AI Copilots, equipped with advanced large language models (LLMs), have emerged as transformative virtual assistants, significantly enhancing productivity across various industries. These AI-powered tools simulate natural conversational abilities, assisting users with tasks like research, writing, data analysis, and even proactive issue detection. For example, 2024 has seen a surge in generative AI adoption, with 67% of organizations planning to increase their AI investments in the next three years, primarily to drive efficiency and automate complex workflows. This rise underscores the growing recognition of AI Copilots’ role in reshaping business operations and boosting revenue, especially in sectors like marketing and supply chain management.
The popularity of chat-based AI, as seen with tools like ChatGPT, has set records, positioning AI Copilots as essential components in digital transformation strategies. As per the recent report, businesses are now not only using AI to automate routine tasks but also integrating it into specialized applications, such as real-time data analysis for industrial operations or personalized customer interactions.
Today, in this blog we will look at what is an AI Copilot and all the essential features related to it! So, let’s get started!
Understanding AI Copilot
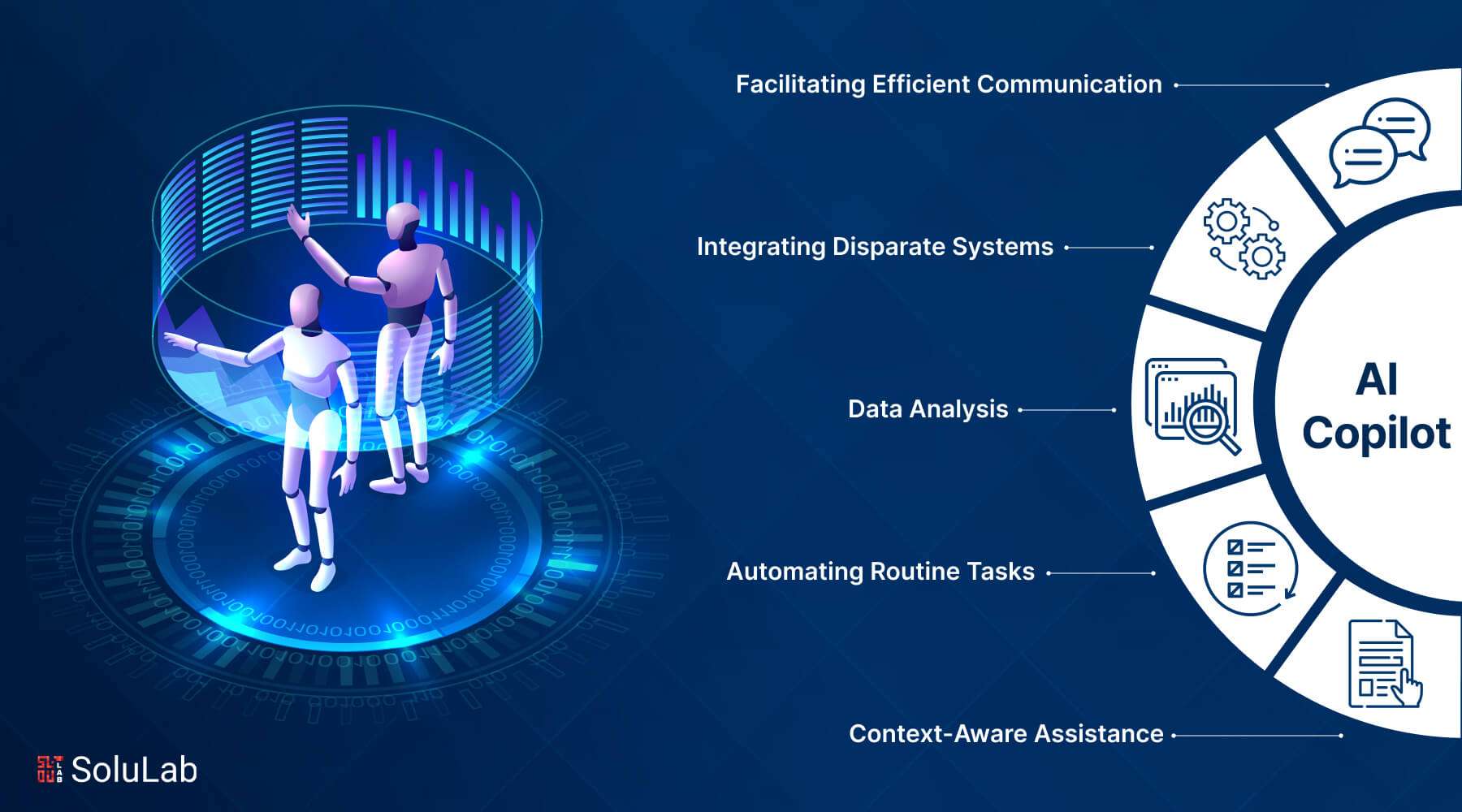
So, you must be wondering what is AI Copilot. AI copilots are essential for increasing efficiency and production since they serve the following functions:
- Context-Aware Assistance: AI copilots can anticipate user demands and react accordingly, guaranteeing pertinent and prompt help throughout crucial decision-making processes.
