Contracts are the linchpin of our professional and personal spheres, serving as the backbone of modern society. They govern myriad aspects of our lives, ensuring order and reliability. Smart Contracts in blockchain emerge as indispensable contributors, playing a pivotal role in elevating the safety and security of transactions. Beyond their fundamental function of facilitating organized exchanges, Smart Contracts extend their impact to enhance the accessibility of applications running on these platforms. Their role transcends transactional facilitation, becoming a cornerstone for a more secure and streamlined digital landscape.
Smart Contracts function as digital agreements that automatically execute and enforce the terms encoded within their code. This automated execution not only eliminates the need for intermediaries but also introduces a new era of trust in transactions, as every step is securely recorded on the blockchain. In this blog, we will delve into the intricacies of Smart Contracts, unraveling their workings, exploring their benefits, and examining real-world applications. From the foundational components that make these contracts possible to the challenges they face and the promising trends that lie on the horizon, this exploration aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the pivotal role Smart Contracts play in shaping the future of blockchain development.
So, let’s get started!
Evolution of Smart Contracts in Blockchain
The inception of smart contracts on blockchain marked a paradigm shift in the way we conceptualize and execute agreements. To trace the evolution, we need to journey back to the introduction of blockchain technology itself. Originally designed as the underlying infrastructure for digital currencies, blockchain laid the groundwork for a decentralized and transparent ledger system. However, it was with the advent of smart contracts that this technology truly came into its own.
The year 2013 saw the introduction of Ethereum, a groundbreaking blockchain platforms that introduced a revolutionary concept – the ability to execute smart contracts on blockchain. Ethereum’s founder, Vitalik Buterin, envisioned a platform that could go beyond simple currency transactions. By integrating a Turing-complete programming language into its blockchain, Ethereum enabled the creation and execution of smart contracts. This watershed moment marked the evolution of blockchain technology from a singular focus on financial transactions to a broader spectrum of decentralized applications (DApps) powered by self-executing code.
The subsequent years witnessed a rapid proliferation of platforms dedicated to hosting smart contracts on the blockchain, each with its unique features and capabilities. This diversification fueled innovation and experimentation, expanding the use cases for smart contracts beyond simple transactions. The evolution of these contracts on the blockchain reflects not only advancements in technology but also a growing recognition of their transformative potential across various industries, from finance to supply chain management and beyond.
Importance of Smart Contracts in Decentralized Systems
In the realm of blockchain technology, the importance of smart contracts in decentralized systems cannot be overstated. At the core of decentralized systems lies the fundamental principle of eliminating intermediaries and fostering peer-to-peer interactions. Smart contracts emerge as a linchpin in realizing this vision, facilitating trustless and automated transactions without the need for traditional intermediaries.
One key facet underscoring the significance of smart contracts in decentralized systems is the enhancement of transparency. The inherent immutability of the blockchain ensures that once a smart contract is deployed, its code and the resulting transactions are permanently recorded and visible to all network participants. This transparency not only fosters trust but also serves as a powerful tool in mitigating fraud and corruption, key challenges that traditional centralized systems often grapple with.
Beyond transparency, the decentralized nature of smart contracts contributes to a more resilient and secure system. Unlike centralized models, where a single point of failure can compromise the entire system, smart contracts on decentralized blockchains distribute their execution across a network of nodes. This decentralized architecture not only enhances security by reducing vulnerabilities but also ensures the continuous operation of the system even in the face of individual node failures or malicious attacks. In essence, the importance of smart contracts in decentralized systems lies in their ability to catalyze a shift towards more transparent, secure, and resilient digital ecosystems.
How Do Smart Contracts Work in Blockchain Development?
Beyond their foundational workings, smart contracts in blockchain technology bring about a revolutionary shift in the dynamics of digital interactions. The self-executing and automated nature of these contracts not only streamlines processes but fundamentally transforms the way agreements are made and executed. This transformation extends beyond mere transactional efficiency to encompass a paradigm where trust is established not through intermediaries but through the immutable logic of code.
