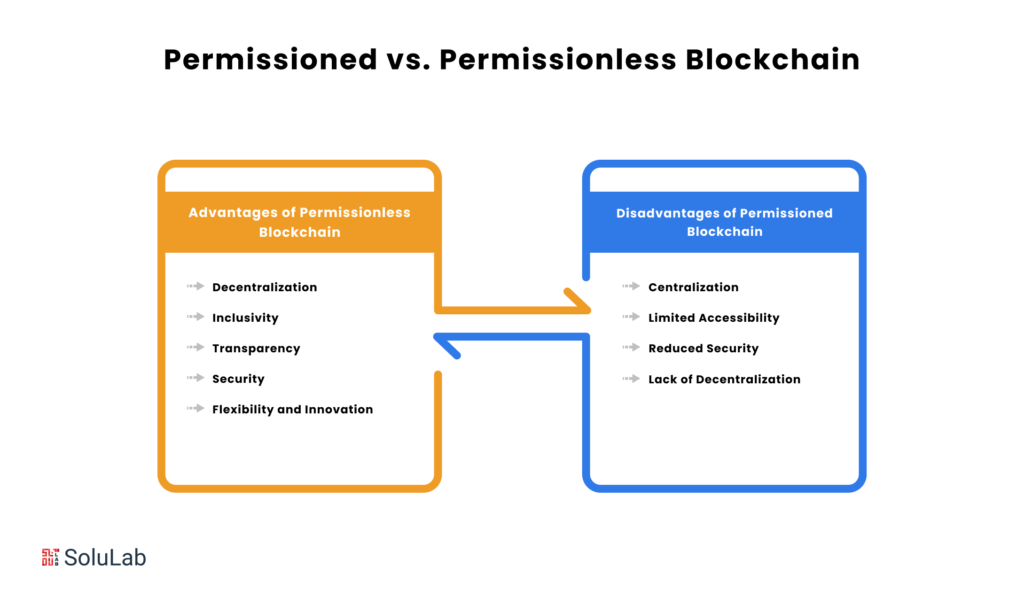
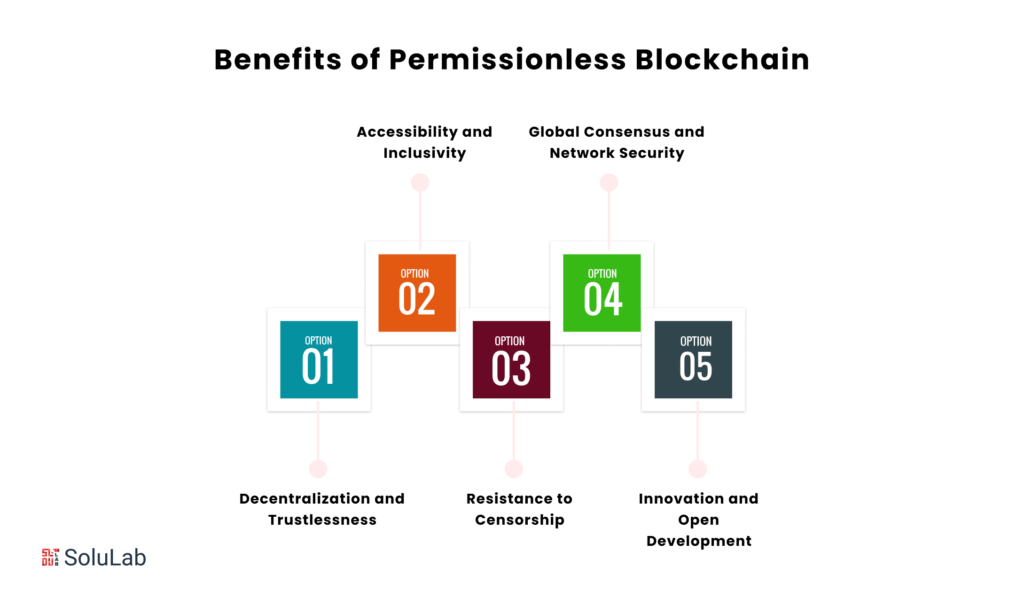
Art has always been an essential component of human history. Although all kinds of art are culturally significant, fine art has unparalleled popularity. That is most likely why fine art galleries and old painting museums outnumber pottery displays. But what remained secret until today was the truth that the authors of all those masterpieces faced difficult times and tried to protect their own work. All the while, a third party was cutting into their profits. However, the situation has greatly improved as new technologies have emerged.
The decentralized world of web3 and blockchain-based technologies, such as NFTs, provide current answers to such challenges, therefore improving the situation of artists. Artists can regain ownership of their works by transforming them into NFTs. Furthermore, NFT art pieces represent a long-term investment for consumers. They can resale the acquired NFT paintings years later for a nice price.
In this blog, we will explore the interesting convergence of Web3 in art industry, showing how this decentralized revolution is transforming the way we perceive, produce, and connect with artistic expressions.
