As 2026 approaches, AI agents are no longer just experimental tools — they’re becoming the backbone of automation across industries. They leverage advanced technologies such as ML and NLP to interact with their environments. They can handle a wide range of tasks, from simple automated responses to complex problem-solving, across various environments.
Over the past few years, the global AI market has been experiencing exponential growth. It is expected to be valued at around $594 billion by 2032. This rise is due to AI agents in services where 54% of companies now employ conversational AI. In this blog, we will explore types of AI agents, benefits, and applications that are driving the future towards innovation.
What Are AI Agents?
Just like a self-driving remote-controlled car, akin to an autonomous vehicle. Equipped with sensors and an intelligent system, this car can analyze its surroundings and determine the optimal path. Think of it as a potential movie plot, but let’s bring it back to reality.
There are two key aspects to consider about what an agent is in AI:
- Its brain is programmed to follow a specific path and avoid obstacles.
- The more it drives, the better it becomes at following its path and avoiding bumps.
Different types of AI agents share similarities with this self-driving remote-controlled car. Instead of wheels, AI agents may utilize various tools such as screens, keyboards, cameras, and microphones.
They operate on the same principle: sensing their environment, analyzing the information, and taking action to achieve a goal. Just as the remote-controlled car improves over time, AI agents can also learn and enhance their capabilities. It’s a fascinating concept, isn’t it?
“Scott Brinker, the ‘godfather of martech,’ kicked off the MarTech Conference on November 4, 2025, explaining how autonomous AI agents are reshaping marketing teams and customer engagement.”
In this context, artificial intelligence and intelligent agents play an important role in creating systems that can adapt and respond intelligently to their environments.
What’s the Working Principle Behind AI Agents?
In Artificial Intelligence (AI), an agent is a system that conforms to the PEAS model. This model encompasses four key elements:
- Performance Measure: A metric that evaluates the AI agent’s effectiveness in accomplishing its objectives.
- Environment: The external world with which the agent interacts, perceived through sensors.
- Actuators: Mechanisms employed by the agent to influence and alter its environment.
- Sensors: Methods for gathering information and data about the environment.
AI agents utilize various techniques such as machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), reasoning, and knowledge representation to perceive their surroundings, make informed decisions, and take actions that lead to the achievement of their goals.
Building on this foundation, let’s explore the different categories of AI agents and their unique characteristics.
The Types of AI Agents
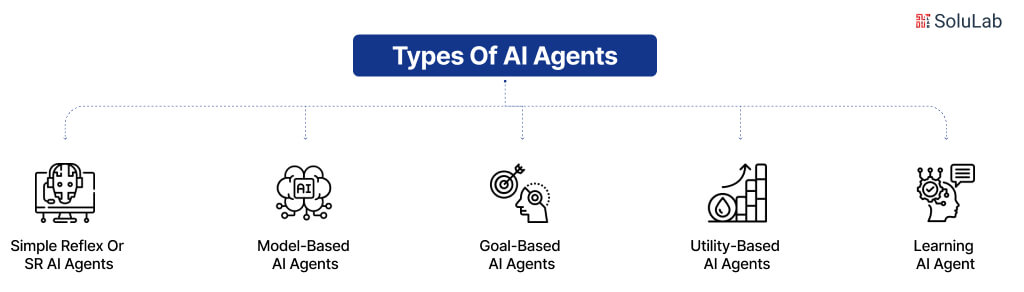
Tasks and environments define the type of AI agent to use. We’ll explain each type in detail. However, here’s a quick glimpse of the types of AI agents:
1. Simple Reflex Agents
In Artificial Intelligence, simple reflex agents serve as the foundational and most comprehensible AI agent types. In essence, they act as instinctive reactors in the AI world.
The operational mechanism of simple reflex agents revolves around a continuous cycle of perception and action. Sensors gather environmental data, which is then compared against a comprehensive set of pre-programmed rules, akin to an extensive “IF…THEN…” list. Based on the matched rule, the agent executes a predetermined action.