In a world increasingly reliant on digital transactions, the precision, and reliability of smart contracts in blockchain contribute to a landscape where parties can engage in agreements with a heightened sense of security and efficiency. The removal of intermediaries reduces costs, minimizes the risk of human error, and accelerates the pace at which transactions are conducted. As we delve deeper into the key components of smart contracts, their role becomes clearer in providing a secure and transparent framework for a multitude of applications, ranging from financial transactions to supply chain management and beyond. The intersection of code execution, automation, and decentralized ledger technology marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of contractual agreements and sets the stage for a more efficient and trustworthy digital future.
Now, let us look at how smart contracts work!
-
Code Execution and Automation
At the heart of smart contracts in blockchain technology lies the concept of code execution and automation. Unlike traditional contracts that rely on human interpretation and enforcement, smart contracts operate on self-executing code. These digital agreements are programmed to execute predefined actions automatically when specific conditions are met. The blockchain, acting as a decentralized and tamper-resistant ledger, ensures that the code’s execution is transparent and verifiable by all participants. This automation not only streamlines processes but also reduces the risk of errors and disputes that may arise from manual execution.
-
Self-executing Contracts
The self-executing nature of smart contracts in blockchain is a game-changer in terms of efficiency and reliability. Once deployed to the blockchain, a smart contract can autonomously execute its coded instructions without the need for intermediaries. This not only removes the delays associated with traditional contract enforcement but also significantly reduces the costs incurred in engaging third parties. The automated execution is triggered by the fulfillment of predefined conditions, providing a trustless and secure framework for the parties involved in the transaction.
Key Components of Smart Contracts
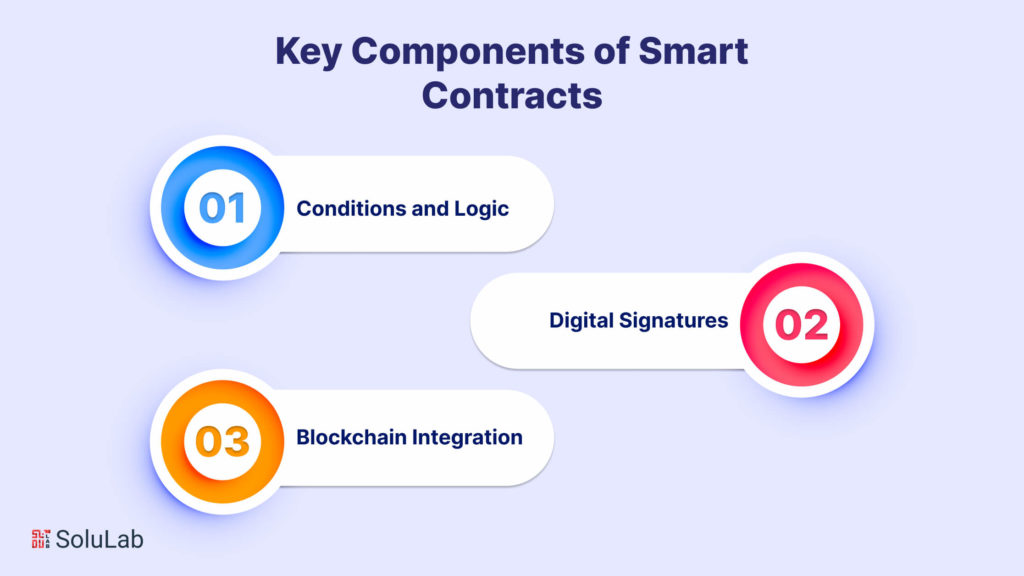
In addition to their precise conditions and logic, the incorporation of digital signatures stands as a robust layer of security within blockchain in smart contracts. These cryptographic signatures not only authenticate the identity and intent of participants but also fortify the integrity of the transaction. Moreover, the seamless integration of smart contracts with blockchain technology ensures that every step of the contractual process is indelibly recorded on the decentralized ledger, fostering transparency and trust. This harmonious fusion of conditions, digital signatures, and blockchain integration underscores the resilience and efficacy of smart contracts, making them an indispensable tool for a diverse array of decentralized applications and industries.
