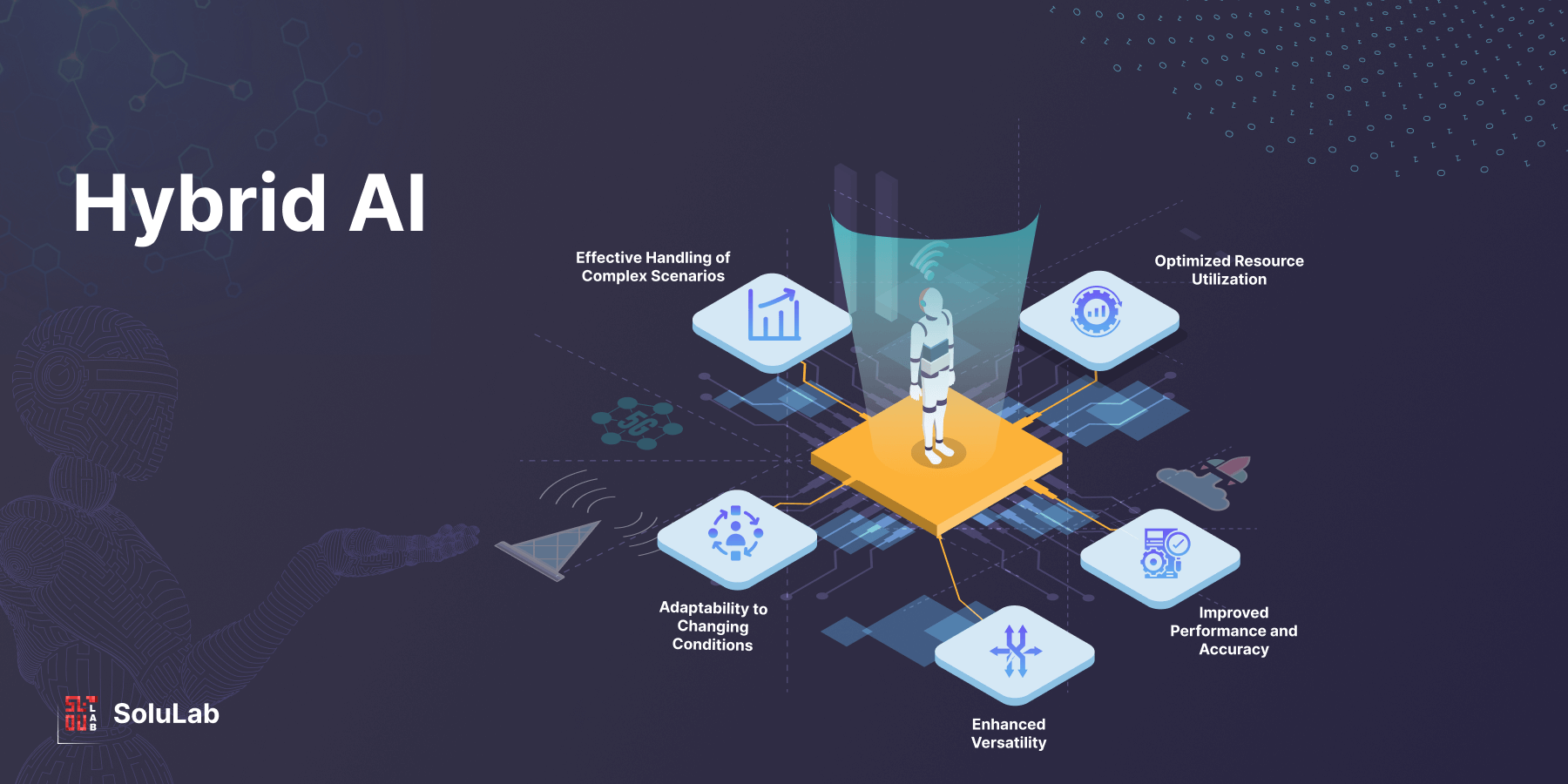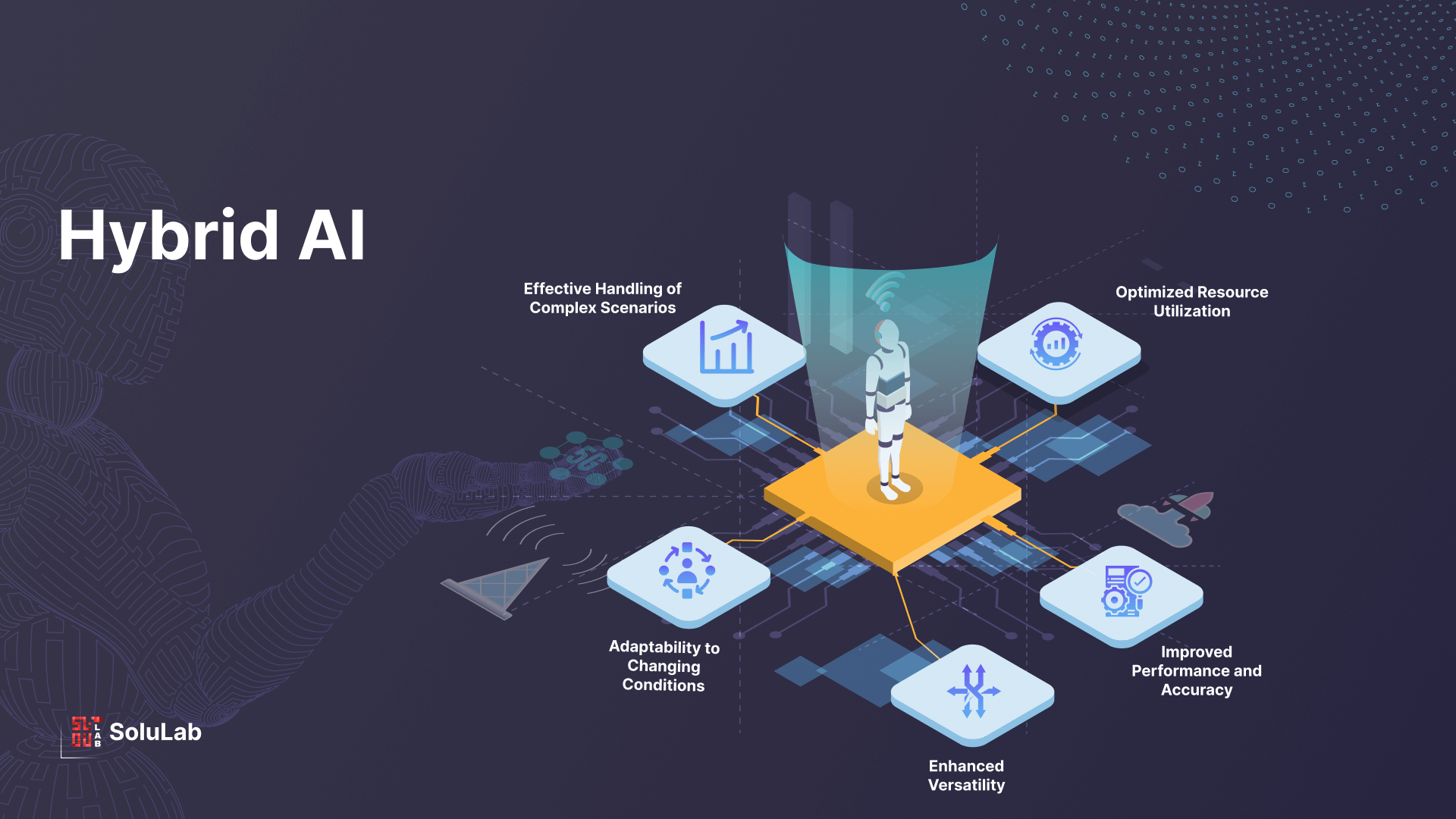
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a subfield of AI that focuses on the interaction between computers and human languages. It aims to enable machines to understand, interpret, and generate human-like text or speech.
