
Carbon credit exchanges have developed as cutting-edge responses to the problem of reducing greenhouse gas emissions as worries about climate change and environmental sustainability continue to rise. These markets provide venues where businesses and private persons may purchase and sell carbon credits, reducing carbon footprints and assisting initiatives that encourage sustainable practices. The idea of what carbon credit marketplaces are, their importance, and how they contribute to a cleaner future will all be covered in this blog article.
What is a Carbon Credit Marketplace?
A carbon credit marketplace is a digital platform that facilitates the trading of carbon credits between entities looking to offset their carbon emissions and those involved in projects that generate verifiable emission reductions. Carbon credits represent the equivalent of one metric ton of carbon dioxide (or another greenhouse gas) that has been reduced, avoided, or removed from the atmosphere.
How Does a Carbon Credit Marketplace Work?
Carbon credit marketplaces operate on the principle of supply and demand. Project developers, such as renewable energy producers, reforestation initiatives, or energy efficiency programs, generate carbon credits through their efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These credits are then listed on the marketplace for potential buyers.
Buyers, such as businesses or individuals seeking to offset their carbon emissions, can browse through the available credits and purchase them to compensate for their own environmental impact. By purchasing carbon credits, buyers effectively support and finance projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a more sustainable future.
What are the Benefits of Carbon Credit Marketplaces?
-
Emissions Reduction
Carbon credit marketplaces incentivize the implementation of projects that directly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By connecting emission reduction projects with interested buyers, these marketplaces drive real environmental change.
-
Financial Support for Sustainable Projects
The revenue generated from carbon credit sales provides financial support for projects aimed at mitigating climate change. This funding can enable the development and expansion of renewable energy installations, reforestation initiatives, and other sustainability-focused projects.
-
Market Efficiency and Transparency
Carbon credit marketplaces provide a transparent platform for buyers and sellers to engage in transactions. They ensure that carbon credits are properly verified and tracked, instilling trust and confidence in the marketplace.
-
Global Impact
Carbon credit marketplaces transcend geographical boundaries, allowing organizations and individuals worldwide to participate in emissions reduction efforts. This global reach maximizes the potential for positive environmental impact on a larger scale.
Read Our Blog Post: Top 10 Carbon Crypto Companies to Watch Out in 2023
What are the Different Types of Carbon Credits?
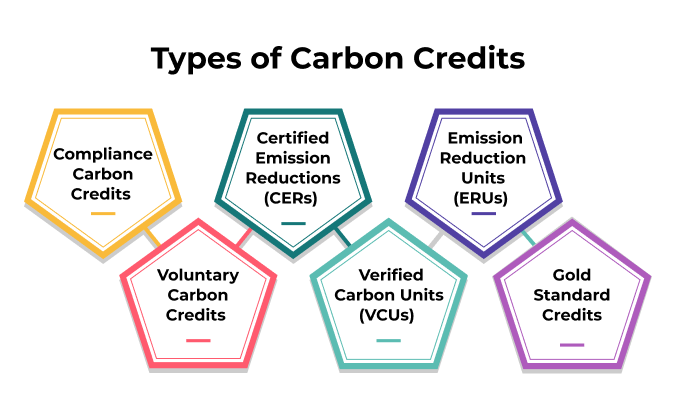
In the pursuit of combating climate change and promoting sustainable practices, carbon credits have gained significant attention as valuable tools. These credits represent the reduction or removal of greenhouse gas emissions from the atmosphere. However, it’s important to understand that not all carbon credits are the same. In this article, we will explore the two different types of carbon credits: “Compliance” and “Voluntary,” their characteristics, and how they contribute to the global effort towards carbon neutrality.
-
Compliance Carbon Credits
Compliance carbon credits, also known as regulatory or mandatory carbon credits, are typically associated with government-imposed regulations or international agreements aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions. These credits are issued based on compliance with specific emission reduction targets or standards.
-
Certified Emission Reductions (CERs)
CERs are generated through Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) projects under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). These projects are typically implemented in developing countries and contribute to sustainable development while reducing emissions. CERs can be used by companies to comply with their emission reduction obligations.
-
Emission Reduction Units (ERUs)
ERUs are created through Joint Implementation (JI) projects, which involve emission reduction efforts in developed countries. JI projects allow countries with emission reduction commitments to invest in emission reduction projects in other participating countries. ERUs can be used by companies to comply with their emission reduction targets.
