According to McKinsey, adoption rates for electric vehicles are predicted to rise from 5% to 50% of new car sales in the 2020s, making this the decade of EVs.The rise in popularity of electric cars (EVs) has increased the demand for electric vehicle energy management systems that are both sustainable and efficient in controlling EV energy use.
Modern EV energy management systems are critical to the advancement of the EV revolution. These models aim to maximize energy consumption, reduce carbon emissions, and enhance the grid’s overall efficiency.
Smart EV energy management systems may be integrated into EV charging infrastructure to ensure that EVs are charged in the most cost-effective and ecologically responsible ways possible. Thus, a more sustainable future is facilitated by helping to balance the grid’s overall energy use with the help of artificial intelligence.
In this blog, we will discuss how advanced energy management systems drive the electric vehicle revolution and change our perception of energy utilization.
What is a Smart Energy EV Management System?
A smart energy management system specifically made for electric vehicles (EVs) is a powerful tool for energy optimization. It allows the grid to balance energy demand and guarantees that EV charging is done economically and efficiently.
These EV smart energy management systems use advanced algorithms and cloud-based platforms to adjust the charging load according to several parameters, including energy costs, pre-established regulations, the needs of EV owners, and the dynamic power grid and renewable sources.
Challenges to the Broad Use of Electric Vehicles
The following are the primary challenges that must be overcome to encourage the adoption of electric vehicle energy management systems.
-
Inadequate Infrastructure for Charging
The broad adoption of electric vehicles is severely hampered by the inadequate infrastructure for charging them. This is especially true in less developed or rural locations, where there are fewer charging stations, deterring drivers from switching to electric cars. A lack of charging infrastructure also brings on range anxiety, since drivers may fear that they won’t be able to locate a charging station while traveling long distances.
