fall under a rigid regulatory system controlled by the central bank.
Cryptocurrencies, on the other hand, tend to operate in a legal gray. They are classified in most places as digital assets or commodities and not as currencies. They are governed by changing regulations, and they are prohibited or banned in some nations.
3. Centralization vs. Decentralization
CBDCs are under the central control of the issuing authority, providing the central bank with full control of transactions, distribution, and monetary policy implementation. Centralization provides more effective policy tools but is a concern with respect to privacy of data and surveillance systems.
Cryptocurrencies are inherently decentralized. They run on peer-to-peer networks where no one has authority. This provides censorship resistance and transparency but restricts the capability to monitor or reverse transactions.
4. Volatility and Stability
CBDCs aim to replicate the value of its nation’s fiat currency, so they remain stable in value. By way of illustration, 1 digital rupee or digital dollar is always equivalent to its physical equivalent.
Most cryptocurrencies, by contrast, are extremely volatile. Their values change according to market demand, speculation, and outside factors. Such volatility makes them good investments but impractical as a means for daily transactions or salary payments.
| Parameter | CBDC | Cryptocurrency |
| Issuer | Central Bank | Decentralized (no issuer) |
| Legal Status | Legal tender | Not universally accepted |
| Regulation | Fully regulated | Partially or unregulated |
| Volatility | Stable | Highly volatile |
| Use Cases | National payments, G2P, trade | Investment, DeFi, NFTs |
CBDCs maintain centralized control and monetary oversight, while cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum offer decentralized, permissionless alternatives.
Why Are Governments Considering CBDCs Now?
As cash use wanes and digital payments surge, central banks worldwide are acting proactively to:
- Keep monetary control in a more digital world
- Push back against the rise of unregulated cryptocurrencies and stablecoins
- Enhance financial inclusion and policy effectiveness
- Upgrade payment systems for domestic commerce and cross-border trade
CBDCs are not a fad—they’re redefining the future of money, making financial systems smarter, more inclusive, and resilient.
1. Monetary Policy Efficiency and Control
CBDCs enable real-time monitoring and control of the money stock, enhancing the efficacy of central bank monetary policy implementation and oversight.
2. Counter to Waning Cash Use
As digital payments have surpassed cash use worldwide, CBDCs provide a state-supported option for digital payment systems versus private ones.
3. Counter to Stablecoins & Cryptocurrencies
CBDCs guarantee national control over money, countering the influence of unregulated stablecoins and crypto tokens.
4. Economic Modernization
They facilitate the digitalization of financial infrastructure to foster innovation, efficiency, and inclusion.
How CBDC Development Is Facilitating Global Economies?
CBDC development is reshaping economies by strengthening monetary policy, boosting inclusion, enabling faster payments, ensuring transparency, and driving financial innovation.
1. Improving Monetary Policy Implementation
CBDCs make it possible for instant policy implementation—tweaking interest rates or managing liquidity in near real time.
2. Increasing Financial Inclusion
In remote or underserved areas, CBDCs facilitate safe and convenient digital wallets without requiring bank accounts.
3. Simplifying Cross-Border Payments
CBDCs minimize friction on international payments, reducing costs and accelerating settlements.
4. Fighting Financial Crime and Tax Evasion
By enhancing traceability and transparency, CBDCs facilitate tracking of illicit behavior and enhancing tax compliance.
5. Enhancing G2P Payments
Stimulus checks, pensions, and subsidies can be distributed directly to citizens by governments via programmable CBDC wallets.
6. Encouraging Innovation in Financial Services
CBDCs enable programmable money, paving the way for:
- Smart contracts
- DeFi integrations
- Custom digital banking solutions
7. Revolutionizing the Way the World Does Business
From cross-border trade settlements to online marketplaces, CBDCs reframe financial infrastructure for speed, cost-effectiveness, and trust.
