
In an age where technological innovation continues to shape and redefine the way we live, work, and interact, one technology has emerged as a frontrunner in transforming industries and ushering in a new era of privacy, speed, and efficiency. Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and immutable ledger system, stands as a game-changer that is reshaping industries across the spectrum.
This article explores the evolution of blockchain technology, its current applications, the top blockchain platforms, emerging trends, and the transformative potential it holds, with a particular focus on its applications in healthcare.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is often described as a distributed ledger system that records transactions in a secure, transparent, and immutable way. At its core, blockchain consists of a chain of blocks, each containing a list of transactions. These blocks are linked together, forming a chronological and unchangeable chain. Key characteristics that define blockchain technology include:
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized systems, blockchain operates on a decentralized network of nodes, ensuring that no single entity has control over the network.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, making it an incorruptible and secure system.
- Transparency: All participants in the blockchain network have access to the same data, ensuring transparency and trust among participants.
- Security: Cryptography and consensus algorithms make blockchain extremely secure, reducing the risk of fraud and data breaches.
What Makes Blockchain Technology the Future?
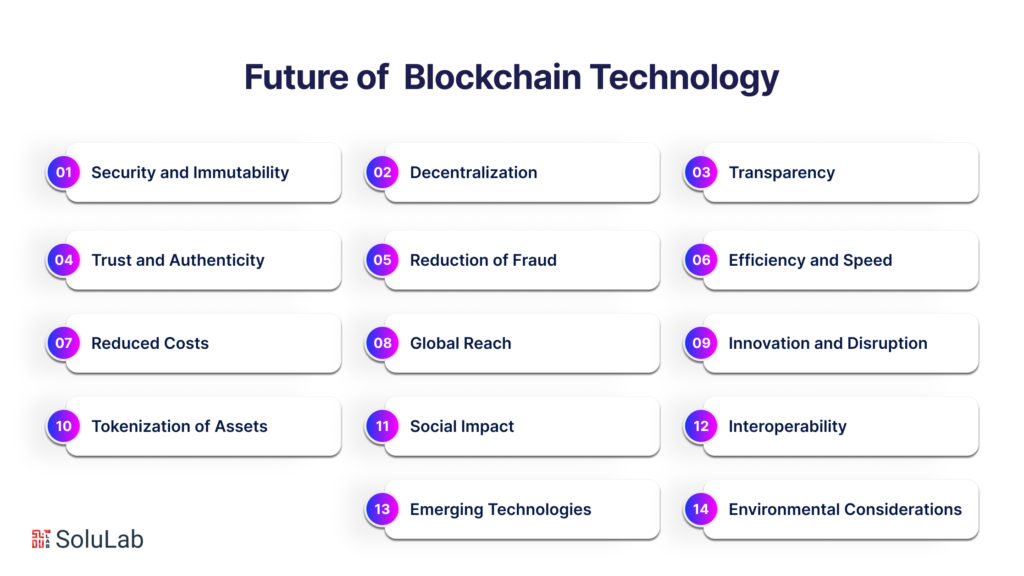
Blockchain technology is often regarded as the future for several compelling reasons. Its potential to revolutionize various industries, its intrinsic features, and its ability to address some of the fundamental challenges of the digital age make it a technology with a promising outlook:
- Security and Immutability: The foundation of blockchain technology is its ability to create secure, immutable, and tamper-proof records of transactions. This feature is essential in a world where data breaches and cyber threats are ever-present concerns.
- Decentralization: Blockchain operates on a decentralized network of nodes, eliminating the need for intermediaries like banks or central authorities. This reduces the risk of single points of failure and enhances trust among participants.
- Transparency: The transparent nature of blockchain means that all participants in the network can access the same data. This promotes trust and accountability, as anyone can verify the authenticity of transactions.
- Trust and Authenticity: The use of cryptographic techniques ensures that transactions and data are secure and authentic. This is especially valuable in industries where trust is paramount, such as supply chain management, healthcare, and finance.
- Reduction of Fraud: Blockchain’s transparency and security measures make it exceedingly difficult for malicious actors to engage in fraudulent activities, whether in financial transactions or document verification.
- Efficiency and Speed: Blockchain can significantly streamline processes by automating tasks through smart contracts. These self-executing contracts remove the need for intermediaries and reduce the time and costs associated with manual processes.
- Reduced Costs: By eliminating intermediaries and streamlining processes, blockchain has the potential to reduce costs in various industries, making it an appealing technology for businesses seeking efficiency and cost savings.
