
Blockchain technology continues to advance at a rapid pace. Many seemingly impossible things have been proven incorrect during the last few decades, including exorbitant transaction costs, double spending, net fraud, recovering deleted data, and so on. However, all of this may now be avoided because of Blockchain technology. Blockchain is currently quite popular among the general public. Its popularity began with the surge in Bitcoin values.
In this blog, we will discuss the importance of blockchain technology not only in real-world settings but also in business and banking.
So, without any further ado, let’s get started!
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a transformative technology that has ushered in a new era of trust, transparency, and decentralization in the digital landscape. At its core, blockchain is a distributed ledger, a secure and tamper-resistant database distributed across a network of computers, or nodes. Unlike traditional centralized databases managed by a single authority, blockchain operates on a decentralized consensus model, empowering a network of participants to collectively validate and record transactions.
The term “blockchain” itself signifies its structure: data is grouped into blocks, and each block is linked to the previous one through a cryptographic hash, forming an immutable chain. This chaining mechanism ensures that once a block is added to the chain, altering any information within it would necessitate changing all subsequent blocks—a computationally infeasible task. The decentralized nature of blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries and central authorities, offering a trustless environment where participants can engage in secure and transparent transactions.
Cryptography is a linchpin of blockchain development, securing the integrity and privacy of data. Transactions are cryptographically signed, and each participant on the network has a pair of cryptographic keys—a public key for identification and a private key for secure access. This cryptographic infrastructure ensures that transactions are verifiable, tamper-resistant, and confidential, making blockchain a foundational technology with applications spanning from finance and supply chain to healthcare and beyond.
How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
Having delved into the fundamental principles of blockchain technology, it’s crucial to appreciate how these factors harmonize to create a secure, transparent, and decentralized system to understand the importance of blockchain technology. The synergy of decentralization, distributed ledger, and cryptography ensures that blockchain is not merely a ledger but a paradigm shift in how information is stored, verified, and transacted in the digital realm.
Blockchain technology operates as a decentralized and distributed ledger system, revolutionizing the way data is recorded, verified, and secured. At its core, a blockchain is a chain of blocks, each containing a list of transactions and a unique identifier linking it to the previous block. This structure ensures a chronological and tamper-resistant record of transactions. The process begins with the initiation of a transaction. Once validated by participants in the network, the transaction is grouped with others into a block. Before this block is added to the chain, it undergoes a process called mining in Proof of Work (PoW) systems, where nodes solve complex mathematical problems to validate the block. In Proof of Stake (PoS) systems, validation is based on the ownership of a significant stake in the network.
Decentralization is a pivotal aspect of blockchain technology. Unlike traditional centralized databases, where a single entity controls the data, blockchain distributes the ledger across a network of nodes. Each node maintains a complete copy of the blockchain, ensuring redundancy and resilience. Decentralization fosters a trustless environment, eliminating the need for intermediaries or a central authority. Furthermore, the distributed nature of blockchain enhances security by eliminating single points of failure and reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Cryptography plays a crucial role in securing transactions within a blockchain. Each participant in the network has a pair of cryptographic keys – a public key for identification and a private key for transaction authentication. Transactions are cryptographically signed, ensuring that only the holder of the private key can initiate and authenticate a transaction. This cryptographic infrastructure not only ensures the confidentiality of transactions but also contributes to the overall integrity of the blockchain.
The consensus mechanism is another key element governing how nodes agree on the state of the blockchain. Popular mechanisms include PoW and PoS. In PoW, nodes compete to solve complex mathematical problems, showcasing computational effort as proof of validity. In PoS, participants with a significant stake in the network validate transactions, considering ownership rather than computational power. Consensus mechanisms prevent malicious activities like double-spending and ensure the security and stability of the blockchain.
In brief, blockchain technology works by creating a decentralized, transparent, and secure ledger of transactions. Through the use of blocks, nodes, consensus mechanisms, and cryptography, blockchain revolutionizes traditional data management systems, offering a tamper-resistant, trustless, and efficient solution with applications across various industries.