What Exactly is Web3?
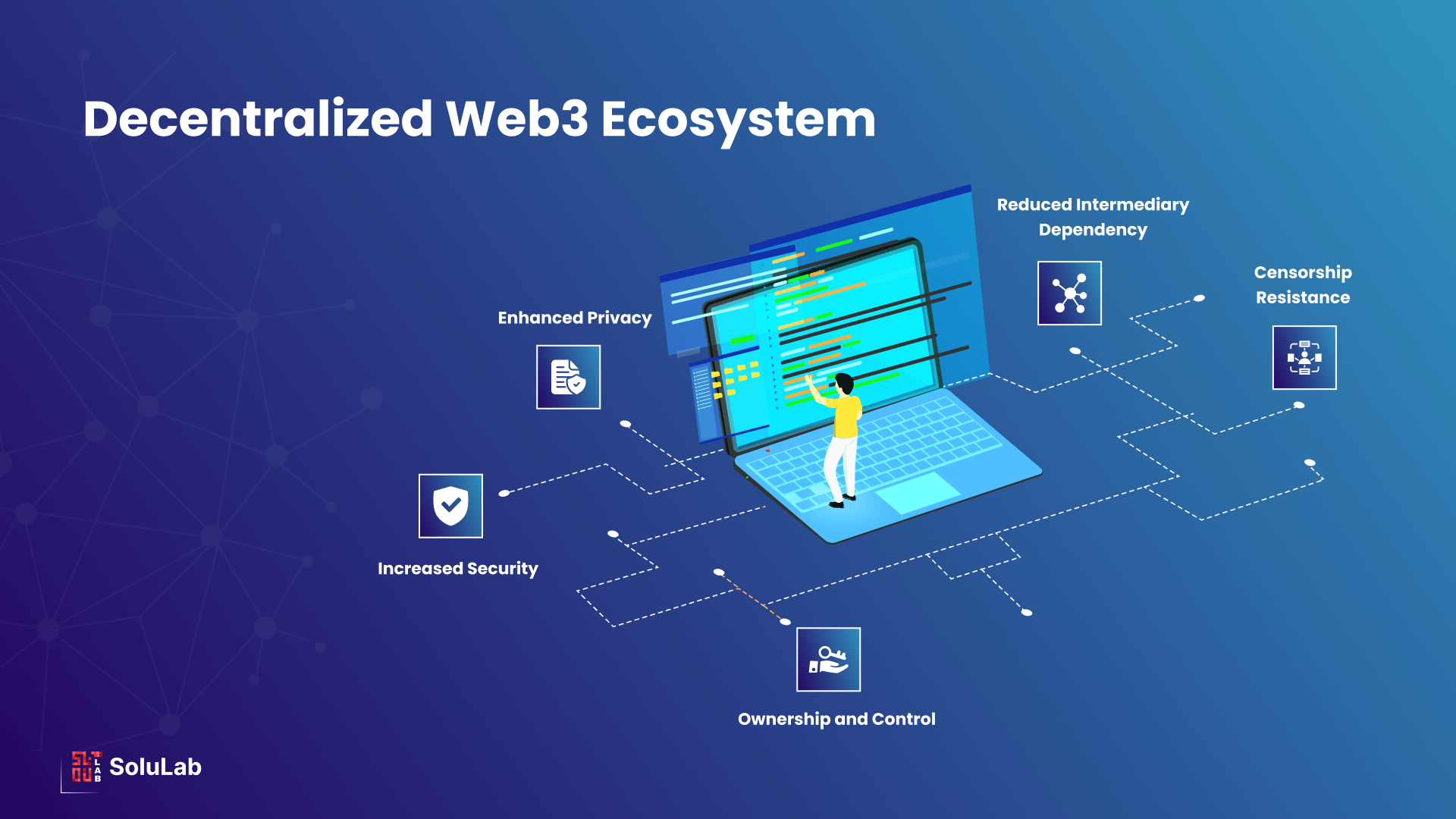
Web3, a concept invented by Gavin Wood, Ethereum’s co-founder, has grown in prominence over the past several years. It was launched with the notion that it would be an effective instrument for technological growth. Previously, the internet’s potential was limited. However, with web3, we have a variant of the internet that is both decentralized and safe.
This is the first time consumers have had ownership over their data online throughout the internet’s inception, owing to blockchain technology and its decentralized concept, which serve as the foundation for web3. Web3 might be deemed revolutionary given its far-reaching ramifications for the World Wide Web.
Problems in the Art Industry
Art is a global language, and the arts industry plays an important role in any country’s social and economic growth. However, the art world now confronts a number of issues, including:
- There are no established rules for pricing art items. Art galleries and other similar institutions are extremely discreet regarding their price structures. As a result, purchasers face unpredictable pricing and artists receive uneven profit shares.