- Global Reach: Blockchain technology is accessible on a global scale. It can facilitate cross-border transactions, making it an excellent solution for industries such as international finance, trade, and remittances.
- Innovation and Disruption: Blockchain has spurred innovation and entrepreneurship, leading to the creation of new applications, business models, and industries. It has already disrupted traditional financial systems, and its potential to disrupt other sectors, such as healthcare, real estate, and supply chain management, is substantial.
- Tokenization of Assets: Blockchain enables the tokenization of real-world assets, from real estate to art. This allows for fractional ownership, increased liquidity, and democratized access to asset classes that were previously reserved for a select few.
- Social Impact: Blockchain can be a powerful tool for addressing social and environmental challenges. It has been used for identity verification, improving access to financial services, and tracking the provenance of goods, which can help combat fraud and support ethical business practices.
- Interoperability: Efforts are underway to make different blockchains interoperable, allowing for seamless data transfer and transactions between networks. This opens up new possibilities for combining the strengths of different blockchain platforms.
- Emerging Technologies: Blockchain is often seen as a complementary technology to other emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI). It can enhance the security and trustworthiness of IoT networks and AI algorithms by providing verifiable data sources and execution of smart contracts.
- Environmental Considerations: While blockchain’s energy consumption has been a concern, ongoing research and the development of more energy-efficient consensus algorithms aim to make blockchain technology more sustainable.

In brief, the future of blockchain technology is promising due to its potential to reshape industries, enhance security, reduce fraud, and promote transparency. As it continues to evolve and find new applications, blockchain is likely to play an increasingly significant role in our digital world, making it a defining technology of the future.
Applications of Blockchain
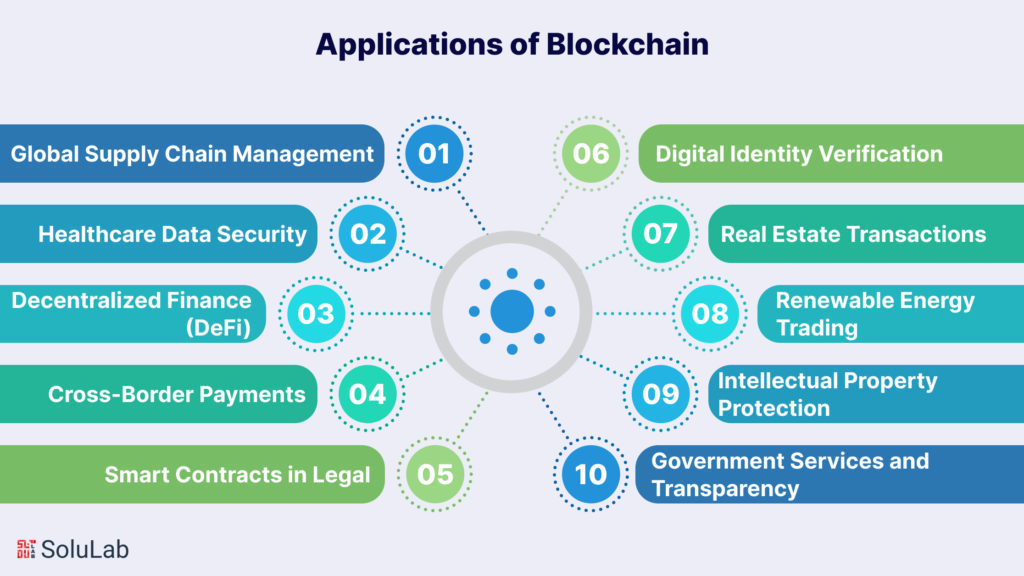
Have a look at some of the Use cases of blockchain that are changing the world of technology:
- Global Supply Chain Management
Blockchain will enable end-to-end transparency in supply chains, tracking products and verifying their authenticity. By 2025, the blockchain supply chain market is projected to reach $9.85 billion, growing at a CAGR of 50.6%. (Source: MarketsandMarkets)
- Healthcare Data Security
Blockchain can secure Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and patient data, enhancing privacy and accessibility. The global blockchain in healthcare market is estimated to reach $1.6 billion by 2025, at a CAGR of 65.5%. (Source: Grand View Research)
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi platforms offer decentralized lending, borrowing, and trading of cryptocurrencies, disrupting traditional finance. DeFi’s Total Value Locked (TVL) exceeded $100 billion in 2021, showcasing rapid growth in the sector. (Source: DeFi Pulse)
-
Cross-Border Payments