Key Components of Blockchain Technology
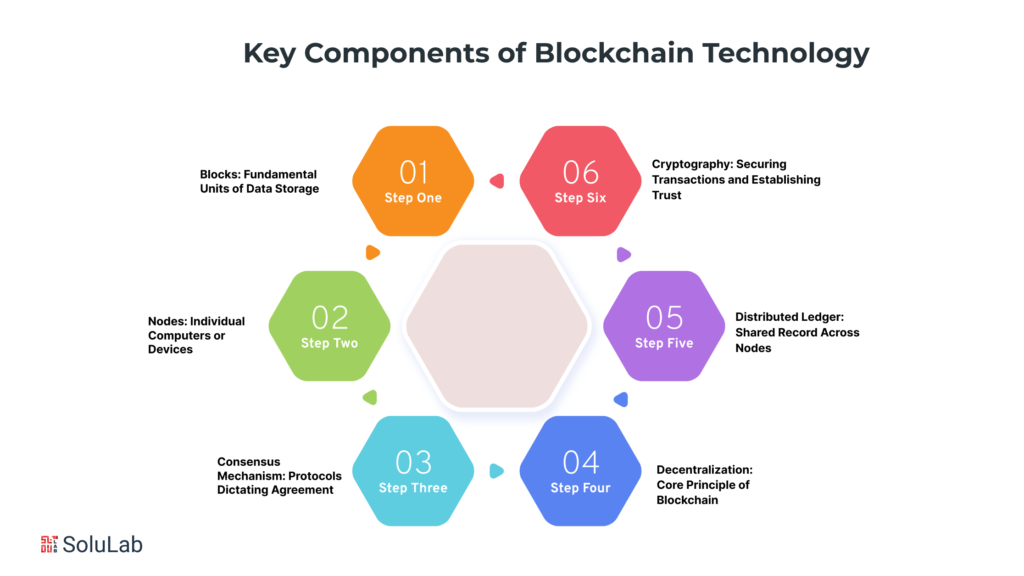
Blockchain in modern technology, renowned for its decentralized and secure nature, comprises several key components that collectively redefine how data is managed, transactions are executed, and trust is established. Let’s delve into these crucial building blocks!
-
Blocks: Fundamental Units of Data Storage
Blocks are the foundational units of a blockchain, representing the bedrock of its structure. Each block encapsulates critical information, including a timestamp, a cryptographic hash linking it to the previous block, and a list of transactions. The timestamp ensures a chronological record, crucial for tracking the sequence of events. The cryptographic hash not only secures the integrity of the block but also establishes an unbreakable link to the preceding block, creating an immutable chain. This chaining mechanism forms the backbone of the blockchain’s security, making it computationally infeasible to alter historical transactions. The list of transactions within a block represents real-world activities, ranging from financial transactions to smart contract executions. In essence, blocks are the containers that safeguard the transparency, security, and orderliness of the entire blockchain.
-
Nodes: Individual Computers or Devices
Nodes are the active participants within the blockchain network, serving as individual computers or devices that collectively uphold the integrity of the system. Each node maintains a comprehensive copy of the entire blockchain, ensuring redundancy across the network. This redundancy is crucial for fault tolerance; if one node fails, others seamlessly continue to operate. Nodes play a pivotal role in the validation and verification of transactions, collectively establishing consensus on the accuracy of the distributed ledger. Their participation in the network reinforces the decentralized nature of blockchain, eliminating the need for a central authority. In a distributed and decentralized environment, nodes collectively contribute to the resilience, security, and reliability of the entire blockchain network.
-
Consensus Mechanism: Protocols Dictating Agreement
Consensus mechanisms are the protocols that govern how nodes within the blockchain network agree on the current state of the ledger. They play a critical role in maintaining the security and stability of the blockchain. Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) are prominent consensus mechanisms, each with its unique approach. PoW involves nodes competing to solve complex mathematical problems, showcasing computational effort as proof of validity. On the other hand, PoS relies on participants with significant stakes in the network to validate transactions, considering ownership rather than computational power. These consensus mechanisms prevent malicious activities like double-spending, ensuring that the blockchain network reaches agreement and operates securely.
