
Blockchain technology has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation, reshaping the way we manage digital transactions and data. In this introduction, we’ll explore the fundamentals of blockchain technology, its inner workings, and its far-reaching applications in the modern digital landscape.
At its core, a blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger. It comprises a chain of blocks, with each block containing a record of multiple transactions. This technology is characterized by its transparency, security, and immutability. Unlike centralized databases, blockchain operates on a network of computers (nodes), enabling every participant to view and validate transactions. Once data is recorded in a block and added to the chain, it becomes exceedingly challenging to alter, ensuring the integrity of the information.
In the digital age, blockchain technology has emerged as a game-changer, offering transparency, security, and efficiency in various domains. From blockchain platforms to development services and consulting, the blockchain ecosystem continues to expand, presenting abundant opportunities for businesses and developers alike. Blockchain technology has given rise to a plethora of companies specializing in various aspects of this revolutionary tech. These companies range from blockchain platform developers to blockchain development service providers.
How Does Blockchain Work?
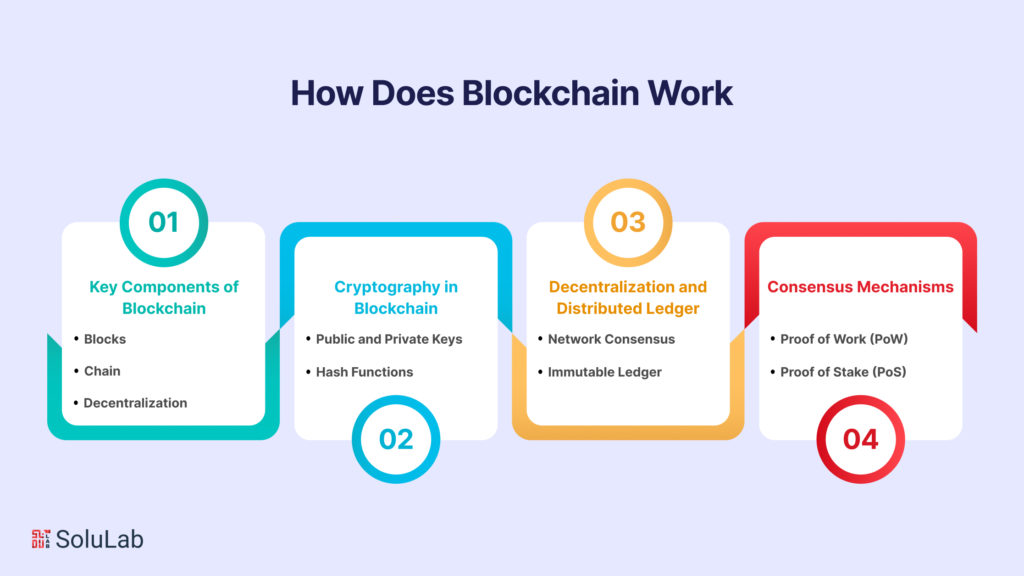
Blockchain technology has garnered significant attention for its potential to revolutionize various industries, from finance to supply chain management. Understanding how blockchain works is essential to grasp its transformative power. This article delves into the key components of blockchain, cryptography’s role, decentralization, and consensus mechanisms.
Key Components of Blockchain
At its core, a blockchain is a distributed and immutable ledger in blockchain that records transactions across a network of computers. Its key components include:
-
Blocks
These are containers that store data about transactions. Each block contains a group of transactions and has a unique identifier called a “hash.”
-
Chain
Blocks are linked together in chronological order, forming a chain. The previous block’s hash is included in each subsequent block, creating a secure connection.
-
Decentralization
Blockchain operates on a decentralized network of computers (nodes). Each node has a copy of the entire blockchain, ensuring redundancy and security.
Cryptography in Blockchain
Blockchain relies heavily on cryptographic techniques to secure data and ensure privacy. Key cryptographic aspects include:
Read Our Blog: Top Blockchain Technology Companies in 2024
-
Public and Private Keys
Users have a pair of cryptographic keys—a public key for identification and a private key for digital signatures. Transactions are signed with the private key and verified with the public key.
-
Hash Functions
Transactions and blocks are transformed into fixed-length alphanumeric strings using cryptographic hash functions. Even minor changes in data result in significantly different hash values, enhancing security.