-
Conditions and Logic
The effectiveness of smart contracts in blockchain is contingent upon the meticulous definition of conditions and logic within their code. These conditions serve as the “if-then” statements, dictating the actions the contract will automatically take when specific criteria are met. The precision in coding conditions and logic is paramount to ensuring the contract operates as intended. Whether it’s releasing funds upon the completion of a task or transferring ownership of a digital asset, the clarity and accuracy of these conditions are vital for the success of the smart contract.
-
Digital Signatures
Security is paramount concerning blockchain in smart contracts. Digital signatures play a pivotal role in ensuring the authenticity and integrity of the contracting parties. Each participant in a smart contract is required to provide a digital signature, which is cryptographic proof of their identity and intent. These digital signatures not only secure the transaction but also serve as an immutable record on the blockchain, providing an auditable trail of actions taken within the contract.
-
Blockchain Integration
The integration of smart contracts in blockchain is a symbiotic relationship. The blockchain serves as the decentralized and distributed ledger that records every transaction and contract execution. This integration ensures that the code, conditions, and outcomes of smart contracts are transparently stored on the blockchain, creating an immutable record accessible to all network participants. The decentralized nature of the blockchain enhances the security and trustworthiness of smart contracts, making them a cornerstone of decentralized applications and systems.
Benefits of Smart Contracts in Blockchain Development
The transformative impact of smart contracts is underscored by a cascade of benefits that redefine the fabric of digital transactions. Offering a bedrock of transparency and security, these contracts leverage the decentralized nature of blockchain to create an unalterable record of transactions. Efficiency and automation, their second hallmark, propel transactions at unprecedented speeds by eliminating intermediaries and automating processes, leading to tangible time savings and reduced operational costs. Crucially, the trust and decentralization they instill revolutionize the dynamics of digital interactions, shifting reliance from intermediaries to code execution and fostering a more equitable ecosystem. The economic benefits, encapsulated in the reduction of costs and time, position smart contracts as a pivotal force reshaping how we conceptualize agreements, catalyzing a future where efficiency, transparency, trust, and financial savings converge seamlessly in the digital realm.
-
Transparency and Security
The foremost among the myriad benefits of smart contracts is their inherent capacity to enhance transparency and security. Operating on the decentralized architecture of blockchain technology, smart contracts ensure that every transaction and contractual execution is permanently recorded and visible to all participants. This transparency not only establishes trust by providing an immutable and auditable record but also acts as a potent deterrent against fraudulent activities. The cryptographic nature of the blockchain ensures that the information within smart contracts is secure, reducing the risks associated with tampering or unauthorized access.
-
Efficiency and Automation
The efficiency gains afforded by smart contracts are monumental, ushering in a new era of streamlined and automated processes. Traditional contract execution often involves multiple intermediaries, leading to delays and increased costs. Smart contracts, however, operate on self-executing code, expediting the entire process. Once predefined conditions are met, these contracts autonomously execute, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the potential for errors. This not only accelerates the pace of transactions but also minimizes the administrative burden, freeing resources for more strategic pursuits.
-
Trust and Decentralization
At the core of the benefits of smart contracts lies the transformation of trust dynamics in digital interactions. By eliminating the need for intermediaries, smart contracts operate in a trustless environment where the execution of agreements is governed by code rather than subjective interpretation. The decentralized nature of these contracts ensures that no single entity has control, mitigating the risk of manipulation or bias. This decentralized trust model empowers participants with a greater degree of confidence in their digital engagements, fostering a more equitable and trustworthy ecosystem.