CBDC Ripple Effect
The use of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) creates a ripple effect on various sectors of the economy. When a central bank launches a CBDC, it not only digitalizes money but also:
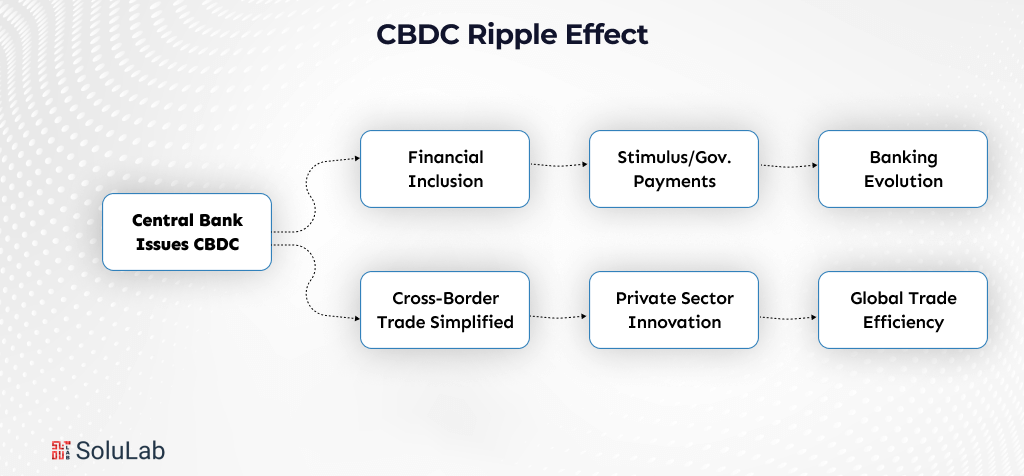
- Encourages financial inclusion through giving access to secure digital payments to unbanked communities
- Streamlines cross-border trade by facilitating quicker, cheaper, and more transparent international transactions
- Enhances government operations, particularly in the distribution of welfare and direct payments to citizens
- Fosters private sector innovation via programmable money and fintech integration
- Reverses the conventional banking model, reshaping commercial banks’ and payment service providers‘ roles
- Enhances global trade efficiency through standardized, interoperable, and transparent payment systems
Generally, CBDC use unleashes a chain reaction of financial modernization, touching every aspect from individual transactions to international trade and policymaking.
The Future of CBDCs
CBDCs are shaping the future of money, with 130+ nations testing digital currencies, global collaborations advancing cross-border use, and long-term potential to transform monetary policy and economies.
1. Global Momentum: Over 130+ countries are experimenting with CBDCs, with flagship initiatives like China’s e-CNY, India’s Digital Rupee, and the EU’s Digital Euro leading the way.
2. Collaborative Innovation: Strategic projects such as mBridge and the BIS Innovation Hub are building multi-CBDC platforms, paving the path for fast, low-cost, and secure cross-border payments.
3. Transformational Impact: Beyond payments, CBDCs promise to redefine monetary policy, strengthen financial inclusion, and accelerate the world’s shift toward cashless, fully digital economies.
Conclusion
Central Bank Digital Currencies are not yet another financial experiment—they’re a foundational change in how the world understands, holds, and uses money. For governments and businesses alike, the news is clear: embracing CBDCs is no longer a choice—it’s a requirement. Early movers will find a competitive advantage in defining the future of financial infrastructure.
As a leading blockchain development company, SoluLab helps governments, financial institutions, and enterprises design and deploy secure, scalable, and compliant CBDC solutions. With deep expertise in blockchain architecture, smart contracts, digital wallets, and regulatory integrations, we empower organizations to unlock the full potential of digital currencies.
If your organization is exploring the potential of Central Bank Digital Currency, contact us to turn vision into reality!
FAQs
1. How can organizations prepare for CBDC integration?
Businesses and financial institutions should focus on upgrading digital infrastructure, ensuring compliance with regulations, and adopting blockchain-based solutions that support seamless CBDC transactions.
2. Are CBDCs already in use globally?
Yes. Countries like China (Digital Yuan), Nigeria (eNaira), and the Bahamas (Sand Dollar) have launched CBDCs. Many others, including the U.S. and European Union, are actively testing or researching them.
3. Will CBDCs replace traditional cash completely?
Not in the near future. CBDCs are expected to coexist with cash and digital payment systems, giving citizens more flexibility while allowing governments to gradually reduce reliance on physical money.
4.How can businesses prepare for a CBDC-driven future?
Businesses should stay updated on regulatory changes, adopt digital-friendly payment systems, and explore blockchain integration to remain competitive as CBDCs reshape financial ecosystems.
5. Why should countries adopt CBDCs if digital banking already exists?
Unlike traditional digital banking, CBDCs are sovereign, programmable, and universally accessible, offering stronger financial inclusion and enabling direct monetary policy tools for governments.