Decentralization and Distributed Ledger
Decentralization is a fundamental principle of blockchain technology. Unlike traditional centralized systems, blockchain operates on a distributed ledger:
-
Network Consensus
Transactions are validated through a consensus mechanism, typically requiring a majority of nodes to agree on their validity.
-
Immutable Ledger
Once a block is added to the blockchain, it becomes virtually impossible to alter past transactions due to cryptographic integrity and the consensus mechanism.
Consensus Mechanisms (e.g., Proof of Work, Proof of Stake)
Consensus mechanisms are pivotal to blockchain’s functionality. They ensure agreement among network participants regarding transaction validity. Two prominent mechanisms are:
-
Proof of Work (PoW)
PoW requires miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles to add new blocks to the chain. This process demands significant computational power and energy but is highly secure.
-
Proof of Stake (PoS)
PoS relies on validators who are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. PoS is more energy-efficient than PoW.
What are the Fundamental Components and Characteristics of a Blockchain Network?
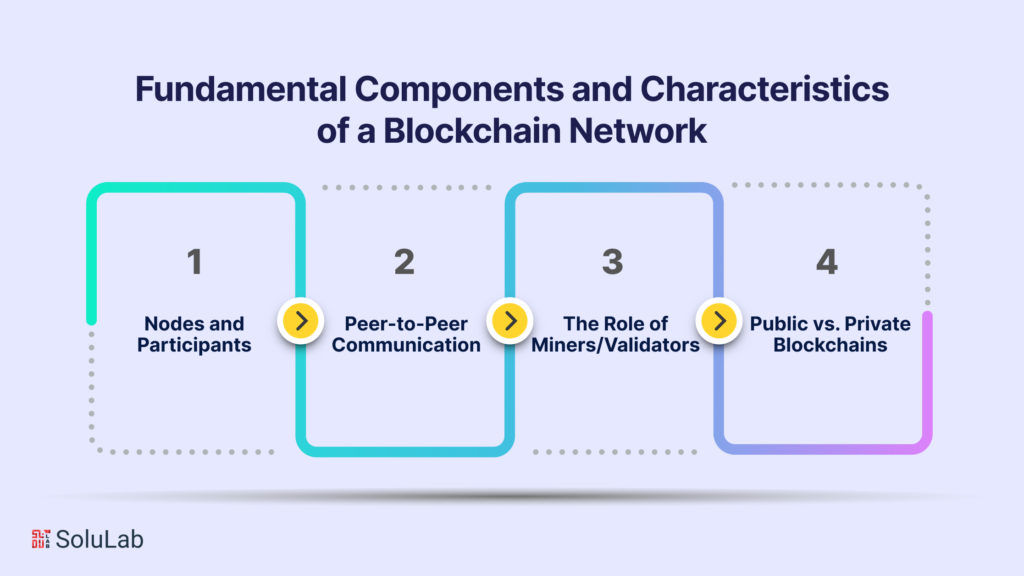
Blockchain technology is at the forefront of digital innovation, offering a secure and transparent way to record transactions and data. To comprehend blockchain fully, it’s essential to delve into the intricacies of its network. In this discussion, we will explore the various facets of a blockchain network, including nodes and participants, peer-to-peer communication, the role of miners/validators, and the distinction between public and private blockchains.
Nodes and Participants
- At the core of a blockchain network are its nodes and participants. Nodes are individual computers or devices connected to the network. They play a crucial role in maintaining the decentralized nature of the blockchain.
- Participants can be individuals, organizations, or entities that engage with the blockchain by creating, validating, or storing transactions. These participants collectively form the network’s ecosystem.
Read Our Blog Post: Best Companies to Hire Blockchain Developers in 2024
Peer-to-Peer Communication
- Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer (P2P) network, where nodes communicate directly with each other without the need for intermediaries. This decentralized structure enhances security and eliminates single points of failure.
- When a participant initiates a transaction or updates the blockchain, the information is broadcast to all nodes in the network. This ensures that all nodes have a consistent and up-to-date copy of the blockchain.
The Role of Miners/Validators
- In public blockchain networks, miners or validators play a critical role in maintaining the integrity of the blockchain. Miners validate transactions by solving complex mathematical puzzles through a process known as consensus (e.g., Proof of Work or Proof of Stake).
- Once a transaction is verified, it is added to a new block, which is then appended to the existing blockchain. Miners are incentivized with rewards, such as cryptocurrencies, for their computational efforts.