-
Decentralization: Core Principle of Blockchain
Decentralization is a core tenet of blockchain technology, challenging the traditional paradigm of centralized control. In a decentralized network, no single entity holds authority; rather, power is distributed among a multitude of nodes. This decentralized structure fosters transparency, resilience, and a trustless environment. It mitigates the risks associated with a single point of failure, ensuring that the system remains operational even if individual nodes falter. Decentralization not only enhances the security and reliability of the blockchain but also promotes collaboration and inclusivity. In the context of modern technology, decentralization stands as a transformative force, reshaping how we perceive authority and trust in digital ecosystems.
-
Distributed Ledger: Shared Record Across Nodes
The distributed ledger is the synchronized record of transactions spread across all nodes in the blockchain network. Each participant holds an identical copy of this ledger, creating redundancy and fault tolerance. This shared record is not confined to a centralized server but is distributed across the entire network, providing real-time access to synchronized information. Altering a transaction requires consensus among the majority of nodes, preserving the immutability and reliability of the ledger. The distributed nature of the ledger enhances the overall reliability and availability of data, which is crucial for applications where transparency and a synchronized version of the truth are paramount.
-
Cryptography: Securing Transactions and Establishing Trust
Cryptography is the bedrock of transactional security within blockchain technology. Participants in the network possess a unique cryptographic key pair, consisting of a public key for identification and a private key for transaction authentication. This cryptographic infrastructure ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of transactions. Through cryptographic signatures, transactions are secured, and the linkage of blocks is established. This layer of security not only safeguards against unauthorized access but also ensures that transactions are verifiable and tamper-resistant. In the broader context of modern technology, cryptography is instrumental in establishing trust within decentralized networks, enabling secure interactions and enhancing the overall integrity of the blockchain.
What are the Features and Advantages of Using Blockchain Technology?
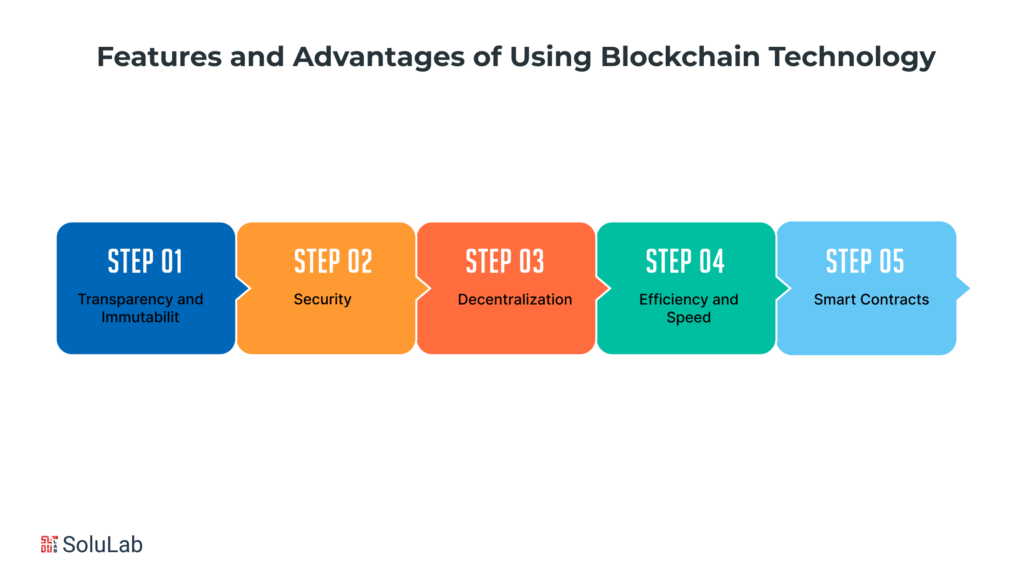
Blockchain technology, characterized by its decentralized and transparent nature, stands as a revolutionary force with transformative implications across a spectrum of industries. At its essence, blockchain represents a departure from traditional centralized models, redefining how data is managed, transactions are executed, and trust is established in the digital realm. The key features and advantages embedded within this technology lay the foundation for a new era of secure, efficient, and trustworthy interactions.
