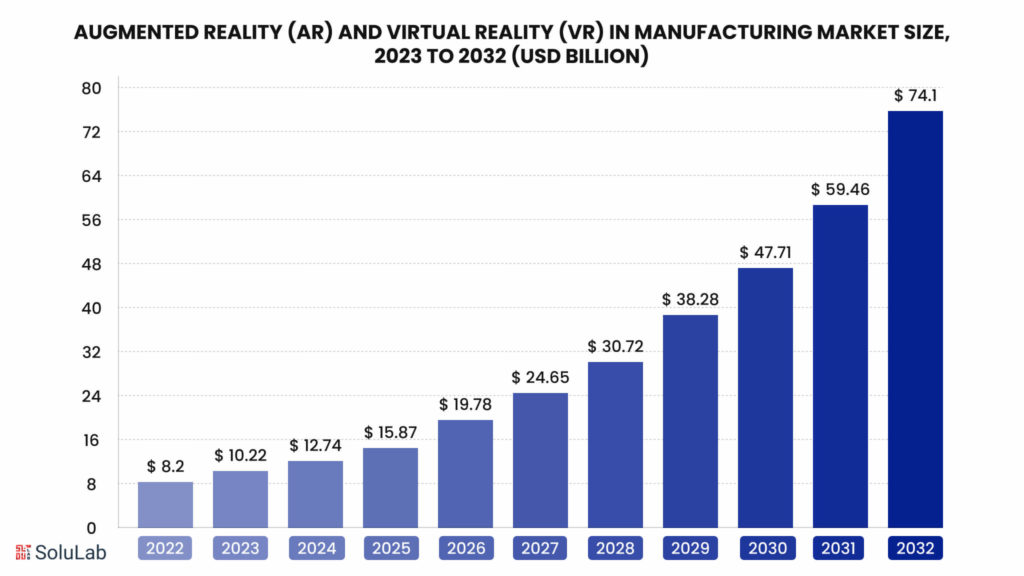
In 2022, the global market for augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) in manufacturing stood at an estimated value of USD 8.2 billion. This figure is projected to experience substantial growth, reaching approximately USD 74.1 billion by 2032, representing a remarkable compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 24.62% from 2023 to 2032.
AR and VR manufacturing, a form of automation, seamlessly integrates digital technology into the production line. By combining the physical world with computer-generated graphics, data, and interactive elements.
Immersive Tech in Manufacturing
Immersive reality technology is revolutionizing the manufacturing industry by providing solutions for maintenance practices. This technology, including AR and VR in manufacturing, offers unique capabilities to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and safety in maintenance operations. AR VR applications in manufacturing empower maintenance professionals with powerful tools to optimize their workflows, providing real-time information, facilitating remote collaboration, and offering immersive training experiences. These advancements lead to improved maintenance practices, reduced downtime, and increased productivity in the manufacturing sector.
A. Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) technology is revolutionizing the manufacturing industry by providing technicians with real-time information about their work environments. AR in manufacturing enables technicians to overlay digital information onto the physical world, allowing them to see and interact with data in a way that was previously impossible. AR applications in manufacturing include the use of connected goggles or glasses, allowing technicians to view detailed instructions, schematics, and other relevant information while working on a task. This information can be drawn from various data sources, including sensors, databases, and even the technician’s knowledge.
One of the key AR in manufacturing examples is that it allows technicians to make faster and more accurate decisions. With access to all relevant information at their fingertips, technicians can quickly identify and resolve problems without referring to manuals or other documents. This significantly reduces downtime and improves productivity.
Another advantage of Augmented Reality (AR) is its application in training new technicians. By providing trainees with a virtual environment to practice their skills, AR helps them learn more quickly and effectively, reducing the time required for training and ensuring new technicians are fully prepared for their jobs.
Overall, Augmented Reality (AR) is a powerful tool that has the potential to transform the manufacturing industry. By providing technicians with real-time information and enabling them to interact with their environment in a new way, AR can improve efficiency, productivity, and safety in the manufacturing sector.
Here are some specific examples of how AR is being used in the manufacturing industry today:
- Technicians can use AR to view assembly instructions for complex products.
- AR can be used to provide remote support to technicians who are working on-site.
- AR can be used to create interactive training simulations for new technicians.
- AR can be used to track and manage inventory in real-time.
- AR can be used to improve safety by providing technicians with warnings about potential hazards.
As AR technology continues to develop, it is likely that we will uses for this technology in the manufacturing industry.