- Automating Routine Tasks: AI copilots greatly increase overall productivity by freeing users to concentrate on strategic and creative work by managing time-consuming and repetitive duties.
- Data Analysis: AI copilots are fast at processing vast volumes of data, and seeing trends and patterns.
- Facilitating Efficient Communication: In interactions with a range of stakeholders, including staff members, clients, and suppliers, AI copilots simplify communication procedures and cut down on misunderstandings and delays.
- Integrating Disparate Systems: AI copilots may serve as the glue holding together various software programs, platforms, and tools under one roof. This will guarantee data interoperability, accessibility, and integrity throughout the company.
AI copilot elevates the user experience and helps organizations achieve their objectives by streamlining complicated activities and offering insightful direction and assistance. AI copilots can completely change how organizations run and compete in the years to come as they continue to develop with better capabilities and deeper integration with corporate ecosystems.
What is an Enterprise AI Copilot and Why is it Necessary?
An enterprise AI copilot is a conversational interface that flows easily between all of your company’s systems and your personnel. It is based on hundreds of machine-learning models that have been adjusted to fit your business’s data. Your corporate copilot, is available on all platforms and multilingual in over 100 languages, making it simpler than ever for your staff to complete tasks.
Employees typically have to navigate and manage a variety of systems as firms become more sophisticated and dependent on a wide range of technological solutions. Cross-system communication issues are frequently not adequately resolved by traditional, isolated solutions, which can result in decreased productivity and inefficiencies. The solution to overcoming these obstacles is a corporate AI copilot.
The integration of corporate systems under a unified conversational interface facilitates information access and job completion for employees. The copilot AI copilot streamlines teamwork, facilitating employees’ success in their roles and greatly increasing total output.
