
When most people hear blockchain technology, they think of Bitcoin. In reality, blockchain is a business infrastructure that helps companies manage data securely, improve transparency, and build trust across operations. The global blockchain market is projected to reach $936 billion by 2030, showing how fast enterprises are adopting it.
What matters for your business is this: companies like JP Morgan, Goldman Sachs, and Fortune 500 enterprises already invest in blockchain development solutions for supply chain tracking, digital identity, cross-border payments, and real-world asset tokenization. If blockchain still feels like just crypto, you are likely overlooking the tokenization market, which is expected to grow into a multi-trillion-dollar opportunity by 2030.
If you want to understand the technology shaping enterprise systems, supply chains, and digital business models, let’s get started.
Think of blockchain technology as a shared digital notebook that many computers keep at the same time. When new data is added, everyone sees the update instantly. Once written, the data cannot be changed or deleted without the network knowing.
Each update is stored in a block that includes data, time, and a secure digital fingerprint called a hash. These blocks connect one after another, forming a chain. Because the data is stored across many computers called nodes, where no single company or person controls it. This makes blockchain secure, transparent, and trust-based by design.
Most traditional systems depend on middlemen like banks to approve payments, insurers to verify claims, and third parties to confirm ownership. These layers add cost, delays, and risk. Blockchain removes the middleman by letting the network verify data automatically using cryptography and consensus rules.
By 2026, blockchain will no longer be experimental as Enterprise spending on blockchain technology crossed $15B, showing that companies now treat it as core digital infrastructure, not a side experiment. Businesses are moving from pilots to production-grade blockchain systems because the ROI is clear and measurable.
From a business point of view, blockchain adoption is driven by results because:
This is why enterprises now work with top blockchain development companies to design systems that actually scale.
Aspect | Traditional Systems | Blockchain Technology |
Control | A single company owns the data | Shared network with no single owner |
Trust | Based on institutions | Based on cryptography & consensus |
Data Changes | Easy to edit or delete | Practically immutable |
Transparency | Limited access | Shared or permissioned visibility |
Failure Risk | Single point of failure | Highly fault-tolerant |
Cost Model | Cheap early, costly long-term | Higher setup with lower lifetime cost |
Best Fit | Internal apps | Multi-party and regulated systems |
In reality, traditional databases work well for internal tools, but Blockchain works best when multiple parties need shared truth, trust, and transparency, like supply chains, finance, identity, and sustainability systems. When designed correctly, blockchain becomes a long-term business layer, not just a technical upgrade.
At its core, blockchain improves how companies handle security, compliance, automation, and trust, especially when multiple parties are involved. These features directly impact how modern businesses operate at scale:
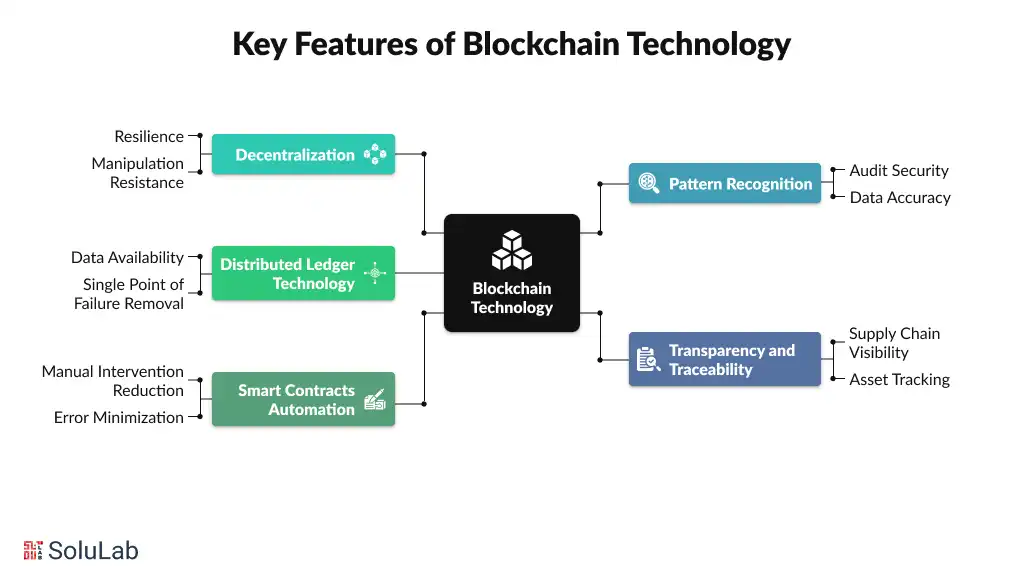
In traditional systems, a single server or authority controls all data, which creates a major risk if that system fails, gets hacked, or is misused. Blockchain removes this single point of control by spreading data across many independent nodes. Because no one party owns the system, it becomes far more resilient and harder to manipulate.
In most databases, data can be edited or deleted by users with the right access, which creates audit issues and trust gaps. With blockchain, once data is written on-chain, it cannot be altered without leaving a permanent record. Every change is time-stamped and traceable, making data integrity verifiable. This feature is critical for regulated industries that rely on accurate historical records.