B. Virtual Reality
VR in manufacturing offers a captivating experience by presenting a distinct and immersive environment to the user. Unlike traditional media, VR virtual reality transports the viewer to a virtual realm that may differ significantly from their physical surroundings. This technology can create entirely new and imaginative worlds or provide a remarkably realistic portrayal of existing environments, making it a valuable tool in smart industries.
In smart industry settings, VR is typically facilitated through the use of a headset, enabling users to fully interact with the virtual environment being presented. The headset serves as a gateway to this digital realm, allowing the user to manipulate objects, explore landscapes, and engage in activities as if they were physically present within the virtual space. This immersive technology is integral to smart manufacturing industry 4.0, where precision, GenAI in Manufacturing, and innovation are key.
One of the most prevalent VR in manufacturing applications is to facilitate a close analogue of interaction with a real-world element, such as a part, component, or machine. In this context, VR enables users to manipulate and examine virtual representations of physical objects with a high degree of accuracy and detail. This capability is particularly valuable for training purposes, allowing users to practice complex procedures and gain familiarity with equipment in a safe and controlled environment.
The key difference between AR and VR lies in the environment they create. While AR overlays digital information onto the physical world, VR places the user in an entirely new and isolated environment. This immersive experience allows users to engage with virtual objects and scenarios as if they were physically present within the virtual space, illustrating the difference between VR and AR in practical applications.
VR in manufacturing has the potential to be in various industries and applications. In addition to its use in training and education, VR is gaining traction in fields such as entertainment, healthcare, engineering, and architecture. By providing realistic and interactive experiences, VR enables users to visualize complex concepts, practice skills, and explore new possibilities in a safe and immersive environment.
As VR virtual reality technology continues to advance, we can expect even more immersive experiences in the years to come. This technology has the potential to transform how we interact with the digital world and open up new frontiers of creativity, collaboration, and learning, particularly in smart manufacturing industry 4.0 contexts.
C. Mixed Reality
Mixed reality (MR) is a technology that seamlessly blends the real world with the virtual world, creating an immersive environment that allows users to interact with both. It combines elements of AR and VR in manufacturing and other sectors, with different implementations leaning more toward one technology or the other.
In smart industries, users can still see and interact with the physical environment around them, but they can also interact with virtual objects and information overlaid onto the real world. This integration offers significant benefits of AR VR in manufacturing, as it allows for a more immersive and interactive environment that combines the best of AR and VR technology. Additionally, Customer Service Automation can be enhanced by leveraging these immersive technologies, providing users with instant, interactive support and improving overall service efficiency.
For example, a technician using mixed reality in a smart manufacturing industry 4.0 setting might see the physical components of a machine they are working on, while also viewing virtual instructions and diagrams overlaid onto those components. This AR/VR in manufacturing application helps identify problems and perform maintenance tasks more efficiently.
Mixed reality is also applicable in entertainment, education, and training. Users can play games that allow them to interact with virtual characters and objects in the real world or explore virtual worlds overlaid onto real-world locations. For the smart industry, mixed reality technology creates immersive training experiences that enable users to practice real-world tasks in a safe and controlled environment.
One of the key benefits of AR VR in manufacturing and mixed reality is the immersive experience it offers, allowing users to interact with both real and virtual worlds simultaneously. This interaction enhances the sense of presence and realism, crucial for smart manufacturing industry 4.0.
Though still a relatively new technology, mixed reality has the potential to affect how we interact with the world around us, from AR VR application in manufacturing to various other sectors. As this technology continues to develop, more creative uses will likely emerge, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in AI in Manufacturing, smart industries and beyond.
Immersive Technology Benefits
Immersive technologies, encompassing augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR), present a plethora of advantages for practices across the manufacturing landscape. Each technology offers unique capabilities and benefits, empowering maintenance technicians and other personnel to work more efficiently, effectively, and safely especially when combined with Data Annotation for precise and accurate information.
AR in maintenance offers a number of benefits, including:
1. Generally unobtrusive: AR and VR in manufacturing allows technicians to work without cumbersome headsets or other equipment, enabling them to focus on their tasks without distraction. This can increase productivity and reduce errors, as technicians are not burdened with additional equipment that can get in the way.
2. A lower barrier to entry: AR VR application in manufacturing makes it easier for technicians of all skill levels to use the technology, as they do not need to learn a new interface or operating system. This reduces training time and cost, and makes it easier for companies to find qualified technicians. Additionally, integrating a Multi Signature Wallet into the process ensures secure and controlled access to sensitive data, further enhancing the safety and reliability of the technology in industrial environments.