Examples
- Thermostat: Equipped with sensors, it monitors the room’s temperature and activates or deactivates the heating system to maintain a desired temperature range.
- Light Sensor in a Street Lamp: Detecting darkness, this sensor starts the street lamp to illuminate, ensuring visibility and safety during nighttime.
2. Model-based Reflex Agents
Model-based reflex agents incorporate an internal model of the environment, extending the capabilities of simple reflex agents. This model enables them to address situations where not everything is directly observable by sensors.
Unlike simple reflex agents, which struggle in partially observable environments, model-based agents build an internal representation of the world based on past sensor readings. When a new situation arises, they consult this model to gain context and make informed decisions by utilizing their pre-programmed rules.
Examples:
- Self-driving cars: They utilize internal models of road networks, traffic lights, lanes, and potential obstacles to navigate safely.
- Robot vacuum cleaners: Advanced models use internal maps of the room to clean efficiently.
3. Goal-based Agents
Goal-based AI agents are designed with a specific objective in mind, actively planning their actions to achieve it. Their planning process involves examining a tree of possibilities, with each branch representing a potential action. They consider the consequences of each action and choose the one that brings them closer to their goal.
Goal-based AI agents rely on knowledge representation to perform effective planning. This knowledge base stores information about the environment, its capabilities, and the relationships between actions and outcomes.
Examples:
- Robot path planning: Robots might use a goal-based approach to navigate around obstacles and reach a specific location.
- Game-playing AI: Chess programs and AI opponents in strategy games make decisions based on goal-based strategies to achieve victory.
4. Utility-based Agents
Utility-based agents evaluate various actions based on a utility function that assigns numerical values to each potential outcome, indicating how desirable it is for the agent. The agent aims to maximize its overall score by selecting actions that lead to outcomes with higher utility values.
These agents gather environmental information through sensors, consider potential actions, and predict outcomes for each action. The utility function assigns a score to each predicted outcome based on its desirability, enabling the agent to select the action that leads to the highest utility value.
Examples:
- Recommendation systems predict user enjoyment by assigning utility scores to products, movies, or music.
- Self-driving cars use utility functions to consider safety, efficiency, and passenger comfort in decision-making.
- Trading robots evaluate investment options and trading decisions based on maximizing ROI through utility functions.
5. Learning Agents
Learning agents, the pinnacle of AI agent categories, possess the remarkable ability to learn and adapt their behavior through interactions with their environment.
Components and Functions of Learning Agents
- Learning Element: Processes new information, continuously updating the agent’s knowledge and decision-making strategies.
- Critic: Evaluates the agent’s performance, providing feedback on how well it meets its goals.
- Performance Element: Based on the agent’s current knowledge and the critic’s feedback, this element selects actions for the agent to take in its environment.
- Knowledge Representation: Stores and organizes information about the environment and the agent itself, enabling efficient processing and decision-making.
Examples:
- Personal Assistants: Virtual assistants such as Siri and Alexa learn user preferences and voice patterns, providing increasingly specific responses over time.
- Self-Driving Cars: These vehicles rely on machine learning to enhance their navigation abilities, continuously improving their response to changing road conditions.
Functions Of An AI Agent
Artificial intelligence (AI) agents are increasingly becoming an integral part of our lives, carrying out various tasks from powering self-driving cars to assisting us in managing our finances. Artificial intelligence, what is an agent in AI, and intelligent agents are designed to mimic the cognitive processes of humans, allowing them to perceive their environment, process information, reason and make decisions, take actions, and learn and improve over time.
Read Also: How Businesses in Every Industry Are Benefiting from AI Agents?
1. Perceive the Environment
AI agents are equipped with sensors that gather information about their surroundings. These sensors can include cameras, microphones, web search functions, or any other sensor modality relevant to their task. This information is then processed to extract meaningful data. For example, a self-driving car might use cameras to detect other vehicles, pedestrians, and traffic signs. Additionally, AI agent in finance can use similar sensors and data processing techniques to analyze market trends and make informed investment decisions.