Instead of one organization controlling the database, the ledger is shared across the network. All participants see the same verified data at the same time. Even if some nodes go offline, the system continues to function. This shared structure removes single points of failure and makes blockchain applications far more reliable.
Traditional systems often struggle to track assets across complex value chains. Blockchain creates a shared, tamper-proof record of transactions that authorized parties can view and verify. This allows easy tracking of assets, ownership, and movement across the entire value chain.
Many business processes depend on manual approvals, paperwork, and intermediaries, which slow things down and introduce errors. Smart contracts are programs that run automatically on the blockchain when conditions are met. Once deployed, they execute exactly as written. This is the foundation of modern smart contract development solutions, enabling faster operations, lower costs, and predictable outcomes.
Together, these features make blockchain technology a secure and reliable foundation for modern digital systems. They enable businesses to manage data, automate processes, and collaborate across multiple parties without relying on central control.
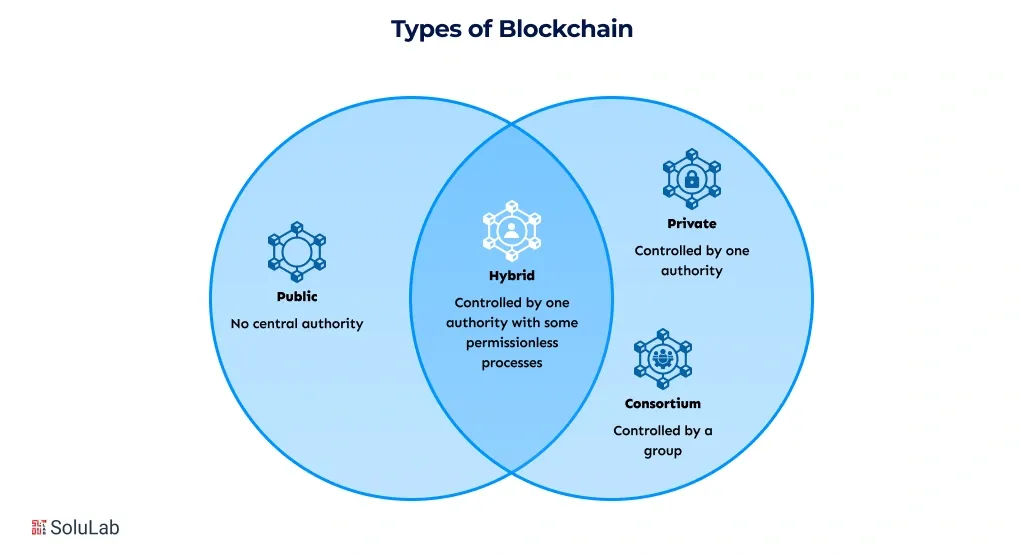
When starting with enterprise blockchain development, one of the first and most important decisions is selecting the right type of blockchain. The architecture you choose directly impacts speed, security, cost, and scalability, and picking the wrong one early can lead to expensive rebuilds. Let’s explore them one by one:
1. Public Blockchain
A public blockchain is fully open, allowing anyone to join, run nodes, and view data. It offers maximum decentralization, high security, and true immutability, making it ideal for applications that need global access and censorship resistance. However, transaction speeds are slower, fees can spike during congestion, and privacy is limited, which may pose challenges for regulated or enterprise-specific use cases.
2. Private Blockchain
A private blockchain restricts access to approved organizations, giving centralized control and high privacy. This type is fast, cost-efficient, and easy to comply with regulations, making it suitable for enterprises, banks, and closed networks. The trade-off is reduced decentralization, limited ecosystem liquidity, and security dependent on the validators managing the network.
3. Consortium Blockchain
A consortium blockchain balances control between multiple approved organizations, offering shared governance, moderate-to-high speed, and strong security. It works well for multi-organization partnerships and regulated industries that need both transparency and privacy. While it mitigates centralization risks, governance is more complex, and external liquidity remains limited compared to public chains.
4. Hybrid Blockchain
A hybrid blockchain combines public and private features, keeping sensitive data private while making core elements transparent. This model is flexible, privacy-focused, and suitable for regulated industries requiring some degree of public trust. Implementation is more complex, and speed and costs are moderate, but by leveraging blockchain layers, businesses can integrate scaling or private modules while maintaining strong security, improving performance, and enhancing efficiency.

| Feature/Type | Public | Private | Consortium | Hybrid |
| Access | Open to everyone | Only approved orgs | Multiple approved orgs | A mix of public and private |
| Examples | Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana | Hyperledger Fabric, Quorum | Energy Web, Marco Polo | IBM, custom enterprise |
| Speed | Slower (12–15 TPS) | Very fast (500+ TPS) | Medium–Fast (50–200 TPS) | Medium–Fast |
| Cost | Higher fees | Low operational cost | Shared cost | Moderate |
| Data Privacy | Fully transparent | High privacy | Balanced | Strong privacy layer |
| Security | Very high | Strong, controlled | Strong and distributed | High |
| Governance | Community-driven | Single owner | Distributed | Flexible |
| Regulatory Fit | Harder for regulated industries | High compliance | Strong fit | Best for regulated hybrid needs |
| Liquidity | Global liquidity | No external liquidity | Limited liquidity | Mixed |
| Best For | Web3, tokens, global platforms | Banks, fintech, insurance | Trade finance, logistics | Healthcare, government, hybrid |
To understand blockchain technology, it helps to see it as a system where multiple technical layers work together to create trust. Each component plays a specific role, but the real power comes from how they connect.