Blockchain technology can streamline cross-border transactions, making them faster and more cost-effective. The global blockchain remittances market is expected to reach $1.35 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 24.8%. (Source: Mordor Intelligence)
-
Smart Contracts in Legal
Smart contracts automate legal processes, such as contract execution and dispute resolution. The global smart contract market is anticipated to reach $345 million by 2026, with a CAGR of 32.5%. (Source: MarketsandMarkets)
-
Digital Identity Verification
Blockchain can securely manage digital identities, reducing identity theft and ensuring user privacy. The global digital identity solutions market is projected to be worth $49.5 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 17.3%. (Source: MarketsandMarkets)
-
Real Estate Transactions
Blockchain simplifies property transactions and enhances property title records. The global blockchain in real estate market is estimated to reach $1.66 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 67.3%. (Source: Allied Market Research)
Read More: Blockchain Technology as a Platform for Digitization
-
Renewable Energy Trading
Blockchain facilitates peer-to-peer energy trading, promoting the adoption of renewable energy sources. Global blockchain-based renewable energy trading is estimated to reach 87.5 GW capacity by 2025, with 460 projects in development. (Source: IRENA)
-
Intellectual Property Protection
Content creators use blockchain to protect intellectual property rights. By 2026, the blockchain for intellectual property market is estimated to reach $5.5 billion, growing at a CAGR of 40.1%. (Source: ResearchAndMarkets)
-
Government Services and Transparency
Governments use blockchain to enhance transparency and efficiency in services, such as land registry and taxation. By 2025, the global blockchain in government market is estimated to reach $30.7 billion, growing at a CAGR of 69.4%. (Source: MarketsandMarkets)
Read More: Top 10 Real World Applications of Blockchain Technology
These applications represent just a fraction of the potential use cases for blockchain technology in the future. As adoption continues to grow, the impact on these industries will become more pronounced, and blockchain will play a pivotal role in reshaping various sectors of the economy.
Blockchain in Healthcare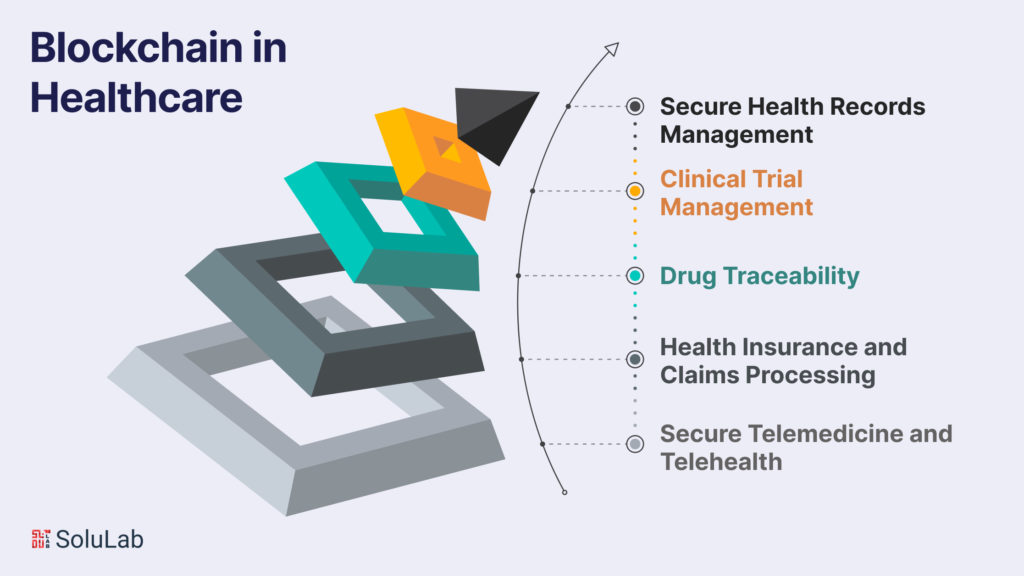
Blockchain technology has the potential to transform the healthcare industry in numerous ways by addressing issues related to data security, interoperability, and patient privacy. Here’s an in-depth look at how blockchain is being applied in healthcare:
Secure Health Records Management
Application: Blockchain can be used to securely store and manage Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and patient data.
Benefits:
- Improved data security: Patient data is encrypted and stored in a tamper-proof manner, reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Data accessibility and control: Patients can grant access to their data as needed, enhancing privacy and control.
Use Case: Estonia, through its e-Health Authority, uses blockchain to secure the health records of its citizens. This has reduced data breaches and increased patient control over their health data.
Clinical Trial Management
Application: Blockchain smart contracts can automate and streamline the management of clinical trial data.
