
The idea of the Metaverse is one of the new digital frontiers that has emerged as a result of the quick development of technology. We are moving from a physical reality to a digital one as technology advances, where virtual experiences and interactions are very valuable. The idea of the Metaverse, a virtual environment that incorporates both real and digital locations and offers consumers an immersive and linked experience, is at the core of this change.
The Metaverse can be defined as a collective virtual shared space that encompasses various virtual worlds, augmented reality, and virtual reality environments. It is a digital realm where users can interact with each other, engage in activities, and create and consume content. In the Metaverse, boundaries between physical and virtual realities blur, allowing users to transcend the limitations of the physical world and enter a realm of endless possibilities.
Non-Fungible Tokens, commonly known as NFTs metaverse, have gained immense popularity in recent years. NFTs metaverse are unique digital assets that are stored on a blockchain, making them secure, transparent, and immutable. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are fungible and interchangeable, NFTs metaverse is indivisible and holds distinct characteristics that set them apart from one another. In this blog, we will talk about the foundation of the next blockchain revolution.
What is the Role of NFTs Metaverse?
The role of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs metaverse) cannot be overstated. NFTs metaverse plays a pivotal role in shaping and defining the virtual universe by providing unique digital assets, ownership verification, and enabling vibrant economies within the Metaverse.
-
Unique Digital Assets
NFTs Metaverse serves as the building blocks, offering a wide range of unique digital assets. These assets can include virtual real estate, virtual identities, artwork, fashion, collectibles, virtual goods, and much more.
Each NFT represents a distinct and irreplaceable item, making it possible for users to own and trade virtual assets that hold inherent value. These digital assets contribute to the immersive and customizable experiences within the Metaverse, allowing users to express themselves and engage with the virtual world on a personal level.
-
Ownership Verification
One of the most significant contributions of the NFTs metaverse to its ability to establish ownership and provenance of digital assets. Through the use of blockchain technology, the NFTs metaverse offers transparent and immutable records of ownership, ensuring that users can prove their rightful ownership of virtual assets.
This ownership verification is essential in the Metaverse, where the value of virtual assets can be substantial. NFTs Metaverse eliminates the risk of fraudulent claims and provides a secure platform for users to buy, sell, and trade their digital assets with confidence.
-
Enabling Vibrant Economies
NFTs metaverse has revolutionized the concept of virtual economies. With the NFTs metaverse, users can participate in dynamic and thriving digital marketplaces, where they can buy, sell, and trade virtual assets. These virtual economies operate on top blockchain platforms, allowing for secure and transparent transactions.
NFTs Metaverse provides creators and artists with new avenues for monetization by tokenizing their work and earning royalties whenever their assets are sold or used. Additionally, users can invest in and speculate on the value of the rare and desirable NFTs metaverse, creating a dynamic market driven by supply and demand.
Read Our Blog Post: Everything You Need to Know About Metaverse NFT Marketplace Development
-
Interoperability and Cross-Platform Functionality
NFTs Metaverse also enables interoperability and cross-platform functionality. By utilizing open standards and protocols, the NFTs metaverse can be transferred and used across various virtual worlds, platforms, and applications.
This interoperability allows users to carry their virtual assets and identities seamlessly between different Metaverse environments, enhancing their overall experience and eliminating the need for asset duplication. NFTs Metaverse enables users to build a digital presence that transcends individual platforms, contributing to a more cohesive and interconnected Metaverse ecosystem.
-
Community Engagement and Participation
NFTs Metaverse fosters vibrant communities. Users can come together to trade, collect, and showcase their NFTs metaverse, creating a social fabric within the virtual realm. These communities provide opportunities for collaboration, creativity, and social interactions.
Users can connect with like-minded individuals, join virtual events, and participate in collaborative projects, all facilitated by the ownership and exchange of the NFTs metaverse. This community-driven aspect adds depth and richness to the Metaverse, making it a truly immersive and engaging environment.
What is the Relationship Between the Metaverse and Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)?
NFTs serve as the foundational elements that power the Metaverse, while the Metaverse provides a fertile ground for the growth and adoption of the NFTs Metaverse. Together, they create a dynamic and transformative digital ecosystem.