NLP has been used in a variety of applications, including:
- Machine translation
- Information retrieval
- Sentiment analysis
- Chatbots
In recent years, NLP has witnessed remarkable advancements, driven by the availability of large datasets of text and speech, the development of new machine learning algorithms, and the increasing computational power of computers. These advancements have made it possible for NLP to be used in a wider range of applications, and to achieve higher levels of accuracy.
NLP is still a relatively young field, and there is still much work to be done. However, the progress that has been made in recent years is very promising, and it is likely that NLP will continue to play an increasingly important role in AI and other fields.
Fundamentals of NLP
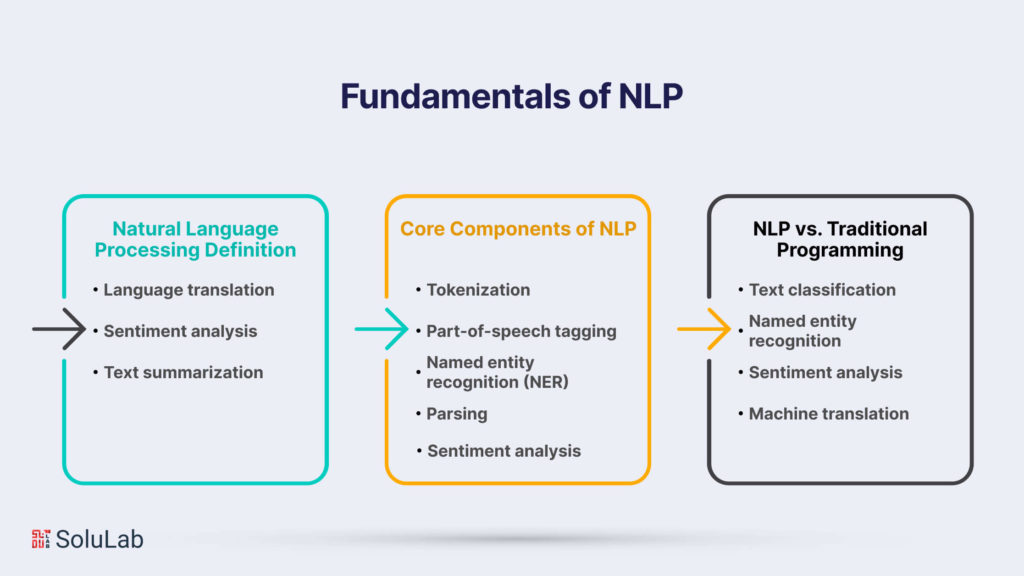
Commence on a journey into the core principles of NLP, understanding the foundational elements that enable machines to process and interpret human language. From tokenization to part-of-speech tagging, this chapter lays the groundwork for a comprehensive grasp of NLP.
Natural Language Processing Definition
At its core, NLP involves the development of algorithms and models that allow machines to comprehend and respond to human language. This includes tasks such as:
- Language translation: Convert text from one language to another.
- Sentiment analysis: Identify the emotional content of a piece of text.
- Text summarization: Reduce a long piece of text to a shorter version.
NLP is a rapidly growing field, and new algorithms and models are being developed all the time. As NLP technology improves, machines will become increasingly capable of understanding and responding to human language. This will have a major impact on a wide range of industries, including healthcare, customer service, and education.
Related: What is an AI Copilot?