-
Overloaded Electrical Grids
The possibility of grid overloading is another obstacle to the widespread use of EVS electric vehicles. The demand for power rises as more and more electric vehicles are connected to the system, increasing the risk of grid overloading during times of peak demand. As a result, there may be issues like blackouts and other issues that compromise the reliability of the electrical system. Effective energy management systems for EVs are essential to prevent grid overloads and ensure stable energy distribution.
-
Low Availability of Minerals Supply
The insufficient availability of vital minerals and rare earth metals required for electric vehicle infrastructure is a significant obstacle to the extensive integration of electric cars. These minerals are needed to produce EV batteries and other necessary parts. However, there is a finite supply of these minerals in the world, and demand is rising quickly as more and more electric vehicles are driven off the road. The adoption of electric vehicles may be slowed as a result of supply chain interruptions and increased expenses for producers of electric vehicle energy.
-
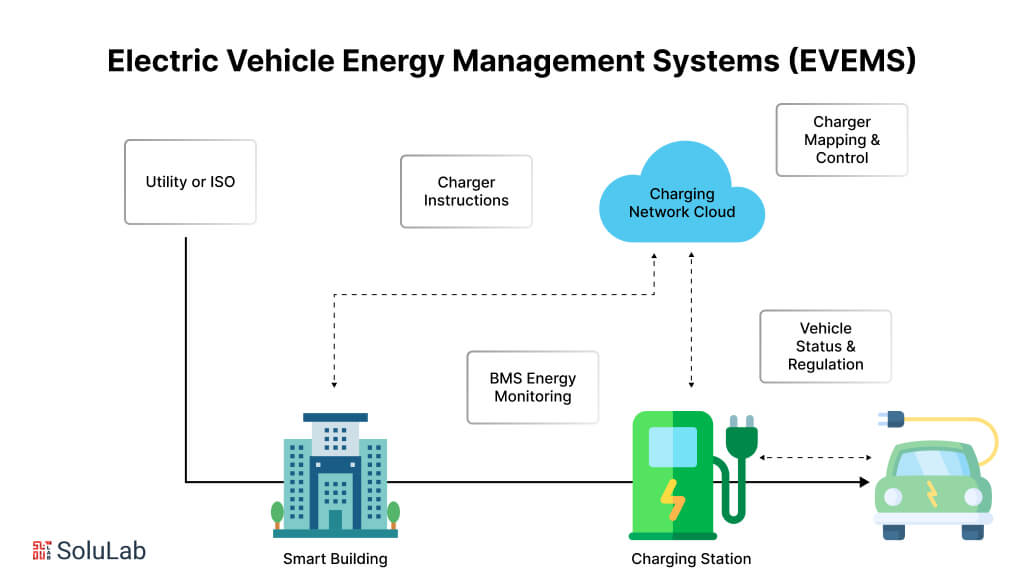
Energy Management Systems in EVs
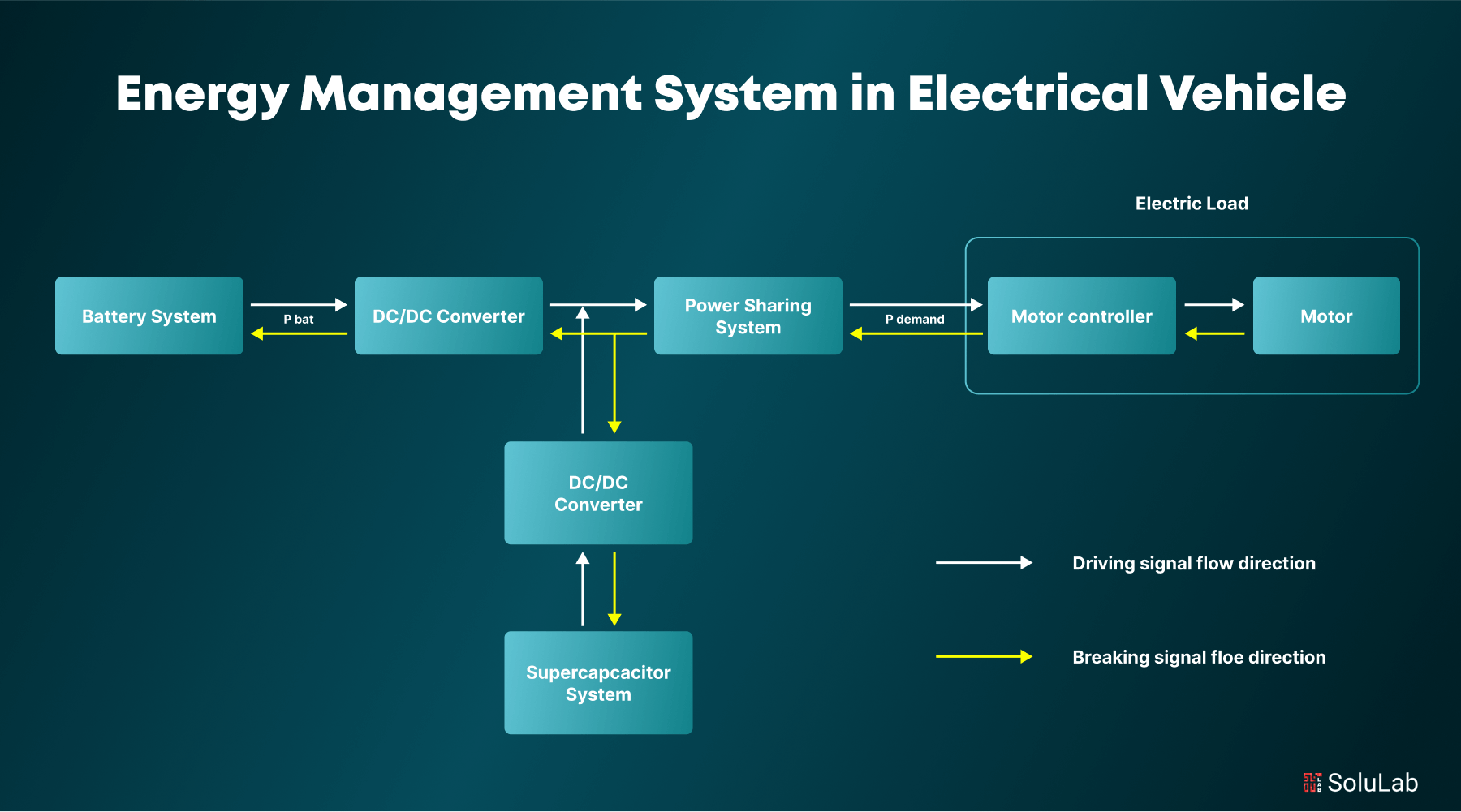
Managing energy efficiently within an EV is critical for optimizing battery life and performance, which is why a reliable Battery management system is essential for monitoring battery health, regulating energy flow, and ensuring safe and efficient operation. However, developing a robust energy management system in electric vehicles is challenging due to the need for real-time monitoring, balancing energy consumption, and integrating with renewable energy sources. These systems must be highly sophisticated to ensure the vehicle’s energy is used effectively without compromising performance.
