With the merging of physical and digital worlds, the metaverse is testing the limits of our technological abilities. In the metaverse’s virtual reality (VR), things from human identity, personality, and reputation to assets, emotions, and history may be interacted with, manipulated, and experienced in completely new ways. As a consequence, end users get a very magical experience! The metaverse is poised to join the mainstream, attracting the interest of investors worldwide, with clear potential for early adopters.
With the metaverse gaining popularity as a revenue-generating possibility among investors, there is a clear need to comprehend this virtual world down to its fundamental levels of construction. According to prominent author and entrepreneur Jon Radoff, who has written extensively on Web3 and related issues, the metaverse consists of 7 layers. These seven layers of the metaverse illustrate the various stages of the market’s value chain.
This guide walks you through each of the seven layers of the metaverse, deepening your comprehension and allowing you to realize its full potential. However, before we get too deep, let us define the metaverse.
What is Metaverse?
The metaverse is a virtual environment that reflects a new frontier, bringing together VR, augmented reality (AR), mixed reality (MR), gaming, social interaction, and commerce to develop encounters that connect the dots between the real and digital worlds. That is why many people see the metaverse development and related Web3 technologies like blockchain, NFTs, cryptocurrencies, and decentralized processing as the beginning of a new internet. What does the metaverse currently offer for its users? Access to commercial prospects, deep social and personal virtual experiences, and solutions to various physical restrictions.
Seven Layers of Metaverse
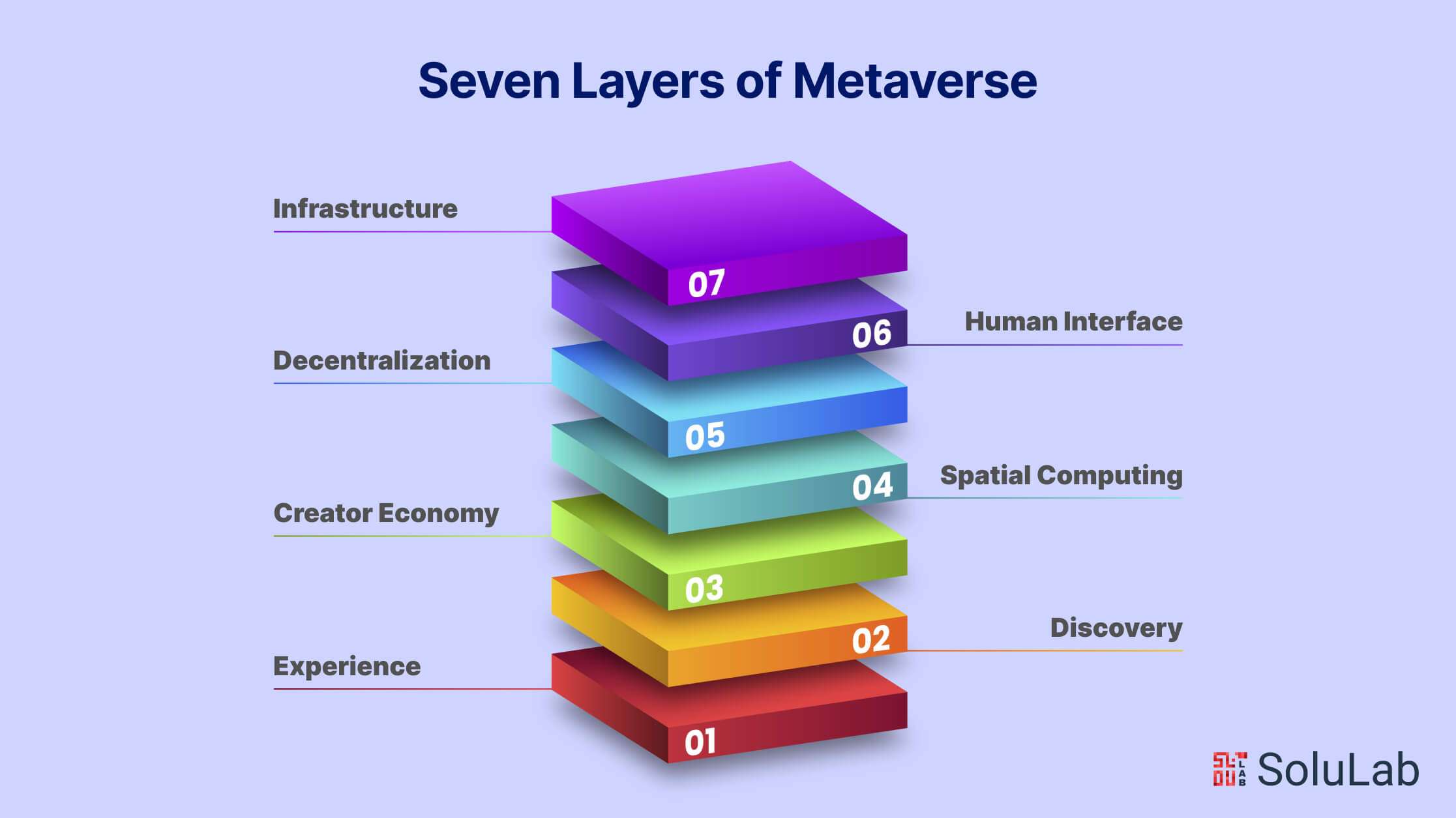
In recent years, the concept of the Metaverse has captured the imagination of tech enthusiasts and futurists alike. Often depicted in science fiction novels and movies, the Metaverse represents a collective virtual space where users can interact, create, and explore in immersive digital environments. As technology advances, the vision of the Metaverse is gradually becoming a tangible reality. Let’s delve into the seven layers that comprise this fascinating digital universe.