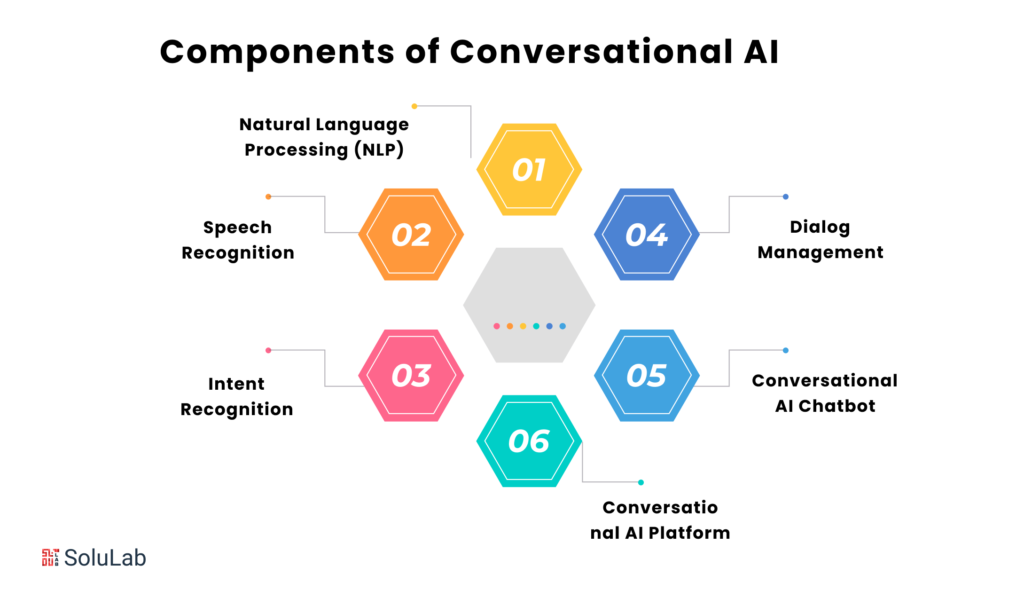
Core Components of NLP
- Tokenization: Breaks text into words or tokens.
- Part-of-speech tagging: Assigns grammatical categories to words.
- Named entity recognition (NER): Identifies and classifies entities.
- Parsing: Analyzes sentence structure to understand relationships between words.
- Sentiment analysis: Determines the sentiment expressed in a piece of text.
NLP vs. Traditional Programming
Unlike traditional programming, NLP relies on machine learning to decipher patterns and relationships in language. This flexibility allows NLP models to adapt to various linguistic nuances, such as slang, idioms, and regional dialects.
In addition to deciphering patterns and relationships in language, NLP models can be trained to perform a variety of tasks, such as:
- Text classification
- Named entity recognition
- Sentiment analysis
- Machine translation
NLP is a rapidly growing field with a wide range of applications. As NLP models become more sophisticated, they will be able to perform more complex tasks and solve more real-world problems.
Challenges and Limitations
Navigate through the challenges that NLP encounters, from the ambiguity of language to biases in models. This chapter addresses the limitations of current NLP technologies and sheds light on the ethical considerations inherent in developing language-processing systems.
-
Ambiguity in Language
Natural language is ambiguous, with words and phrases having multiple meanings based on context. This can make it difficult to understand natural language text.
There are a number of ways to address the problem of ambiguity in natural language. One approach is to use a knowledge base to provide additional context for words and phrases. Another approach is to use machine learning to learn the different meanings of words and phrases based on the context in which they are used.
The problem of ambiguity in natural language is a challenging one, but it is an important one to address. As natural language processing techniques become more sophisticated, it will become increasingly important to be able to understand natural language text accurately, even when it is ambiguous.
-
Handling Slang and Informal Language
NLP models may struggle with slang and informal language, which are prevalent in real-world communications. This is because these models are typically trained on formal, standard English.
There are a number of ways to address this issue. One approach is to augment the training data with slang and informal language. Another approach is to develop new models that are specifically trained on slang and informal language.
Addressing the issue of slang and informal language is an important area of research for NLP.