How Does AI Copilot Work?
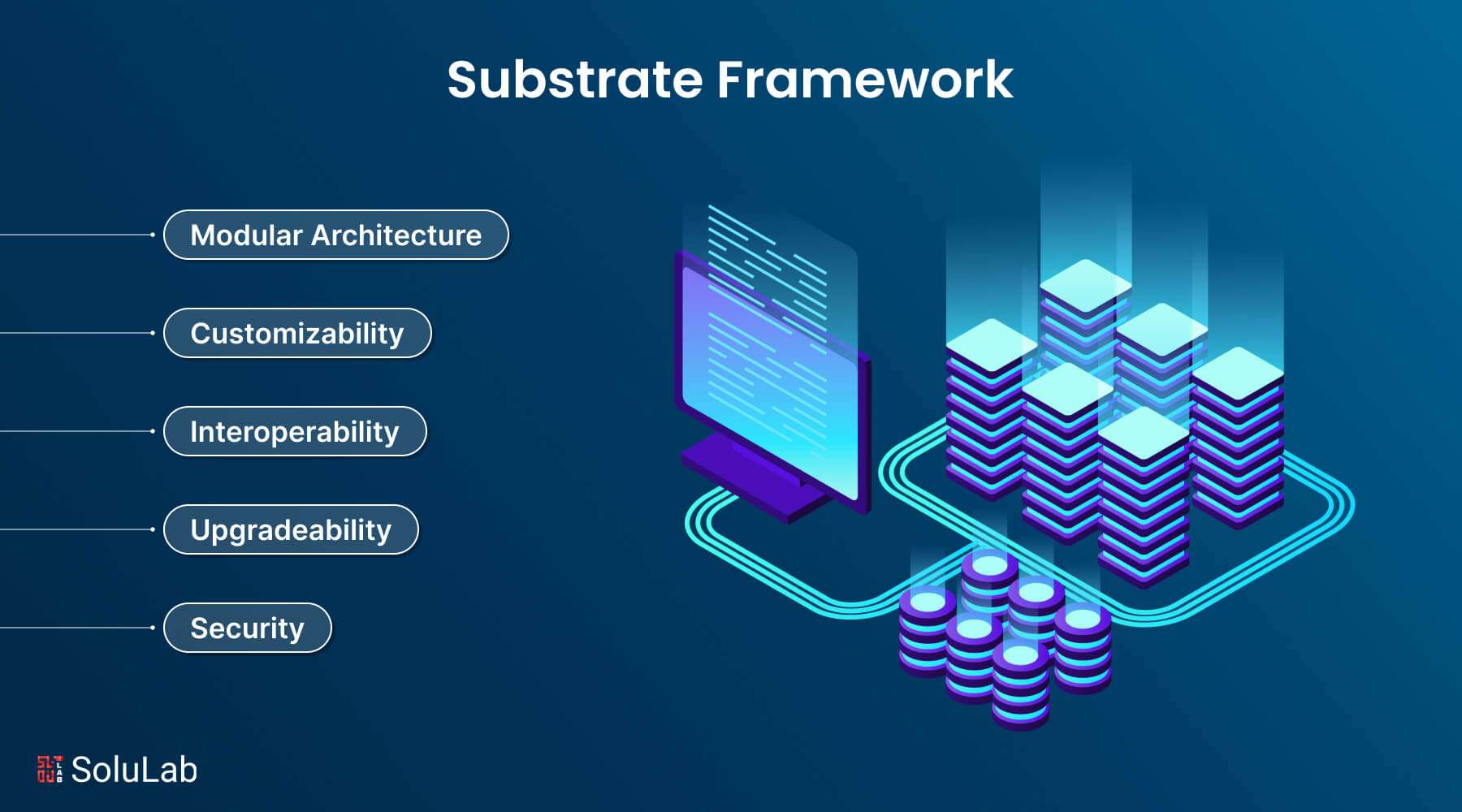
The two key components of artificial intelligence and system integrations provide the solid foundation of AI copilots.
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies used in machine learning, context awareness, and natural language processing allow copilots to know what a user wants and make well-informed recommendations. AI copilots may interface with a wide variety of devices through integrations, resulting in a single, networked platform for smooth job management and communication.
The four-tiered AI copilot strategy framework should be noted to comprehend the advantages and disadvantages of this approach to learning about AI copilots.
- Tier-one: Basic API calls to LLMs are the cornerstone of Tier-one AI copilots’ AI architecture. Low entrance barriers and a simple lift are made possible by this. These copilots provide a wealth of broad information, but their lack of domain-specific expertise may cause hallucinations.
- Tier-two: A tailored implementation of an optimized LLM based on an organization’s data is what Tier-two AI copilots entail. Although this is a little more expensive, the results are better for security and privacy and are more tailored to the company. Because they rely on the outputs of a single LLM, they can only achieve limited performance and are restricted to one-step use cases.
- Tier-three: To create complicated pipelines tailored for multi-step use cases, Tier-three AI copilots connect many LLMs, utilizing each LLM’s unique strengths and capabilities. Tier-three AI copilots are thus better equipped to handle problems in more complex domains, solve a wider range of use cases, and increase productivity and efficiency.
- Tier-four: The issues of enabling autonomous decision-making and extending staff support are tackled by tier-four AI copilots. These tier-four copilots have advanced LLM development systems that are particularly made for enterprise-wide deployment. They include premium features like analytics, security, privacy, and a reasoning engine in addition to custom connections that meet the specific needs of big businesses.