This structure is what makes blockchain development reliable for businesses using blockchain in enterprise-grade systems.
Everything in a blockchain starts with blocks. A block is a secure data container that stores transactions along with time, identity, and verification data. Each block carries a cryptographic fingerprint and is linked to the block before it, forming a continuous chain. Because every block depends on the previous one, changing data later becomes nearly impossible. This is how blockchains protect data using math, not human trust.
Once data is placed into blocks, it must be stored and checked by the network. This is where nodes come in. To understand blockchain nodes, think of them as independent computers that hold copies of the blockchain and verify new data. Different nodes handle storage, validation, or long-term records, depending on the network design. Because data lives across many nodes, the system stays online, secure, and resistant to manipulation.
With so many nodes involved, the network needs a way to agree on what is true. Consensus algorithms solve this problem. They define how transactions are verified and who gets to add new blocks. Some systems utilize computing power, while others employ staked value or permissioned validators. The key idea is simple: dishonest behavior is rejected by the network, making fraud extremely difficult in blockchain networks.
Once trust is established, blockchain goes beyond record-keeping. AI smart contracts automate the system. These are programs stored on the blockchain that execute actions when conditions are met. Because they run on the network itself, they remove manual steps and reduce operational risk. This is why modern blockchain applications and enterprise systems rely on smart contracts for efficiency.
The blockchain network is peer-to-peer, meaning every participant communicates directly without a central server. This decentralization distributes data and responsibilities, making the system more resilient and censorship-resistant. A P2P structure ensures that information flows transparently, supporting traceability and accountability in various industries.
All of this runs on a shared foundation called Distributed Ledger Technology. Instead of one central database, the ledger is shared across the network. Every participant sees the same verified data, and no single party controls it. If someone tries to alter their copy, the network rejects it instantly. This shared structure is what enables blockchain in sustainability, transparency, and long-term business trust.
Behind every block, node, and transaction is cryptography. Hashing protects data by locking it into fixed digital fingerprints, while public and private keys prove ownership and authorization. Building and maintaining these components requires strong fundamentals in cryptography, smart contracts, distributed systems, and security, which are core competencies for professionals working in blockchain developer skills. Every action on the blockchain is cryptographically signed, making forgery nearly impossible. This security layer ensures that blockchain data stays accurate, verifiable, and trustworthy at scale.
If you want to know how does the blockchain works, it operates as a shared digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers instead of a single central server. Every transaction is verified, recorded, and stored in a manner that ensures its security, transparency, and tamper-resistance.
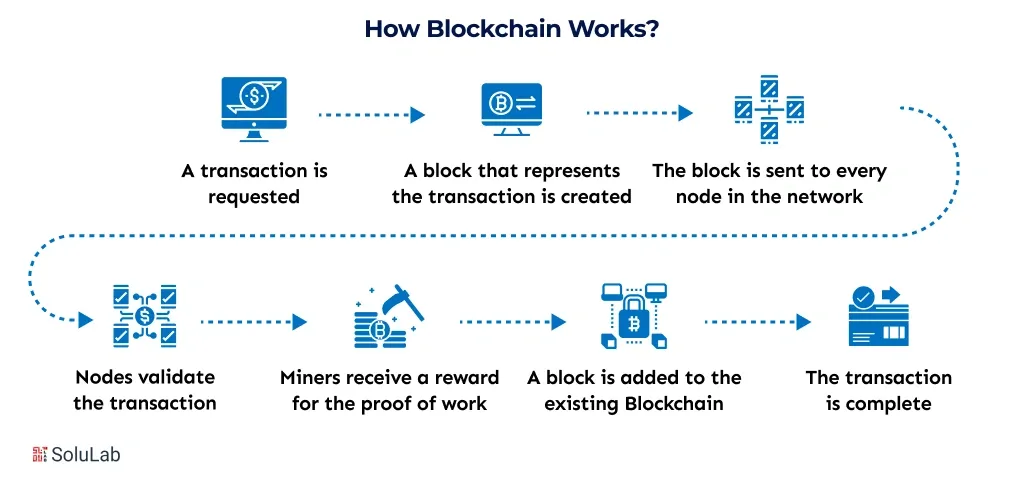
A blockchain transaction begins when a user requests an action, such as sending cryptocurrency, transferring a digital asset, or executing a smart contract. This request includes key details like sender, receiver, amount, and a digital signature for authentication.
The transaction is broadcast to a P2P network of nodes. Each node independently checks whether the transaction follows network rules, such as sufficient balance, valid signatures, and correct formatting.
Verified transactions are bundled together into a block. Each block contains:
This linking of blocks creates a chain, which is where blockchain gets its name.