1. Experience
Contrary to popular belief, the metaverse is more than just a 3D representation of the real world for us to passively observe. It will instead be an accurate depiction of spatial dimensions and distances, involving the dematerialization of actual things enabled by photorealistic visual components.
The limits that materiality imposes may no longer exist within the metaverse as it dematerializes physical space. The metaverse’s VR can give experiences unavailable in the actual world.
This is one of the primary reasons why many well-known businesses are investing in large interactive live events or MILEs. These events, offered on platforms like Roblox and Decentraland, provide an example of how things that happen in the metaverse could express interaction. Failed to obtain a front-row seat to a concert? In the metaverse, all tickets will provide a front-row experience.
The metaverse revolves around experiences. The hype it has generated and the money it has garnered are all a result of the lifelike experiences it is ready to provide. A genuine metaverse, with its holistic and real-time nature, has the potential to revolutionize a variety of human activities, from gaming and social interactions to retail, theater, and eSports.
2. Discovery
This layer discusses the actual discoveries that arise from a constant “push and pull” of information. It is this information “push and pull” that introduces people to new experiences. Whereas “pull” is an inbound system in which users actively seek information and experiences, “push” is more outbound and entails procedures that tell users about the opportunities that await them in the Metaverse. The discovery layer is the most profitable for enterprises. Here are some examples of how inbound and outbound discoveries occur.
Inbound:
- Community-driven content
- Real-time presence
- Search engines
Outbound:
- Display advertising
- Notifications
- Emails and social media
Community-generated material will be a significant inbound source for finding metaverse experiences. It is, in fact, one of the most affordable options for people eager to learn about the metaverse.
If someone is interested in anything, they will spread the word. They discuss the notion, their experiences, and any relevant events in which they have participated. Because such information is easily shared, it may soon become a marketing asset. Such community-driven material can also assist in disseminating awareness of the metaverse’s principles, enabling technology, and experiences.
Real-time presence is another effective facilitator of incoming discovery. Exploration of experiences in the metaverse will not come just from content, but also from understanding what other individuals interested in the metaverse are doing at the moment. After all, the metaverse is primarily about human connections and shared experiences.
When you connect to Steam, Battle.net, Xbox, or PlayStation, you may view what games your friends are presently playing. These gaming systems have cleverly utilized real-time presence to increase in-game involvement. Nongaming systems like Clubhouse have also utilized the power and adaptability of real-time presence, permitting users to pick whatever room they wish to join according to their friends’ location.
In the metaverse, real-time involvement will be crucial in improving users’ interactive experiences, therefore increasing their comprehension of this virtual reality.
The metaverse has the potential to digitize social institutions and establish a decentralized identity environment, shifting power away from a few monolithic entities and toward social groupings, enabling the frictionless flow of knowledge and experiences.
The most efficient outbound discovery channels include display advertising, alerts, emails, and social media. Metaverse developers can also help people find new experiences by placing relevant information in front of them through outbound techniques.
3. Creator Economy
The metaverse aims to build a complete 3D environment with interconnected virtual regions that reflect reality. These environments, driven by AR, VR, and other related technologies, will be particularly created to attract guests capable of doing almost anything within them. The virtual world has enormous opportunities for economic growth. As the concept of the metaverse becomes more widely accepted, the number of organizations constructing metaverse areas is almost expected to increase significantly.
Content creators will play an important part in shaping this new environment. They have been finding excellent success on social media platforms and are still going to be a significant driver of development in the metaverse virtual world. Experts predict the metaverse will transform the creative economy into a multibillion-dollar business. And who makes up the creator economy? Independent creatives who create digital material, such as photographs and videos, as well as digital commodities including e-books, webinars, art, and blog entries.
It is only logical for this group of innovators to strive for opportunities in the metaverse as it evolves. They will establish their own metaverse environments in which their fans may connect, hang out, and communicate with them. As technology progresses, creators will be able to easily transition their followers to the metaverse. However, in order to fully utilize the metaverse, builders must prioritize skill development.