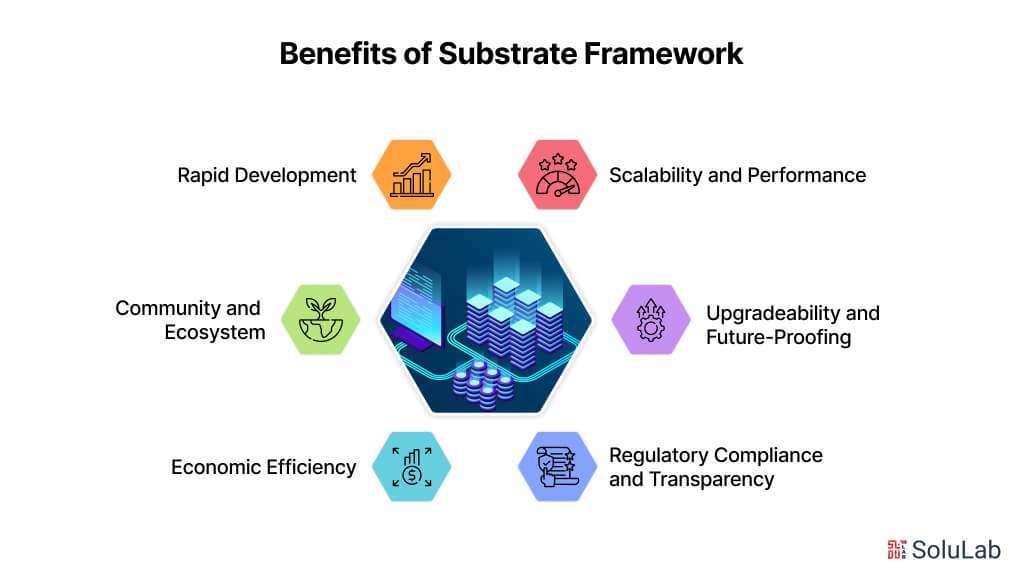
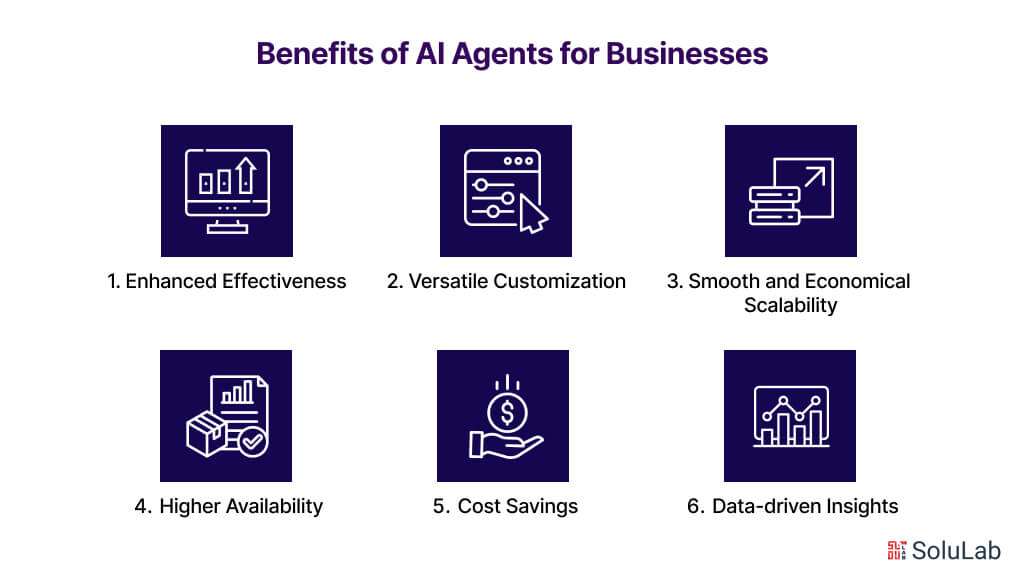
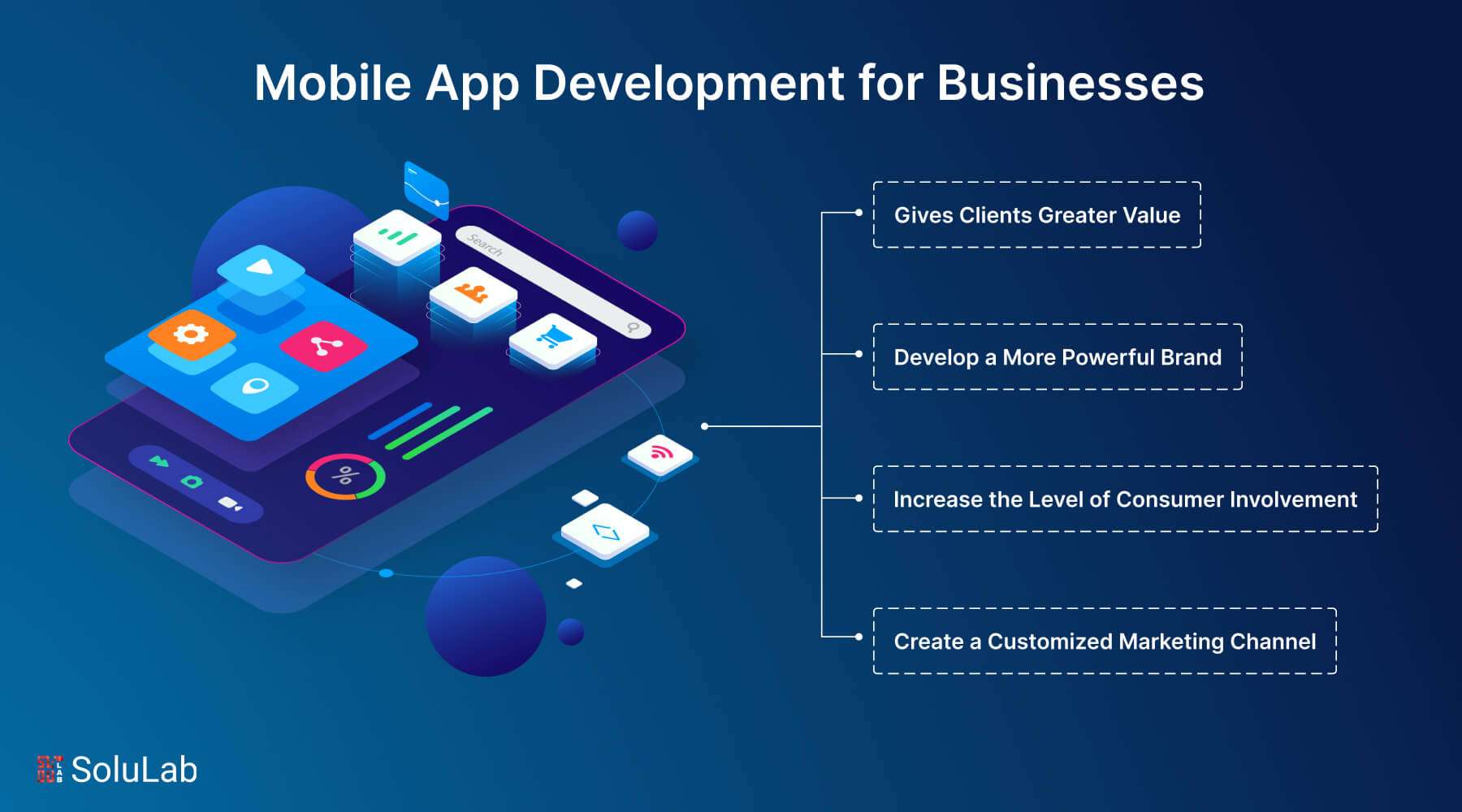
Benefits of AI Copilot for Businesses
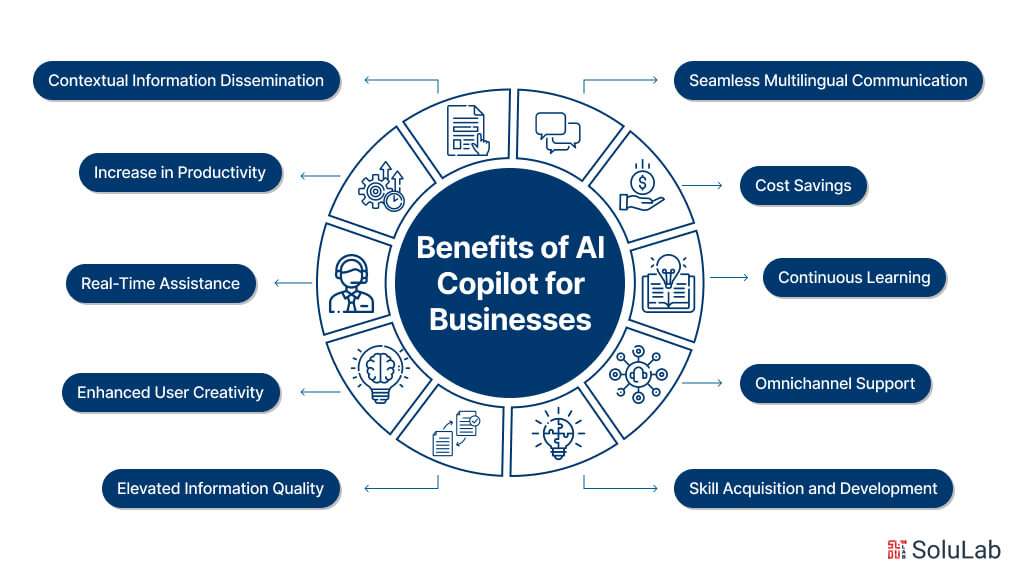
AI copilots leverage artificial intelligence and seamless integrations to anticipate user needs and deliver timely, relevant, and proactive suggestions, revolutionizing various aspects of business operations including customer service, e-commerce, and lead generation. Here are several ways in which AI-powered copilots provide value to businesses:
1. Increase in Productivity: AI copilots anticipate user needs and suggest actions to streamline workflows and boost productivity. By integrating with popular enterprise applications, they automate mundane tasks, freeing up human resources to focus on more strategic initiatives.
