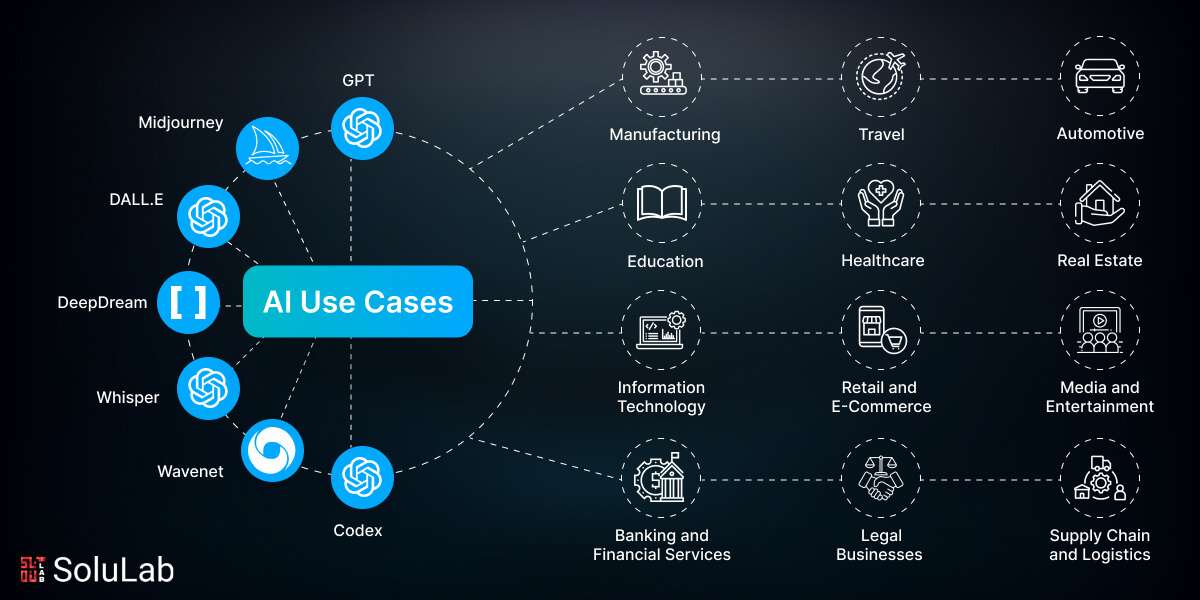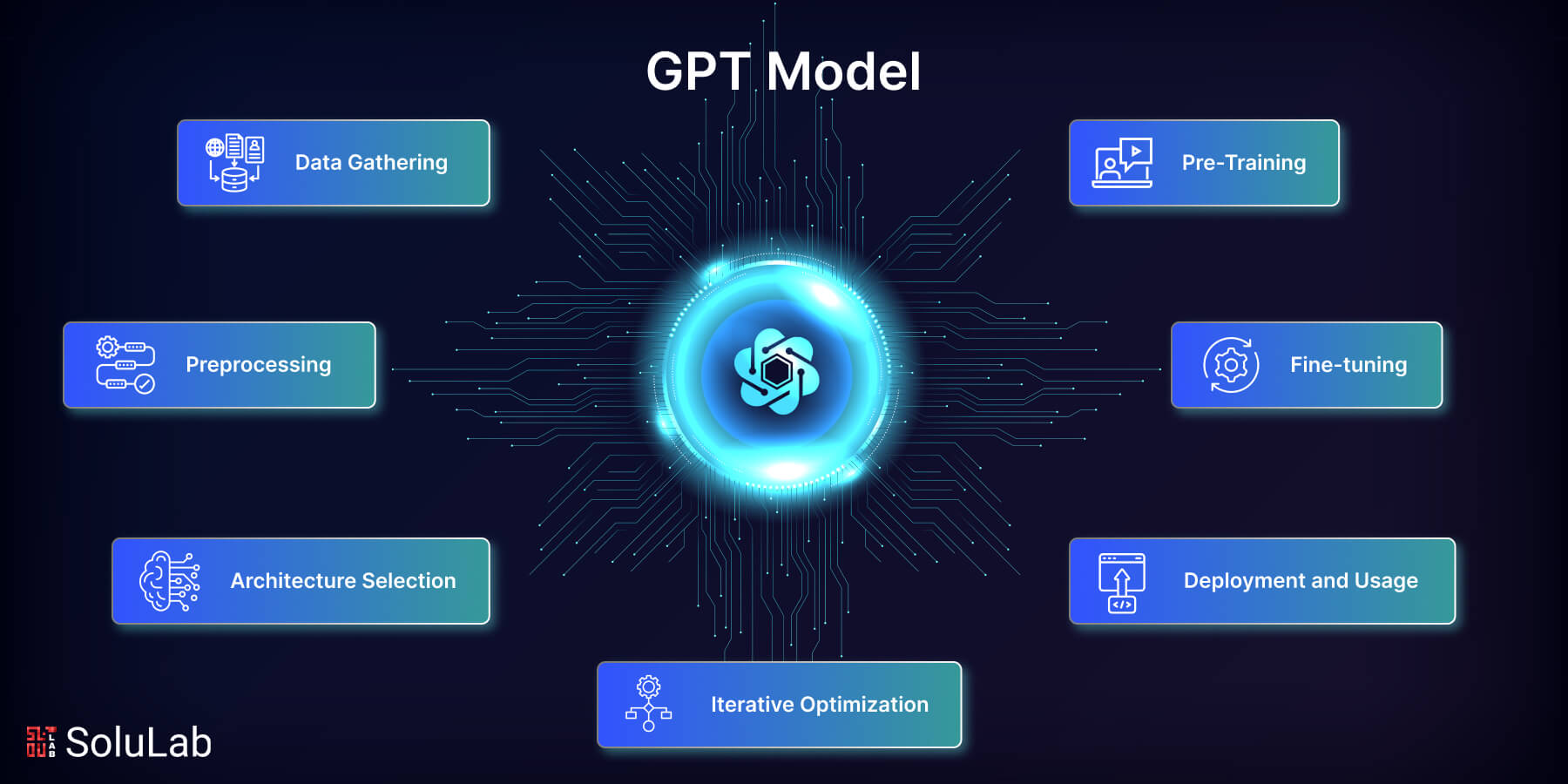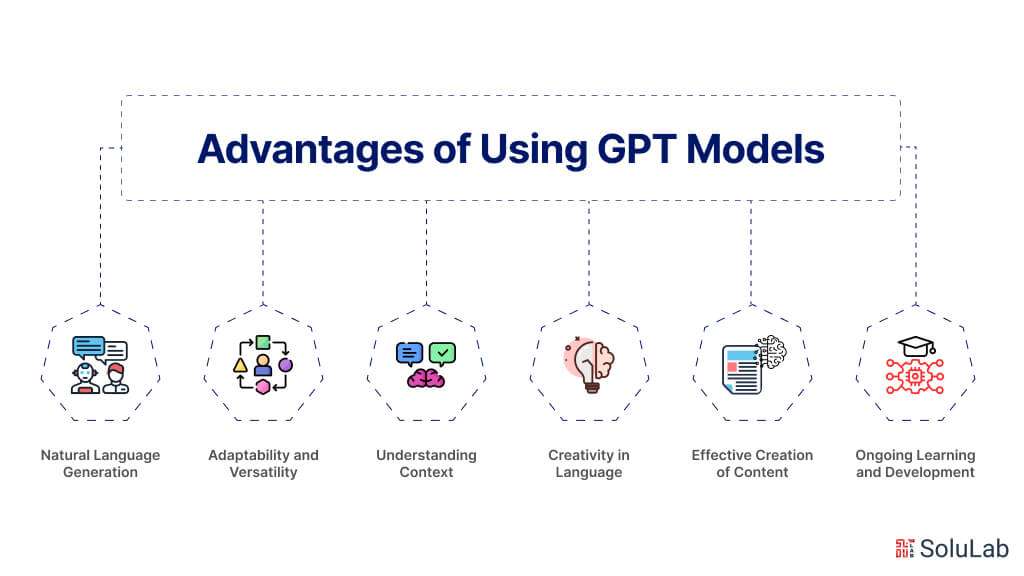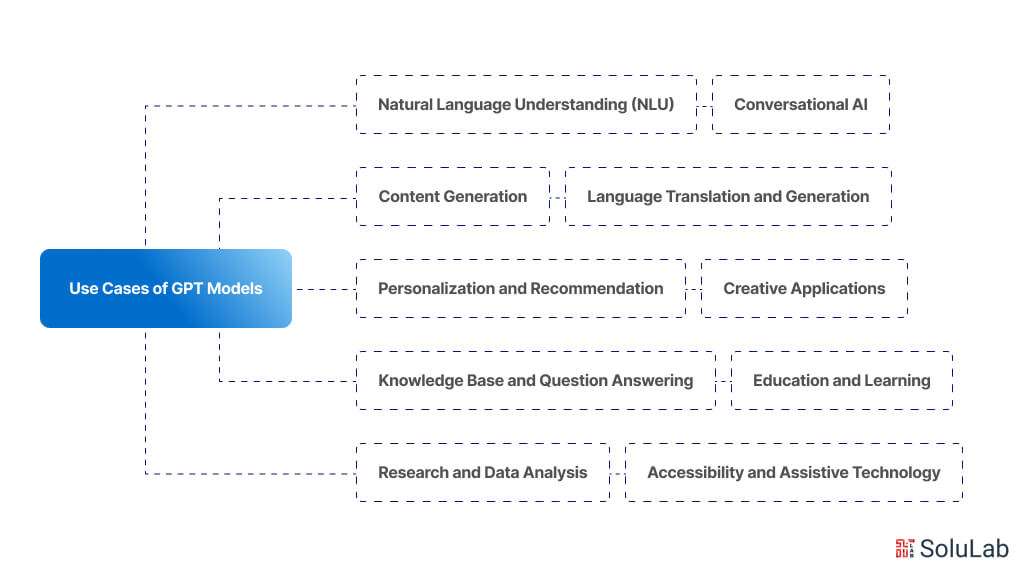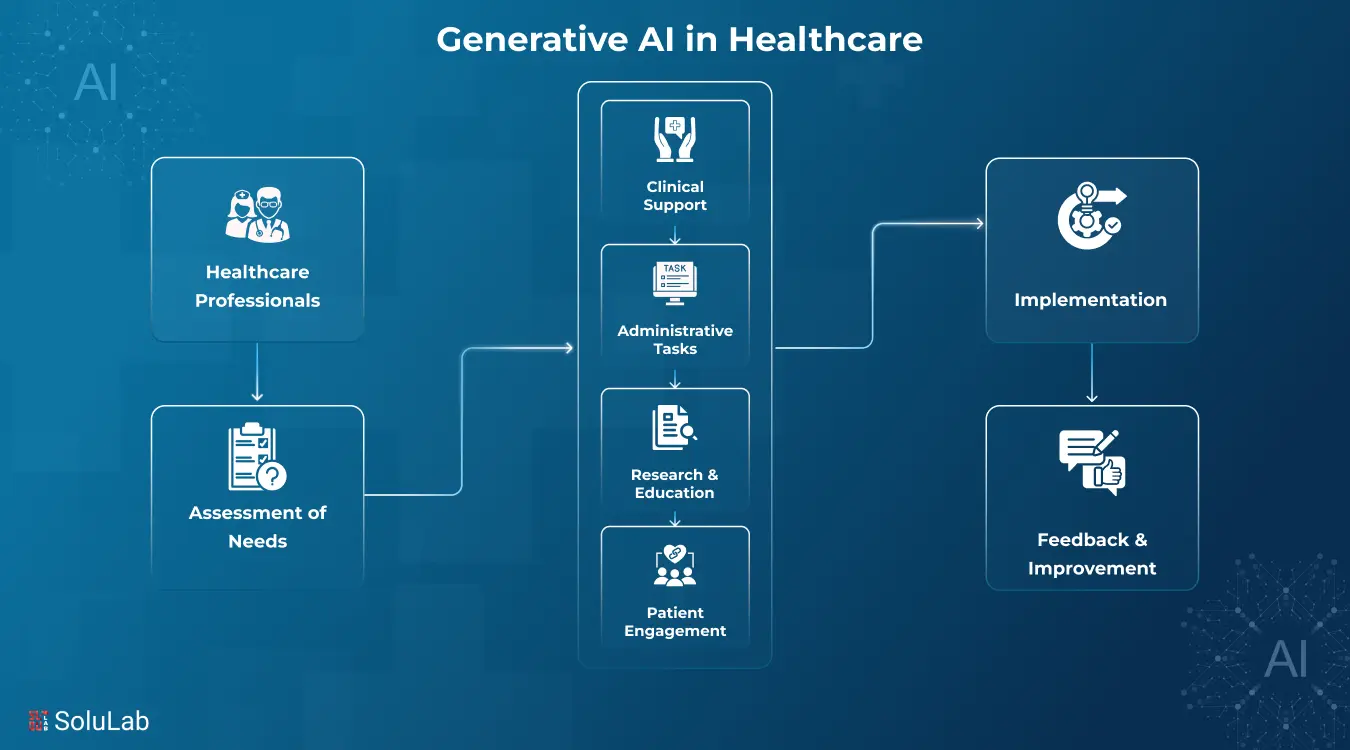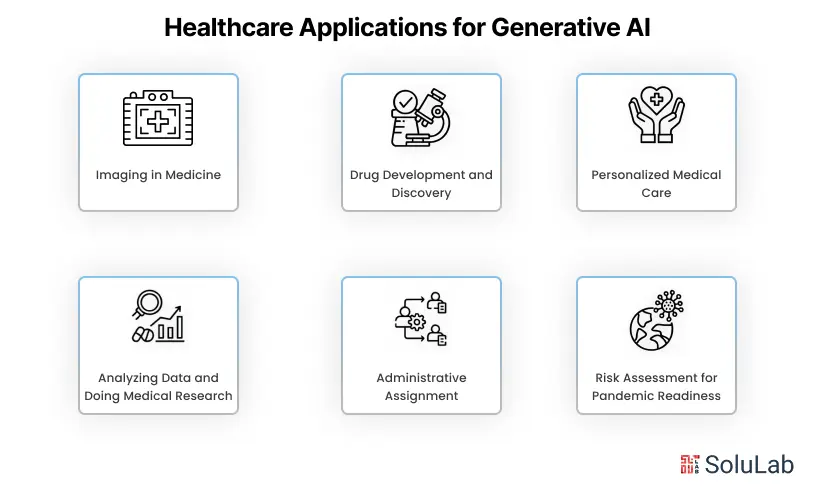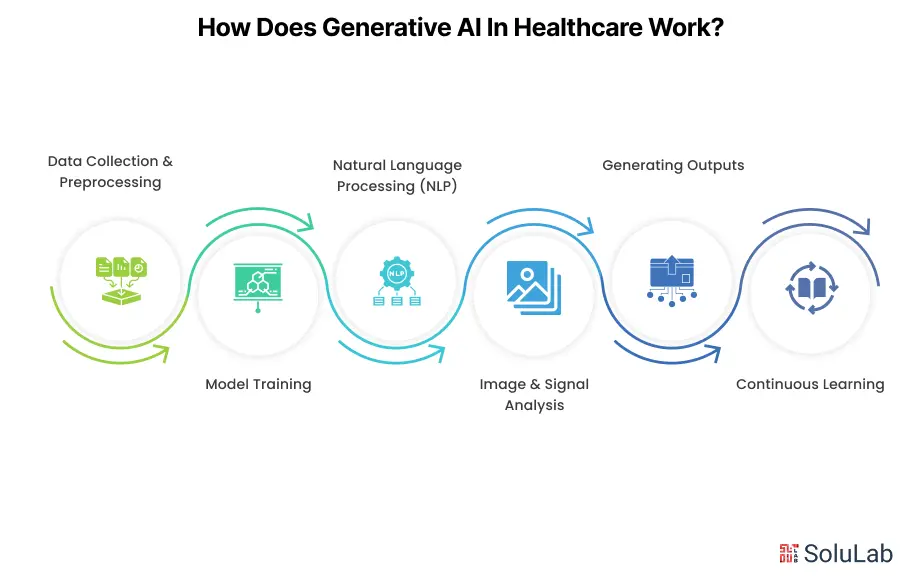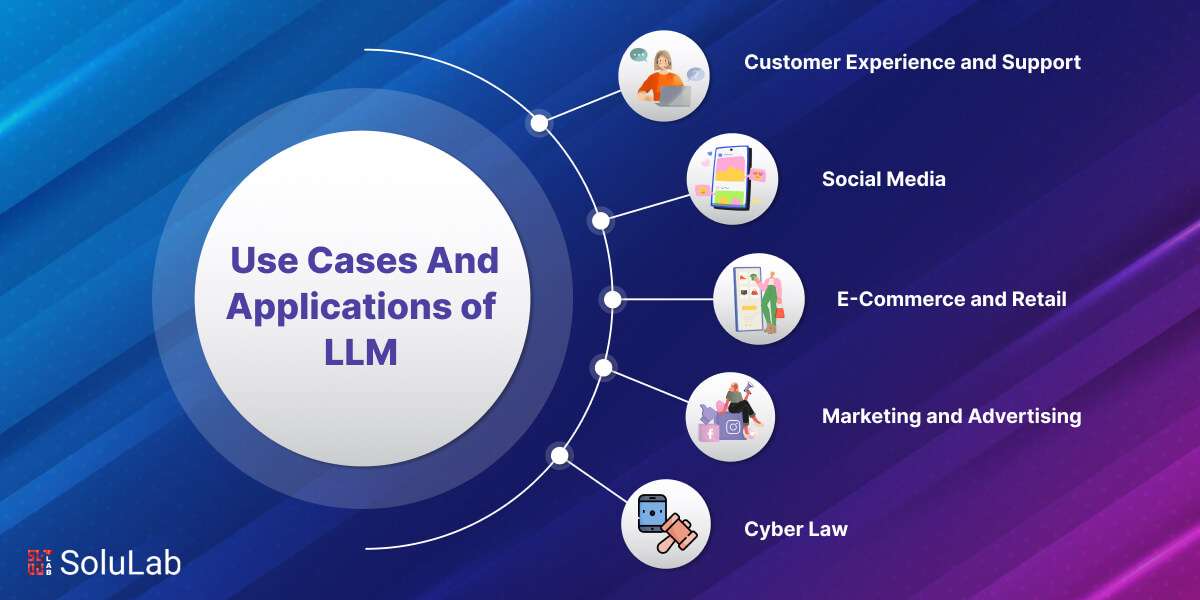
In the Internet era, large language models (LLMs) are fast rising to the top of the most anticipated technological advancements.
As more people explore generative artificial intelligence (AI) tools like ChatGPT, Google Bard, and Bing Chat, analysts predict that the generative AI industry will reach a value of $1.3 trillion by 2032.
The use cases for LLMs in the industry have yet to be established, as the technology is still in its early stages.
On the surface, LLMs are applicable in every situation where a company wants to extract insights from an input text or dataset or analyze, process, summarize, rewrite, edit, or transcribe. Several LLM use cases seem promising, and acceptance of them is growing.
This extensive blog will include some real-world instances of LLM applications as well as an in-depth look at the fascinating world of Large Language Model use cases and applications and how these linguistic superheroes are changing industries.
So, let’s get started!