-
Cost Reduction and Time Savings
Smart contracts contribute significantly to the bottom line by facilitating substantial cost reduction and time savings. The removal of intermediaries, coupled with the automation of processes, leads to operational efficiencies and cost-effectiveness. Parties involved in transactions benefit from reduced fees associated with intermediaries, while the automated execution of contractual terms accelerates the overall process. The efficiency gains translate directly into tangible time savings, enabling businesses to allocate resources more strategically and respond swiftly to market demands. In a landscape where time is money, the cost-effectiveness and time-saving attributes emerge as pivotal benefits of smart contracts.
Use Cases of Smart Contracts
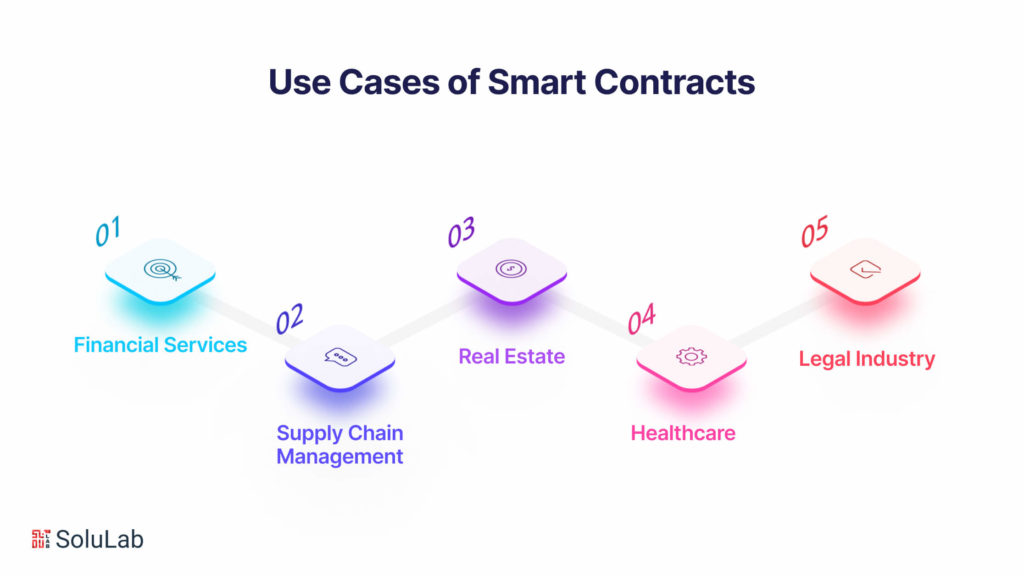
Smart contracts, nestled within the framework of blockchain technology, have proven to be dynamic tools with versatile applications across various industries. In financial services, they expedite transactions in banking and payments while streamlining insurance claims through automated payout processes. Supply chain management benefits from enhanced traceability, reducing discrepancies in the movement of goods. Real estate transactions become more secure and transparent with automated contract execution. In healthcare, smart contracts facilitate the secure and compliant sharing of patient data, and the legal industry witnesses increased efficiency as routine processes are automated, expediting legal proceedings. The pervasive application of smart contracts in blockchain exemplifies their transformative impact, ushering in a new era of efficiency, security, and transparency.
In this section, we will delve into the smart contract use cases in more detail!
-
Financial Services
Smart contracts redefine the landscape of financial transactions by streamlining banking processes and expediting payments. From automated fund transfers to seamless loan disbursements, these contracts eliminate intermediaries, ensuring secure and efficient financial transactions. In the insurance sector, smart contracts automate claims processing and policy execution. When predefined conditions are met, such as in the case of an insurable event, the contract autonomously triggers payouts, reducing administrative overhead and enhancing the speed of settlements.
-
Supply Chain Management
Smart contracts revolutionize supply chain management by enhancing transparency and traceability. These contracts automate and authenticate each stage of the supply chain, from manufacturing to distribution, reducing errors and ensuring a tamper-proof record of the product’s journey.
-
Real Estate
In the real estate industry, smart contracts simplify and secure property transactions. These contracts automate the execution of agreements, ensuring that funds are transferred only upon meeting specified conditions. This not only expedites the buying and selling process but also minimizes the risk of fraud.