2. Cost Savings: By automating repetitive tasks, AI copilots help reduce operational expenses, allowing businesses to invest in innovative solutions that enhance overall efficiency and competitiveness.
3. Contextual Information Dissemination: Leveraging AI and machine learning, copilots provide context-aware suggestions and solutions tailored to the enterprise, reducing time spent on research and ensuring accurate responses.
4. Continuous Learning: AI copilots continuously learn and adapt to changing enterprise needs, improving over time and becoming more effective in various tasks and decision-making processes.
5. Real-Time Assistance: Providing immediate, context-aware support, AI copilots enhance employee productivity and optimize business operations by offering timely assistance and automated issue resolution.
6. Omnichannel Support: AI copilots facilitate seamless conversational interfaces across multiple channels, ensuring uninterrupted interaction for customers and employees across various platforms.
7. Seamless Multilingual Communication: With built-in multilingual capabilities, AI copilots enable businesses to provide superior support to diverse users across the globe, enhancing the overall customer and employee experience.
8. Enhanced User Creativity: AI copilots empower users to resolve tasks, troubleshoot, and communicate in human-like conversations, fostering creativity and enriching work products.
9. Elevated Information Quality: By ensuring response accuracy and relevance through contextual understanding and access to enterprise-specific data sets, AI copilots enhance the quality of information delivered to users.
10. Skill Acquisition and Development: Through AI assistance, copilots help users acquire and up-level their skills, enabling them to excel in their current roles and explore new areas of learning and development.
Best Practices for Selecting AI Copilots
When choosing an AI copilot, it’s essential to consider several factors to ensure seamless implementation and optimal performance. Here are some key aspects to keep in mind:
1. Enterprise Context: Ensure that the AI copilot can understand and utilize your company-specific data to provide accurate and relevant interactions tailored to your organization’s needs.
2. Data Security and Compliance: Prioritize platforms that adhere to strict security, compliance, and privacy standards, safeguarding sensitive data at individual, group, and tenant levels.
3. Scalability and Integrations: Select an AI copilot capable of integrating with multiple applications and scaling alongside your business, offering a flexible and robust solution that can grow with your organization.