-
Voluntary Carbon Credits
Voluntary carbon credits, as the name suggests, are not tied to any regulatory requirements but are purchased voluntarily by individuals, organizations, or businesses aiming to offset their carbon footprints and demonstrate environmental responsibility. These credits are typically used to support projects that go beyond regulatory requirements and make additional emission reductions.
-
Verified Carbon Units (VCUs)
VCUs are generated from projects that follow recognized methodologies and undergo rigorous third-party verification. These projects can include renewable energy installations, reforestation and afforestation efforts, energy efficiency initiatives, and more. VCUs allow individuals and organizations to voluntarily offset their emissions and demonstrate their sustainability commitment.
-
Gold Standard Credits
Gold Standard credits are a type of voluntary carbon credit that meet rigorous environmental and social criteria. They are issued to projects that demonstrate exceptional sustainable development outcomes, such as poverty reduction, biodiversity protection, and community engagement, in addition to emission reductions. Gold Standard credits provide an even higher level of confidence and credibility to buyers.
Check Out Our PR Article: SoluLab Bridging the Gap Between Technology And Innovation
Carbon Credits Explained: How Do Carbon Credits Work?
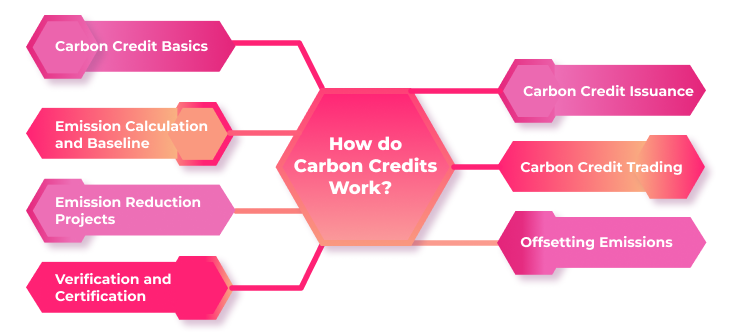
As the world tackles the challenges of climate change, carbon credits have emerged as a crucial mechanism to incentivize and facilitate the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how carbon credits work, their purpose, and the underlying mechanisms that drive their effectiveness in combating climate change.
-
Carbon Credit Basics
A carbon credit represents a unit of measurement that quantifies the reduction, avoidance, or removal of one metric ton of carbon dioxide (CO2) or its equivalent in other greenhouse gases. The concept is based on the principle that each emission reduction has a positive environmental impact and contributes to achieving carbon neutrality.
-
Emission Calculation and Baseline
To initiate the process, a baseline or reference level of emissions is established. This baseline represents the projected amount of emissions that would occur without any emission reduction efforts. It serves as a benchmark against which the actual emissions are measured to determine carbon credit eligibility.
-
Emission Reduction Projects
Entities, such as businesses or organizations, can engage in emission reduction projects to lower their carbon footprint. These projects can encompass various strategies, including the adoption of renewable energy, energy efficiency improvements, afforestation or reforestation initiatives, or the implementation of clean technologies. The emission reductions achieved through these projects form the basis for carbon credits.
-
Verification and Certification
Once an emission reduction project is implemented, it undergoes a rigorous verification and certification process. Independent third-party organizations assess the project’s adherence to specific methodologies and criteria. The verification ensures the accuracy and validity of the emission reductions claimed, instilling confidence in the integrity of the carbon credits.
-
Carbon Credit Issuance
Upon successful verification, carbon credits are issued to the project owner or entity responsible for the emission reduction efforts. Each carbon credit represents one metric ton of CO2 equivalent reduction. These credits are registered and assigned a unique identification number to maintain traceability and prevent double-counting.
-
Carbon Credit Trading
The trading of carbon credits occurs through various mechanisms, including compliance markets and voluntary markets. Compliance markets operate under regulatory frameworks, where companies with emission reduction obligations can buy and sell carbon credits to meet their targets. Voluntary markets, on the other hand, facilitate the trading of carbon credits on a voluntary basis, allowing individuals and organizations to offset their carbon footprint or demonstrate environmental responsibility.
-
Offsetting Emissions
Buyers of carbon credits can use them to offset their own emissions. By purchasing carbon credits, individuals or organizations effectively finance emission reduction projects and contribute to global efforts in combating climate change. The offsetting process involves retiring the purchased carbon credits, ensuring that they are not reused or double-counted.
Why do People Use Carbon Credits?