Before a block is added, the network must agree that it is valid. This happens through a consensus mechanism, such as:
Consensus prevents fraud and ensures that no single entity controls the ledger.
Once approved, the block is permanently added to the blockchain. The data becomes immutable, meaning it cannot be changed without altering all following blocks, which is computationally impractical.
The updated blockchain is automatically synced across all nodes in the network. Every participant now holds the same version of the truth, ensuring transparency and trust without intermediaries.
Enterprise spending on blockchain technology has surpassed $15 billion in 2025, showing that the benefits are real, measurable, and tied directly to ROI. Here is why they are pushing towards implementing blockchain into their legacy systems:
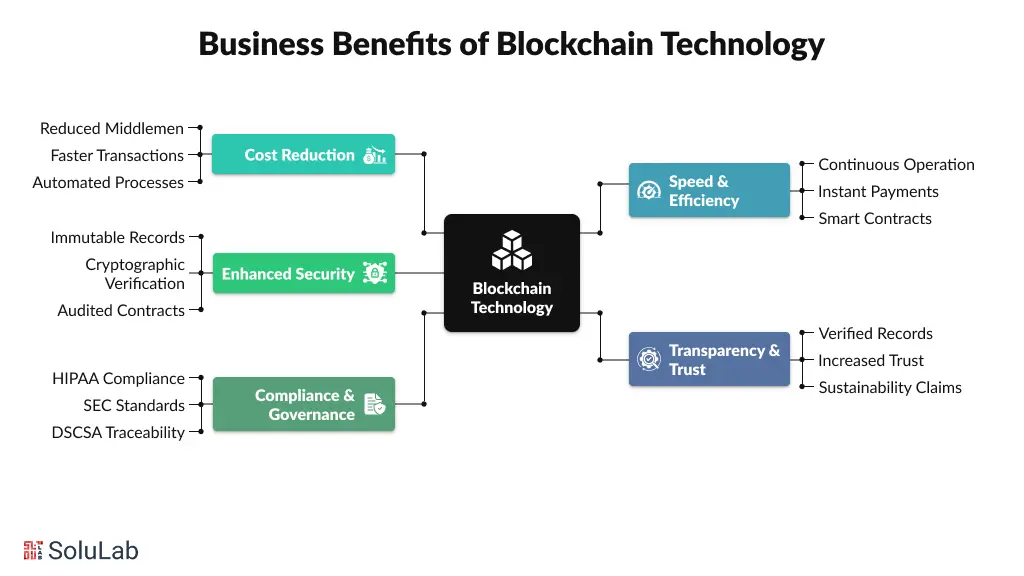
Blockchain reduces reliance on middlemen, cutting costs across payments, supply chains, and administrative processes. Cross-border transactions that once took days and carried 2–4% fees now settle in seconds with minimal costs. Supply chain verification that previously required weeks of manual checks can be completed in days, while insurance and contractual operations see automation reduce overhead by up to 60%.
Blockchain operates continuously, eliminating delays caused by business hours or intermediaries. Payments, settlements, and operational workflows happen instantly, while programmable smart contracts automate complex processes without manual intervention. This always-on capability drives efficiency, increases throughput, and allows enterprises to scale without adding proportional costs.
Blockchain provides immutable records and cryptographic verification, creating a zero-trust environment where approvals and transactions are secure and auditable. Audited smart contracts have a 0.2% exploit rate compared to 8.5% for unaudited contracts, demonstrating the security advantages enterprises gain. Multi-signature workflows, permanent audit trails, and regulatory-ready records protect data integrity and reduce operational risk.
With blockchain, customers and partners can verify product origin, ownership, and movement at every step. Verified digital records increase trust, support sustainability claims, and allow enterprises to charge a premium, with industry data showing 5–15% higher willingness to pay for authenticated goods. Blockchain also reduces disputes, strengthens brand reputation, and ensures compliance with ESG and sustainability requirements.
Blockchain enables permanent, auditable records that satisfy regulatory requirements across sectors. Healthcare data can remain HIPAA-compliant and tamper-proof, finance transactions can meet SEC standards, and supply chain operations can ensure traceability for DSCSA and other regulations. Energy and environmental markets also benefit from verifiable carbon credits and renewable certificate tracking, improving transparency and reducing fraud risk.

Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) is a cloud-based model where providers manage and host the blockchain infrastructure, allowing businesses to deploy blockchain networks, smart contracts, and decentralized applications (dApps) without building their own servers or managing complex infrastructure.
This approach enables enterprises to leverage the power of blockchain technology while focusing on business operations instead of IT overhead.
BaaS lets businesses deploy blockchain networks and applications without managing infrastructure. Key functions handled by providers include:
BaaS is ideal for startups, enterprises, fintechs, banks, and government agencies that want blockchain capabilities without IT overhead. It enables rapid deployment, secure operations, and competitive advantage across industries that need trust, transparency, and efficiency.
BaaS simplifies blockchain adoption and provides businesses with:
Enterprises use BaaS for applications like secure transactions, supply chain transparency, digital identity, and regulatory compliance. It supports scalable networks and integration with existing systems, enabling businesses to leverage blockchain for efficiency, transparency, and long-term value creation.