4. Learning Capability: Choose an AI copilot with the ability to continuously learn and adapt its skill set to evolving organizational and industry requirements, ensuring long-term relevance and effectiveness.
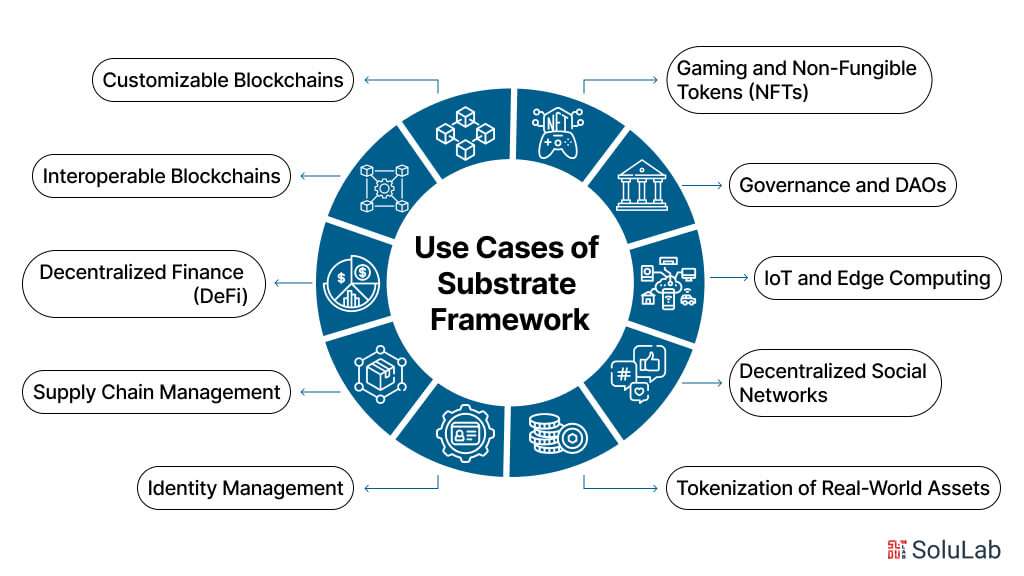
AI Copilot Use Cases
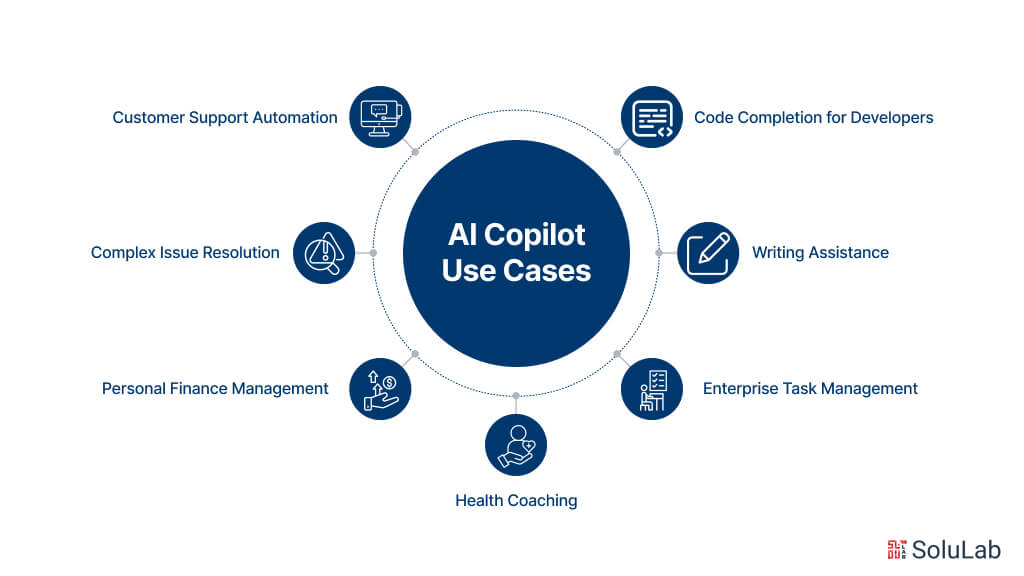
AI Copilots are revolutionary for increasing output and resolving issues. For jobs that would normally require a significant investment of time and resources, they offer immediate assistance. These use cases include solving complicated problems using past data, helping account representatives with routine inquiries in real-time, and generating prompt answers to often requested questions.
There is almost no end to the efficiency and cost reductions across retail and e-commerce, insurance, healthcare, telecom & utilities, hotel & travel, banking & finance. Here are some of the use cases of AI Copilot:
- Customer Support Automation: AI Copilots can automate responses to frequently asked questions, reducing the workload on customer support representatives and improving response times for customers.
- Complex Issue Resolution: Leveraging historical data and machine learning algorithms, AI Copilots can help in solving complex issues efficiently, drawing insights from past experiences to find optimal solutions.
- Code Completion for Developers: AI-powered algorithms aid software developers in coding by predicting code snippets based on context, reducing errors and enhancing productivity.
- Writing Assistance: Copilots like Jasper, Writer, and OpenAI’s ChatGPT offer real-time support in refining grammar, punctuation, style, and clarity, improving writing quality and efficiency.
- Personal Finance Management: AI Copilots provide budgeting insights, expense tracking, investment recommendations, and customized financial advice, assisting individuals in managing their finances effectively.
- Health Coaching: AI health coaches assist individuals in optimizing fitness, training, and nutrition plans, helping them achieve their health and wellness goals efficiently.
- Enterprise Task Management: Enterprise-grade Copilots from companies like Salesforce, Microsoft, and ServiceNow streamline operations by assisting employees in collaboration, task management, and productivity enhancement across diverse systems and processes.
Understanding the Differences: AI Copilots vs. AI Chatbots vs. Virtual Agents
Distinguishing between AI copilots, AI chatbots, and virtual agents is crucial to grasp the distinct benefits they offer. Although they all harness artificial intelligence, their roles, capabilities, and approaches to user interactions differ significantly.