- Artists must trust third-party businesses, like art galleries and auction houses, to sell their works. As a result, the profits are shared. In most situations, artists receive far less than the real profit generated by their artwork.
- Copyright is another critical problem confronting the art business. Because there is no surefire method to save information about a specific work of art, particularly its original owner and price, replication is both simple and profound. This is a significant disadvantage for artists, as their original artworks lose their distinctiveness and exclusivity.
- Furthermore, the art sector is uncontrolled across the world, resulting in massive losses for everyone involved.
Such limitations to the art business limit its total expansion. Thus, web3 adoption was required to address such long-standing difficulties and assist the sector evolve in creative ways. In Web3 in art industry, decentralization and transparent royalties will be the standard.
How is Web3 Affecting the Art World?
It’s been a long time since art was regarded as the most active and coveted market. While art’s global and diversified nature appears to assist, significant obstacles persist. Thus, there is an immediate need to reform the sector.
The good news is that improvements to the art sector are already on the way. Thanks to web3 technology, new solutions are being developed for addressing long-standing industrial concerns. The inclusion of web3 into the art sector is transforming the way art is purchased, sold, developed, and delivered.
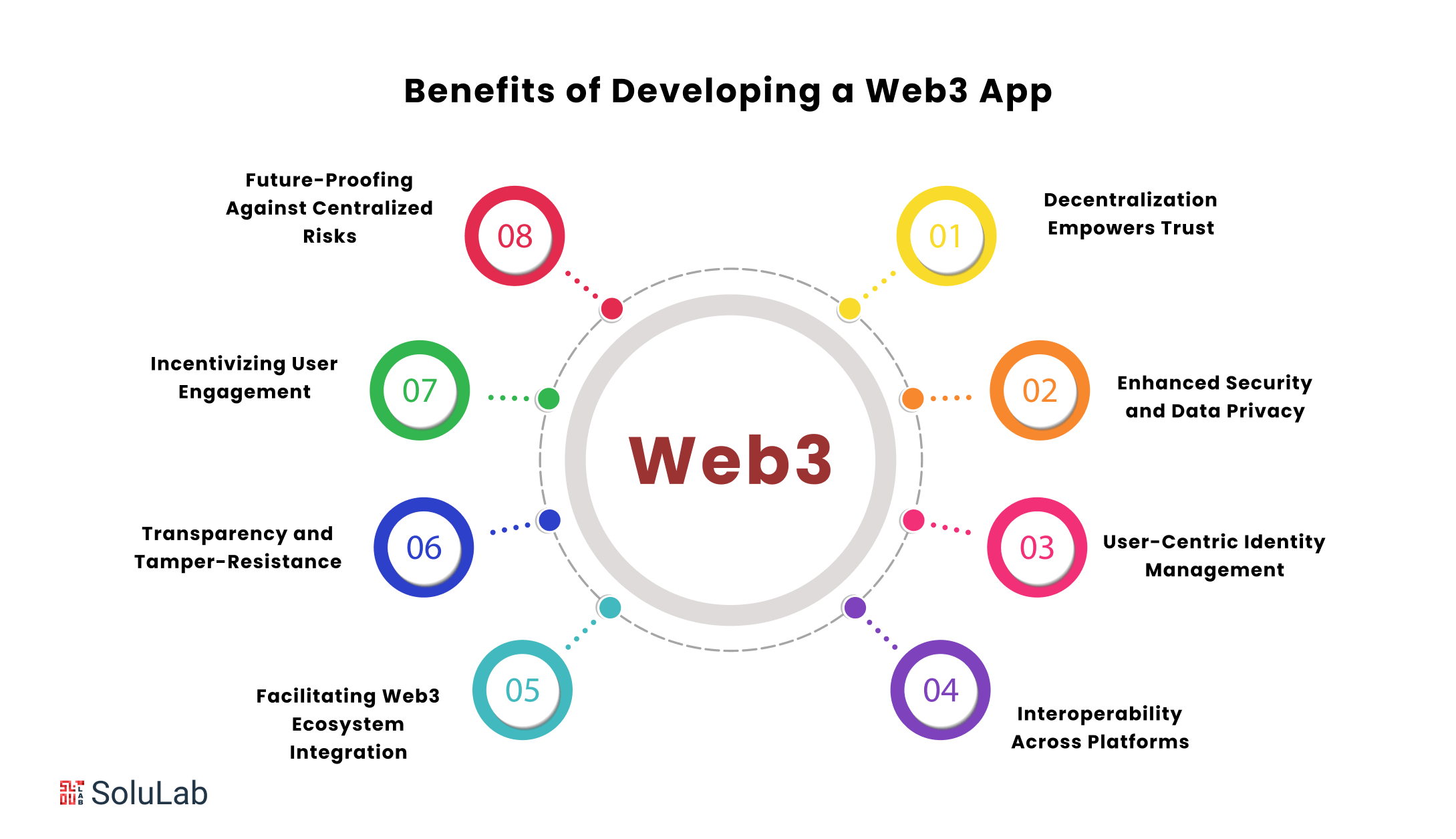
Web3 services, for example, make it simple for art collectors to acquire and sell artwork on liquid marketplaces. This allows art fans to build more diverse art portfolios without needing to pay more money or face the danger of complete ownership. Other benefits of web3 in the art sector include authenticity for artworks and legitimate certificates of origin for each piece.