Future Trends in NLP
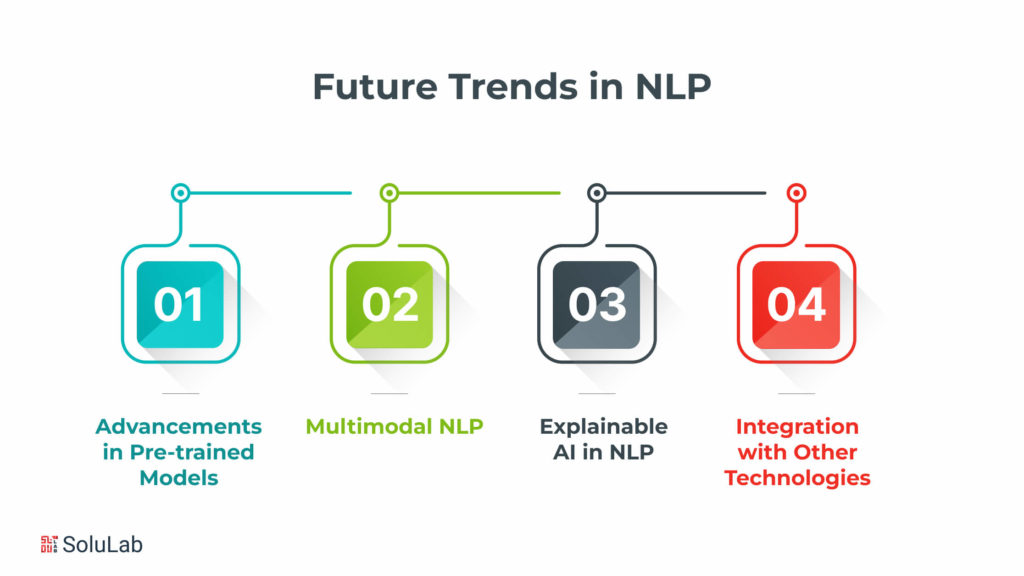
Peer into the future of NLP, where advancements in pre-trained models, multimodal NLP, conversational AI, and collaborations with emerging technologies promise to reshape language understanding. This chapter forecasts the trends that will define the evolution of NLP.
-
Advancements in Pre-trained Models
Continuous advancements in pre-trained language models are expected, which will enhance their language understanding capabilities and expand their applications. These models are trained on massive datasets of text and code, and they can learn to understand the meaning of words and phrases, as well as the relationships between them. This allows them to perform a wide variety of tasks, such as natural language inference, question answering, and text summarization.
As pre-trained language models continue to improve, they will become more and more capable of understanding and manipulating human language. This will have a significant impact on a wide range of industries, including healthcare, education, and customer service. For example, pre-trained language models can be used to help doctors diagnose diseases, create personalized learning experiences for students, and provide better customer service.
The potential applications of pre-trained language models are vast, and it is likely that we will see even more innovative uses for these models in the years to come.
-
Multimodal NLP
Integrating NLP with other modalities, such as images and videos, will lead to more comprehensive and context-aware models.
For example, an NLP model trained on text data alone may not be able to accurately identify the emotion of a person in a video. However, by incorporating video data, the NLP model can learn to identify the facial expressions and body language of the person, which can help it to better understand the emotions that they are feeling.
The integration of NLP with other modalities is still a relatively new field, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way that we interact with computers. By combining the power of NLP with the richness of other modalities, we can create more intelligent and user-friendly systems that can better understand the world around us.
-
Explainable AI in NLP
NLP models are often used to make decisions that can have a significant impact on people’s lives. To build trust in these models, it is important to make them more transparent and interpretable. This can be done by using visualization techniques to show how the model makes decisions, or by providing explanations for the model’s predictions.
-
Integration with Other Technologies
NLP is increasingly integrated with AR and VR to create immersive experiences.
NLP can be used to power chatbots in AR and VR environments, providing users with information and guidance.