7 Exceptional Large Language Model Use Cases You Should Be Aware Of
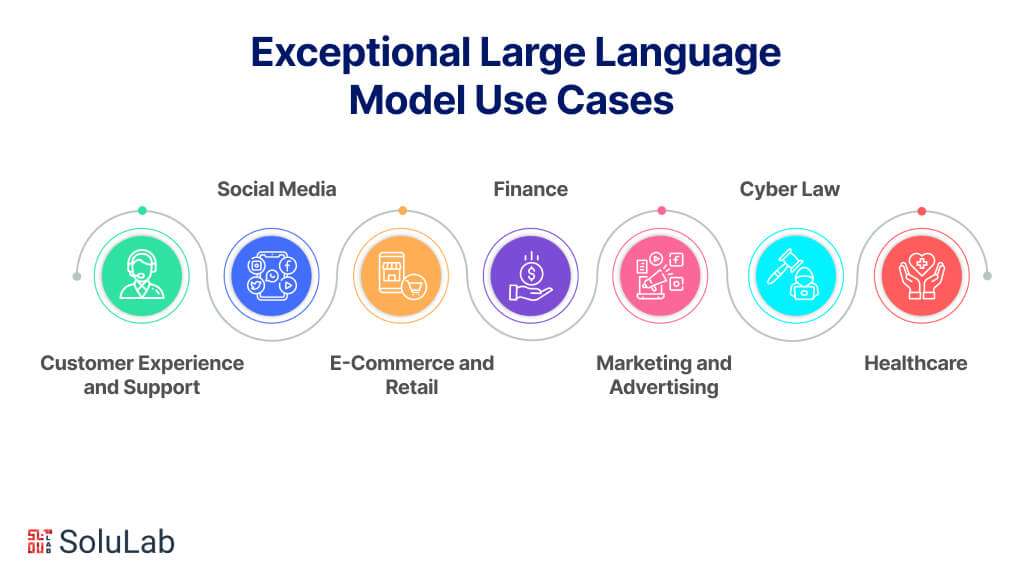
Applications for large language models in a variety of sectors are common large language model (LLM) use cases, demonstrating its adaptability and potential to improve productivity and decision-making. Let’s investigate seven distinct applications of large language models (LLM).
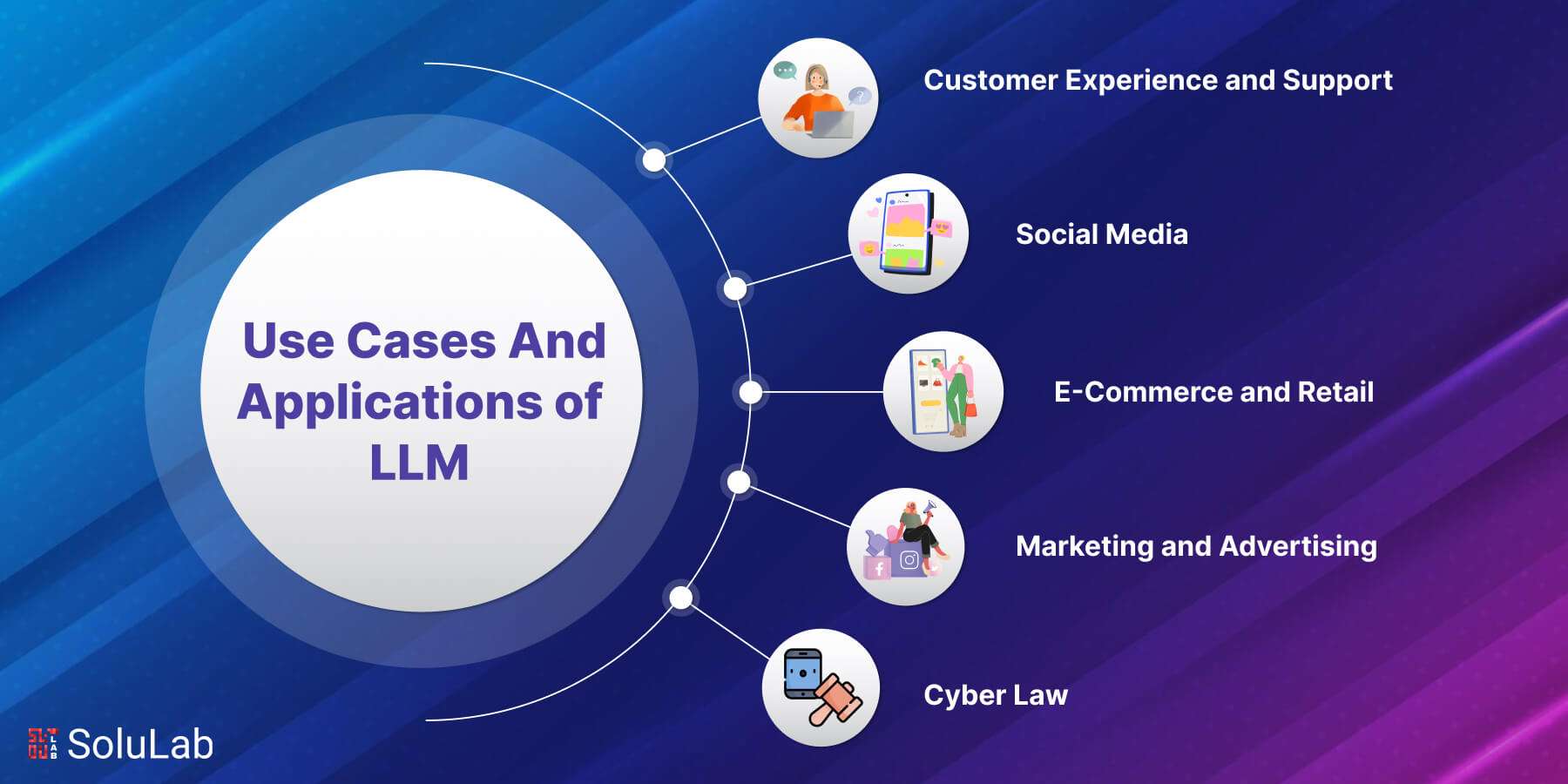
1. Customer Experience and Support
Large language models allow businesses to use chatbots to provide individualized customer service, use virtual assistants to automate customer care, and use sentiment analysis to obtain insightful data. By strengthening client connections and enhancing customer experiences, these applications improve customer service and support.
The following three customer care and support domains are where LLMs have shown to be quite helpful:
-
Chatbots for Tailored Customer Experiences
Think of a AI-powered chatbot as your virtual best friend rather than just a robot! These chatbots, which are powered by LLMs, may converse with you in a human-like manner and assist you with troubleshooting and product information alike. With the help of LLM-powered chatbots, businesses can provide effective and customized customer support. These chatbots are capable of carrying on natural language discussions, comprehending client inquiries, and responding appropriately. Chatbots may answer a variety of consumer questions, offer product details, solve problems, and even help with transactions when they are used in conjunction with LLMs. LLM-powered chatbots’ capacity to decipher and evaluate user communications facilitates the delivery of timely and precise answers, which raises customer happiness.