Blockchain technology has evolved into multiple protocols and platforms, each designed for specific use cases. Choosing the right foundation is critical for businesses, as different protocols optimize for speed, cost, privacy, and interoperability while enabling smart contracts, tokenization, and enterprise applications:
1. Layer-1 Protocols (Base Chains)
Layer-1 blockchains are the main networks that process transactions directly on-chain. Layer 1 blockchain platforms like:
Choosing the right one from the top Layer-1 blockchains ensures the network fits your speed, security, and governance needs.
2. Layer-2 Solutions (Scaling Layers)
Layer-2 solutions run on top of Layer-1 chains to increase speed and lower costs. Layer 2 solutions like:
These solutions deliver faster, cheaper transactions while keeping security anchored to Layer-1 networks.
3. Layer 3 Blockchains (Application-Oriented)
Layer 3 blockchain platforms focus on specific business applications, enabling custom features, cross-chain interoperability, and user-friendly APIs. They are particularly useful for enterprise dApps, tokenization, and AI-integrated blockchain systems. Examples of Layer 3 Platforms:
4. Enterprise Platforms
Enterprise blockchain platforms focus on security, privacy, and business integration. For Example, Hyperledger Fabric offers private channels and modular consensus for supply chains, R3 Corda secures financial transactions across 350+ institutions, Quorum enables private Ethereum-compatible networks, and IBM Blockchain provides managed enterprise solutions with compliance-ready templates. These platforms let businesses implement blockchain efficiently while protecting sensitive data and maintaining control.
Blockchain security practices function via cryptography and consensus. Every transaction is digitally signed, verified with private keys, and stored in tamper-proof blocks, so altering old records breaks the chain. Here are a few other ways blockchain helps:
1. Attack Vectors Prevention
While blockchain is robust, enterprises must be aware of potential attacks. Network compromise, such as 51% node attacks, identity flooding (similar to Sybil attacks), double-spending, and smart contract bugs, can occur. However, on mature networks, these risks are extremely low. Few solutions, like decentralized validators and Proof-of-Stake systems, drastically reduce vulnerabilities and ensure transactional integrity.
2. Additional Preventive Measures
Businesses can further secure blockchain systems by using audited smart contracts, multi-signature wallets, hardware key storage, and role-based access control. So staying updated with software patches, monitoring transactions in real-time, and choosing battle-tested blockchain platforms ensures operations remain tamper-proof, reliable, and trustworthy.
3. Blockchain for Identity & Trust
Blockchain enables self-sovereign identity (SSI) and verifiable credentials, giving users full control over their personal data without intermediaries. Through blockchain identity management, platforms like Polygon ID, Worldcoin, and CIVIC show how digital credentials, professional licenses, and KYC/AML verification can be completed faster, cheaper, and with better privacy, while reducing fraud and improving trust across enterprises.
The biggest shift in 2025 and beyond is not blockchain technology alone, but how AI in blockchain works. AI brings intelligence and automation, while blockchain brings trust, security, and verification. Together, they turn areas like DeFi, supply chains, healthcare, and governance into reliable, data-driven systems that enterprises can actually use at scale:
AI is changing how smart contract security works. Instead of slow, manual audits, AI models now scan smart contract code to detect bugs and exploits before launch. This reduces audit costs by 30–50%, lowers exploit risk, and helps businesses pursue secure blockchain technology applications faster. For a blockchain company, this means safer contracts, quicker deployments, and fewer costly failures.
As AI becomes core to business decisions, organizations must ensure their top AI models are accurate and not manipulated. Blockchain technology creates tamper-proof records of AI model training, updates, and performance over time. This helps enterprises meet compliance needs, verify AI claims, and track model degradation.
Many people think Bitcoin and blockchain are the same, but they are not. Bitcoin is a digital currency created to transfer value, while blockchain technology is the system that makes Bitcoin work. Think of Bitcoin as an application and blockchain as the underlying technology that powers it.
For businesses, the real value lies in blockchain development, not Bitcoin itself. Blockchain can be used to build secure records, smart contracts, digital identity systems, and supply chain tracking platforms. This is why enterprises implement blockchain as core infrastructure across industries, far beyond cryptocurrency.
| Aspect | Bitcoin | Blockchain |
| What is it | Digital currency | Distributed ledger technology |
| Purpose | Transfer of value (payments) | Used for contracts, records, identity, and supply chains |
| Created | 2009 by Satoshi Nakamoto | 1991 (concept), 2008 (practical use) |
| Use cases | Payments, store of value | Finance, healthcare, media, real estate, and voting |
| Supply | Fixed at 21 million coins | Unlimited use cases |
| Blockchain use | Uses blockchain technology | Powers many applications beyond Bitcoin |
A traditional database is controlled by one company or administrator. Only approved users can edit or delete data, which makes databases fast, simple, and cost-effective for internal systems.