-
NFTs as Building Blocks of the Metaverse
NFTs metaverse acts as the building blocks, providing unique digital assets that populate the virtual universe. These assets can represent virtual real estate, virtual identities, artwork, fashion, collectibles, virtual goods, and much more.
NFTs Metaverse gives users ownership over these assets, allowing them to buy, sell, and trade within the Metaverse. Without NFTs, the Metaverse would lack the distinct and valuable digital assets that make it an immersive and engaging environment.
-
Ownership and Provenance in the Metaverse
One of the key challenges in the virtual realm is establishing ownership and provenance of digital assets. NFTs Metaverse solves this problem by utilizing blockchain technology to create transparent and immutable records of ownership.
In the Metaverse, users can prove their ownership of NFTs, ensuring that their digital assets are secure and protected. This ownership verification adds value and trust to the virtual assets within the Metaverse, enabling users to confidently engage in transactions and interactions.
-
Monetization and Empowerment of Creators
NFTs empower creators within the Metaverse by offering new avenues for monetization. Artists, musicians, game developers, and other content creators can tokenize their work as NFTs metaverse, retaining ownership rights and earning royalties whenever their creations are sold or used.
This model allows creators to showcase their talent, reach a global audience, and establish sustainable revenue streams. NFTs Metaverse provides a direct and decentralized means for creators to engage with their audience and monetize their digital creations within the Metaverse.
Check Out Our PR Article: SoluLab Bridging the Gap Between Technology And Innovation
-
Interoperability and Cross-Platform Functionality
The Metaverse is a vast and interconnected digital landscape that encompasses various virtual worlds, platforms, and applications. NFTs metaverse enables interoperability and cross-platform functionality within this complex ecosystem. Through the use of open standards and protocols, the NFTs can be transferred and used across different Metaverse environments.
Users can carry their NFTs metaverse seamlessly between virtual worlds, ensuring the continuity and consistency of their digital assets. This interoperability enhances the overall user experience and facilitates the seamless integration of NFTs into the Metaverse.
-
Community Engagement and Participation
NFTs foster vibrant communities within the Metaverse. Users can come together to trade, collect, and showcase their NFTs metaverse, creating a social fabric within the virtual realm. These communities provide opportunities for collaboration, creativity, and social interactions.
Users can connect with like-minded individuals, join virtual events, and participate in collaborative projects, all facilitated by the ownership and exchange of the NFTs metaverse. This community-driven aspect adds depth and richness to the Metaverse, making it a truly immersive and engaging environment.
What is the Usability of NFTs and Metaverse?
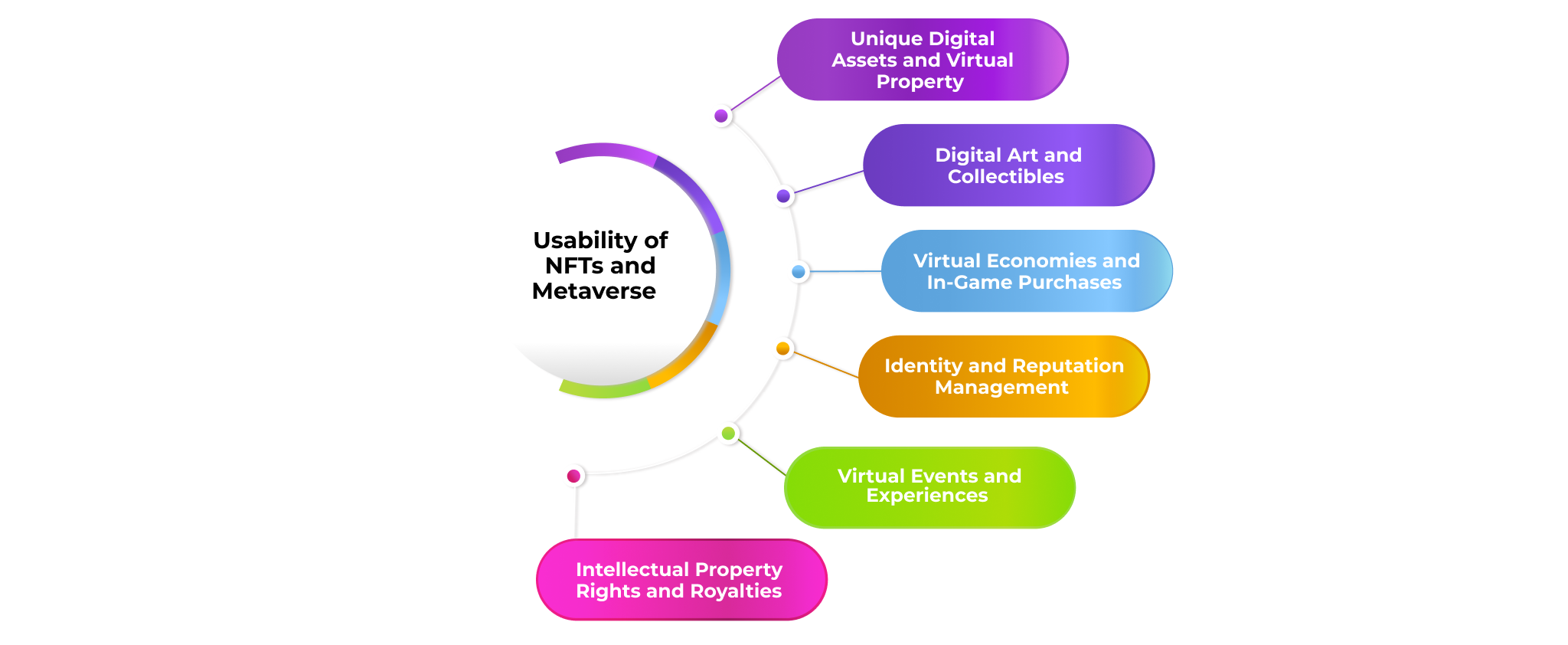