As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and the need for sustainable practices, carbon credits have gained significant traction as a valuable tool in the fight against greenhouse gas emissions. This article explores the reasons why individuals, organizations, and businesses choose to use carbon credits and highlights the benefits associated with their utilization.
-
Mitigating Carbon Footprint
One of the primary motivations for using carbon credits is the desire to mitigate one’s carbon footprint. By purchasing carbon credits, individuals and organizations can offset their own greenhouse gas emissions, taking responsibility for their environmental impact. This proactive approach allows them to contribute to the reduction of global emissions and support projects that foster sustainability.
-
Demonstrating Environmental Responsibility
Using carbon credits serves as a tangible demonstration of environmental responsibility. It sends a clear message that individuals and organizations are committed to mitigating climate change and taking action beyond regulatory requirements. By investing in emission reduction projects through carbon credits, they showcase their dedication to sustainability and inspire others to follow suit.
-
Achieving Carbon Neutrality
Carbon credits play a pivotal role in achieving carbon neutrality goals. By calculating and offsetting their emissions through the purchase of carbon credits, individuals and organizations can balance out their carbon footprints. This commitment to carbon neutrality aligns with the global objective of limiting global warming and transitioning to a low-carbon economy.
-
Supporting Sustainable Projects
Carbon credits provide a valuable source of financial support for sustainable projects. When individuals or organizations purchase carbon credits, they contribute to funding emission reduction initiatives, renewable energy projects, reforestation efforts, and other sustainability-focused endeavors. This financial backing not only promotes sustainable practices but also encourages the development and expansion of environmentally friendly projects.
-
Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
For businesses operating within regulatory frameworks, using carbon credits helps them meet mandatory emission reduction targets and comply with environmental regulations. By purchasing carbon credits, companies can offset a portion of their emissions, demonstrating their commitment to meeting regulatory obligations while supporting sustainable projects.
-
Enhancing Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Carbon credits align with the principles of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) by enabling businesses to address their environmental impact and engage in sustainable practices. By incorporating carbon credits into their CSR initiatives, companies can demonstrate their commitment to the environment, strengthen their brand reputation, and attract environmentally conscious customers and partners.
-
Encouraging Innovation and Market Transformation
The utilization of carbon credits fosters innovation and market transformation. The demand for carbon credits incentivizes the development of new emission-reduction technologies, clean energy solutions, and sustainable practices. This drives market forces towards a low-carbon economy, encouraging businesses to adopt innovative approaches and transition to more sustainable business models.
Launch Your Own Carbon Credit NFT Marketplace with SoluLab
What do You Need to Know Before Using Carbon Credits?
How do carbon credits work and have gained prominence? As a tool to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainability. However, before diving into the world of carbon credits, it is essential to understand certain key aspects to ensure their effective and meaningful utilization. In this article, we will explore what you need to know before using carbon credits to maximize their environmental impact and align with your sustainability goals.
-
Carbon Footprint Calculation
Before purchasing carbon credits, it is crucial to calculate your carbon footprint accurately. Understanding your carbon emissions across various activities, such as energy consumption, transportation, and waste generation, provides a baseline to assess your offsetting needs. Consider utilizing reputable carbon calculators or engaging sustainability experts to help you in this process.
-
Setting Clear Objectives
Define your objectives and goals for using carbon credits. Whether it is achieving carbon neutrality, supporting specific emission reduction projects, or aligning with regulatory requirements, clarifying your intentions will guide your decision-making process. Clearly outlining your objectives will also help you choose the most appropriate carbon credit projects to support.
-
Quality Assurance and Certification
Ensure that the carbon credits you purchase are from verified and certified sources. Look for internationally recognized standards and certifications, such as the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) or Gold Standard. These certifications guarantee that the emission reductions associated with the credits are accurately measured, verified by independent auditors, and adhere to robust methodologies.
-
Additionality and Permanence
Consider the concept of additionality when selecting carbon credits. Additionality ensures that the emission reductions achieved through supported projects would not have occurred without the financial support from carbon credit sales. Projects with strong additionality contribute to real and tangible emission reductions. Additionally, assess the permanence of the emission reductions to ensure the long-term sustainability of the projects you choose to support.
-
Project Selection and Impact
Research and evaluate the projects associated with the carbon credits. Understand the types of emission reduction activities, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, reforestation, or waste management, and assess their alignment with your sustainability values. Consider the geographic location of the projects, their social and environmental co-benefits, and the transparency of project information to gauge their impact and credibility.