-
Virtual Assistance For Digital Customer Service
When you can have a virtual assistant, who needs a real one? LLM-powered virtual assistants revolutionize customer service by automating repetitive chores and offering real-time support. Virtual assistants powered by LLM may answer routine client questions, direct customers via self-service choices, and provide immediate assistance. These helpers may help with purchase monitoring or account administration, comprehend complicated inquiries, and offer tailored advice. Virtual assistants use LLMs to speed up reaction times, cut down on client wait times, and improve customer service in general.
-
Sentiment Analysis to Comprehend Customer Input
By enabling sentiment analysis, LLMs help businesses learn from client feedback. Customer reviews, social media posts, and other textual data may be analyzed by LLMs to ascertain the emotions that consumers have toward particular goods, services, or brand experiences. It’s similar to having a mind reader, except this one can also forecast how well-liked your products will be in the future. Sentiment analysis use cases for large language models assist businesses in determining areas for improvement, understanding consumer satisfaction levels, and quickly resolving issues. Businesses may increase their comprehension of consumer sentiment, tailor their offerings accordingly, and make data-driven choices that boost customer service by using LLMs for sentiment analysis.
2. Social Media
In the social media sector, LLMs are revolutionizing the procedures involved in generating and creating content. LLMs improve processes for content production in a number of ways, including automated article writing, the development of blog and social media posts, and the generation of product descriptions. Businesses may increase the efficiency with which they create personalized, high-quality content, engage their audience, convert leads, and maintain a competitive edge by utilizing these methods.
The following three social media platform content production and generating categories are where LLM use cases have shown to be extremely helpful:
-
Automatic Writing of Articles
Because LLMs automate certain portions of composing articles, the journalistic industry is undergoing a change. These days, journalists may use LLMs to discuss ideas, create drafts with a few keystrokes, and even select intriguing, original headlines. With the help of these algorithms, which examine enormous volumes of data, spot trends, and provide pertinent information recommendations, authors may produce material more quickly without sacrificing accuracy or quality.
-
Writing for Blogs and Social Media Posts
Content Creators may easily create captivating blog articles and social media material with the help of LLMs. Professionals in marketing and content creation may swiftly produce blog pieces, social media updates, and marketing messages by utilizing the language production capabilities of LLMs. Are you in need of an incredible blog article or tweet that will make the people who follow you wonder? These models will support you in producing interesting, viral content that will pique viewers’ interest and leave them wanting more! By being able to comprehend the intended material’s context, style, and tone, these models help organizations create engaging content that is specifically tailored to their target audience.
-
Creating Product Descriptions
When creating product descriptions, e-commerce systems find great use in LLMs. These Large Language Model use cases may automatically generate engaging and instructive descriptions by analyzing market trends, customer feedback, and product attributes. Business time and resources are saved since LLMs guarantee consistent quality and increase the effectiveness of creating descriptions for a wide variety of products.

3. E-Commerce and Retail
By offering real-time translation capabilities, enabling effective document translation for international firms, and assisting with the customization of software and websites, LLMs are revolutionizing the e-commerce and retail sectors. These companies may overcome language hurdles, increase their worldwide reach, and provide a localized experience for customers from a variety of backgrounds by utilizing these LLMs. Around the world, LLMs are removing boundaries like language and fostering greater human connection.
The following three Large Language Model use cases and applications have shown to be very beneficial for all kinds of businesses:
-
Tools for Real-time Translation
Imagine being able to communicate with people from various linguistic backgrounds without having to take a crash course in every language by having a global translator at your disposal! Language barrier-breaking real-time translation technologies are powered by LLMs. These tools enable efficient communication between people who speak various languages by instantaneously translating text or speech between languages. Businesses that employ LLMs may give users instantaneous translation capabilities, enhancing cross-cultural communication and fostering international cooperation.
-
Translation of Documents for International Businesses
The translation of documentation for international firms is being revolutionized by LLMs. Companies may automatically employ LLMs to translate documents quickly and precisely, unlike traditional translation services. LLMs are capable of analyzing source texts, such as technical manuals, marketing materials, or contracts, and producing accurate translations that save money and time while maintaining localized and consistent content.
-
Localization of Websites and Software
When it comes to localizing websites and software for foreign markets, that’s where the use cases for large language models are essential. Businesses may translate menus, user interfaces, and other textual components to make their goods and services more culturally and linguistically appropriate by utilizing these models. LLMs contribute to the creation of a more captivating and user-friendly consumer experience by ensuring that the translated material is correct linguistically and culturally. They make sure that your material appeals to people all throughout the world.
4. Finance
In the financial services sector, LLMs have found a wide range of applications that are revolutionizing the way financial organizations function and engage with their clientele. These linguists are revolutionizing consumer experiences, investment choices, and security protocols. Financial organizations can evaluate credit risks more quickly than ever, keep one step ahead of fraudsters, and analyze market patterns like seasoned traders with the help of LLMs.
The following three financial services domains demonstrate the great utility of LLMs:
-
Fraud Identification and Prevention
LLMs operate similarly to undercover agents spotting financial scammers. Large amounts of financial data, including transactional data, customer records, and historical trends, may be analyzed by LLMs in fraud detection systems. LLMs may stop financial fraud by detecting abnormalities, spotting fraudulent trends, and sending out real-time alerts by utilizing natural language processing and machine learning algorithms. These models assist financial organizations in reducing losses and proactively safeguarding their clients.
-
Analysis and Trading of Financial News
When evaluating market data and financial news to make investing decisions, LLMs are crucial. To extract pertinent data and sentiment, these programs may comb through vast volumes of news articles, reports on markets, and social media data. Traders, analysts, and asset managers may make better investing decisions with the assistance of LLMs, which provide insights into investor moods, market trends, and corporate performance.
-
Assessment of Credit Risk and Loan Underwriting
LLMs are lending superheroes, assisting banks in evaluating credit risks more quickly than a bullet. Large amounts of consumer data, such as bank account records, credit histories, and loan applications, may be analyzed by these models. They analyze client information, go into credit reports, and provide insightful analysis to help make better loan choices. Financial companies may reduce risk and give their consumers quick, equitable access to financial services by automating and improving loan underwriting with LLMs.