-
Healthcare
Smart contracts in healthcare facilitate secure and interoperable sharing of patient data. With patient consent encoded in the contract, healthcare providers can access relevant information, ensuring data privacy compliance and fostering a more efficient and collaborative healthcare ecosystem.
-
Legal Industry
The legal industry undergoes a transformation with the application of smart contracts. Routine legal processes, such as contract execution and validation, are automated, reducing the time and resources required for legal proceedings. Smart contracts bring efficiency and transparency to the legal landscape, enabling faster resolution of disputes and contracts.
These diverse use cases exemplify the versatility and transformative potential of smart contracts across industries. By automating processes, enhancing security, and fostering transparency, smart contracts continue to redefine the way business is conducted in various sectors, paving the way for a more efficient and decentralized future.
Popular Smart Contract Platforms
As the demand for decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts continues to rise, several blockchain platforms have emerged as pioneers in providing robust smart contract functionalities. Ethereum stands as a trailblazer, offering a versatile platform for decentralized applications. Utilizing the Solidity programming language, Ethereum’s smart contracts power a wide array of applications and digital assets. Noteworthy are the ERC-20 and ERC-721 standards, defining fungible and non-fungible tokens respectively, and contributing to the explosion of the decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible token (NFT) ecosystems. Binance Smart Chain, introduced by the Binance exchange, is gaining traction for its compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and cost-effectiveness. Cardano distinguishes itself with a focus on scalability, sustainability, and interoperability, aiming to provide a secure and scalable environment for smart contract deployment. Polkadot, with its unique approach to interoperability, connects multiple blockchains, allowing for seamless data and asset transfer between different networks. As we explore these platforms, it becomes evident that the choice of a smart contract platforms plays a crucial role in shaping the capabilities and reach of decentralized applications.
Following the introduction to these platforms, it’s essential to delve into the unique features and capabilities of each, showcasing how they contribute to the broader landscape of smart contract development.
1. Ethereum
- Ethereum Smart Contract Language (Solidity):
Ethereum’s success in the smart contract space is largely attributed to the Solidity programming language. This high-level language is designed explicitly for writing smart contracts, providing developers with a familiar and powerful toolset.
- ERC-20 and ERC-721 Standards:
The introduction of Ethereum’s token standards, specifically ERC-20 for fungible tokens and ERC-721 for non-fungible tokens, has been instrumental in the creation and standardization of tokens on the blockchain. These standards have played a pivotal role in the explosive growth of the decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible token (NFT) ecosystems.
-
Binance Smart Chain
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) has emerged as a formidable contender in the smart contract landscape, offering a parallel blockchain to Binance Chain with enhanced functionality. Its compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) has proven advantageous, as developers can seamlessly migrate decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts from Ethereum to BSC, capitalizing on its faster transaction speeds and lower fees. Binance Smart Chain’s consensus algorithm, a variant of Proof of Stake known as Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), contributes to its efficiency and lower energy consumption compared to some other platforms. The native BNB token plays a pivotal role in facilitating transactions, staking, and participating in the platform’s decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, showcasing the multifaceted nature of the Binance Smart Chain in the decentralized landscape.
-
Cardano
Cardano often hailed for its academic rigor and commitment to scalability, sustainability, and interoperability, positions itself as a unique smart contract platform. Utilizing the Haskell programming language, Cardano’s smart contracts are designed with a focus on security and reliability. The platform introduces the concept of “layers” in its architecture, allowing for future upgrades without disrupting existing functionalities. Cardano’s consensus algorithm, Ouroboros, aims to provide a secure and scalable environment for smart contract deployment. As the platform evolves, Cardano seeks to bring financial services to the unbanked and underserved populations, emphasizing a more inclusive and equitable approach to decentralized finance (DeFi) and smart contract deployment.