Essentially, web3 promotes openness and combats fraud in the art sector. Web3 technology is also creating new opportunities for artists and customers to communicate directly.
Learn about the many facets of web3 in art and the shifts that will take place when a powerful technology (web3) and a massive industry (art) combine.
How Web3 Emerges in the Art Industry?
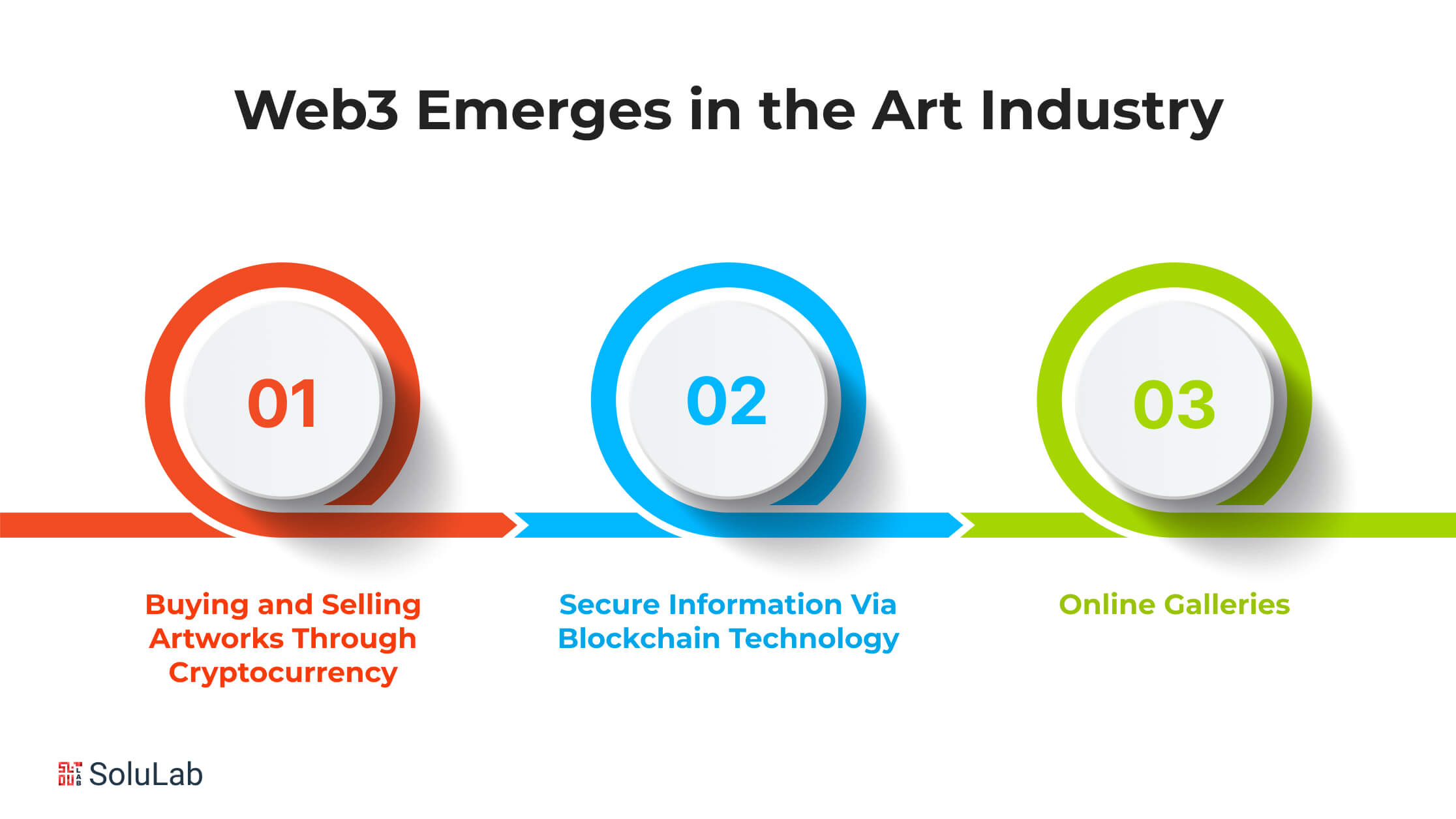
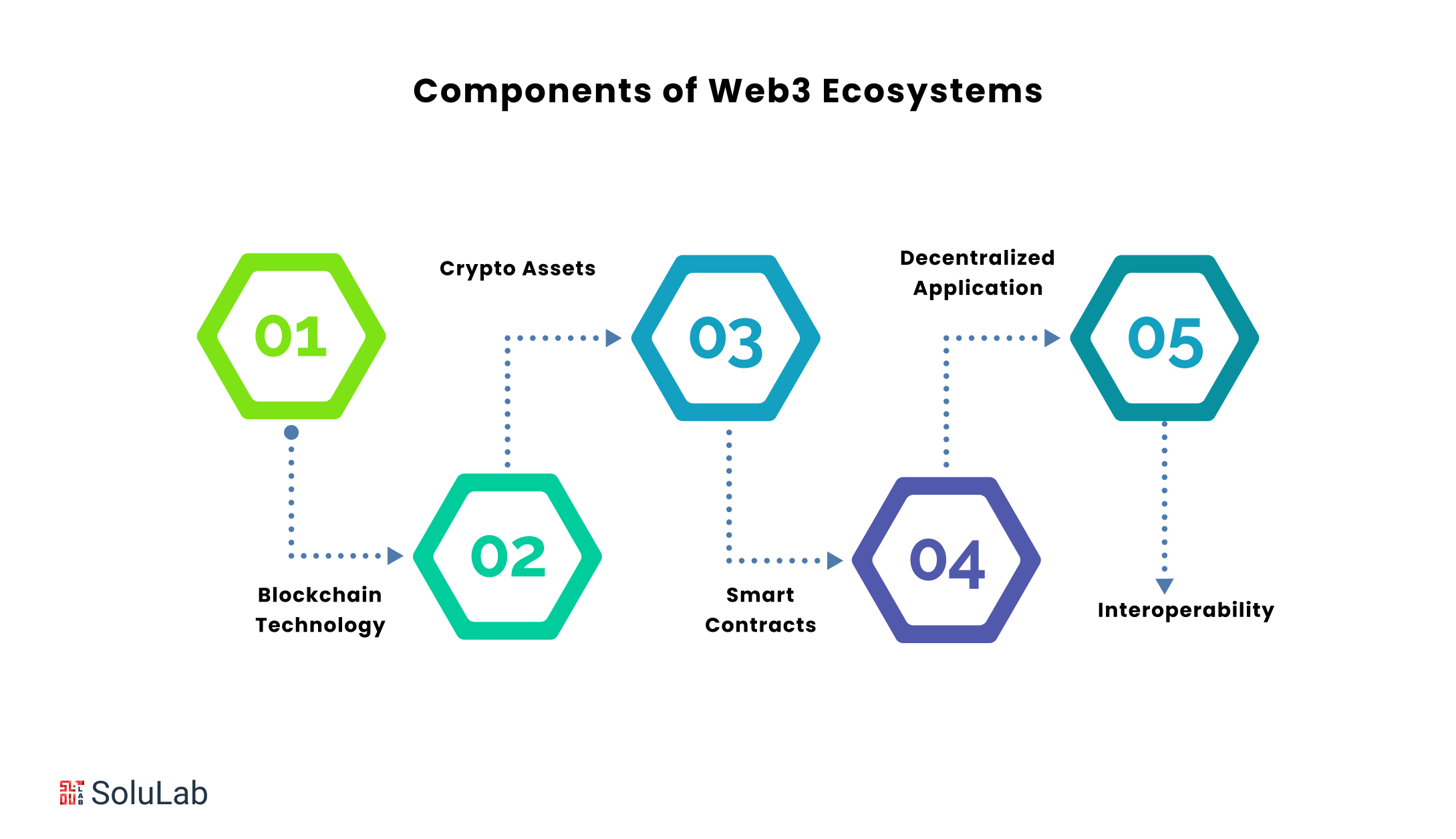
Web3’s popularity and industrial applicability are increasing due to its distinguishing features, such as decentralization, immutability, and utilization of a transparent distributed ledger. Essentially, these characteristics of web3 contribute to it being one of the most significant technologies of the twenty-first century. Web3 is the most secure and trustworthy technology available, and it has several potential applications in the art business. Let us look at them.
1. Buying and Selling Artworks Through Cryptocurrency
Bringing blockchain-backed web3 technology into the art field enables the purchase and sale of digital art using cryptocurrency. This allows the sector to avoid the participation of intermediaries like banks and approve transactions unilaterally.
2. Secure Information Via Blockchain Technology
The launch of web3 allows for the registration of all relevant information about a work of art on the blockchain, which greatly benefits art purchasers. NFTs of digital artworks are published on the blockchain, resulting in an accessible and distributed record. As a consequence, every piece of information relating to a work of art is kept safe since web3 technology prevents hacking and data manipulation.
3. Online Galleries
No matter how much the world progresses, the demand for art galleries will never diminish. Thus, web3 has managed to generate several significant advances, like online art exhibitions. So, with the support of blockchain-based art galleries, all operations such as purchasing and selling artworks have become digital.