AI Copilots
AI copilots are sophisticated systems designed to assist users constantly, offering personalized guidance and support across various tasks. They adapt to user behavior, providing contextually relevant suggestions throughout complex operations. Examples include code completion tools, virtual writing assistants, and integrations with enterprise systems.
AI Chatbots
AI chatbots engage users in text-based or voice-based conversations using natural language processing and machine learning algorithms. While simpler than AI copilots, they handle a variety of customer requests, primarily facilitating interactions, answering FAQs, and providing support in areas like customer service and e-commerce. Some chatbots may be pre-programmed for specific scenarios with limited learning capabilities.
Virtual Agents
Virtual agents utilize programmed rules and conversational AI to offer basic services or assistance. They represent a broader category of online services, encompassing chatbots, voice bots, and interactive voice response systems. While chatbots are a specific type of virtual assistant designed for text-based communication, virtual agents can communicate through various mediums, including voice response over the phone. They find applications in customer support, sales, and technical assistance across diverse domains.
While the terms AI copilots, AI chatbots, and virtual agents are often used interchangeably, it’s important to recognize their distinctions. Each offers different levels of functionality and sophistication. To select the right tool for your business, consider your operational needs, the level of user assistance required, and the ability to learn and adapt to your organization’s context.
The Future Outlook for AI Copilots
As AI copilots advance and refine, the synergy between humans and machines will reach new heights, resulting in heightened productivity and superior problem-solving abilities.
With their ability to seamlessly integrate with various enterprise systems and provide contextually relevant assistance, AI copilots emerge as invaluable assets in today’s dynamic business world.
Before implementing an AI copilot, it’s crucial to grasp its unique attributes, understand its potential impact on operations, and differentiate it from other AI-driven solutions like chatbots and virtual agents.
Ultimately, the successful adoption of AI copilots hinges on selecting a platform that meets the organization’s specific needs while prioritizing robust security, scalability, and continuous learning capabilities.
Choosing the right AI copilot empowers organizations to drive growth, streamline operations, and enhance the overall experience for both employees and customers.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, the emergence of AI copilots represents a pivotal step towards enhancing productivity and problem-solving across various industries. By seamlessly integrating with existing systems and offering personalized assistance, these intelligent systems bridge the gap between humans and machines, paving the way for smoother operations and improved decision-making. As organizations navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape, the adoption of AI copilots promises to unlock new levels of efficiency and innovation, ultimately driving growth and success in the digital era.
Looking to utilize the power of AI copilots for your organization? SoluLab stands ready to assist as a leading AI copilot development company. With our expertise in AI technologies and custom development solutions, we help businesses unlock the full potential of AI copilots to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and deliver unparalleled customer experiences. Contact us today to explore how we can tailor AI copilot solutions to meet your specific needs and propel your business forward.
FAQs
1. What exactly is an AI copilot?
An AI copilot is an advanced artificial intelligence system designed to work alongside users, providing constant guidance and personalized assistance in achieving various tasks. It learns from user behaviors, adapts to their needs, and offers contextually relevant suggestions throughout complex operations.
2. How does an AI copilot differ from other AI-driven solutions like chatbots?
While both AI copilots and chatbots utilize artificial intelligence, they serve different purposes and have distinct functionalities. AI copilots are sophisticated systems that provide continuous guidance and assistance, often integrating with enterprise systems to offer contextually relevant support. In contrast, chatbots primarily engage in text-based or voice-based conversations, handling a variety of customer requests and facilitating interactions.
3. What are some examples of AI copilot applications?
AI copilot applications span various industries and functions. They include code completion tools for software developers, virtual writing assistants for content creation, and integrations with enterprise systems to streamline operations. Additionally, AI copilots can assist in personal finance management, health coaching, and more.
4. How can an AI copilot benefit businesses?
AI copilots offer several benefits to businesses, including enhanced productivity, improved decision-making, and streamlined operations. By providing personalized assistance and automating routine tasks, they help organizations achieve greater efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver superior customer experiences.
5. What should businesses consider when implementing an AI copilot?
When implementing an AI copilot, businesses should consider factors such as data security and compliance, scalability and integrations, and the platform’s learning capabilities. It’s essential to choose a solution that aligns with the organization’s specific needs and prioritizes robust security, scalability, and continuous learning to maximize the benefits of AI copilot technology.