Blockchain technology stores data across a decentralized network instead of one central owner. Once data is added, it becomes immutable and cannot be changed without network consensus.
| Aspect | Traditional Database | Blockchain Technology |
| Control | Managed by a central authority | Decentralized across a network |
| Data Structure | Editable records | Immutable blocks of data |
| Transparency | Limited access | Shared and verifiable |
| Security | Depends on central server | Cryptographically secured |
| Trust Model | Requires trust in owner | Trustless, consensus-based |
| Failure Risk | Single point of failure | No single point of failure |
Blockchain has moved beyond experiments and is now used in real production systems across industries. Enterprises adopt blockchain technology to reduce costs, increase transparency, automate trust, and unlock new digital business models. Below are the blockchain use cases actively driving enterprise spending today.
Blockchain development for finance enables faster and cheaper cross-border payments, reducing settlement from days to seconds with near-zero fees. Banks also use blockchain for lending, credit, and trading, where tokenized assets allow 24/7 markets, instant settlement, and global access. Platforms like JPM Coin, Ripple, and Partior show how blockchain removes intermediaries while improving liquidity and operational efficiency.
Blockchain in healthcare secures patient records with immutable timestamps, enabling compliant data sharing and faster audits. It also improves drug traceability, helping eliminate counterfeit medicines by tracking products from manufacturer to patient. Companies like Pfizer, CVS Health, and Guardtime use blockchain to strengthen data integrity, regulatory compliance, and trust across healthcare systems.
Blockchain in supply chain management gives every product a verifiable digital identity, allowing end-to-end tracking from source to customer. Enterprises use blockchain to reduce disputes, automate compliance, and enable instant payment upon delivery. Companies like Walmart, Nestlé, Carrefour, and DHL use blockchain to improve transparency, reduce fraud, and respond faster to quality issues.
Blockchain for smart cities enables transparent energy trading, real-time utility billing, and automated settlements. Households can trade excess solar power, while cities track water usage and payments without disputes. Platforms like Power Ledger and digital governments such as Estonia show how blockchain improves efficiency in public systems.
Blockchain in real estate simplifies property ownership by creating tamper-proof land and title records. Tokenization enables fractional ownership, faster closings, and global investor access. Platforms like Propy, RealT, and Lofty use blockchain to reduce fraud, cut paperwork, and unlock liquidity in traditionally slow markets.
6. Retail & E-commerce
Blockchain development for retail verifies product authenticity, reduces counterfeits, and increases customer trust. Blockchain also powers tokenized loyalty programs that work across brands and platforms. Companies like LVMH, Cartier, and Alibaba use blockchain to protect brand value, improve supply chain visibility, and increase buyer confidence.
Blockchain for governments is used for digital identity, land registries, and public records to reduce fraud and improve transparency. Blockchain-based voting systems create tamper-proof results and faster verification. Countries like Estonia, Ukraine, and Brazil show how blockchain improves governance while protecting citizen privacy.
Blockchain development for media and entertainment focuses on ownership, royalties, and content authenticity. Creators use smart contracts to receive automatic payments, while blockchain timestamps protect original work from plagiarism. Platforms like Audius, Mirror, and SuperRare help creators monetize directly without centralized platforms.
Blockchain for agriculture enables farm-to-table traceability by tracking products from harvest to shelf. Buyers can verify origin, storage conditions, and sustainability claims through QR codes. Companies like Nestlé, Carrefour, and Walmart use blockchain to reduce waste, improve food safety, and support premium pricing for verified products.
Blockchain for sportbetting enables provably fair games, instant payouts, and true digital ownership. Players own in-game assets as NFTs and can trade them freely across platforms. Projects like Axie Infinity and NBA Top Shot show how blockchain builds trust, transparency, and new revenue models in gaming ecosystems.
Building a production-ready blockchain system is not about writing smart contracts alone. It requires clear business thinking, the right technology choices, and disciplined execution. Below is the 7-step blockchain development process enterprise teams use to move from idea to a scalable, secure, and compliant solution.
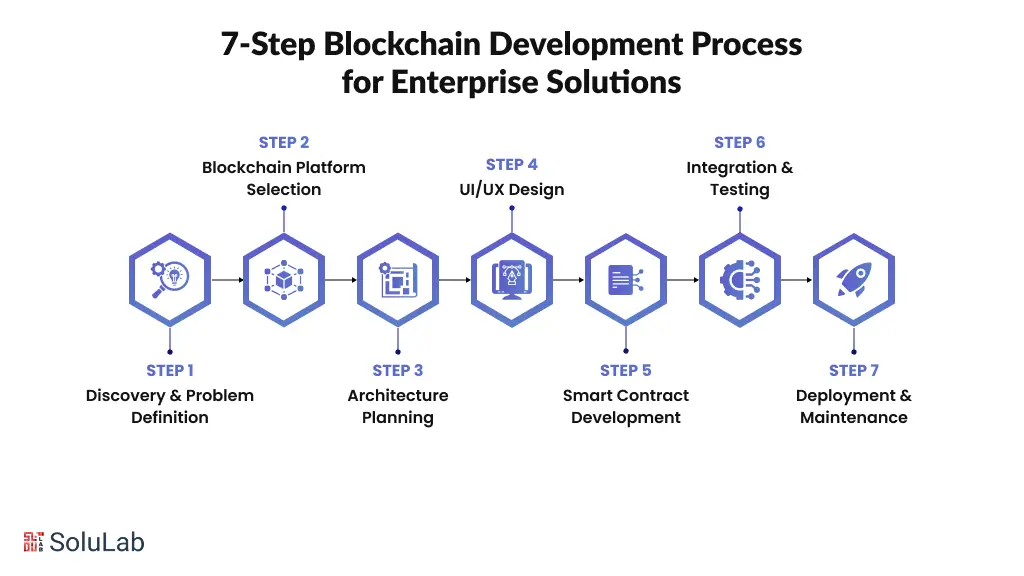
Every successful blockchain development project starts with clarity. We define the real business problem, map current workflows, identify stakeholders, and confirm whether blockchain is truly required or if a simpler system would work. At this stage, we also define ROI goals, compliance needs, and success metrics like cost reduction, speed, or transparency. This step usually takes 1–2 weeks and saves months of rework later.