3. Real-time: Augmented Reality (AR) provides data that helps technicians identify problems early on, preventing costly downtime. It also aids in learning how to operate and maintain equipment more effectively, leading to increased productivity, reduced maintenance costs, and improved equipment reliability.
4. Quick access: AR in manufacturing helps technicians avoid repeating mistakes and identify trends in equipment performance. It also tracks the effectiveness of maintenance procedures, helping technicians improve their skills and knowledge, and assisting companies in identifying areas for improvement in maintenance procedures.
5. Transmits institutional knowledge: AR applications in manufacturing bridge the gap between experienced and new technicians, ensuring that the knowledge and skills of the older generation are not lost. This maintains a high level of expertise within the workforce and reduces the time and cost associated with training new technicians.
6. More accessible: AR in manufacturing examples demonstrate how technology can help technicians unfamiliar with specific equipment to perform maintenance tasks more effectively and efficiently. This reduces training time and cost, and aids companies in finding qualified technicians.
Benefits of VR in maintenance include:
1. Virtual Access: With VR in manufacturing, engineers and technicians can remotely inspect and interact with parts, components, equipment, and machinery as if they were physically present. This eliminates the need for costly and time-consuming travel and on-site visits, making it easier for teams in smart industries to collaborate and make decisions quickly. Integrating AI-powered RFX into these processes further streamlines decision-making by automating and optimizing request-for-quote (RFQ) and proposal (RFP) processes. VR virtual reality enables real-time monitoring and remote diagnostics, allowing experts to provide guidance and support from anywhere in the world. This significantly improves maintenance efficiency and reduces downtime, fitting into the smart manufacturing industry 4.0 framework.
2. Reduced Costs: VR in manufacturing can significantly cut costs associated with travel and on-site visits. By eliminating the need for engineers and technicians to travel physically, companies can save money on transportation, accommodation, and other expenses. Additionally, VR virtual reality reduces the need for physical prototypes, which can be expensive and time-consuming to produce.
3. Virtually Represent Parts: VR in manufacturing allows engineers and designers to create virtual prototypes of parts, products, and components based on technical drawings and data, enabling teams to visualize and test designs before they are physically manufactured. This helps identify potential issues early on and reduces the risk of costly mistakes. Smart industry applications of VR virtual reality also include creating virtual showrooms for customers to experience products in a realistic and engaging way.
4. Effective Communication: VR in manufacturing provides a more immersive and interactive way for manufacturers and customers to communicate. Instead of discussing components based on technical drawings or CAD models, teams can use VR virtual reality to view and interact with components in a “real world” setting. This improves understanding, reduces miscommunication, and streamlines the product development process. Virtual reality also creates interactive training modules, providing employees with a more engaging and memorable learning experience.
5. Fully Immersive Training: VR in manufacturing can be used to provide fully immersive training simulations, allowing employees to practice and learn new processes and procedures in a safe, risk-free environment. By eliminating the risk of error or injury, VR virtual reality training can improve employee confidence and competence. It can also simulate dangerous or high-risk scenarios, providing experience and knowledge without putting employees in harm’s way. Integrating Robotic Process Automation with VR can further streamline training processes, ensuring that repetitive tasks are automated, and allowing employees to focus on more complex scenarios. Understanding the difference between AR and VR or the difference between VR and AR enhances how these technologies can be utilized effectively for training and development.
Mixed reality benefits include:
1. Full Interactivity: AR and VR in manufacturing enable full interactivity for remote maintenance, allowing technicians to access and control on-site equipment as if they were physically present. Using AR and VR technology, technicians can view virtual representations of the equipment in real-time, aiding in quicker and more efficient diagnostics and repairs. This integration of AR VR application in manufacturing enhances the benefits of AR VR in manufacturing, aligning with smart industries and the smart manufacturing industry 4.0.
2. Access to the Best Talent: Remote maintenance facilitated by AR/VR in manufacturing allows companies to tap into global talent pools, as technicians can remotely manage equipment from any location. This eliminates the need for travel to remote sites, leveraging AR and VR in manufacturing to access top-tier expertise without geographical constraints.
3. Real-Time Collaboration: AR and VR technology enhances real-time collaboration and communication among team members by enabling remote access and control of equipment. This ar vr application in manufacturing helps improve problem-solving capabilities and maintenance efficiency, contributing to the smart industry landscape.
4. Error Reduction: By providing technicians with a real-time view of equipment through AR and VR technology, remote maintenance reduces errors. Technicians can use AR in manufacturing and VR virtual reality to view virtual representations of equipment, leading to more accurate problem identification and quicker fixes, which aligns with the benefits of AR VR in manufacturing.