5. Marketing and Advertising
Through the provision of content classification, targeted advertising, and enhanced search engine results, LLMs increase tailored suggestions and targeting. Businesses may provide more individualized experiences, improve user engagement, and maximize their marketing campaigns by utilizing these capabilities. With the help of LLMs, businesses may provide consumers with personalized information and suggestions, giving them the impression that they have a personal genie coming to their aid!
The following three categories of marketing and advertising are where large language models use cases and applications have shown to be extremely helpful:
-
Content Classification for Personalized Suggestions
Businesses may classify material and offer tailored suggestions depending on customer preferences thanks to LLMs. LLMs are your virtual taste buds; via examining user activity, interaction trends, and content attributes, they may find commonalities and offer suggestions that suit personal tastes. This improves customer happiness, user experience, and user engagement by providing pertinent and interesting material.
-
Personalized Marketing and Promotion
In focused marketing and advertising initiatives, LLM use cases are essential. By examining user data, demographics, and behavior, these models are able to generate tailored advertising messages that resonate well with particular target populations. By providing tailored advertisements, promotions, and deals, LLMs help businesses maximize their marketing efforts, which raises conversion rates and increases return on investment (ROI).
-
Enhancing Results from Search Engines
No more leafing through page after page of unimportant details! By comprehending user queries and delivering more precise and pertinent search results, LLMs contribute to the improvement of search engine results. By examining the semantics, purpose, and context of search queries, LLMs can provide more precise search results, reducing users’ time and supplying the required data. This improves customer pleasure and the search experience. To further optimize visibility and performance tracking, many marketers and SEO analysts combine LLMs with tools like residential proxies. These proxies help simulate real user behavior across locations, enabling accurate SERP tracking, ad verification, and geo-targeted content monitoring. Alongside VPNs and crawler bots, residential proxy providers offer reliable infrastructure for data-driven marketing strategies.
6. Cyber Law
In order to handle the intricate legal issues related to cyberspace, LLMs have proven to be invaluable instruments in the field of cyber law. With the use of these models, attorneys may investigate the intricate legal terrain of cyberspace, guarantee adherence to privacy laws, and handle legal issues resulting from cyber events. Through their insights, counsel, and assistance in efficiently addressing cyber-related legal challenges, LLMs strengthen the discipline of cyber law.
These are the three extremely successful LLM model use cases under cyber law:
-
Privacy Policy Analysis and Compliance
Legal liaison managers, or LLMs, are racing through policies like a bullet train! To find any possible holes, these models may examine terms of service, privacy policies, and data protection laws. Legal Litigation Managers (LLMs) provide support to legal professionals in evaluating compliance needs, creating privacy frameworks, and guaranteeing conformity to privacy rules and regulations, including the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
-
Case Analysis and Legal Research
When it comes to cyber law, LLMs are useful for case analysis and legal research. These models can provide important insights into cybercrime, digital rights, and new legal concerns by processing and analyzing pertinent laws, case law, and legal precedents. Legal language models (LLMs) are useful in the identification of pertinent instances, legal research, and preparation of legal arguments in the realms of cybersecurity, online privacy, and the protection of intellectual property rights.
-
Response to Cybersecurity Incidents
By examining vast volumes of data about malware assaults, network intrusions, and security breaches, LLMs assist in cybersecurity incident response. Legal practitioners can benefit from these models by using them to promote regulatory compliance, recognize potential legal ramifications, and comprehend the nature and consequences of cyber events. Risks are reduced, suitable answers are developed, and efficient communication between the technical and legal teams is facilitated by LLMs.
7. Healthcare
By assisting in medical diagnosis, facilitating literature reviews and study analysis, and providing tailored therapy recommendations, LLMs are revolutionizing biomedicine and healthcare. These models guarantee the provision of tailored care, promote scientific progress and improve the precision and effectiveness of medical decision-making.
The following three healthcare domains demonstrate the great utility of LLMs:
-
Help with Medical Diagnosis
By evaluating patient symptoms, medical histories, and clinical data, LLMs assist medical experts in making diagnoses. They act as a medical professional’s sidekick, sans the lab coat. In order to assist in decision-making, these models can propose possible diagnoses, offer possible courses of therapy, and present pertinent research articles. Healthcare professionals can benefit greatly from LLMs as they aid in timely and correct diagnosis, particularly in difficult or uncommon instances.
-
Review of Literature and Research Analysis
In biology, LLMs are frequently used for research analysis and literature reviews. Large volumes of scientific material may be processed and analyzed using these models, which aids researchers in finding pertinent data, seeing trends, and producing insightful conclusions. LLMs expedite the research process, making it easier to find novel therapies, technological breakthroughs, and relationships among biological ideas.
-
Analysis of Patient Data for Personalized Care
Personalized therapy suggestions can be supported by the analysis of patient data made possible by LLMs. LLMs may assist in finding patterns and connections in genetic data, medical reports, and electronic health records, which can result in more individualized treatment regimens and better patient results. LLMs enable medical professionals to perform precision medicine and tailor treatment plans to the unique needs of each patient.
Use Cases for the Large Language Model (LLM) Model
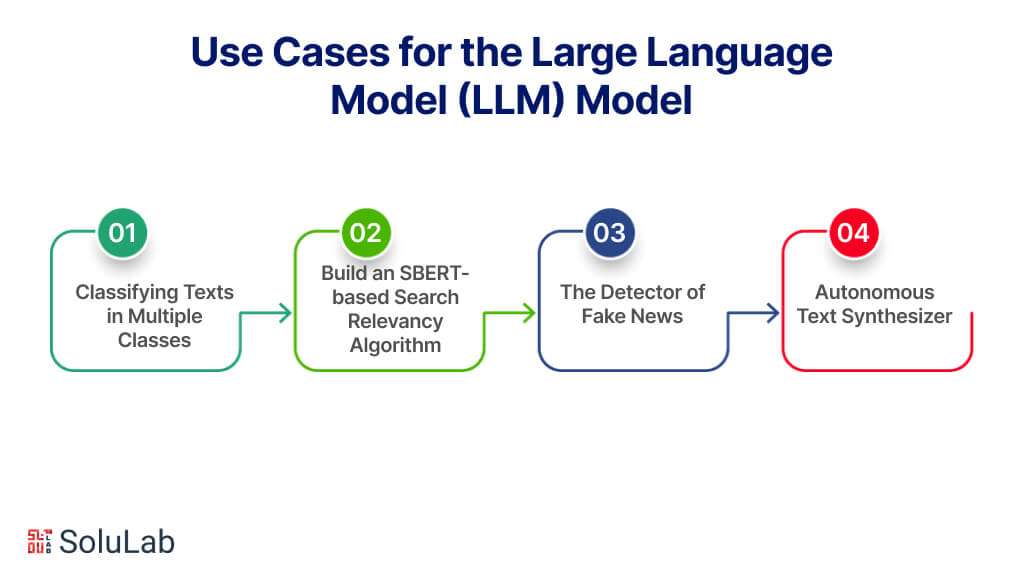
The following intriguing LLM project ideas will help you comprehend these models’ operation even more:
1. Classifying Texts in Multiple Classes
You will learn how to use the pre-trained BERT model to create a multi-class text classification framework in this LLM project. After loading the necessary libraries and datasets, you will prepare the textual data using several NLP approaches, such as Sentence Segmentation, word tokenization, Text Lemmatization, Stop-word elimination, etc.. You will learn about the LSTM model’s design and how it handles sequence-to-sequence learning by working on this project. You will get extensive knowledge of the BERT Base and Large models, as well as the architecture of the BERT model and how pre-training is carried out.