Understanding Smart Contracts and Their Role in the Arts
Smart contracts, powered by blockchain technology, have emerged as a revolutionary tool reshaping the landscape of various industries, and the arts are no exception. These self-executing contracts encode and automate the terms of an agreement, eliminating the need for intermediaries and providing a transparent, tamper-proof record of transactions. In the realm of the arts, smart contracts bring a myriad of possibilities, from streamlining royalty payments to enabling new models of artistic collaboration.
Royalty Automation:
- Smart contracts can automate royalty payments for artists, ensuring a fair and transparent distribution of earnings based on predefined terms.
- Artists can set specific conditions for royalty disbursement, such as percentage splits among collaborators or automatic payouts triggered by sales or usage.
Immutable Art Provenance:
- Blockchain, the underlying technology of smart contracts, provides an immutable ledger in blockchain that records the provenance of digital and physical artworks.
- This transparency helps combat issues of art forgery and establishes a trustworthy history of ownership and creation.
Tokenization of Art Assets:
- Smart contracts enable the creation of tokens representing ownership of digital or physical art assets, facilitating the fractional ownership of valuable pieces.
- This asset tokenization can democratize access to art investments and redefine how art is bought, sold, and shared.
Exploration of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) Supporting Collaborative Art Initiatives
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are entities governed by code and consensus, embodying the principles of decentralization and collective decision-making. In the arts, DAOs have become a catalyst for collaborative projects, fostering a sense of community and shared ownership among artists and enthusiasts.
1. Collective Decision-Making
- DAOs allow artists and stakeholders to collectively decide on project directions, funding allocations, and creative choices through a transparent and democratic process.
- This decentralized decision-making model eliminates centralized authority, empowering participants to have a direct say in the development of collaborative art initiatives.
2. Funding and Resource Pooling
- DAOs enable crowdfunding and resource pooling for collaborative art projects, breaking down traditional barriers to financing creative endeavors.
- Contributors, often token holders within the DAO, can participate in funding decisions and share in the project’s success through transparent revenue-sharing mechanisms.
3. Global Collaboration
- With DAOs, artists from diverse geographical locations can seamlessly collaborate on projects without the need for centralized coordination.
- The global nature of DAOs facilitates cross-cultural exchange, broadening the scope and impact of collaborative art initiatives.
Related: Web3 in social networking
4. Token-based Incentives
- DAOs often use tokens as a means of governance and incentives. Contributors receive tokens representing their stake in the DAO, aligning their interests with the success of the collaborative project.
- Token-based incentives foster a sense of ownership and loyalty among participants, encouraging active engagement and commitment to the collective goals of the DAO.
How NFTs are Transforming the World of Art?
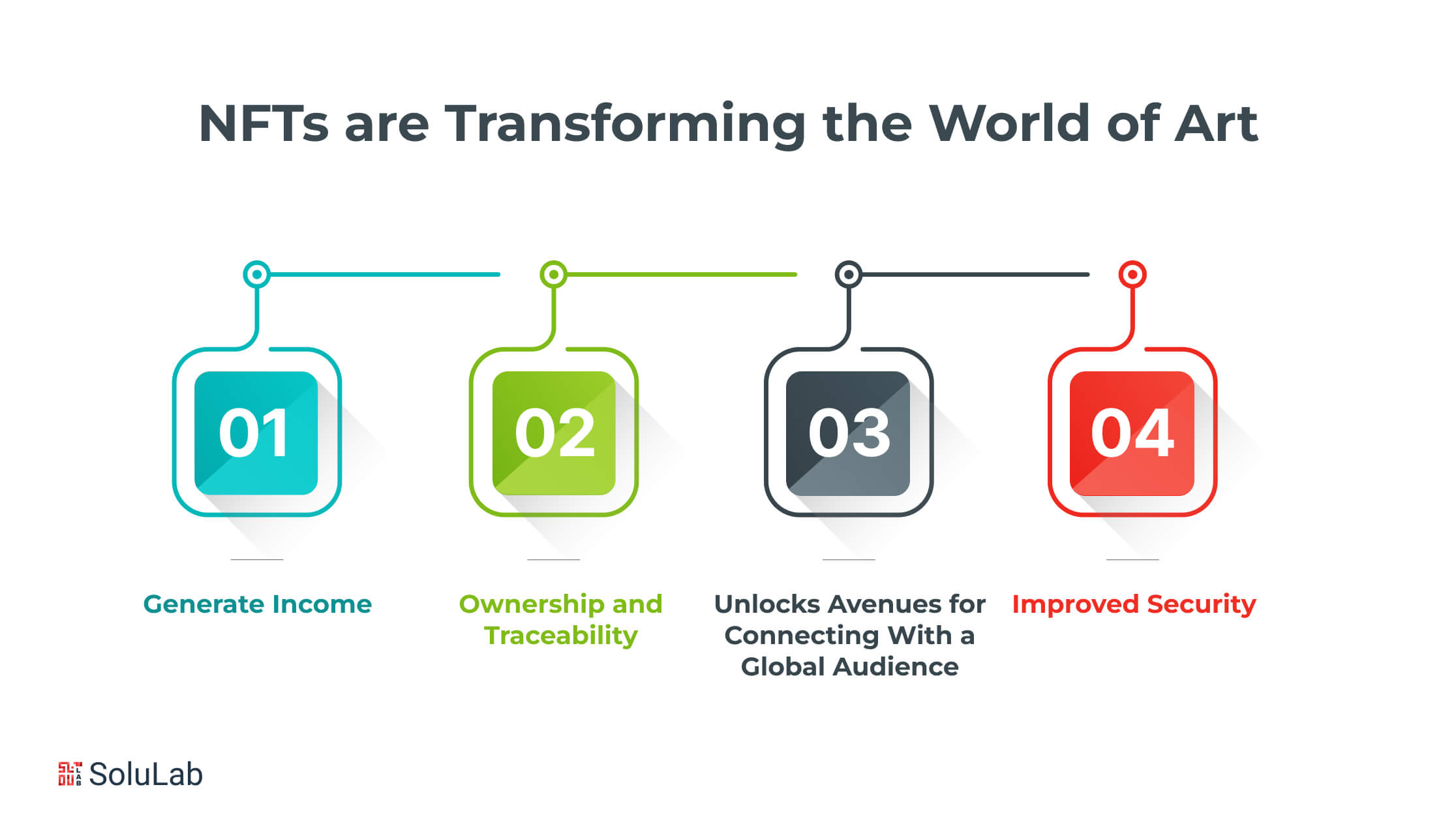
Non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, are frequently used, particularly in the art business. These digital tokens are in high demand among artists, collectors, and communities because they provide actual ownership. The NFT token provide a decentralized means to sell and buy art. Furthermore, they enable artists to communicate effectively with their audience while also providing clients with easy access to unique artworks.