Public vs. Private Blockchains
Blockchain networks can be categorized as either public or private, each with distinct characteristics:
-
Public Blockchains
These are open and permissionless networks accessible to anyone. They are decentralized, transparent, and often used for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Public blockchains are maintained by a global network of miners.
Read Also: What Are The Benefits of Hiring a Blockchain Developer?
-
Private Blockchains
In contrast, private blockchains are restricted to specific participants or organizations. They are permissions, meaning that only authorized entities can validate transactions and access the blockchain. Private blockchains are commonly used for enterprise applications, supply chain management, and consortiums.
Understanding the blockchain network’s structure, participants, and communication mechanisms is crucial for grasping how blockchain technology works. It forms the foundation for various applications, including secure digital transactions, supply chain traceability, and even the creation of decentralized applications (DApps). As blockchain technology continues to evolve, it opens up new avenues for innovation, leading to exciting developments and trends in the field.
Companies and developers are actively engaged in blockchain development, offering services and solutions to harness the full potential of this transformative technology. Blockchain consulting services can assist businesses in navigating the complexities of blockchain adoption and integration, ensuring they remain at the forefront of digital transformation.
What are the Applications of Blockchain Technology?
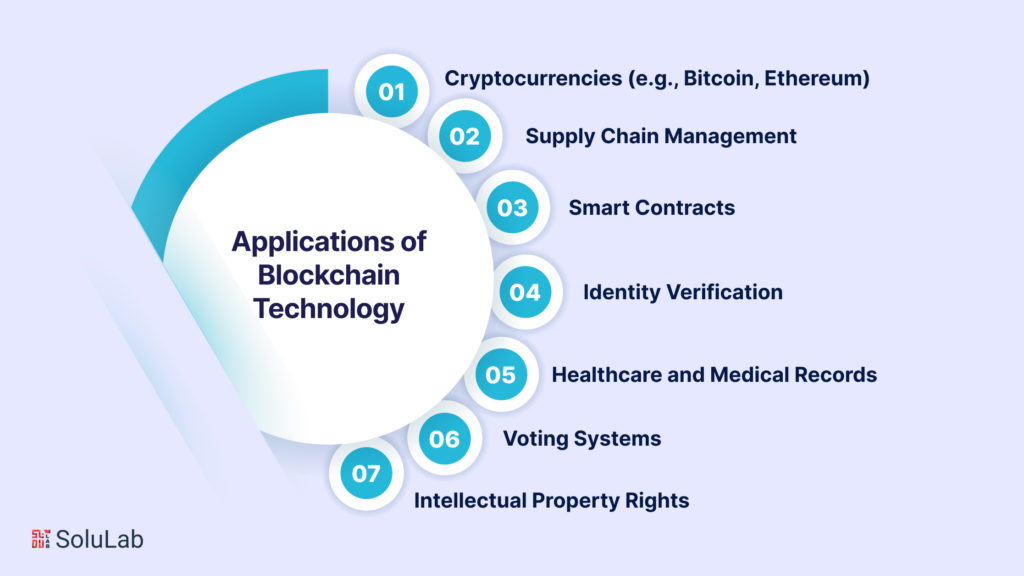
Blockchain technology, often referred to as the backbone of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, is a revolutionary innovation that has found applications far beyond the realm of digital currencies. It is a distributed ledger system that provides transparency, security, and immutability to transactions. Let’s explore various applications of blockchain technology:
-
Cryptocurrencies (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum)
Blockchain’s most well-known application is in the creation and management of cryptocurrencies. It serves as a decentralized ledger that records all transactions. Users can conduct peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks.
-
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology is transforming supply chain management by providing end-to-end visibility and transparency. It allows tracking of products from their origin through every touchpoint in the supply chain. This reduces fraud, ensures the authenticity of products, and enhances efficiency.
Read Our Blog: What Are The Top 10 Companies To Hire Blockchain Developers from
-
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically execute when predefined conditions are met. Blockchain’s security and trustworthiness make it an ideal platform for deploying smart contracts, which find applications in legal agreements, insurance, and more.
-
Identity Verification
Blockchain can be used for secure and tamper-proof identity verification. Individuals can have control over their data and selectively share it with trusted entities, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud.
-
Healthcare and Medical Records
Blockchain ensures the integrity and confidentiality of medical records. It enables patients to grant access to their medical data securely, streamlining the sharing of information among healthcare providers while maintaining privacy.