NLP can also be used to generate text and audio in AR and VR, making experiences more realistic and engaging.
As NLP develops, we will see even more innovative ways to integrate it with AR and VR.
NLP in Industries
Explore how NLP transcends industry boundaries, revolutionizing healthcare, finance, education, legal, and customer service. This chapter delves into specific use cases, showcasing the transformative impact of NLP in various sectors.
1. Healthcare
NLP can be used to process vast amounts of medical literature and extract insights to improve clinical decision-making. For example, NLP can be used to identify patients who are at risk of developing a particular disease, which can then be used to provide patients with preventive care or to develop new treatments for the disease.
2. Finance
In the finance sector, NLP is employed for a variety of tasks, including:
- Sentiment analysis in stock trading: NLP can be used to analyze the sentiment of financial news articles and social media posts to help traders make informed decisions about which stocks to buy or sell.
- Fraud detection: NLP can be used to identify fraudulent transactions by analyzing patterns in customer behavior.
- Customer service automation: NLP can be used to automate customer service tasks, such as answering FAQs and providing account information.
NLP is a powerful tool that can be used to improve the efficiency and accuracy of financial processes. By employing NLP, financial institutions can better understand their customers, detect fraud, and provide better customer service.
3. E-commerce
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of artificial intelligence that gives computers the ability to understand and process human language. In e-commerce, NLP is used to power features that enhance the customer experience, including:
- Recommendation systems: NLP can be used to analyze customer reviews and other data to generate personalized recommendations for products and services.
- Chatbots: NLP can be used to create chatbots that can provide customer support 24/7.
- Review analysis: NLP can be used to analyze customer reviews to identify trends and patterns that can be used to improve product quality, customer service, and marketing campaigns.
NLP is a powerful tool that can be used to improve the e-commerce experience for customers.
4. Education
NLP applications in education include:
- Automated grading: NLP can be used to automatically grade student essays, tests, and other assignments. This can save teachers time and provide students with immediate feedback on their work.
- Language learning platforms: NLP can be used to create interactive language learning platforms that provide students with personalized feedback and instruction. These platforms can help students learn new languages like German or Chinese more effectively and efficiently.
- Personalized learning experiences: NLP can be used to track student progress and identify areas where students need additional support. This information can be used to create personalized learning experiences that are tailored to each student’s individual needs.
NLP is a powerful tool that can be used to improve the quality of education. By automating grading, creating interactive language learning platforms, and providing personalized learning experiences, NLP can help students learn more effectively and efficiently.
5. Legal
NLP is a subfield of Hybrid AI that deals with the interaction between computers and human language. In the legal field, NLP can be used to assist legal professionals by:
- Analyzing legal documents to extract information such as the parties involved, the facts of the case, and the legal issues.
- Summarizing legal documents to help legal professionals quickly identify the key points of a case.
- Generating legal documents, such as contracts and pleadings.
By automating these tasks, NLP can help legal professionals to improve their research efficiency and focus on the more complex aspects of their work.
6. Customer Service
Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by NLP can enhance customer service by providing quick responses and resolving queries. These tools can automate tasks typically handled by human customer service representatives, freeing up human representatives to focus on more complex issues. Additionally, chatbots and virtual assistants can improve customer satisfaction by reducing wait times and providing easy access to information.
Building NLP Projects
For those eager to embark on NLP projects, this chapter serves as a guide. From data preparation and model training to deployment, learn the steps involved in creating NLP applications. Discover the tools and frameworks that empower developers in building impactful NLP projects.