-
Battery Technology and Costs
The cost and efficiency of batteries remain significant challenges. Although battery technology has improved, the high cost of batteries contributes to the overall expense of EVs. Additionally, the limited range of batteries requires advancements in EV energy management systems to maximize the driving distance between charges.
-
Consumer Acceptance and Awareness
Despite growing interest in EVs, some consumers are still hesitant due to concerns about range anxiety, charging times, and the long-term reliability of EVs. Overcoming these perceptions requires not only technological advancements but also educational efforts to raise awareness about the benefits and capabilities of EVs.
How Smart Energy Management Systems Can Help Overcome These Challenges?
Here’s how smart EV energy management systems and AI in transportation may assist in overcoming all of these challenges.
1. Utilizing Charging Infrastructure Efficiently
Smart energy management systems in electric vehicles can address the challenge of insufficient charging infrastructure by optimizing the use of existing resources. By analyzing factors such as energy consumption, renewable energy generation, and cost efficiency, these systems can maximize the usage of charging stations without overwhelming the power grid. This approach minimizes the need for costly infrastructure expansions while enhancing the reliability and accessibility of charging networks. Additionally, electric vehicle energy management systems and related mobile apps provide real-time data on charging station availability and locations, further improving the effectiveness of the charging infrastructure.
2. Load Balancing to Prevent Grid Overload
Energy management systems for electric vehicles offer a viable solution to the risk of grid overload. These sophisticated systems can balance the load on the power grid by shifting charging activities to off-peak times when electricity demand is lower. By doing so, Energy Management Systems (EMS) help prevent excessive strain on the grid during peak hours, ensuring stability and reliability. Moreover, these systems can optimize the integration of renewable energy by utilizing power generated during off-peak periods, such as when solar or wind energy is more readily available.
3. Battery Monitoring and Recycling to Reduce EVs’ Carbon Footprint
Effective battery monitoring and recycling are key to reducing the environmental impact of electric vehicles. Energy management systems in electric vehicles play a crucial role by collecting and analyzing data on battery health and usage patterns, allowing for optimal battery performance. Additionally, these systems ensure that batteries are recycled responsibly at the end of their life cycle, minimizing the ecological footprint of EVs. This process includes recovering valuable materials and rare earth elements used in battery manufacturing, thereby reducing the need for mining and lowering the carbon footprint associated with battery production.
Why Should You Use a Smart Energy Management Application for EVs?
A smart energy management application for EVs optimizes energy consumption, leading to cost savings, enhanced efficiency, and more sustainability. With the integration of GenAI in the Automotive Industry, such applications empower EV owners to control their vehicle’s battery consumption, manage charging times, and access other energy-related features. This advanced technology enhances decision-making for optimal energy use, ensuring that electric vehicles operate efficiently while contributing to a greener and more sustainable future.
-
Detailed User Analytics
The smart EV app’s ability to provide extensive data is one of its primary energy management advantages. The adoption of EV smart energy management systems can help analyze and monitor a user’s energy consumption patterns. In turn, this can assist owners of electric vehicles (EVs) in locating inefficient locations and in making data-driven decisions that optimize their energy use.
EV owners may acquire a complete insight into their energy use, charging history, and driving trends by leveraging sophisticated user statistics, such as those given by the Tesla app. Furthermore, tailored recommendations may be given to increase energy efficiency, such as lowering energy use throughout peak hours and maximizing charging times to minimize excessive energy waste. The execution of these recommendations may result in an increased range for the EV and a general increase in the driving experience.