2. Process Information
Once the AI agent has gathered information about its environment, it must process this information to make sense of it. This stage involves techniques such as image recognition, natural language processing, or simply analyzing sensor readings. For instance, a self-driving car might use image recognition to identify pedestrians and traffic signs and natural language processing to understand voice commands from the driver, which are all great AI agents examples in action.
3. Reason and Make Decisions
Based on their understanding of the environment and their programmed goals, AI agents employ reasoning algorithms to determine the best course of action. This step includes planning a sequence of actions, evaluating different options, or simply reacting to a stimulus based on predefined rules. For example, a self-driving car might use reasoning algorithms to decide when to accelerate, brake, and turn. These processes are common in various AI agents use cases, helping to optimize decision-making in real-time environments.
4. Take Actions
AI agents utilize actuators to influence the environment. These tools could involve robots moving their limbs, software programs generating text or recommendations, or any other action that achieves the agent’s goals. For instance, a self-driving car might use actuators to control its steering, brakes, and throttle, demonstrating the capabilities of an AI intelligent agent in real-world applications.
5. Learn and Improve
Certain types of AI agents can learn from their experiences and adapt their behavior over time. This learning process can involve techniques such as supervised learning, unsupervised learning, or reinforcement learning. For example, a self-driving car might use reinforcement learning to enhance its driving skills by learning from its mistakes.
Read Also: How to Build an AI Agent System?
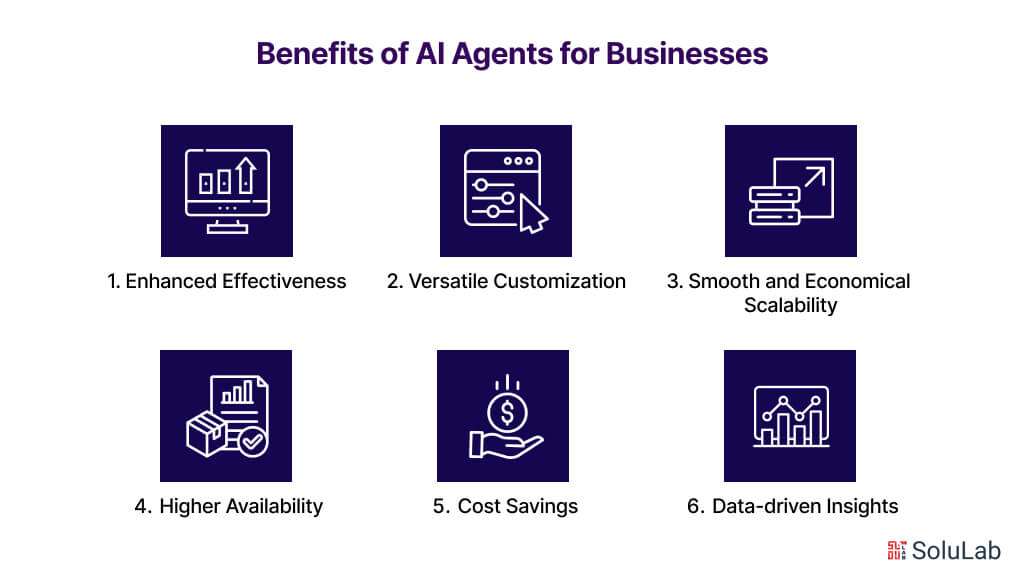
Benefits of AI Agents for Businesses
The use of AI agents in your company’s operations can have a number of benefits that have a big impact on your bottom line. Artificial intelligence (AI) agents are changing corporate operations by improving consumer experiences and operational efficiency. Additionally, it improves how companies thrive and compete in the contemporary economy. Building what is an agent in AI is crucial for businesses seeking to harness these benefits.
The following is a more detailed examination of the main advantages of using AI agents in the workplace:
1. Enhanced Effectiveness
Artificial intelligence (AI) agents are particularly good at tackling routine and repetitive activities that need a lot of time and human resources to complete. It covers duties including scheduling, data input, answering client questions, and simple analysis. Businesses can increase overall productivity by reallocating their human resources to more strategic and creative initiatives by automating these operations.