As we delve deeper into the importance of blockchain technology, it becomes evident that its decentralized architecture, transparency, immutability, security mechanisms, operational efficiency, and the innovative potential of smart contracts collectively reshape the landscape of modern systems. Blockchain is not merely a technological advancement; it is a paradigm shift, challenging conventional notions of authority, trust, and efficiency, and heralding a decentralized future where participants have greater control and transparency in their digital interactions.
-
Transparency and Immutability
One of the hallmark features of blockchain is transparency. Every participant in the network has access to an identical copy of the distributed ledger, ensuring that transactions are visible and verifiable. The immutability of the blockchain, achieved through cryptographic hashing and the chaining of blocks, means that once a block is added, it cannot be altered without changing subsequent blocks. This ensures an unforgeable and tamper-resistant record of transactions, instilling trust among participants and providing a transparent and auditable history of events.
-
Security
Security is a paramount advantage of using blockchain technology. The decentralized nature of the network and the cryptographic mechanisms employed in transaction verification make it highly resistant to hacking and fraud. Each participant has a unique cryptographic key pair, ensuring secure identification and authentication. Additionally, the consensus mechanism, whether Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, prevents malicious activities like double-spending. The combination of these security features makes blockchain a robust solution for safeguarding sensitive data and transactions.
-
Decentralization
Decentralization is a fundamental principle of blockchain, eliminating the need for a central authority. The distributed ledger is maintained across a network of nodes, ensuring that no single entity has control. This not only enhances the security of the system by eliminating single points of failure but also reduces the risk of censorship and unauthorized manipulation. Decentralization promotes a trustless environment where participants can engage in transactions without relying on intermediaries, fostering a more democratic and inclusive digital ecosystem.
-
Efficiency and Speed
Blockchain introduces efficiency and speed into traditional processes. Transactions are verified and added to the blockchain through consensus mechanisms, streamlining the need for time-consuming manual verification processes. The removal of intermediaries and the direct peer-to-peer nature of transactions contribute to faster processing times. In financial sectors, for instance, cross-border transactions that typically take days can be completed in a matter of minutes with blockchain technology. This efficiency not only reduces costs but also enhances the overall speed and responsiveness of transactional processes.
-
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, represent a powerful feature of blockchain. These programmable contracts automate and enforce the execution of contractual agreements when predefined conditions are met. Smart contracts enhance efficiency, reduce the risk of errors, and eliminate the need for intermediaries, resulting in faster and more cost-effective contract execution. In sectors like supply chain management and legal processes, smart contracts bring a new level of automation and transparency, revolutionizing the way agreements are executed.