-
Polkadot
Polkadot takes a novel approach to smart contracts by focusing on interoperability between multiple blockchains. Founded by Ethereum co-founder Dr. Gavin Wood, Polkadot allows different blockchains to transfer messages and assets in a trust-free fashion. Its relay chain acts as a bridge connecting different blockchains, fostering a more interconnected and collaborative decentralized ecosystem. Polkadot’s unique design enables specialized blockchains, known as parachains, to operate independently while still benefiting from the security and shared features of the overall network. This innovative approach positions Polkadot as a promising solution for scalability and collaboration in the smart contract space.
Future Trends and Innovations in Blockchain Development
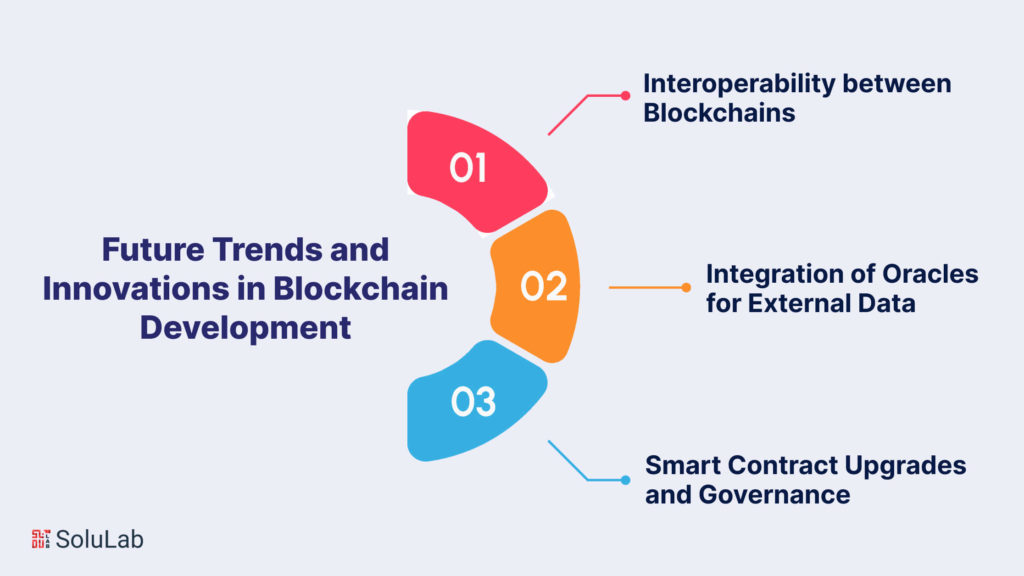
The future of smart contracts on blockchain is characterized by a transformative trajectory, ushering in an era of heightened connectivity and adaptability. As blockchain development matures, the integration of sophisticated smart contract upgrades, cross-chain interoperability, and decentralized governance models emerges as a visionary roadmap, promising to redefine the very fabric of decentralized applications. These trends underscore a relentless pursuit of innovation within the smart contract space, laying the groundwork for a more interconnected, resilient, and community-driven blockchain landscape.
-
Interoperability between Blockchains
Interoperability stands as a pivotal trend, addressing the current challenge of isolated blockchain networks. The future holds the promise of seamless communication and collaboration between diverse blockchains. Initiatives like Polkadot, Cosmos, and interoperability protocols aim to create a connected ecosystem, enabling assets and information to move freely across different blockchain networks. This interoperability not only enhances the overall efficiency of decentralized applications but also fosters a more interconnected and collaborative blockchain landscape.
-
Integration of Oracles for External Data
As smart contracts expand beyond their initial applications, integrating external data becomes increasingly crucial. Oracles, mechanisms that provide smart contracts with real-world data, are emerging as a key innovation. Future smart contracts are likely to leverage oracles for a more comprehensive range of applications, including decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and insurance. This integration ensures that smart contracts can respond to real-world events and conditions, making them more versatile and applicable to a broader spectrum of use cases.