Choosing the right platform is critical for performance, cost, and compliance. We evaluate public, private, consortium, and hybrid blockchains based on your use case. Enterprises often use Hyperledger Fabric or Quorum, while Ethereum, Polygon, or Solana work well for tokenization and Web3 applications. This decision phase typically takes 1 week.
We design the full blockchain system architecture, including smart contracts, data models, integrations, and security layers. We plan how blockchain connects with your existing ERP, databases, or APIs, while ensuring scalability and audit readiness. The output includes technical diagrams, contract specs, and security assessments. This phase usually takes 2–3 weeks.
Blockchain adoption fails without a good user experience. We design simple, role-based interfaces for admins, partners, auditors, and end users, while ensuring compliance and traceability. Prototypes are tested early so business teams can give feedback before development begins. This phase takes 2–3 weeks and ensures the product is usable, not just functional.
This is the stage where core business logic moves on-chain through a smart contract in blockchain development. We design and deploy secure, production-ready smart contracts using Solidity and industry-proven frameworks like OpenZeppelin. Access controls, input validation, upgrade paths, and testing are built in from day one. Depending on complexity, this phase takes 4–6 weeks and forms the backbone of your blockchain solution.
Smart contracts are integrated with frontend apps, backend systems, and external services. We perform full end-to-end testing, including unit tests, integration tests, load testing, and professional security audits. Audited systems reduce exploit risk from 8.5% to under 0.2%, making this step mandatory for production. This phase takes 3–4 weeks.
Once deployed, blockchain systems require continuous monitoring, not a one-time launch. We manage production deployment, performance tracking, security updates, scaling, and compliance monitoring. As usage grows, the system evolves with upgrades and optimizations. This phase is ongoing and ensures your blockchain solution remains reliable and future-ready.
Read Our Blog: How to Build a Blockchain PoC?
Transparent budgets would prevent delays and failed builds. So, here is a clear view of how blockchain development costs and timelines actually work today.
| Project Type | What You Get | Timeline | Investment |
| MVP / PoC | Simple smart contract + basic frontend | 4–12 weeks | $10,000 – $75,000 |
| Mid-Range Product | Custom chain logic + full dApp | 10–24 weeks | $80,000 – $150,000 |
| Enterprise Platform | Scalable, secure, compliance-ready | 6–12 months | $200,000+ |
Blockchain technology is evolving from experiments into a real business infrastructure. By 2026, enterprises will be actively adopting top blockchain trends to automate workflows, ensure regulatory compliance, and tokenize real-world assets at scale across industries.
The focus is shifting toward intelligence, privacy, scalability, and enterprise-grade adoption, not speculation. Here are a few areas where enterprises are focusing on:
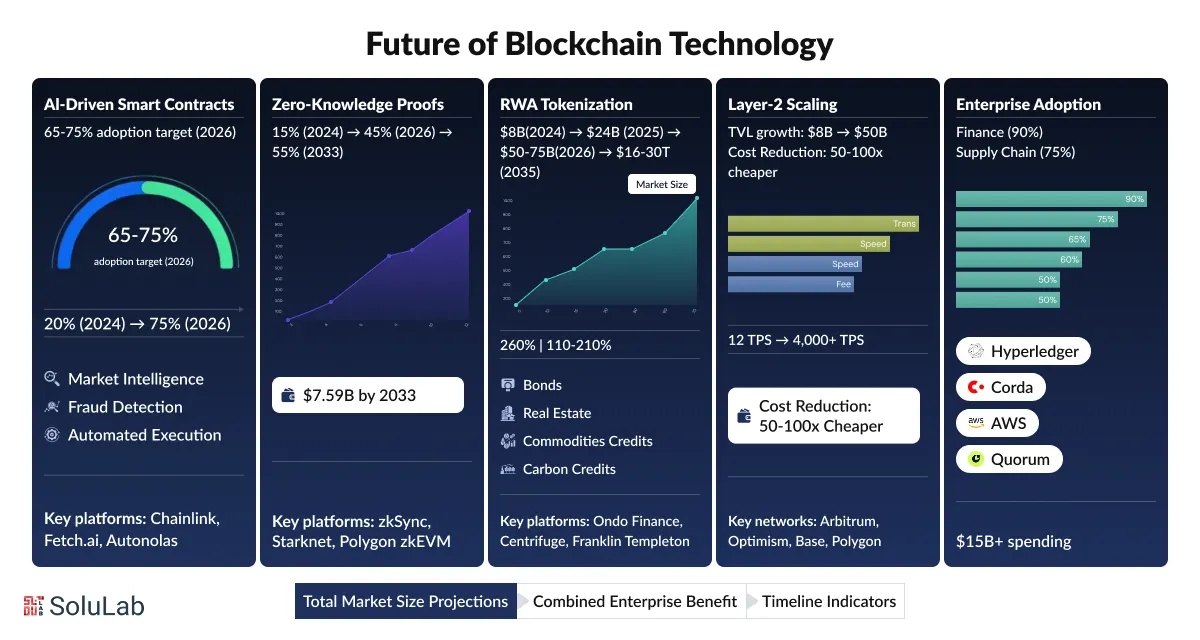
Smart contracts are becoming smarter with AI integration solutions. Platforms like Chainlink Functions, Fetch.ai, and Autonolas are already enabling contracts that react to market data, detect fraud, and execute complex rules automatically. For businesses, this means less manual control, faster decisions, and lower operational risk built directly into blockchain systems.