2. Versatile Customization
The capacity of AI agents to offer clients individualized experiences is one of its most notable qualities. By examining client information, preferences, and previous exchanges, AI agents are able to customize replies, recommendations, and services to each user’s specific needs. In the context of AI agents in HR, this degree of customization helps tailor employee interactions, improving satisfaction and engagement. Customers who receive this degree of customization feel understood and appreciated, which increases customer satisfaction and encourages loyalty and repeat business.
3. Smooth and Economical Scalability
AI programs are scalable by nature. They don’t require corresponding improvements in infrastructure or resources to meet a rising amount of jobs or interactions. This scalability is particularly beneficial because the need for resources might rise sharply during peak business seasons, new launches, or market expansions. Moreover, Conversational AI enhances scalability by enabling seamless interactions across various platforms without compromising performance.
4. Higher Availability
AI agents can work continuously without pauses, exhaustion, or downtime, in contrast to human employees. In today’s fast-paced industry, it is essential for organizations to be able to provide continuous service, support, or monitoring, and this is ensured by their 24/7 availability. However, it’s also crucial to implement responsible AI practices to ensure ethical and fair use of these technologies. AI agents are always available, so each time a consumer has a question, it can be quickly answered, enhancing their experience and happiness.
5. Cost Savings
Significant cost reductions can result from the use of AI agents. Businesses may save money on salaries, training costs, and other associated costs by eliminating the need for a big workforce to handle regular activities. Top AI agent development companies can help organizations implement AI agents to find efficiencies and optimize processes, which eventually lowers operating expenses even further.
6. Data-driven Insights
Large amounts of data can be effectively gathered and processed by modern AI agents. Consequently, companies using AI agents may learn important lessons about consumer behavior, industry trends, and operational effectiveness. By using these data, businesses may adjust their plans, make better judgments, and outperform the competition.
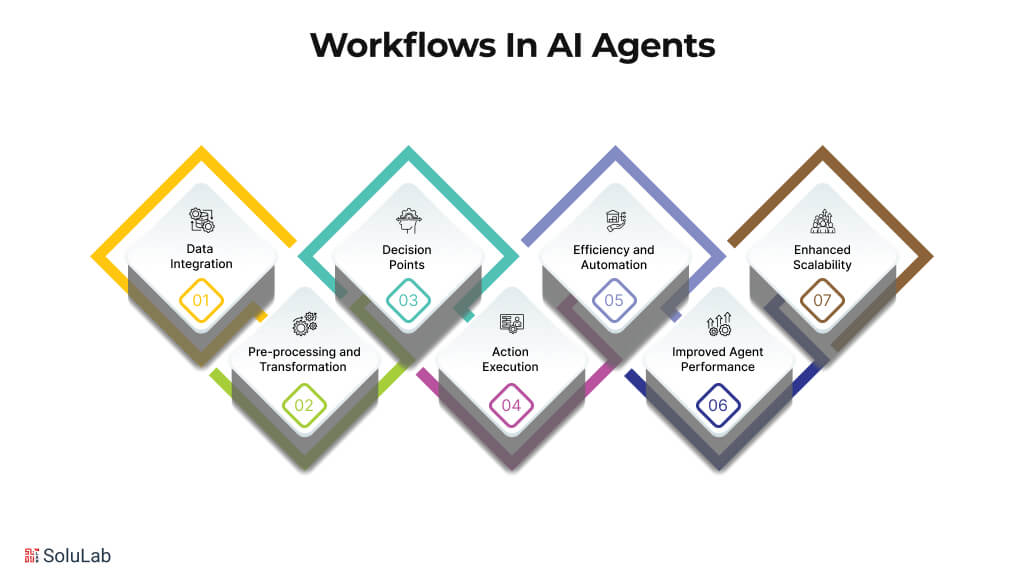
Workflows In AI Agents
Workflows in AI agents refer to the structured processes that outline how agents carry out their tasks. These workflows serve as a roadmap for agents, ensuring that they take the necessary steps to reach their objectives while utilizing their capabilities seamlessly.