-
Voting Systems
Blockchain-based voting systems offer secure and transparent elections. Each vote is recorded as a transaction, making it nearly impossible to tamper with results. This application enhances trust in the democratic process.
Read Also: Investing in Blockchain Development: A Strategic Guide for Businesses
-
Intellectual Property Rights
Blockchain can be used to prove ownership and protect intellectual property rights. Artists, writers, and creators can timestamp their work on the blockchain, providing undeniable proof of creation and ownership.
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, it opens up new possibilities across various industries. Companies and organizations are exploring innovative ways to leverage blockchain for increased efficiency, security, and transparency in their operations. The trends in blockchain point to a future where blockchain’s impact will be even more significant, ushering in a new era of digital transformation.
What are the Latest Trends in Blockchain Technology?
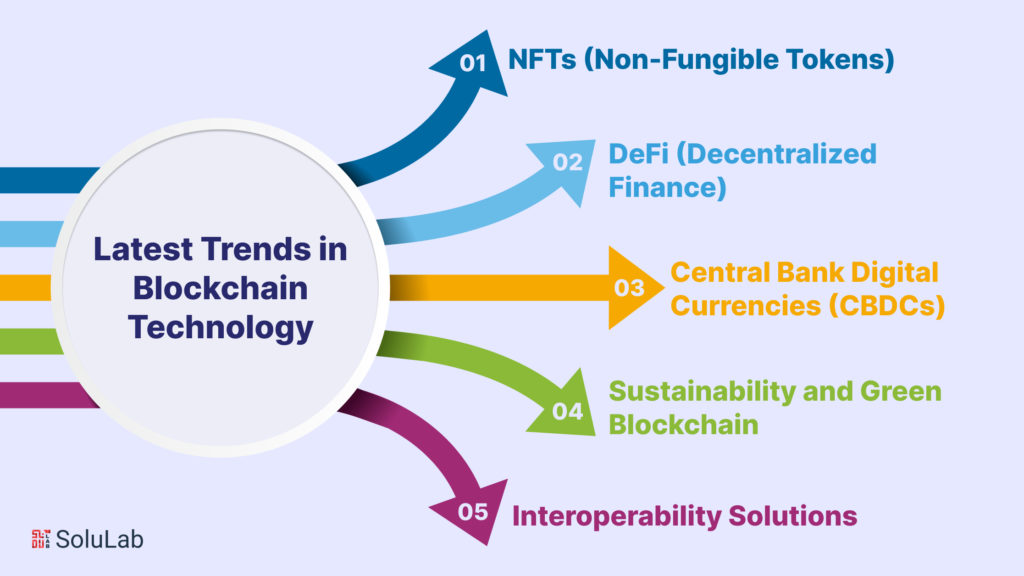
Blockchain technology, initially introduced as the underlying technology for cryptocurrencies, has evolved significantly in recent years. Today, it extends far beyond digital currencies, with various trends shaping its trajectory.
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens)
- Non-Fungible Tokens, or NFTs, have taken the digital art and collectibles world by storm. NFTs are unique digital assets that represent ownership of digital or physical items. They utilize blockchain technology to establish ownership and provenance, making them highly valuable in the world of art, music, gaming, and even virtual real estate.
- NFTs have introduced a new paradigm for ownership and authenticity verification, challenging traditional copyright and intellectual property norms. Artists, musicians, and creators are leveraging NFTs to monetize their digital works directly, eliminating intermediaries.
DeFi (Decentralized Finance)
- Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, is revolutionizing the traditional financial sector. Built on blockchain networks, DeFi applications provide open and permissionless access to financial services like lending, borrowing, trading, and yield farming. DeFi platforms eliminate intermediaries like banks, enabling users to have more control over their assets.
- The DeFi trend has seen exponential growth, attracting both users and developers. However, it also comes with challenges, such as security vulnerabilities and regulatory concerns, that need to be addressed for long-term sustainability.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
- Central Bank Digital Currencies are digital versions of fiat currencies issued by central banks. These CBDCs aim to combine the advantages of blockchain technology with the stability of traditional currencies. Governments and central banks worldwide are exploring the potential of CBDCs to modernize payment systems, enhance financial inclusion, and combat illicit activities.
- CBDCs represent a significant shift in the financial landscape and could impact the adoption and use of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and stablecoins.