Benefits:
- Improved transparency: Trial data is stored in an immutable and transparent way, reducing fraud.
- Faster and more efficient trials: Smart contracts automate tasks like consent management and data sharing, reducing the time and costs associated with clinical trials.
Use Case: Mediledger is a blockchain platform that verifies the authenticity of pharmaceuticals in clinical trials, ensuring drug safety and reducing fraud.
Drug Traceability
Application: Blockchain can track the production and distribution of drugs, ensuring the authenticity and provenance of pharmaceuticals.
Benefits:
- Reduced counterfeit drugs: Blockchain’s transparency can help verify the legitimacy of drugs, reducing health risks.
- Enhanced drug recalls: Blockchain can quickly identify the source of contaminated or recalled drugs.
Use Case: The U.S. FDA is exploring blockchain for tracking and tracing prescription medications to combat counterfeit drugs in the pharmaceutical supply chain.
Health Insurance and Claims Processing:
Application: Blockchain can streamline health insurance claims processing by automating verification and payments through smart contracts.
Benefits:
- Reduced fraud: The transparent and secure nature of blockchain can reduce fraudulent claims.
- Faster and more efficient claims processing: Automation reduces administrative costs and processing times.
Use Case: Several insurance companies, such as Aetna and Humana, are exploring blockchain for claims processing and fraud prevention.
Secure Telemedicine and Telehealth:
Application: Blockchain enhances the security of telemedicine platforms, protecting sensitive patient data.
Benefits:
- Secure data sharing: Patient information is encrypted and shared securely, ensuring confidentiality.
- Trust in remote healthcare: Patients and healthcare providers can have confidence in the security of telehealth interactions.
Use Case: The Solve.Care platform combines blockchain and telehealth to provide secure and efficient remote healthcare services.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is not just a buzzword but a transformative force that is reshaping industries and redefining the way we interact with data, value, and trust. Its applications in healthcare and various other sectors hold the promise of greater security, transparency, and efficiency. As the technology continues to evolve, it is crucial for businesses and individuals to stay informed and leverage the potential of blockchain for a better future. With its growing ecosystem, blockchain is set to remain the defining technology of our future, and its impact will only continue to expand.
SoluLab stands as a leading blockchain development company with cutting-edge blockchain development services, offering businesses the means to propel themselves into the future. Their team, comprised of top-tier blockchain developers, demonstrates exceptional proficiency in crafting and implementing tailored blockchain solutions that cater to real-world applications.
Collaborating with SoluLab affords businesses the opportunity to tap into a reservoir of seasoned Hire blockchain developers well-versed in the intricacies of blockchain ecosystems and protocols. These experts adeptly shepherd clients through the entire journey, commencing from the initial ideation stage and culminating in the seamless integration of blockchain technology into their operations. Whether one is in the process of exploring blockchain’s potential or seeking to enhance existing blockchain applications, SoluLab emerges as one of the best blockchain development companies poised to bring these aspirations to fruition.
FAQs
1. What is Blockchain technology, and how does it work?
Blockchain is a new age technology that records transactions across a network of systems. It works by creating a chain of data blocks, where each block contains a set of transactions. Once added, these blocks are cryptographically linked, forming a secure and unchangeable record. This decentralized nature ensures that no single entity has control, enhancing security and transparency.
2. What are the key benefits of Blockchain technology?
The main advantages of Blockchain technology include enhanced security due to its tamper-proof nature, increased transparency through open access to data, decentralization, which reduces the risk of central authority manipulation, and the ability to streamline processes and reduce intermediaries, resulting in cost savings and increased efficiency.
3. Is Blockchain technology only for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin?
No, Blockchain technology has a broader range of applications beyond cryptocurrencies. While Bitcoin is one application of blockchain, the technology can be used in various industries such as supply chain management, healthcare, finance, voting systems, and more, where secure, transparent, and tamper-proof data management is required.
4. How does Blockchain impact data security and privacy?
Blockchain improves data security by encrypting and decentralizing data of the users. Once data is recorded, it is extremely challenging to alter, ensuring its integrity. It also offers selective data sharing, where users have control over who can access their data, thus promoting privacy.
5. Are there any climatic concerns related to Blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology, particularly Proof of Work (PoW) systems like Bitcoin, has faced criticism for its energy consumption. However, newer consensus algorithms, like Proof of Stake (PoS), are more energy-efficient. Additionally, efforts are being made to mitigate environmental impacts through eco-friendly blockchain solutions.