Key aspects of AI agent types workflows include:
- Data Integration: Workflows often begin with data integration from diverse sources such as sensor readings, user inputs, historical data, or any other information relevant to the agent’s assignment.
- Pre-processing and Transformation: Raw data may require pre-processing and transformation to make it comprehensible and usable for the agent. This may involve cleaning, filtering, or formatting the data.
- Decision Points: AI agent workflows frequently incorporate decision points where the agent leverages its capabilities to make informed choices.
- Action Execution: Based on the decisions made, the workflow dictates how the agent takes action, which could involve sending control signals to robots or actuators, generating text or recommendations for users, or updating internal models or knowledge bases.
Workflows offer several benefits, including:
- Efficiency and Automation: Workflows streamline processes and enable automation, enhancing the overall efficiency of AI agents.
- Improved Agent Performance: Well-defined workflows contribute to improved agent performance by ensuring that agents operate consistently and effectively.
- Enhanced Scalability: Workflows facilitate scalability by enabling agents to handle increased workloads and adapt to changing environments.
Future Development of AI Agents
AI agents will shift from single-task helpers to coordinated, memory-enabled systems that act across apps and the web. Expect smarter, specialized agents that collaborate, remember context, and run persistently to automate complex workflows.
- Agents will retain memory of past interactions, offering continuity and deeply personalized assistance across sessions.
- Rather than working solo, multiple agents will team up to manage multi-step business processes end to end.
- Advances in infrastructure will drive always-on agents, from cloud to edge devices, enabling real-time responsiveness at scale.
- Standardization and safe protocols will enable smoother, transparent interaction between agents and third-party services.
- Enterprises will adopt domain-specific agents for areas like customer service, IT support, or research, gradually entrusting them with more autonomy.
Conclusion
The growth of AI agents is taking a new turn. With the above information, you might have already understood how and why AI agents are important to your business. To enhance your customer service with chatbots to automate complex tasks, AI agents are opening their wide wings.
If you’re also looking for an AI agent development partner, then Solulab is here to assist you in every stage. We, at SoluLab, an AI development company, customize AI agents as per your business goals and customer requirements. Our team of AI developers is dedicated to seamlessly integrating state-of-the-art AI services into your business offerings, processes, and growth strategies, no matter the industry you’re in.
Contact us today to discuss your plan for AI agent integration in your system.
FAQs
1. How can startups leverage AI agents without heavy infrastructure costs?
Startups can adopt API-first AI agent frameworks or cloud-hosted platforms that handle training, hosting, and scaling, eliminating upfront hardware investments while enabling quick proof-of-concept deployment.
2. What factors influence the total development cost of an AI agent in 2025?
Costs depend on model complexity, training data size, integration depth, and cloud usage. Expect $10K+depending on features, scalability, security, and compliance requirements.
3. How are AI agents expected to evolve in late 2025, according to recent reports?
Recent tech news highlights autonomous “collaborative agents” capable of memory retention and task chaining. Major enterprises are piloting them for R&D automation and customer lifecycle management.
4. Which AI agent architecture suits early-stage startups the most?
Goal-based or model-based agents are ideal; they’re lightweight, data-efficient, and easy to customize. They allow startups to scale intelligently before shifting to full learning or utility-based systems.
5. How can businesses ensure ethical and transparent use of AI agents?
Implement explainable AI frameworks, monitor model decisions, and follow governance standards like ISO/IEC 42001:2025. Transparency reports and periodic audits build stakeholder trust and brand credibility.
6. How can startups get SoluLab expert help to build custom AI agents?
It’s simple to contact SoluLab. All you have to do is fill out the form at the bottom of our AI agent development webpage. After that, our team contacts you to discuss your goals and requirements.