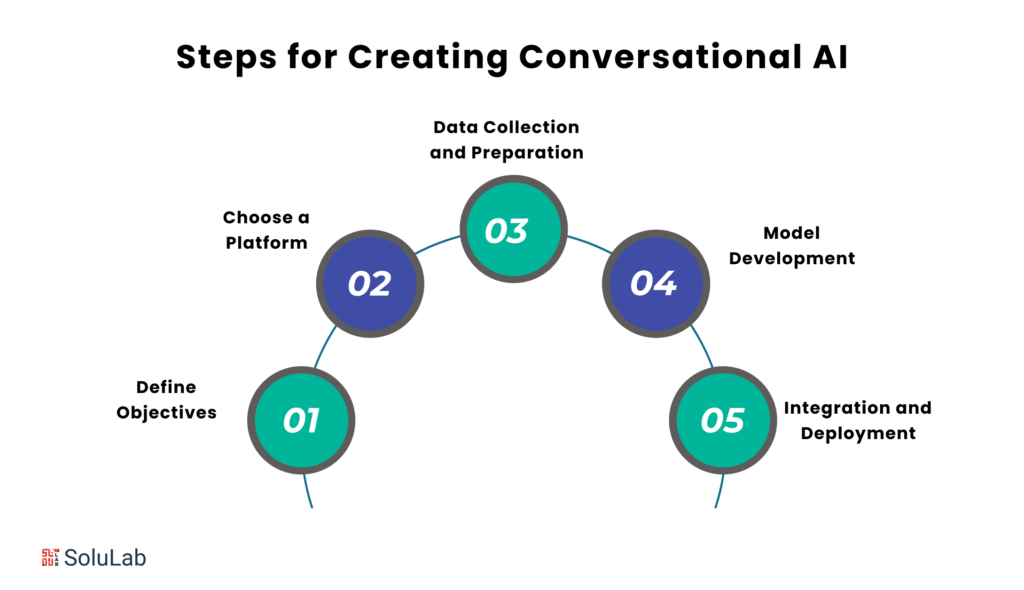
Steps to Develop an NLP Project
- Define Objectives: This step is critical to the success of any NLP project. It is important to clearly outline the goals and tasks that the project aims to achieve. This will help to ensure that the project stays on track and that the resources are used effectively.
- Data Collection: Once the objectives have been defined, the next step is to gather relevant and diverse datasets for training and testing the model. The size and quality of the dataset will have a significant impact on the performance of the model.
- Preprocessing: The data collected in the previous step will often need to be cleaned and prepared before it can be used to train the model. This process, known as preprocessing, can include tasks such as tokenization, normalization, and removal of stop words.
- Model Selection: Once the data has been prepared, the next step is to choose an appropriate NLP model. There are a variety of different NLP models available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The best model for a particular project will depend on the specific objectives and requirements.
- Training: The model selected in the previous step will need to be trained on the prepared dataset. This process involves feeding the data into the model and adjusting the model’s parameters so that it learns to perform the desired task.
Related: How is Geospatial AI Mapping the Transforming Analytics By Spatial Intelligence?
- Evaluation: Once the model has been trained, it is important to evaluate its performance using relevant metrics. This will help to ensure that the model is accurate and reliable.
- Deployment: The final step is to deploy the model into the desired application or system. This may involve integrating the model with a web application, a mobile app, or a business intelligence platform.
It is important to note that the steps outlined above are not always followed in a linear fashion. In some cases, it may be necessary to iterate through the steps several times in order to achieve the desired results. Additionally, the specific steps and tasks involved in each step may vary depending on the specific NLP project.
Tools and Libraries for NLP Development
- NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit) is a comprehensive library for natural language processing. It includes a wide range of features for text processing, such as tokenization, stemming, part-of-speech tagging, and named entity recognition. NLTK is a popular choice for NLP research and development, and it is also used in a variety of commercial applications.
- Spacy is an open-source library designed for NLP tasks such as tokenization and named entity recognition. It is built on top of NLTK, and it provides a number of additional features, such as support for multiple languages and a more user-friendly interface. Spacy is a popular choice for NLP developers, and it is used in a variety of commercial applications.