The following are the most prevalent reasons why the art industry has begun to focus on NFTs.
1. Generate Income
NFTs are digital tokens used to monetize artwork. This is a significant advantage for both artists and art consumers. NFTs have enhanced practically every aspect of the art business, from the purchasing and selling of artworks to the worth of art and who it appeals to. Transactions and records have also grown more transparent, with no intermediaries present.
Artists may now get direct payments and earn their royalties. NFT in art also has a lot of appeal for customers. These digital art pieces are undoubtedly valuable since they may be used as an investment and sold for a profit.
Related: NFTs and Gaming
2. Ownership and Traceability
NFT artwork is unique. Why? Because Web3 is built on blockchain technology and uses it to create digital artwork. As a result, each digital artwork is assigned its own unique identification. Furthermore, all of the information is saved on a distributed ledger that is accessible to everybody. This makes tracking the ownership of digitally made art simple.
3. Unlocks Avenues for Connecting With a Global Audience
Connecting to the global market is essential for every organization today. The art sector has effectively entered the global competition with the support of NFT in art. This work may be rapidly produced, purchased, and sold anywhere in the globe. As a result, artists and collectors may collaborate without regard for geography.
4. Improved Security
As we all know, NFTs are blockchain’s finest use case. After all, each NFT art piece is recorded on the blockchain with unique records of legitimacy and chain of ownership. Furthermore, once saved on the blockchain, the NFT art’s data is hard to change or erase. This guarantees that the rarity and authenticity of digital artworks are preserved indefinitely and fosters a high level of confidence among collectors and artists.
In addition to the benefits listed above, converting physical art to NFT in art enhances supply chains and speeds up artwork production and dissemination. Long story short, NFTs have the potential to increase market efficiency in the art business by improving verification and transaction procedures.
Why are NFTs Significant for Artists and Art Collectors?
Non-fungible tokens are one of web3’s most profound uses, with the potential to modernize the conventional art sector. The promise of NFTs in art is being realized right before our eyes. Aside from bringing exciting new developments for art galleries and museums, NFTs have also proven to benefit artists and art collectors. Let’s look at how NFTs assist artists and collectors.
Benefits of NFTs for Artists
Though the digital revolution has created new prospects for everyone, artists continue to confront challenges due to the loss of originality in their work. Thank you to NFTs for assisting artists in securing their spot in the space. These digital tokens of art serve as a mark of authenticity for an artist’s work, granting them complete ownership, presentation, access, and resale rights.
Furthermore, artworks tied to NFTs have smart contracts at their heart. Smart contracts development are set up to be carried out when a piece of art is sold and exchanged among collectors. This allows original artists to get a portion of each sale. Additionally, the immutable and encrypted character of the web3 allows you to show exactly when and where the work was created, as well as who has owned it subsequently.
Benefits of NFTs for Art Collectors
People have always enjoyed acquiring valuable artworks that reflect their culture or emotional condition. For the same reason, people are enthusiastic about collecting digital art. NFTs provide art purchasers with more convenience in every manner. Art collectors may now buy, access, and exchange digital assets with a few clicks on their smartphones or PCs.