-
Cost Savings
By optimizing energy use, Automotive AI and ML, an intelligent EV energy management system may lower charging expenses for electric car (EV) owners, increasing the general cost-effectiveness of their automobiles.
As an example, a powerful EV smart energy management system may identify charging infrastructure inefficiencies and continually monitor charging operations in real-time. By using this information to make educated decisions about where and how to power their electric automobiles, owners of EVs may reduce energy waste and related costs.
Moreover, modern EV energy management systems can automate the charging process. One strategy may be to plan the EV’s charging for off-peak hours when energy prices are lower or to use less energy during times of high demand.
-
Improved Experience for Users
Improved user experience is only one of the many benefits that EVs provide for energy management. Developing a strong EV energy management system may greatly improve the experience for the final user. First off, owners of electric vehicles can monitor and control their charging sessions with ease thanks to the user-friendly interface provided by EV energy management software, which increases convenience and flexibility.
To make charging easy and pleasurable, the energy management software for electric vehicles, for instance, may offer personalized charging schedules based on the user’s driving tastes and behaviors.
-
Enhances Synchronization
Some robust energy management systems (EMS) designed for electric cars (EVs) can improve communication between power grids, EV drivers, and the charging infrastructure. With the help of the EV smart energy management application, drivers of electric vehicles may plan the most effective routes and steer clear of needless detours by accessing real-time information on the availability and status of charging stations.
Additionally, by enabling two-way communication between EV drivers and power grids, the EV energy management program may improve the synchronization of energy supply and demand. The program ensures that electricity demands stay balanced and maintains grid stability by adjusting the billing rate based on the accessible capacity of the grid.
Through the use of the EV energy management system, which may provide them with insights into their energy consumption and carbon footprint, EV owners may additionally make informed decisions regarding their energy usage and its ecological impact. Additionally, by encouraging EV drivers to charge their cars during off-peak hours, the EV energy management system can help reduce peak demand, ease grid stress, and lessen the chance of blackouts.
-
Decrease in the Consumption of Essential Elements
An intelligent energy management app for electric vehicle owners may optimize their energy usage and offer tools to prolong the life of the battery and check its condition. The energy management software for EVs monitors temperature, charging habits, and battery consumption to help identify possible problems and make recommendations for enhancing battery performance. Consequently, the software can help reduce the quantity of rare earth materials required to build new EV batteries as well as the demand for them.
Furthermore, the EV energy management system and Generative AI automotive systems may offer information on correct battery disposal and recycling, which is critical for minimizing environmental effects.
Factors to Consider When Developing An Effective Smart Energy Management System
To develop the most effective energy management techniques for EV charging infrastructure, one must understand the primary elements involved. Here are some of the important considerations.
1. Maintain Awareness of the Existing Condition: To create a highly effective EV energy management system, it is critical to investigate and analyze the present charging framework and energy grid. This entails understanding energy demand and supply patterns, as well as detecting potential pain areas. By evaluating the data, analysts may find holes in the framework, increasing the value of the smart energy management system development. This also helps to build and implement an intelligent energy management framework that is tailored to the unique demands and problems of the localized energy environment.
2. Integration and Interoperability: Integration and interoperability are critical features of smart energy management for electric vehicles and their current revolution. It entails merging several systems and technologies to produce a streamlined and efficient energy environment. For example, EV charging stations should be linked with the energy grid to allow for efficient energy distribution, and the charging process should be compatible with EVs from various manufacturers and models. This guarantees that the charging procedure is accessible to all-electric vehicles.
3. Selecting the Appropriate Hardware and Software: Choosing the right hardware and software is critical to effectively creating a successful energy management system for electric vehicles. One should carefully pick gear that is compatible with the EV charging infrastructure and capable of meeting the load-balancing criteria. Similarly, to find appropriate charging times, EV charging energy management software must be developed that connects with the hardware and does data analytics. Additionally, the software has to feature an easy-to-use interface that makes managing and monitoring the charging process straightforward. By meticulously choosing the relevant features, EV charging infrastructure operators may guarantee that their smart EV energy management system is effective in optimizing energy use, lowering costs, and concurrently lowering their carbon footprint.