Use Cases of Blockchain Technology
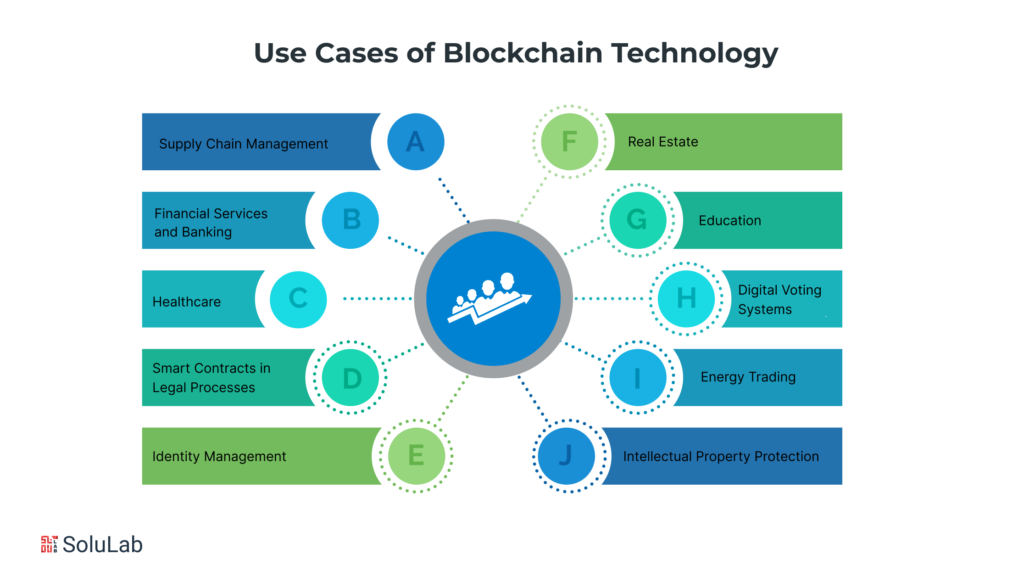
Blockchain technology’s versatility extends far beyond its origins in cryptocurrency, and its adoption continues to gain momentum across diverse industries. Exploring the various blockchain technology use cases reveals its transformative potential in reshaping traditional processes and establishing new paradigms of trust and efficiency.
1. Supply Chain Management
Blockchain’s transparency and immutability make it an ideal solution for enhancing supply chain visibility. From the origin of raw materials to the final product delivery, blockchain ensures a secure and traceable record of every transaction and movement. This use case significantly reduces the risk of fraud, improves accountability, and streamlines the entire supply chain process.
2. Financial Services and Banking
Blockchain has disrupted traditional financial services by offering faster, more secure, and cost-effective solutions. Cross-border payments benefit from the decentralized nature of blockchain, reducing the reliance on intermediaries and expediting transaction processing. Additionally, blockchain facilitates smart contracts, automating complex financial agreements and reducing the potential for disputes.
3. Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, blockchain enhances the management of patient records, ensuring secure and interoperable data sharing among healthcare providers. Patients gain greater control over their health data, and healthcare professionals can access a comprehensive and tamper-resistant record, improving accuracy and patient care.
4. Smart Contracts in Legal Processes
The use of smart contracts automates and enhances various legal processes. From contract execution to property transfers, smart contracts enable self-executing agreements when predefined conditions are met. This not only reduces the need for intermediaries but also ensures accuracy and transparency in legal transactions.
5. Identity Management
Blockchain provides a robust solution for identity management, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud. Individuals can have control over their digital identities, granting access to specific information as needed. This use case is particularly valuable in sectors like voting systems, where secure and verifiable identities are crucial.
6. Real Estate
Blockchain simplifies and secures real estate transactions by providing a transparent and tamper-resistant ledger. Property records, titles, and ownership transfers can be securely stored on the blockchain, reducing fraud and minimizing the need for intermediaries in the real estate industry.
7. Education
Blockchain can streamline and authenticate academic credentials. Academic certificates, degrees, and other qualifications can be securely stored on the blockchain, making it easy for employers and institutions to verify the authenticity of an individual’s educational achievements.
8. Digital Voting Systems
Blockchain can enhance the integrity and security of voting systems. By providing a transparent and immutable ledger, blockchain ensures that each vote is securely recorded, reducing the risk of tampering or fraud in elections.
9. Energy Trading
Blockchain facilitates peer-to-peer energy trading by securely recording and validating transactions on a decentralized ledger. This use case enables individuals and businesses to buy and sell excess renewable energy directly, fostering a more efficient and sustainable energy ecosystem.
10. Intellectual Property Protection
In the realm of intellectual property, blockchain can be used to establish and protect ownership rights. Digital assets such as patents, copyrights, and trademarks can be securely registered on the blockchain, providing a transparent and tamper-proof record of ownership.