2. Build an SBERT-based Search Relevancy Algorithm
To maximize search relevancy for news items, you will learn how to develop and implement an accurate and reliable search algorithm on AWS employing the Sentence-BERT (SBERT) model and the ANNOY exact closest neighbor library in this one-of-a-kind and creative LLM project. The preprocessed news articles will be used to train the SBERT model and provide semantically relevant embedded sentences once the dataset has been preprocessed. Furthermore, the ANNOY library will be utilized for indexing the SBERT embeddings, facilitating efficient and rapid approximation of nearest-neighbor searches. You may facilitate users’ ability to search and locate pertinent news items by utilizing Docker containers to set up the project on AWS and make it available as a Flask API.
3. The Detector of Fake News
A big language model, like GPT-2 or GPT-3, can be used to construct a false news detector that can identify news stories as real or fraudulent. To begin, gather tagged news article datasets from sources such as Kaggle Fake News Challenge and FakeNewsNet. Next, you’ll use Python and NLP packages like NLTK and spaCy to preprocess the text data. Using features from the LLM, you will train a machine learning model (such as Naive Bayes or SVM) on the preprocessed data. The LLM has to be adjusted using a variety of transfer learning strategies in order to identify false news. For testing and assessment purposes, you may also use web scraping applications such as BeautifulSoup or Scrapy to get real-time news data.
4. Autonomous Text Synthesizer
One of the key components of developing an automatic text summarizer is using a broad language model, like BART or T5. Preprocessing the text data, which includes news stories and scholarly publications (e.g., PubMed), will be your first step. Tokenize, clean, and prepare the text using Python and NLP tools such as spaCy and NLTK. You will apply strategies such as sentence rating according to relevance or significance for extractive summarization. On a summarization assignment, you have to fine-tune the LLM using methods like transformer model fine-tuning or pre-training. To evaluate the caliber of the summaries produced by the LLM, you will also use assessment metrics like BLEU (Bilingual Evaluation Understudy) and ROUGE (Recall-Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation).

Conclusion
In conclusion, the myriad applications of large language models (LLMs) underscore their transformative potential across various industries. From enhancing customer service and automating repetitive tasks to driving innovation in healthcare and education, LLMs have emerged as indispensable tools for businesses seeking to stay ahead in an increasingly digitized world. However, as we embrace the opportunities presented by LLMs, it is crucial to remain mindful of ethical considerations, including biases and data privacy concerns, to ensure responsible and equitable deployment.
At SoluLab, we understand the power of LLMs and are committed to leveraging our expertise as an LLM Development Company to help businesses harness their full potential. Our team of skilled developers and data scientists specializes in crafting tailored AI solutions that align with our client’s unique objectives and challenges. Whether it’s building custom LLM applications, implementing robust data governance frameworks, or providing ongoing support and maintenance, SoluLab is dedicated to empowering organizations to thrive in the age of AI. Contact us today to learn about large language models and drive meaningful business outcomes.
FAQs
1. What are large language models (LLMs) and how do they differ from traditional language processing algorithms?
Large language models (LLMs) are advanced artificial intelligence (AI) models capable of understanding and generating human-like text. Unlike traditional language processing algorithms, LLMs leverage deep learning techniques and vast amounts of data to develop a nuanced understanding of language patterns, enabling them to generate contextually relevant responses and perform complex language-related tasks with remarkable accuracy.
2. What are some practical applications of large language models in business and industry?
Large language models (LLMs) find applications across various industries, including customer service automation, content generation, sentiment analysis, and document summarization. Businesses leverage LLMs to automate repetitive tasks, enhance customer interactions through chatbots, generate personalized content at scale, analyze customer feedback for sentiment insights, and summarize lengthy documents for improved efficiency.
3. How do ethical considerations come into play when deploying large language models?
Ethical considerations are paramount when deploying large language models (LLMs) due to concerns regarding biases, data privacy, and potential misuse. Organizations must ensure that LLMs are trained on diverse and representative datasets to mitigate biases, implement robust data governance practices to safeguard user privacy, and establish clear guidelines for responsible AI usage to prevent unintended consequences or harmful outcomes.
4. What challenges might businesses face when implementing large language models, and how can they overcome them?
Businesses may encounter challenges such as data scarcity, model complexity, and integration issues when implementing large language models (LLMs). To overcome these challenges, organizations can collaborate with experienced AI consulting partners like SoluLab, who offer expertise in data acquisition and preprocessing, model optimization, and seamless integration with existing systems, ensuring a smooth and successful deployment.
5. How can SoluLab assist businesses in harnessing the power of large language models?
SoluLab, as an AI Development Company, offers comprehensive solutions to help businesses harness the power of large language models (LLMs). From designing and developing custom LLM applications to providing ongoing support and maintenance, SoluLab’s team of skilled AI developers and data scientists leverages their expertise to tailor AI solutions that align with client’s specific objectives and challenges, empowering businesses to unlock the full potential of LLM technology.