The usability of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs metaverse) within the Metaverse holds tremendous potential, offering users a wide range of practical applications and benefits. As the Metaverse continues to evolve, NFTs play a crucial role in enhancing user experiences, facilitating transactions, and enabling seamless interactions within the virtual realm.
-
Unique Digital Assets and Virtual Property
NFTs Metaverse provides users with the ability to own and trade unique digital assets. These assets can include virtual real estate, virtual identities, artwork, fashion, collectibles, and more. By utilizing the NFTs metaverse, users can establish ownership of virtual properties, customize their virtual identities, and showcase their collections. This usability feature allows individuals to express their creativity, establish their digital presence, and engage with the Metaverse on a personal level.
-
Digital Art and Collectibles
NFTs Metaverse has revolutionized the world of digital art and collectibles. Artists can tokenize their creations as NFTs metaverse, providing unique and verifiable proof of ownership. Collectors can then purchase and own these digital artworks and collectibles, knowing they possess a one-of-a-kind item. The usability of the NFTs metaverse in this context not only enables artists to monetize their work but also empowers collectors to build valuable and curated collections within the Metaverse.
-
Virtual Economies and In-Game Purchases
NFTs metaverse serves as a foundation for virtual economies, allowing for the creation and exchange of digital currencies and goods. Users can utilize the NFTs metaverse to purchase virtual assets, participate in in-game transactions, and engage in virtual commerce. This usability feature facilitates a seamless and secure environment for buying, selling, and trading virtual goods, enhancing the overall user experience and enabling vibrant virtual economies within the Metaverse.
Read Our Blog: What is the Virtual Reality Metaverse?
-
Identity and Reputation Management
NFTs metaverse can be employed for identity and reputation management. Users can create and customize their virtual identities, attaching NFTs metaverse that represents their unique characteristics, achievements, and reputation. These NFT-based identities can be utilized for social interactions, networking, and establishing trust within the virtual realm. The usability of the NFTs metaverse in this context allows for seamless and reliable identity management, enabling users to build their digital personas and participate in virtual communities.
-
Virtual Events and Experiences
NFTs Metaverse offers usability in the realm of virtual events and experiences. Event organizers can issue limited-edition NFT tickets, granting access to exclusive virtual gatherings, concerts, conferences, and more. These NFT tickets can provide unique perks, bonuses, or collectible elements, enhancing the overall value and experience for attendees. The usability of NFTs metaverse in this context ensures secure and verifiable access to virtual events, while also providing additional benefits to participants.