Future Trends in Blockchain Technology
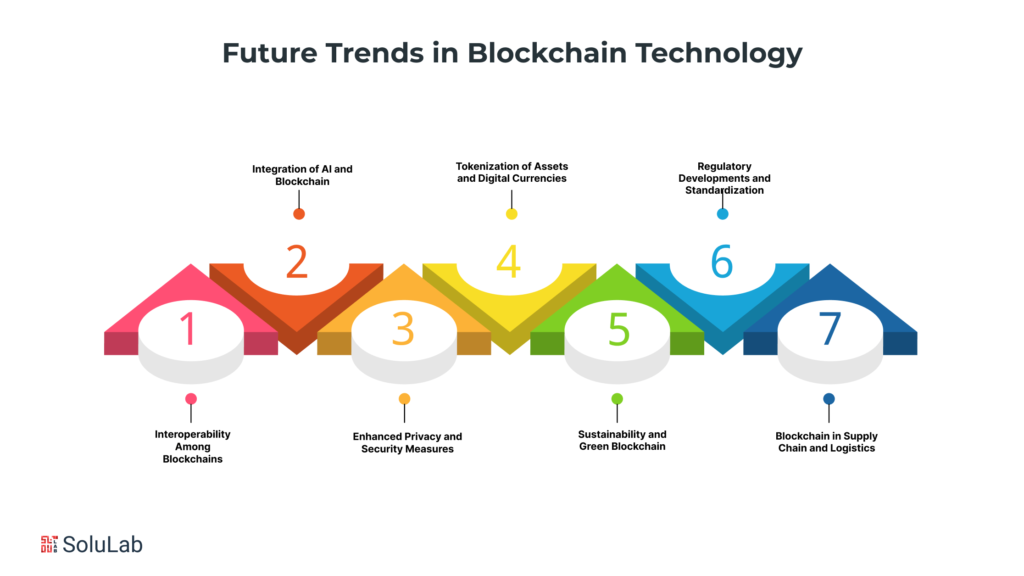
The future of blockchain technology promises to be dynamic and transformative, with several trends shaping its trajectory. As we look ahead, the continued evolution of blockchain is anticipated to influence diverse sectors, and blockchain technology companies are at the forefront of driving these advancements.
- Interoperability Among Blockchains: Blockchain technology companies are increasingly focused on developing solutions that facilitate interoperability among different blockchain networks. The future will likely see the emergence of protocols and standards allowing seamless communication and collaboration between disparate blockchains. This interoperability is essential for scaling the technology and fostering a more interconnected and efficient digital ecosystem.
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Blockchain: The convergence of blockchain technology and artificial intelligence is poised to redefine the technological landscape. Blockchain companies are exploring ways to integrate AI algorithms with blockchain platforms, enhancing data analytics, automation, and decision-making processes. This synergy could lead to more intelligent and adaptive blockchain solutions with applications ranging from predictive analytics to enhanced security protocols.
- Enhanced Privacy and Security Measures: As concerns over data privacy continue to rise, blockchain technology companies are investing in the development of enhanced privacy features. Technologies like zero-knowledge proofs and advanced cryptographic techniques are being integrated into blockchain ecosystem protocols to ensure secure and private transactions. This trend aligns with the growing demand for data protection and confidentiality in various industries.
- Tokenization of Assets and Digital Currencies: Blockchain technology is poised to revolutionize the way assets are represented and traded. Blockchain companies are exploring asset tokenization, which involves converting real-world assets into digital tokens on the blockchain. This can include anything from real estate to art. Additionally, the continued rise of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) and the exploration of decentralized finance (DeFi) underscore the evolving landscape of digital currencies.
- Sustainability and Green Blockchain: With the increasing awareness of environmental impact, blockchain technology companies are exploring sustainable solutions. The energy consumption associated with some consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work, has raised concerns. Future trends may witness a shift towards more environmentally friendly consensus mechanisms and the adoption of sustainable practices within the blockchain industry.
- Regulatory Developments and Standardization: As the blockchain landscape matures, regulatory frameworks are expected to evolve. Blockchain technology companies are actively engaging with regulators to establish clear guidelines and standards. The future will likely bring more clarity in terms of legal frameworks, which is crucial for the widespread adoption and integration of blockchain solutions across industries.