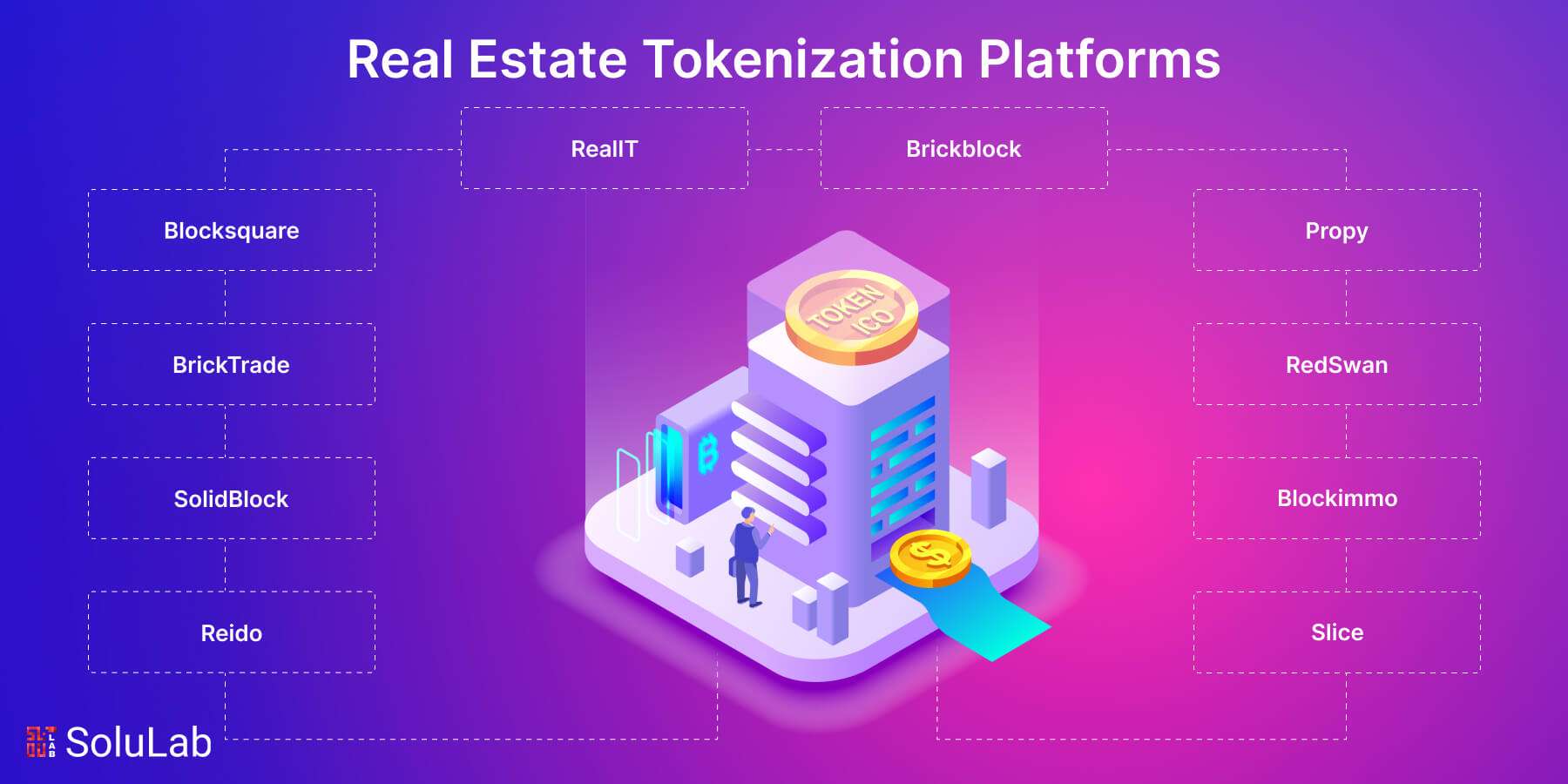
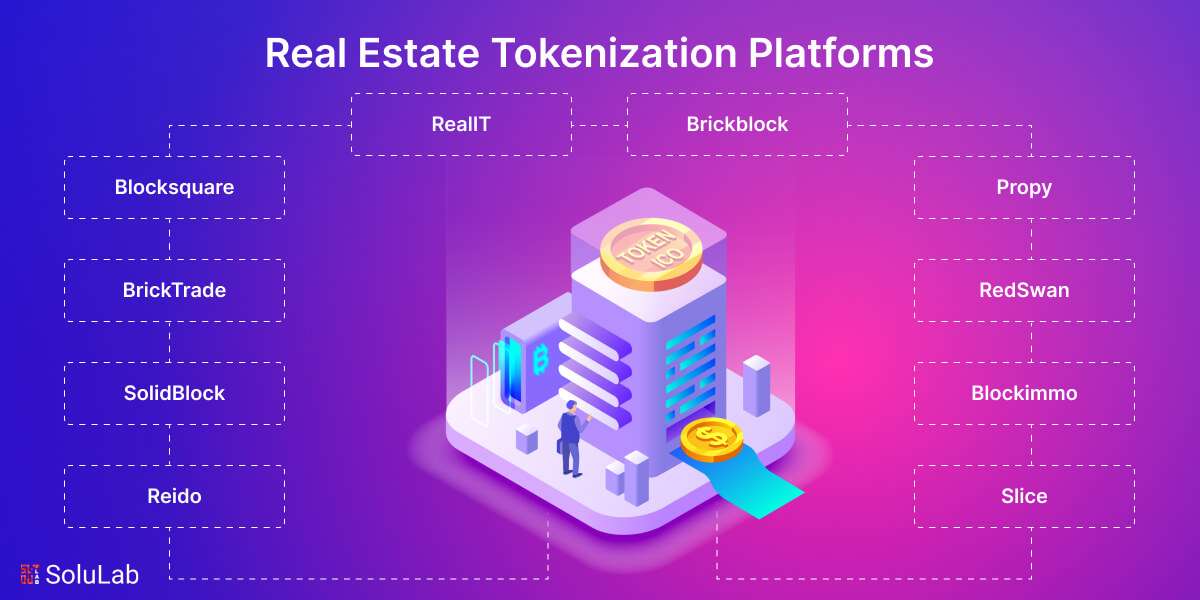 With an expected worth of $613 trillion in 2022 and a projected value of $637.80 trillion in 2024, the global real estate services industry is predicted to stay one of the world’s largest. Almost everyone is involved with real estate, whether as a renter, owner, or employee in an office, retail business, or factory. The real estate market is experiencing a massive upheaval, with real estate tokenization heading the way. In the present day, the importance of these platforms in transforming real estate investing cannot be overemphasized. In this blog, we’ll look at the top 10 real estate tokenization platforms that are already transforming the property investing market.
So, without any further ado, let’s get started!
With an expected worth of $613 trillion in 2022 and a projected value of $637.80 trillion in 2024, the global real estate services industry is predicted to stay one of the world’s largest. Almost everyone is involved with real estate, whether as a renter, owner, or employee in an office, retail business, or factory. The real estate market is experiencing a massive upheaval, with real estate tokenization heading the way. In the present day, the importance of these platforms in transforming real estate investing cannot be overemphasized. In this blog, we’ll look at the top 10 real estate tokenization platforms that are already transforming the property investing market.
So, without any further ado, let’s get started!