5. More Efficient Maintenance: The use of AR/VR in manufacturing boosts maintenance efficiency by enabling technicians to diagnose and repair issues remotely. This reduces the need for on-site visits, saving time and money while improving repair speed and accuracy. The integration of smart manufacturing industry 4.0 principles ensures that maintenance processes are streamlined and effective.
Immersive Technology Use Cases
Immersive technology, encompassing augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR), has maintenance procedures and workflows in the manufacturing sector. These technologies unlock a range of benefits, empowering maintenance technicians and other personnel to operate more efficiently, accurately, and safely.
Uses of AR include:
1. Real-time Performance Data: With AR and VR in manufacturing, real-time performance data for equipment is displayed through a heads-up display, allowing technicians to monitor critical metrics such as temperature, pressure, and vibration at a glance. This capability, exemplified by AR applications in manufacturing, helps in early issue identification and proactive measures to prevent equipment failures.
2. Personnel Information: Augmented Reality (AR) provides ready access to information about personnel on the floor, including availability, specialization, training, and current location. This feature of AR in manufacturing facilitates efficient task assignment, ensuring the right personnel handle specific maintenance tasks.
3. Step-by-Step Maintenance Instructions: The system offers step-by-step maintenance instructions through AR VR application in manufacturing, guiding technicians through complex procedures. This reduces the risk of errors and ensures that maintenance tasks are performed correctly and consistently, showcasing AR in manufacturing examples.
4. Effective Decision-Making: AR and VR in manufacturing enhance decision-making by providing real-time data and insights. Technicians can quickly assess situations, identify root causes, and determine the best course of action, improving the overall efficiency of maintenance processes.
5. Predictive Maintenance: The system provides insights into potential failure conditions for equipment, enabling more proactive and predictive maintenance. By analyzing historical data and monitoring key indicators, AR and VR technology helps in identifying at-risk components and taking preventative actions.
6. Enhanced Training: AR applications in manufacturing support more effective training processes by offering interactive virtual simulations and tutorials. This immersive training environment enhances understanding and retention, making Augmented Reality (AR) a powerful tool for technician education.
7. Support for All Skill Levels: The system aids in maintenance for personnel who may not be familiar with the equipment. By providing real-time guidance and step-by-step instructions through AR and VR in manufacturing, it empowers technicians of all skill levels to perform tasks efficiently and effectively.
Virtual reality uses include:
1. Global Inspection and Vetting: Utilize VR in manufacturing and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies to conduct comprehensive vetting and inspection of processes from anywhere in the world. This approach eliminates the need for costly and time-consuming on-site visits, allowing for efficient evaluation of suppliers, manufacturers, and partners, regardless of their geographic location. Smart industries benefit from real-time examination of facilities, machinery, and products, identifying potential issues and ensuring compliance with standards, making smart manufacturing industry 4.0 a reality.
2. Remote Interaction with Large Parts: Interact with parts that are too large or heavy to be transported efficiently using VR virtual reality and AR in manufacturing. Engineers, designers, and quality control professionals can examine and assess these parts remotely, identifying defects, performing measurements, and making design modifications without physical handling. Integrating AI Automation with AR VR applications in manufacturing also facilitate collaboration among team members from different locations, enhancing productivity.
3. Collaborative Design and Prototyping: VR and AR technologies enable collaboration on parts that have not yet been built. Teams can interact with digital prototypes, review designs, and identify potential issues before physical manufacturing. This streamlines the product development process, reduces costs, and allows engineers and designers to make informed decisions early on, showcasing the difference between AR and VR in product development.
4. Virtual Facility Planning: VR and AR technologies allow businesses to plan and redesign floor footprints and facilities virtually. By creating realistic simulations of facilities, companies can optimize space utilization, improve workflow, and enhance operational efficiency. This eliminates the need for costly physical changes and facilitates collaboration among stakeholders, exemplifying smart industries and smart manufacturing industry 4.0.
5. Design and Component Development: Design parts and components virtually with AR and VR in manufacturing. Engineers and designers can collaborate in real-time to create, modify designs, assess functionality, and conduct stress tests. This results in faster, more efficient product development cycles and demonstrates the difference between VR and AR in design and development.
6. Immersive Training: VR and AR provide immersive training environments for new hires and upskilling existing technicians. Trainees can learn and practice complex procedures in a safe, controlled environment without needing physical equipment. AR VR application in manufacturing facilitates remote training, allowing organizations to train employees from different locations effectively.