-
Intellectual Property Rights and Royalties
NFTs Metaverse provides usability in terms of intellectual property rights and royalty management. Creators can tokenize their work as NFTs metaverse, retaining ownership rights and setting up smart contracts that automatically distribute royalties whenever their NFTs metaverse is sold or used. This usability feature ensures that creators receive fair compensation for their contributions to the Metaverse, while also protecting their intellectual property rights in a transparent and enforceable manner.
How Can You Purchase a Metaverse NFT?
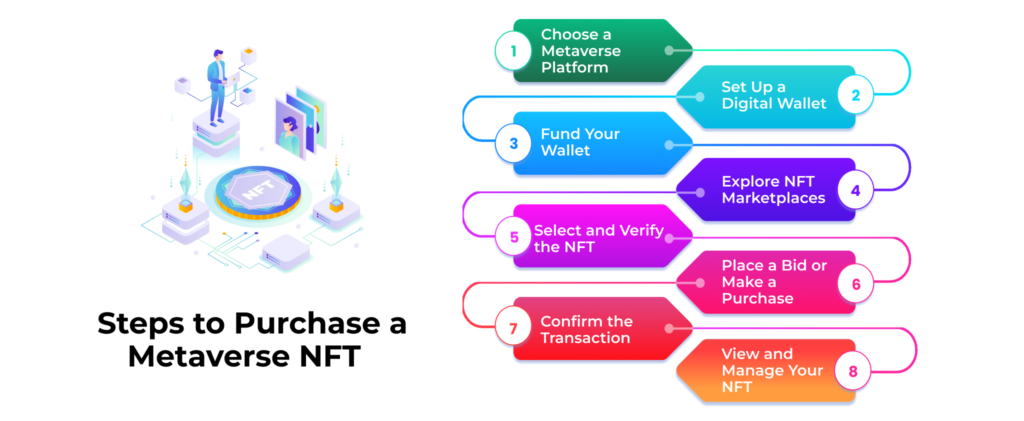
Purchasing a Metaverse NFT (Non-Fungible Token) is an exciting process that allows individuals to own unique digital assets within the virtual realm. While the specific steps may vary depending on the platform or marketplace, here is a general guide on how you can purchase a Metaverse NFT:
1. Choose a Metaverse Platform
First, you need to identify the Metaverse platform where the NFTs metaverse you’re interested in is available. Popular platforms include Decentraland, Cryptovoxels, Sandbox, Somnium Space, and others. Research and explore these platforms to find the one that aligns with your interests and preferences.
2. Set Up a Digital Wallet
To purchase and store NFTs metaverse, you’ll need a digital wallet that supports the blockchain network on which the NFTs metaverse are minted. Ethereum is the most commonly used blockchain for the metaverse, so a wallet compatible with Ethereum (such as MetaMask or Trust Wallet) is often necessary. Set up your wallet by following the instructions provided by the wallet provider and ensure you secure your private keys or seed phrases.
3. Fund Your Wallet
Once your wallet is set up, you’ll need to acquire the cryptocurrency (usually Ether, or ETH) used on the platform to purchase NFTs Metaverse. You can buy ETH from popular cryptocurrency exchanges and transfer it to your wallet. Ensure that you have enough funds in your wallet to cover the cost of the NFT you want to purchase, as well as any transaction fees associated with the blockchain network.
Check Out Our Press Release: SoluLab Honored By GoodFirms as Winner of the Trusted Choice Award 2023
4. Explore NFT Marketplaces
NFTs Metaverse is typically bought and sold on specialized marketplaces. Each platform may have its marketplace, or there might be dedicated NFT marketplaces like OpenSea, Rarible, or SuperRare that support multiple Metaverse platforms. Browse through these marketplaces to find the NFTs metaverse that captures your interest.
5. Select and Verify the NFT
Once you find an NFT you want to purchase, click on the listing to view its details, including the description, artwork, and any additional information provided by the creator. Take the time to understand what you are buying and ensure that the NFT meets your expectations. Pay attention to factors such as the rarity, provenance, and authenticity of the NFT.