Check Out Our Press Release: SoluLab Honored By GoodFirms as the Winner of the Trusted Choice Award 2023
What are the Examples of Companies Using Carbon Credits?
Numerous companies across different industries have recognized the importance of reducing their carbon footprint and have implemented carbon credit initiatives as part of their sustainability strategies. Here are a few examples of companies that have utilized carbon credits:
1. Microsoft
Microsoft has made a commitment to being carbon negative by 2030. To achieve this, they have implemented a carbon fee and have been purchasing carbon credits to offset their remaining emissions. They have also launched the Microsoft Carbon Removal Marketplace, which allows customers to purchase verified carbon removal credits.
2. Salesforce
Salesforce, a cloud computing company, has taken significant steps to reduce its environmental impact. They achieved net-zero greenhouse gas emissions in 2017 and continue to offset emissions through the purchase of high-quality carbon credits. They have invested in projects that promote renewable energy, energy efficiency, and reforestation.
3. Unilever
Unilever, a multinational consumer goods company, has set ambitious sustainability goals, including becoming carbon positive by 2030. They have been actively investing in renewable energy projects and have used carbon credits to offset their emissions. Unilever focuses on projects that align with its values and contribute to social and environmental co-benefits.
4. Delta Air Lines
Delta Air Lines, a major airline, has implemented various measures to reduce its carbon emissions. In addition to fleet efficiency improvements, they have invested in carbon offset projects, such as forest conservation and renewable energy. Delta offers customers the option to purchase carbon offsets to mitigate the emissions associated with their flights.
5. Apple
Apple has made significant progress in reducing its carbon footprint and has committed to being carbon-neutral across its entire supply chain by 2030. They have invested in renewable energy projects, improved energy efficiency, and implemented carbon offset initiatives. Apple has supported projects like forest conservation and the development of solar and wind farms.
Conclusion
What is a carbon credit marketplace? Creating a carbon credit marketplace is a complex undertaking that requires careful planning, collaboration, and a deep understanding of the principles underlying carbon offsetting. In this ultimate guide to creating a carbon credit marketplace, we have explored the key components and considerations involved in establishing an effective and successful platform.
From understanding the concept of carbon credits and their role in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions to the technical and operational aspects of building a marketplace, we have covered a wide range of topics. We have delved into the importance of robust verification and certification processes, the significance of transparency and traceability, and the role of technology in facilitating transactions and ensuring market integrity.
We have also discussed the various stakeholders involved in a carbon credit marketplace, including project developers, buyers, and verifiers, and emphasized the importance of fostering partnerships and collaboration among these actors. Furthermore, we have highlighted the need to align with internationally recognized standards and methodologies to ensure the credibility and quality of the carbon credits traded on the marketplace.
SoluLab, a well-known company in the field of carbon credit marketplace development, has a specialization in providing outstanding carbon credit marketplace development services and solutions. With a team of expert professionals, SoluLab has achieved remarkable success in creating Carbon NFTs for a wide range of business models. For more information, contact SoluLab today.
FAQs
1. What is a carbon credit marketplace?
A carbon credit marketplace is a platform or system that facilitates the buying and selling of carbon credits. It serves as a marketplace where buyers, such as companies or individuals, can purchase carbon credits to offset their carbon emissions, while sellers, such as emission reduction project owners, can sell their verified emission reductions in the form of carbon credits.
2. What is a carbon credit? Why create a carbon credit marketplace?
Creating a carbon credit marketplace is important to promote and incentivize emission reduction efforts. It provides a transparent and efficient platform for buyers and sellers to engage in carbon credit transactions, encouraging the development of emission reduction projects and supporting the transition to a low-carbon economy.
3. How do carbon credits work?
A carbon credit marketplace typically operates by bringing together buyers and sellers of carbon credits. Sellers can register their emission reduction projects and have them verified by independent auditors. Once verified, the emission reductions are converted into carbon credits, which can be listed on the marketplace. Buyers can browse and purchase these credits to offset their own carbon emissions.
4. What are carbon credits and their key components?
A carbon credit marketplace consists of several key components, including project registration and verification processes, credit listing and trading mechanisms, robust tracking and accounting systems, and secure payment and settlement methods. It should also incorporate transparent reporting and auditing mechanisms to ensure the integrity and credibility of the marketplace.