Creators will be able to transform the metaverse into a revenue-generating potential through
- Selling commercial items, NFTs, and IRL things.
- Showing and selling NFT collections.
- Working with and promoting brands.
- Influencing purchasing behavior by having their avatars wear virtual fashion goods and accessories such as trainers or clothing.
- Hosting parties and get-togethers for their fans to improve relationships and increase purchases.
The metaverse development will provide a potential new market for the creative economy. The finest thing is that it benefits everyone involved: artists, users, and the metaverse.
4. Spatial Computing
Our lives have already been made easier by spatial computing thanks to ride-hailing applications and virtual assistants. Enabling customers to try on clothing in virtual changing rooms, has improved shopping convenience and added pleasure to the fashion process. With the current state of spatial computing, you may work, shop, and interact with others as an avatar in a rich, three-dimensional virtual environment that replicates the actual one.
AR, VR, and MR are all combined in spatial computing to realize the concept of the “metaverse.” The idea of a three-dimensional, simultaneous virtual environment that interacts with the actual world and never turns down can come true with spatial computing. You can play a game against the backdrop of your near real-world surroundings, for example, if it makes use of spatial computing. The game’s characters will be able to communicate with the real-world things in your environment, such as a sofa in your living room, in addition to just detecting them. In essence, spatial computing enables simultaneous, real-time interaction with the virtual and physical worlds.
With time, spatial computing has developed into a significant technological field that gives us access to and control over 3D areas for more immersive experiences.
Hardware and specialized software are needed for spatial computing to function as intended. Only the necessary software components will be covered in this section; the hardware will be covered in the “human interface” layer which is covered later in the article. The following is a list of many features of the software layer that underpins the metaverse:
- Unity and Unreal Engine for displaying geometry and animation.
- Using object recognition and geographic mapping, one may map and analyze both the physical and digital worlds.
- recognition of gestures and voices.
- Internet of Things to integrate device data.
- biometrics of humans for identity reasons.
- UIs of the future generation built to handle simultaneous information streams and processing.
5. Decentralization
Roundhill Investments projects that the metaverse market will expand at a 13.1% compound annual growth rate in the upcoming years. As more people have access to the metaverse, this growth will only quicken.
According to Epic Games CEO Tim Sweeney, the metaverse is a “multi-trillion-dollar sector of the world economy” that, like the internet as it exists today, is not owned by any one company.
But at the moment, all the hype around the metaverse is coming from the largest IT giants that are joining the market. It is obvious that large enterprises will be crucial to the metaverse’s continued growth and development. This begs the question, will they bring about the same problems with data protection and privacy that already beset the internet?
Let’s use Facebook as an example. The company’s business strategy is centered on user data, which it collects and utilizes to allow outside parties to display customized advertisements to its consumers.
Imagine the whole metaverse under the authority of a single company or organization. The ruling authority would have limitless options in this scenario to examine user activity within the metaverse and use the information that results as required. Then, by providing access to this data, the authority might create the metaverse’s functionality in a way that helps companies and advertising.
Regular users would find it challenging to confirm who had gained access to the data and under what circumstances if it were kept in a central location. This may result in security problems, which would annoy users. A centralized metaverse may face privacy and data protection concerns. Blockchain technology presents a novel approach to address these issues. Because of the blockchain’s intrinsic security and decentralization, countless blockchain-based apps, or dApps, are being developed and deployed across sectors.
Using a decentralized blockchain network, financial goods may be made available through decentralized finance, or DeFi. DeFi wallets, like MetaMask and Trust Wallet, are accessible to everyone without the need to use banks or brokerages. It is not necessary to have a social security number, government-issued ID, or documentation proving your nationality in order to use a DeFi wallet. By guaranteeing anonymity, this also improves privacy.
Blockchain technology is already being used by a number of decentralized metaverse initiatives to offer user-owned experiences that are resistant to censorship and guarantee interoperability. The most commonly recognized instance of a decentralized metaverse is probably Decentraland. The Ethereum blockchain powers this decentralized virtual environment, which is governed by a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) that is subject to popular voting to make changes to its policies.
People and businesses are already snatching up property in these dispersed metaverse realities.
Transparency and traceability in transaction and interaction processes are essential for the metaverse to reach its full potential. Crypto assets and blockchain technology both provide a way to solve this issue. In the meantime, NFTs will guarantee that there are no disagreements about who owns what in the metaverse. While the metaverse is undoubtedly amazing in and of itself, blockchain, crypto assets, and NFTs will undoubtedly be crucial in allowing this technology to realize its full potential.
6. Human Interface
The technology or gadgets that will allow users to feel the genuine enchantment of the metaverse are discussed at the human interface layer.