6. Place a Bid or Make a Purchase
Depending on the marketplace, you may have different options to acquire the NFT. You can either place a bid or make an outright purchase. If you place a bid, you’ll need to wait for the auction to end and see if your bid is successful. If you choose to make an immediate purchase, you can typically do so by clicking the “Buy Now” button and following the prompts to complete the transaction.
7. Confirm the Transaction
After you’ve selected the purchase option, you’ll be prompted to confirm the transaction. Review the details, including the price, gas fees (transaction fees), and any other relevant information. Once you’re satisfied, approve the transaction using your wallet. This will initiate the transfer of funds and the ownership of the NFT to your wallet address.
8. View and Manage Your NFT
Once the transaction is confirmed and completed, you can view and manage your NFT in your wallet. The NFT will be associated with a unique token ID and metadata, which you can access through your wallet interface or by exploring the blockchain explorer specific to the blockchain network.
Conclusion
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs metaverse) are undeniably the foundation of the next blockchain revolution within the Metaverse. The intersection of the NFTs metaverse has ushered in a new era of digital ownership, unique virtual assets, and immersive experiences. NFTs serve as the backbone of the Metaverse, providing users with ownership of one-of-a-kind digital assets that range from virtual real estate and artwork to collectibles and virtual identities.
The Metaverse, a virtual universe where users can interact, create, and engage with digital environments, relies on NFTs to establish ownership, provenance, and value within its vast landscape. NFTs metaverse ensures that each digital asset is distinct, verifiable, and securely owned by an individual. This ownership verification fosters trust and enables vibrant virtual economies to thrive, where users can buy, sell, and trade the NFTs metaverse seamlessly and transparently.
Moreover, NFTs play a vital role in enhancing the user experience within the Metaverse. Through the NFTs metaverse, users can customize their virtual identities, express their creativity, and engage with virtual communities. Artists and creators can tokenize their work as NFTs, empowering them to monetize their digital creations and establish direct relationships with their audience. NFTs also enable participation in virtual events, access to exclusive experiences, and the establishment of reputations and identities within the Metaverse.
SoluLab is a reputable company renowned for its extensive expertise in developing a diverse range of NFT solutions. They are known for their meticulous attention to detail and a wide array of features in their NFT marketplace development services. With a proven track record in delivering top-notch solutions, SoluLab excels in various NFT-related endeavors, including artwork, digital collectibles, gaming, and asset tokenization. Additionally, as a leading provider of metaverse development services, SoluLab specializes in turning visionary Metaverse projects into reality. Utilizing cutting-edge tools and state-of-the-art technologies, their skilled team of metaverse experts is dedicated to delivering tailored solutions that align with the specific needs of clients. For further information and assistance, contact SoluLab today.
FAQs
1. How do the NFTs and the Metaverse intersect?
NFTs Metaverse intersects by allowing users to purchase, own, and trade unique digital assets within the virtual realm. NFTs Metaverse provides ownership verification enables monetization for creators, facilitates virtual economies, and enhances community engagement.
2. Can NFTs Metaverse be used on multiple platforms?
Yes, NFTs Metaverse can be used on multiple platforms, thanks to its interoperability and cross-platform functionality. Open standards and protocols allow the NFTs metaverse to be transferred and used across various virtual worlds, platforms, and applications, providing users with seamless access and utilization of their digital assets.
3. How do the NFTs contribute to the Metaverse?
NFTs Metaverse contributes to the Metaverse by serving as unique digital assets that can represent virtual real estate, artwork, fashion, collectibles, and more. They establish ownership and provenance, enable vibrant virtual economies, foster community engagement, and facilitate interoperability within the virtual realm.
4. Is NFT part of metaverse?
NFTs Metaverse provides a mechanism for establishing ownership and authenticity of digital assets. Each NFT is unique and verifiable, ensuring that users can prove their ownership of virtual properties, artwork, collectibles, and more. This ownership verification adds value and trust to the assets within the Metaverse, enabling secure and transparent transactions.