Privacy-focused blockchain adoption is accelerating with Zero-Knowledge (ZK) proofs. Projects like zkSync, Starknet, Polygon zkEVM, and Aztec allow enterprises to prove compliance without revealing sensitive data. This enables confidential transactions, private DeFi, and regulatory-ready blockchain systems, especially for finance and supply-chain use cases.
RWA tokenization is one of the fastest-growing blockchain use cases. Platforms such as Ondo Finance, Centrifuge, RealT, and Franklin Templeton’s tokenized funds are bringing bonds, real estate, commodities, and carbon credits on-chain. For businesses, blockchain development enables 24/7 liquidity, fractional ownership, and global investor access for traditionally illiquid assets.
To scale efficiently, enterprises are moving to Layer-2 networks like Arbitrum, Optimism, Base, and Polygon. These networks offer faster transactions, lower fees, and better user experience, while still inheriting security from main blockchains. Most modern blockchain applications are now L2-first and multi-chain by default.
Enterprise adoption is being driven by compliance-ready blockchains and mature tooling. Solutions like Hyperledger Fabric, R3 Corda, ConsenSys Quorum, and AWS Blockchain Services support audit trails, permissioning, and regulatory controls. At the same time, Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) and industry-specific chains are accelerating deployment across finance, healthcare, supply chains, and real estate.
The future of blockchain is about building scalable, compliant, and revenue-generating systems. Companies that partner with an experienced blockchain consulting company like SoluLab can move faster, avoid costly mistakes, and design solutions that deliver real business value from day one.

Blockchain is a real, production-ready technology transforming industries from finance and supply chains to healthcare and government. Companies adopting blockchain gain faster operations, verified traceability, and measurable business advantages, while creating new revenue opportunities through tokenization, smart contracts, and on-chain ecosystems.
At SoluLab, a leading blockchain development company, we help businesses turn blockchain potential into real results. From identifying the right use case to building secure, compliant, and integrated solutions, our team ensures your enterprise can unlock efficiency, trust, and growth.
Early adopters are already seeing cost reductions, faster audits, and higher pricing for verified products. So, if you want to grab the best, contact us now!
Beginners can start by exploring user-friendly blockchain platforms, wallets, and decentralized apps (dApps). For businesses, partnering with a blockchain app development company helps integrate secure, scalable solutions while leveraging top blockchain trends like AI integration, asset tokenization, and enterprise-grade smart contracts.
No. While technical knowledge helps, beginners can grasp blockchain concepts through simple analogies like digital ledgers, blocks, and nodes. Many platforms now offer beginner-friendly guides, tutorials, and hands-on simulations for making investing in blockchain development easy.
Custom blockchain development provides tailored solutions to meet specific business goals, industry compliance, and workflow automation needs. Unlike off-the-shelf solutions, custom development ensures scalability, security, and integration with existing systems for maximum efficiency.
Yes. Combining AI and blockchain allows businesses to create real-time predictive systems, automated decision-making, and fraud detection. AI models analyze data securely on the blockchain, enabling insights while preserving immutability and transparency.
Hiring a skilled blockchain developer ensures your project is secure, scalable, and efficient. Developers help implement smart contracts, integrate enterprise-grade blockchain platforms, and optimize workflows, reducing errors and accelerating time-to-market.
Depending on complexity, end-to-end blockchain solutions, from architecture and smart contracts to full deployment, can be implemented in 4–12+ weeks with an experienced development partner, accelerating time-to-market and reducing pilot-to-production delays.
SoluLab has delivered 150+ blockchain projects, maintains 95% client retention, and offers expertise across DeFi, Web3, AI-powered blockchain apps, and enterprise solutions. Our proven methodologies ensure faster delivery, secure systems, and measurable business impact.