4. Scalability: As the demand for EVs increases, it is critical to guarantee that the infrastructure and energy systems can keep up. It involves charging station accessibility, grid capacity, and renewable energy supply. Investment in novel technologies like smart grids and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems can assist in improving scalability. Smart networks may improve energy distribution to EV charging stations, while V2G systems enable EVs to store and return energy to the grid amid peak demand. This improves grid stability and dependability, hence enhancing EV charging energy management.
5. Managing Cyber Risk: As the system’s connectivity increases, it becomes increasingly exposed to cyber threats such as hacking, data breaches, and ransomware attacks. These risks can disrupt the grid and cause power outages, jeopardizing the system’s security and dependability. For example, the 2015 Ukraine power system cyber-attack was brought about by a malware infestation, resulting in power disruptions in various locations. Strong cybersecurity measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption, are required to safeguard the smart energy management system from cyber-attacks. Regular security assessments must be done to quickly detect and remedy possible vulnerabilities.
The Bottom Line
Incorporating a robust energy management system in electric vehicles can significantly enhance overall performance by optimizing energy consumption, improving battery efficiency, and ensuring sustainable operation. By effectively managing how and when energy is used, these systems can extend battery life, reduce operational costs, and increase the driving range of electric vehicles. Additionally, electric vehicle energy management systems and Generative AI contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly transportation solution by integrating renewable energy sources and optimizing charging patterns.
Despite the clear benefits, implementing an energy management system for electric vehicles comes with its own set of challenges, including the complexity of integrating with existing infrastructure, ensuring real-time responsiveness, and managing large amounts of data. As an AI development company, SoluLab helped Turboplus improve its e-charging app by adding key features for iOS and Android. We developed charging station mapping, charging status, and remote charger control. Our contributions improved user experience, making EV charging and efficient artificial general intelligence enables us to develop intelligent, adaptive systems that enhance the performance and sustainability of electric vehicles. Contact us to learn how we can help you overcome these challenges and drive innovation in the electric vehicle industry.
FAQs
1. What is an Energy Management System (EMS) in electric vehicles?
An Energy Management System (EMS) in electric vehicles is a sophisticated technology designed to monitor, control, and optimize energy usage within the vehicle. It ensures that the battery is used efficiently, manages charging schedules, and integrates renewable energy sources when possible. The EMS helps extend the vehicle’s range, improve battery life, and reduce overall energy costs, making the vehicle more efficient and sustainable.
2. How does an Energy Management System improve battery performance in electric vehicles?
An energy management system in electrical vehicles improves battery performance by monitoring real-time data on battery usage, health, and charging patterns. It optimizes the energy flow to and from the battery, ensuring that it operates within optimal parameters. This not only extends the battery’s lifespan but also enhances the vehicle’s driving range by maximizing energy efficiency.
3. What role does an EMS play in preventing grid overload?
An electric vehicle energy management system plays a crucial role in preventing grid overload by intelligently managing the timing of vehicle charging. The EMS can shift charging to off-peak hours when the demand for electricity is lower, balancing the load on the grid. This helps avoid excessive strain during peak hours, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply.
4. What challenges are associated with implementing an Energy Management System in EVs?
Implementing an energy management system for electric vehicles presents several challenges, such as the complexity of integrating the system with existing infrastructure, managing large amounts of real-time data, and ensuring the system is responsive and adaptive to changing conditions. Overcoming these challenges requires advanced AI and machine learning techniques, which can be provided by experienced AI development companies like SoluLab.
5. How can SoluLab assist in developing an Energy Management System for EVs?
SoluLab, as an AI development company, can assist in developing a customized energy management system electric vehicle solution by leveraging unique AI and machine learning technologies. We provide tailored solutions that address the unique challenges of EMS implementation, ensuring optimized performance, sustainability, and integration with existing systems. Contact us to discuss how we can help enhance your electric vehicle projects with advanced energy management solutions.