Technology is gradually drawing us nearer to our gadgets. Donna Haraway, a distinguished technology and science studies professor, emphasized the reality of the dwindling gaps between people and technology in her 1985 article “A Cyborg Manifesto.” The term “cyborg” was used by the author to describe a person with superhuman physical powers made possible by internal mechanical components. Today, everything she dreamed about in 1985 is beginning to come true. As technology develops more compact, intelligent, and portable, it will likely become more integrated into our bodies and cause us to become semi-cyborgs.
Are we going to become total robots? Despite the fact that we do not yet know the answer, we have strong reason to think that we do thanks to smartwatches and smart eyewear. That being said, an immersive, lifelike metaverse experience depends on people and robots becoming closer. We will soon be able to experience the metaverse in the same way that we perceive the physical world, thanks to advancements in spatial computing and appropriate interface design.
7. Infrastructure
This layer deals with the technology infrastructure needed to build an interoperable and fully working metaverse.
The metaverse is powered by five technological clusters:
- The network and processing capacity includes GPU servers, edge computing, real-time network transmission, and virtual scene fitting, as well as spatial positioning algorithms.
- Artificial Intelligence
- Technologies used in video games, such as 3D game engines like Unity and Unreal Engine, to create animations, audio, and visuals
- Display innovations like AR, VR, MR, ER, and XR provide for both an immersive audiovisual experience and the ability to modify the experience over time to accommodate users’ evolving tastes and preferences.
- Blockchain technology. It will ensure value ownership and circulation with the use of settlement metaverse platforms, smart contracts, and decentralized value transfer methods.
In terms of hardware, the metaverse is supported by robust computers, semiconductors, network devices, communication components, sophisticated, high-resolution cameras, powerful display systems, accurate freedom optical systems, and mixed reality equipment.
Final Words
Since digital behemoths like Google, Apple, Facebook, and Microsoft have made it clear that they are obsessed with the metaverse and are willing to spend a lot of money to make it a reality, the metaverse has gained a lot of attention from both ordinary people and interested investors. Everyone is interested in learning about the metaverse, including its definition, location, and powers. However, because the metaverse does not yet exist in its whole, real form, understanding it might be difficult. Knowing the seven layers of the metaverse is an excellent method to get a better knowledge of it. Every layer is an essential component of the metaverse and cannot function independently of the other six levels.
The understanding of how the layers interact and complement each other to form the vast network of three-dimensional environments that is the metaverse is another significant advantage of breaking the metaverse down into layers.
Experienced in creating immersive metaverse environments, SoluLab is a metaverse development company with highly qualified metaverse developers onboard. For further information on metaverse development, hire metaverse developers from SoluLab today!
FAQs
1. What is the significance of exploring the layers of the Metaverse?
Exploring the layers of the Metaverse provides insights into the complex ecosystem of virtual environments and technologies shaping the future of the metaverse. By understanding each layer, users can grasp the interconnectedness and potential of the Metaverse to revolutionize various aspects of our lives.
2. How do the layers of the Metaverse interact with each other?
The layers of the Metaverse are interconnected, with each layer building upon the other to create a cohesive and immersive digital experience. For example, the infrastructure layer provides the foundation for the platform layer, which in turn enables the creation of virtual experiences within the experience layer, and so forth.
3. What are some real-world applications of the Metaverse layers?
The layers of the Metaverse have numerous real-world applications across industries such as gaming, entertainment, education, healthcare, and remote work. For instance, spatial computing technologies enable virtual training simulations in healthcare, while the creator economy layer facilitates the monetization of digital art and music.
4. How can individuals and businesses get involved in the development of the Metaverse?
Individuals and businesses can participate in the development of the Metaverse by leveraging their skills and resources to create virtual experiences, develop innovative technologies, and contribute to open-source projects. They can also collaborate with industry partners, invest in Metaverse-focused startups, and stay informed about emerging trends and opportunities.
5. What are some challenges and considerations associated with the Metaverse layers?
While the Metaverse holds immense potential, it also presents various challenges and considerations, such as privacy concerns, digital rights management, interoperability issues, and the need for inclusive design. Addressing these challenges requires collaboration, innovation, and a commitment to ethical and responsible development practices.
6. How does SoluLab contribute to the development of the Metaverse?
SoluLab- a metaverse development company plays a vital role in advancing the Metaverse by providing innovative development solutions and expertise. Through its comprehensive suite of services, SoluLab helps companies and organizations build immersive virtual environments, develop innovative spatial computing applications, integrate decentralized technologies, and optimize infrastructure for seamless Metaverse experiences with its metaverse development services. With its deep understanding of emerging technologies and industry trends, SoluLab collaborates closely with clients to bring their Metaverse visions to life, ensuring scalability, security, and user engagement every step of the way.