- Transformers (Hugging Face) is a library offering pre-trained models for various NLP applications. These models are trained on large datasets of text and code, and they can be used for a variety of tasks, such as text classification, summarization, and question-answering. Transformers are a popular choice for NLP developers, and they are used in a variety of commercial applications.
- TensorFlow and PyTorch are popular deep-learning frameworks used for building NLP models. These frameworks provide a variety of tools and libraries for training and deploying deep learning models. TensorFlow and PyTorch are a popular choice for NLP researchers and developers, and they are used in a variety of commercial applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Natural Language Processing (NLP) has evolved into a transformative force within the realm of artificial intelligence, bridging the gap between human communication and machine understanding. As we explored the fundamental principles, applications, techniques, and future trends in NLP, it became evident that NLP is a dynamic field with vast potential. The applications of NLP are multifaceted, permeating various industries such as healthcare, finance, e-commerce, education, legal, and customer service. From sentiment analysis to virtual assistants and language translation, NLP models have demonstrated their prowess in enhancing efficiency and user experiences. While the journey of NLP has witnessed significant milestones, it is crucial to acknowledge the challenges, including language ambiguity, bias, and ethical considerations. Navigating these hurdles responsibly is imperative to ensure the ethical and equitable use of NLP technologies. Looking forward, the future of NLP holds exciting prospects. Advancements in pre-trained models, the integration of NLP with other modalities, and the emphasis on explainable AI are paving the way for more sophisticated and context-aware language understanding.
In this world of innovation, SoluLab- an AI development company stands as a prominent player, contributing to the advancements in NLP and AI. With a commitment to delivering modern solutions, SoluLab harnesses the power of NLP models and techniques to address real-world challenges across industries. SoluLab’s expertise extends to developing customized NLP applications, from sentiment analysis tools to interactive chatbots. Leveraging state-of-the-art models and frameworks, SoluLab ensures that clients benefit from the latest advancements in NLP technology. For businesses seeking to leverage NLP for enhanced customer interactions, efficient data processing, and innovative applications, SoluLab serves as a strategic partner. Through a combination of domain knowledge, technical proficiency, and a commitment to ethical AI practices, SoluLab empowers organizations to unlock the full potential of NLP. As we navigate the future of AI and NLP, SoluLab remains at the forefront, driving innovation and delivering solutions that redefine how we interact with and harness the power of natural language. Hire our AI developers at SoluLab for a transformative NLP-driven journey into AI development services.
FAQs
1. What is Natural Language Processing (NLP)?
NLP is a subfield of artificial intelligence that focuses on enabling machines to understand, interpret, and generate human-like language. It involves the development of algorithms and models to process and analyze textual and spoken data.
2. How does NLP differ from traditional programming?
Unlike traditional programming, where explicit rules are coded, NLP relies on machine learning to decipher patterns and relationships in language. This flexibility allows NLP models to adapt to various linguistic nuances.
3. What are the core components of NLP?
NLP involves several core components, including tokenization (breaking down text into tokens), part-of-speech tagging, named entity recognition, parsing, and sentiment analysis.
4. How is NLP applied in real-world scenarios?
NLP finds applications in various industries, including healthcare, finance, e-commerce, education, legal, and customer service. It powers language translation, sentiment analysis, chatbots, and information extraction.
5. What challenges does NLP face?
Challenges in NLP include the ambiguity of language, difficulty in handling slang and informal language, biases in models, and ethical considerations. NLP models may struggle with multiple meanings of words based on context.
6. What are the future trends in NLP?
Future trends in NLP include advancements in pre-trained models, the integration of NLP with other technologies (multimodal NLP), a focus on explainable AI, and collaboration with emerging technologies like augmented reality and virtual reality.
7. How can businesses leverage NLP for innovation?
Businesses can leverage NLP for innovation by implementing applications such as sentiment analysis for customer feedback, chatbots for enhanced customer service, language translation for global reach, and information extraction for data insights.