-
Smart Contract Upgrades and Governance
The ability to upgrade smart contracts post-deployment is becoming a critical focus for blockchain developers. Innovations in smart contract governance models are expected to facilitate transparent and democratic decision-making processes regarding contract upgrades. Projects like DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations) are pioneering community-driven governance structures, allowing token holders to have a direct say in the evolution of smart contracts. This shift towards decentralized governance ensures that smart contracts can adapt to changing needs and technological advancements without compromising their integrity.
As we look ahead, these trends and innovations in interoperability, data integration, and governance are poised to drive the next wave of advancements in smart contract technology. The future promises a more interconnected, versatile, and community-driven ecosystem that harnesses the full potential of decentralized applications.
Final Words
In conclusion, the trajectory of smart contracts in blockchain technology is nothing short of revolutionary, paving the way for a decentralized future characterized by transparency, efficiency, and innovation. The identified trends such as interoperability, oracle integration, and decentralized governance stand as pillars guiding the evolution of smart contracts, offering a glimpse into the profound transformations awaiting the decentralized applications landscape. As these technologies mature, the potential applications of smart contracts across diverse industries, from finance and supply chain to healthcare and real estate, will continue to expand, further solidifying their position as a cornerstone of the blockchain ecosystem.
As we navigate this dynamic landscape, SoluLab emerges as a beacon of expertise and innovation in smart contracts on blockchain development. Leveraging a wealth of experience and a dedicated team of blockchain developers, SoluLab is committed to ushering in the future of decentralized applications. Whether it’s harnessing the power of Ethereum’s Solidity programming language, exploring interoperability with platforms like Binance Smart Chain, or crafting customized smart contract solutions, SoluLab stands at the forefront of blockchain innovation. Empowering businesses with tailored smart contract development services, SoluLab ensures that clients not only stay abreast of the latest trends but also carve their paths in the ever-evolving blockchain ecosystem protocols.
Embark on your journey into the world of decentralized applications with SoluLab, where innovation meets expertise. Contact us today to explore how our solutions can elevate your business in the era of smart contracts on the blockchain.
FAQs
1. What are smart contracts, and how do they work in blockchain development?
Smart contracts constitute self-executing digital contracts that are powered by blockchain technology. They automate and enforce the terms of a contract through code, ensuring transparent and tamper-proof execution of predefined conditions. Once deployed on a blockchain, these contracts automatically execute when specific conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries and enhancing the efficiency and security of transactions.
2. What are the key benefits of implementing smart contracts in various industries?
Implementing smart contracts brings numerous benefits, including transparency and security through blockchain’s decentralized nature, efficiency and automation by eliminating intermediaries, trust and decentralization through code execution, and significant cost reduction and time savings. Industries such as finance, supply chain, real estate, healthcare, and legal services can leverage these benefits to streamline processes and enhance overall operational efficiency.
3. How do smart contracts contribute to the evolution of blockchain technology?
Smart contracts contribute to the evolution of blockchain technology by expanding its use beyond simple financial transactions. They enable the creation of decentralized applications (DApps) that go beyond currency exchanges, fostering a broader range of applications such as decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, real estate transactions, and more. This evolution enhances the versatility and applicability of blockchain technology in various sectors.
4. Which are the popular platforms for deploying smart contracts, and what distinguishes them?
Popular platforms for deploying smart contracts include Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Cardano, and Polkadot. Ethereum stands out with its Solidity programming language and ERC-20/ERC-721 token standards. Binance Smart Chain emphasizes compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and cost-effectiveness. Cardano focuses on scalability and sustainability, while Polkadot pioneers interoperability between different blockchains, connecting diverse networks seamlessly.
5. What does the future hold for smart contracts, and how can SoluLab assist in their development?
The future of smart contracts involves trends like enhanced interoperability, oracle integration, and decentralized governance. SoluLab, with its wealth of experience and expert blockchain developers, is well-equipped to navigate this evolving landscape. Whether it’s leveraging Ethereum’s Solidity language, exploring interoperability with platforms like Binance Smart Chain, or crafting customized solutions, SoluLab ensures businesses stay at the forefront of blockchain innovation, offering tailored smart contract development services to meet specific needs.