Read Our Blog Post: Top 20 Supply Chain Startups That Are Using Blockchain Technology
Sustainability and Green Blockchain
- Sustainability is a growing concern in the blockchain space. The energy-intensive nature of some blockchain networks, particularly Proof of Work (PoW), has raised environmental concerns. As a result, there’s a growing trend towards developing and adopting more eco-friendly consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Stake (PoS).
- Green blockchain initiatives aim to reduce the carbon footprint of blockchain technology while maintaining its security and decentralization benefits. These efforts align with broader global sustainability goals.
Interoperability Solutions
- Interoperability is a critical challenge in the blockchain industry. Different blockchain networks often operate in isolation, limiting the flow of assets and data between them. Interoperability solutions seek to bridge these gaps, enabling seamless communication and value transfer between disparate blockchain networks.
- Projects and protocols dedicated to interoperability, like Polkadot and Cosmos, are gaining traction. They facilitate cross-chain communication and the creation of interconnected blockchain ecosystems.
How is SoluLab Pioneering the Digital Revolution Through its Blockchain Development Expertise?
Blockchain technology, often referred to as the backbone of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has transcended its initial purpose. It is now a transformative force driving innovation across various industries. In this era of digitalization, understanding how blockchain works, its applications, and leveraging it effectively are paramount. SoluLab, a leader in blockchain development and consulting, is at the forefront of this revolution.
At its core, a blockchain is a decentralized and immutable digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. It operates on a peer-to-peer basis, utilizing complex cryptography to secure data. Each “block” in the chain contains a set of transactions, and they are linked in chronological order, ensuring transparency and security.
Blockchain Development with SoluLab
-
Blockchain Platforms
SoluLab leverages leading blockchain platforms like Ethereum and Hyperledger to create scalable and secure solutions. These platforms provide the foundation for building decentralized applications (DApps) and enterprise-grade blockchain networks.
-
Role of Blockchain Development Companies
SoluLab plays a pivotal role in guiding organizations through their blockchain journey. They offer consultation, development, and implementation services to ensure seamless integration into existing systems.
-
Blockchain Development Services
SoluLab offers end-to-end blockchain development services, including smart contract development, decentralized application development, blockchain consulting, and blockchain integration into existing systems.
In conclusion, blockchain technology is reshaping industries, and SoluLab is your trusted partner in harnessing its power. With their expertise in blockchain development and consulting services, they pave the way for organizations to unlock the full potential of this transformative technology.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SoluLab stands as a beacon of innovation and expertise in the realm of blockchain technology. As we’ve explored the intricacies of what blockchain is and how it works, it becomes evident that this revolutionary technology has become the cornerstone of digital transformation. SoluLab’s commitment to excellence and its status among leading blockchain companies are testament to its prowess in developing blockchain solutions.
With an in-depth understanding of blockchain technology, SoluLab not only explains the nuances of this groundbreaking technology but also empowers businesses with cutting-edge blockchain development services. In a landscape where blockchain trends continue to evolve, SoluLab remains at the forefront, ready to adapt and harness blockchain’s potential to drive digital transformation.
For those seeking to harness the power of blockchain, SoluLab is the go-to blockchain development company. The ability to hire top blockchain developers and access comprehensive blockchain consulting services sets SoluLab apart. In an era where blockchain is more than just a buzzword, SoluLab paves the way for businesses to unlock the full spectrum of opportunities presented by blockchain technology, ushering in a new era of innovation and efficiency.
FAQs
1. What is a Blockchain?
A blockchain is a distributed and decentralized digital ledger technology that securely records transactions across multiple computers. It consists of a chain of blocks, each containing a batch of transactions, and is designed to be transparent, immutable, and resistant to tampering.
2. How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain works through a network of nodes (computers) that validate and record transactions into blocks. Once verified, these blocks are linked in chronological order, forming a chain. Consensus algorithms ensure agreement among nodes, and cryptographic techniques secure the data.
3. What Are Some Applications for Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology has diverse applications, including cryptocurrency transactions (e.g., Bitcoin), supply chain management, identity verification, voting systems, healthcare record management, and smart contracts in various industries.
4. What Are the Key Trends in Blockchain Technology?
Current trends in blockchain technology include the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), and sustainability efforts to reduce blockchain’s energy consumption.
5. How Can I Develop Blockchain Solutions?
To develop blockchain solutions, you can either hire top blockchain developers or engage with blockchain development companies. It involves designing and implementing smart contracts, choosing the right blockchain platform, and ensuring security and scalability.