Mixed reality uses include:
1. Building a Global Workforce: By leveraging AR and VR in manufacturing, companies can build a skilled and knowledgeable technical workforce that transcends geographical barriers. AR VR application in manufacturing enables seamless collaboration among technicians, allowing them to communicate and interact as if they were physically present in the same room. This fosters a sense of unity and enhances teamwork, aligning with the vision of smart industries and smart manufacturing industry 4.0.
2. Step-by-Step Maintenance Training: Implement a maintenance training program that uses AR/VR in manufacturing to provide comprehensive, step-by-step instructions. This training empowers technicians with the knowledge and skills needed to perform maintenance tasks effectively, ensuring that equipment and systems are well-maintained and functioning optimally. The benefits of AR VR in manufacturing include enhanced training and improved maintenance practices.
3. Work Tracking System: Establish a work tracking system enhanced by AR and VR technology to boost efficiency and effectiveness. This system allows technicians to track work progress, monitor maintenance schedules, and identify potential issues. Seamless communication between technicians and management is facilitated, keeping everyone informed about maintenance activities and contributing to smart industry practices.
4. Efficient Personnel and Process Management: Develop strategies for resource allocation, personnel utilization, and process optimization using AR and VR in manufacturing. These strategies will improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance productivity, supporting the goals of smart industries and the smart manufacturing industry 4.0.
5. Real-Time Communication Solutions: Implement real-time communication tools that leverage AR VR applications in manufacturing to facilitate instant, seamless communication among technicians, management, and stakeholders. Tools such as video conferencing and instant messaging will enable real-time information sharing, problem-solving, and decision-making, enhancing collaboration and responsiveness.
Conclusion
The integration of AR and VR in manufacturing is revolutionizing the smart industry by enhancing efficiency, safety, and productivity. From AR applications in manufacturing that provide real-time data overlays to VR in manufacturing that allows for immersive training and simulation, these technologies are reshaping the smart manufacturing industry 4.0. The benefits of AR VR in manufacturing include reduced downtime, improved quality control, and enhanced worker training, making them indispensable tools for modern industries. AR/VR in manufacturing offers practical solutions to complex challenges, such as visualizing assembly processes, facilitating remote assistance, and streamlining maintenance tasks.
AR in manufacturing examples include overlaying digital instructions on physical machinery, while VR virtual reality is used for training workers in a risk-free environment. The difference between AR and VR lies in their approach: AR augmented reality enhances the real world with digital elements, while VR creates an entirely virtual environment. At SoluLab, we specialize in developing AR technology development for the smart manufacturing industry 4.0. Our expertise in AR VR application in manufacturing ensures that our clients can harness the full potential of these technologies. Whether you’re looking to explore ar vr use cases in manufacturing or want to understand what is augmented reality ar, SoluLab is here to guide you through the digital transformation journey. Partner with us to stay ahead in the rapidly evolving world of smart industries.
FAQs
1. What is the role of AR and VR in manufacturing?
AR and VR are transforming the manufacturing sector by enhancing productivity, safety, and operational efficiency. These technologies offer immersive experiences and real-time data visualization, making them vital tools in smart industries.
2. What are some common AR applications in manufacturing?
Common AR applications in manufacturing include providing real-time data overlays for assembly processes, maintenance guidance, and quality control. These ar in manufacturing examples demonstrate how Augmented Reality (AR) can streamline operations and improve accuracy.
3. How do AR and VR technologies benefit the Smart Manufacturing Industry 4.0?
The benefits of AR VR in manufacturing for Smart Manufacturing Industry 4.0 include reduced downtime, enhanced worker training, and improved quality assurance. These technologies enable manufacturers to optimize processes and adapt to changing demands more efficiently.
4. Can you provide some AR/VR use cases in manufacturing?
Some ar vr use cases in manufacturing include virtual prototyping, immersive training environments, and augmented maintenance procedures. These applications help in reducing errors and improving overall production efficiency.
5. What is the difference between AR and VR in manufacturing?
The difference between AR and VR lies in their approach: AR augmented reality enhances the real world with digital overlays, while VR virtual reality creates an entirely simulated environment. Both have unique applications in the manufacturing industry.
6. Why should manufacturers consider adopting AR and VR technology?
Manufacturers should consider adopting ar and VR technology due to its potential to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance worker safety. The ar vr application in manufacturing offers solutions to traditional challenges, making it a, suitable strategy for modern smart industries.
7. How is AR in manufacturing driving innovation in smart industries?
AR in manufacturing is driving innovation by enabling real-time data access, improving decision-making, and enhancing product quality. This integration is key to advancing the smart industry and maintaining competitiveness in the evolving market.





