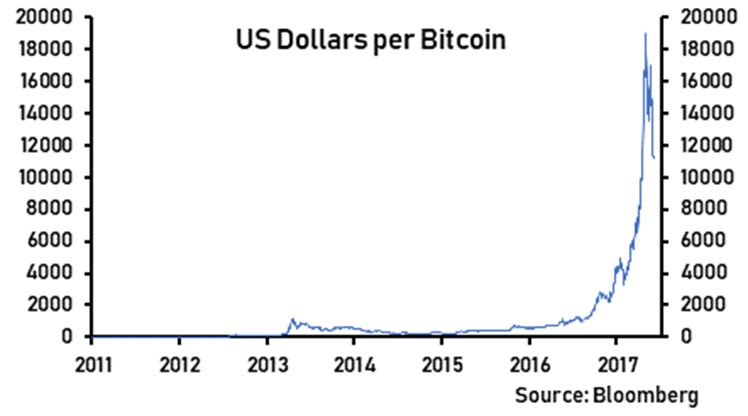
For all the investor hype around Bitcoin, which became an international sensation in the second half of 2017, the cryptocurrency still lacks the fundamental attributes of money and is behaving more like a speculative commodity. Ultimately, Bitcoin’s star could fade as rival cryptocurrencies overcome its inherent technical flaws and governments continue to crack-down on its use.
Blockchain technology, which is beginning to gain significant attention, possesses far more future potential than Bitcoin. There is just one snag, which has heretofore been largely ignored: energy use.
Bitcoin Basics
Created in 2009, Bitcoin is the first cryptocurrency released. For much of its existence, it was consigned to the periphery of finance, failing to generate much interest. However, in the latter half of 2017, Bitcoin mania descended upon investors who began piling into the cryptocurrency, with prices rising exponentially. To many, it was reminiscent of Dutch ‘tulip mania’ from the 1600s.
Bitcoin, unlike typical notes and coins, is not backed by a single central bank.
It was created by an unidentified developer who goes by the name of Satoshi Nakamoto; lending a certain mystique to the cryptocurrency.
Its developer purportedly developed Bitcoin as an alternative to national currencies because he was sceptical of the vast QE programmes national central banks undertook following the 2008 financial crisis.
Bitcoin is not alone as a cryptocurrency, although it garners most of the attention and has the largest market capitalisation. There are over 1,300 different types of cryptocurrencies and new ones spring up as creators try to overcome the technical challenges faced by rivals.
Bitcoin Basics
Bitcoin uses “blockchain technology.” This phrase has become synonymous with Bitcoin – in reality, most cryptocurrencies use blockchain technology. The blockchain, as it is commonly known, is a continuously updated, distributed digital ledger. It permanently records all transactions and, by design, it is practically unalterable.
Most importantly, it provides both parties with a transaction with the assurance provided by an unbiased third party, without the expense of intermediation. The word ‘block’ comes from the fact that transactions are bundled together to form a new ‘block’. Meanwhile, when it is created, it is combined like a ‘chain’ to all previous blocks.
The blockchain ledger replicates all historical transactions across millions of computers. This prevents a single user from tampering with history, as all records across the computers have to be in accordance with one another. Information can only be added to the blockchain, not altered. Furthermore, since transactions take place on the blockchain – which is public – a transaction of an item can be verified as unique. Finally, because the transaction does not require a third party (such as a bank) to adjudicate it, blockchain technology is decentralised.
Bitcoin transactions are ‘verified’ through a global computer network that performs the computational heavy lifting required to facilitate secure transactions. Verification takes place through the process of cryptography – mathematical code. Computers are required to provide a unique solution to a given challenge. This verification solves the double-spending problem. It prevents a user copying coins so as to appear to pay another user. Because this verification process is extremely energy-intensive, the bitcoin ‘miner,’ as they are known, who successfully solves the problem is rewarded with bitcoins for their efforts.
Moreover, computers are competing with one other to solve the challenge. There is an upper limit of 21
million bitcoins that can be mined, and to date, 16.75 million have been mined. Therefore, individuals who verify the transactions will no longer receive a reward as the upper supply limit is reached.
The expectation is that once the supply of bitcoins has been exhausted, transaction fees will be introduced in order to maintain an incentive for ‘miners’ to continue to verify transactions. One must remember that the process of verifying transactions is extremely energy intensive and ‘miners’ therefore require a reward for their efforts. However, the introduction of transaction fees is likely to discourage users, as the transaction costs fall on them. This provides an opportunity for rival coins with a superior technological concept that have virtually zero transaction costs.
<h2″>The Problem of Power
The process of cryptography is extremely energy-intensive. Racks of powerful computer graphics cards are required to process advanced calculations to verify transactions. Some estimate the annual total power consumption from the ‘mining’ industry to be greater than that of Ireland. What is more, most of the Bitcoin activity takes place in China, which uses mostly coal-fired plants. In short, Bitcoin transactions are ‘killing the planet’.
So far, a crisis has been averted as ‘mining’ equipment has become vastly more efficient since 2009. But it is unlikely that such gains are repeatable indefinitely. There is also the question of what happens if cryptocurrencies eventually become widely adopted. While there is active research in the field, a breakthrough has yet to materialise. Energy consumption, therefore, remains a significant obstacle to worldwide adoption.
The Potential of Blockchain Technology
If Bitcoin, through the use of the blockchain, is designed to retire burdensome middlemen, what other bureaucratic authorities can blockchain technology help render irrelevant?
There is a lot of potential behind the use of smart contracts. Smart contracts are agreements that can be understood and executed using machines. This renders a third-party arbitrator irrelevant. Moreover, the smart contract can also perform due diligence duties. An example of a smart contract is a car lease programmed to prevent an individual from driving their car if they are seriously behind on their payments.
It is worth stressing that these concepts are in their infancy and are a topic of discussion rather than an inevitable outcome. In the case of the smart car contract, there is the issue of an individual, behind on their payments, being remotely blocked from driving their car in the case of an emergency. This would be unacceptable. Such inflexibility leaves complex problems that will require careful thought in order to have smart contracts that factor in the human quality of flexibility.
In a more positive example, blockchain technology could be used to create ‘coloured’ coins whereby certain properties are assigned to a currency. One such property would be the possibility to view previous transactions to see generally where the coin has been. This could be used to spot money from criminals or from sanctioned countries. Therefore, it would be possible for a user to block transactions from criminal individuals.
Finally, blockchain could prove to be a controversial technology, as all information is stored forever. This would appear to violate the right to be forgotten. In the end, a solution will need to be devised that affords sufficient privacy to users.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology could be another case where an adaptation of an original invention goes on to eclipse its original function. For example, the internet was born out of a US defence project (to provide resilient communications in the event of a cold war) that went on to revolutionise twenty-first-century business and communication.
Today, the internet’s spectacular rise leaves people wondering how they ever lived without it. Could blockchain technology go on to become another core utility, long after Bitcoin becomes obsolete? A lot still hinges on the ability to store and process vast quantities of data without expending unacceptable amounts of fossil fuel energy. At this stage, it is too soon to tell.