- Blockchain in Supply Chain and Logistics: The use of blockchain in supply chain is gaining momentum, and this trend is expected to intensify. Blockchain technology companies are leveraging the decentralized and transparent nature of blockchain to enhance traceability, reduce fraud, and streamline logistics processes. The future holds the potential for a more interconnected and efficient global supply chain ecosystem.
In brief, the future trends in blockchain technology are marked by innovation, collaboration, and a deepening integration into various sectors. Blockchain technology companies play a pivotal role in driving these advancements, pushing the boundaries of what is possible and contributing to the continued evolution of this transformative technology. As these trends unfold, the blockchain landscape is poised to redefine the way we interact with digital assets, data, and transactions.
Final Words
In conclusion, the evolution and widespread adoption of blockchain technology are ushering in a new era of innovation and efficiency across industries. From transforming supply chain management and securing financial transactions to redefining healthcare processes and ensuring the integrity of legal agreements, the use cases of blockchain are as diverse as they are impactful. As we navigate this landscape of decentralization, transparency, and security, it is evident that blockchain is not merely a technological advancement but a paradigm shift with the potential to reshape the very foundations of how we conduct business and manage data.
In the dynamic realm of blockchain technology, SoluLab stands out as a crucial player, especially for businesses seeking to harness the transformative power of blockchain. As a leading blockchain development company, SoluLab brings a wealth of expertise and experience to the table. Their innovative solutions, tailored for diverse industries, encompass everything from blockchain development and implementation to smart contract creation. SoluLab’s commitment to staying at the forefront of blockchain advancements ensures that businesses can leverage cutting-edge technology to enhance efficiency, security, and transparency. With a focus on delivering scalable and sustainable solutions, SoluLab emerges as a key partner for businesses looking to navigate the complexities of blockchain technology and unlock its full potential for sustainable growth and innovation.
FAQs
1. How does blockchain ensure the security of transactions in financial services?
Blockchain ensures the security of transactions in financial services through cryptographic techniques and consensus mechanisms. Each participant has a unique cryptographic key pair, and transactions are cryptographically signed, ensuring only authorized parties can engage. Consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake prevent malicious activities, providing a secure and transparent environment for financial transactions.
2. How can blockchain enhance supply chain management?
Blockchain enhances supply chain management by providing transparency and traceability. Each transaction in the supply chain is recorded in a block, creating an immutable and tamper-resistant ledger. This ensures a secure record of every movement, reducing the risk of fraud and improving accountability. Blockchain’s decentralized nature also streamlines the entire supply chain process by eliminating intermediaries and enhancing overall efficiency.
3. What is the role of smart contracts in legal processes?
Smart contracts automate and enhance various legal processes by translating contractual agreements into code. When predefined conditions are met, these self-executing contracts automatically execute, reducing the need for intermediaries and ensuring accuracy in legal transactions. This innovation streamlines processes reduces the risk of errors, and enhances the overall efficiency of legal agreements.
4. How does blockchain contribute to intellectual property protection?
Blockchain contributes to intellectual property protection by providing a secure and tamper-proof ledger for registering ownership rights. Digital assets such as patents, copyrights, and trademarks can be securely recorded on the blockchain, establishing a transparent and verifiable record of ownership. This enhances the integrity of intellectual property management.
5. Why is SoluLab important in blockchain technology for businesses?
SoluLab is crucial in blockchain technology for businesses due to its expertise and commitment to innovation. As a leading blockchain technology company, SoluLab offers tailored solutions for diverse industries, covering everything from development to smart contract creation. Our focus on staying at the forefront of blockchain advancements ensures businesses can leverage the best technology for enhanced efficiency, security, and transparency. SoluLab emerges as a key partner for businesses seeking to navigate the complexities of blockchain technology and unlock its full potential for sustainable growth and innovation.