The fundamental advantage of Web3 for art collectors is that it links them directly to the artists. The direct link between artists and art consumers allows them to form powerful, long-lasting partnerships.
Regardless you are an artist or an art collector, one thing remains constant: web3 apps will create new chances for you and the industry to grow.
Benefits of Integrating Web3 into Art Auctions
The fine art auction industry is about to undergo a substantial structural upheaval. Web3 in art has significant ramifications, including fairer trade for artists, transparency for purchasers, and integrity in auction houses.
Web3 services assist the art auction sector in overcoming a number of obstacles while also providing significant benefits.
1. Authenticity
As we all know, some of the most expensive artworks are historical. As a result, verifying the legality of artwork origin and ownership is virtually difficult. The inability to verify the validity of a work of art may be regarded as the most basic challenge in the art industry.
Using web3 technology in the sector has brought significant solutions to the forefront. Art auction companies can create everlasting ownership records for their artworks. Because all information is saved on the blockchain, data modification is impossible. With web3 records, the art data cannot be used to unjustly increase or decrease its value.
2. Better Royalties and Transparency
Previously, art auctions did not appropriately compensate artists for their work and originality. Web3 reintroduced new approaches and equality into the art auction market. Thus, web3 into art auctions is working wonders for artists. They may now use public ledgers to track and collect royalties on their artwork sales.
Furthermore, due to web3, art information is now more accessible than ever. Blockchain-based digital recordings of art can be made public. This allows purchasers to better grasp an artwork’s history, former placements, and actual worth. With web3 collaboration, the art auction industry’s environment is expected to change, introducing new means of making art, acquiring, selling, and collecting. The industry will use this new technology to solve issues such as data background information, authenticity, transparency, copyright, and art fraud.
Related: Concept of NFTs and Their Use Cases
3. Adoption of Web3 in Art Galleries and Museums
Museums and exhibits play an important role in the art market because they link artists with art collectors. They are used to exhibit artwork, which lets artists and fans connect. The usage of web3 in museums, exhibitions, and art galleries provides transparency, reliability, security, precise tracking, and decentralization. In other words, web3 technology is causing a significant transformation in the museum and exhibition area.
- It is expected that the web3 model-equipped art market will expand more quickly. This is due to the opportunity that technology affords for shared ownership and democratization.
- With Web3-powered galleries and museums, artists may now directly sell their pieces of art without the help of a middleman, realizing the full worth of their labor.
- Because web3 digital artworks are built on NFT, their USPs will be traceability and scarcity.
- NFTs are kept on the blockchain, as far as we know. As a result, copying artwork won’t be a problem.
- Thanks to web3, museum passes and other forms of art may likewise be recorded as NFTs.
Upcoming Trends and Technologies to Look Out for
The growing field of Web3 in the arts portends a future full of breakthroughs and game-changing opportunities. Looking ahead, a number of new developments in technology and trends come to light, influencing the future of creative expression and participation.
1. Metaverse Integration
- The metaverse, an immersive virtual space, is poised to play a pivotal role in the future of Web3 arts. Artists may explore creating virtual exhibitions, performances, and installations within these digital realms, expanding the boundaries of audience interaction.
2. Interoperability of Blockchain Networks
- The interoperability of different blockchain networks is becoming a focus, allowing artists to seamlessly navigate and collaborate across various decentralized finance platforms. This can lead to increased flexibility and accessibility for both creators and audiences.
3. Environmental Sustainability Solutions
- Addressing concerns about the environmental impact of blockchain, innovative solutions are emerging to make Web3 more sustainable. Energy-efficient consensus mechanisms and eco-friendly blockchain networks are being developed to reduce the carbon footprint associated with decentralized technologies.
4. Enhanced Intellectual Property Protections
- Advances in decentralized technologies may lead to more robust solutions for protecting artists’ intellectual property rights. Smart contracts could evolve to offer enhanced mechanisms for copyright enforcement, ensuring artists receive fair compensation for their creations.
Final Words
The synergy between Web3 technology and the art industry has ushered in a radical transformation, promising not only a positive impact on society but also a pivotal role in elevating cultural engagement. The collaborative efforts between Web3 and the art world have sparked a revolution in art’s creation, distribution, and value, and web3 development companies are at the forefront of unlocking its true potential.
For those seeking robust web3 development services, SoluLab emerges as a key player in the field. Their team of skilled developers stands ready to assist in transforming innovative ideas into reality. Whether you are looking to hire web3 developers or embark on a journey to explore the vast potential of Web3 in art, SoluLab is your strategic partner in navigating this dynamic intersection of technology and artistic expression. Contact us today to embark on a transformative journey into the world of Web3 development services and redefine the future of art.
FAQs
1. How does Web3 impact the traditional art market?
Web3 challenges the dynamics of the traditional art market by introducing decentralized technologies like NFTs and smart contracts. This shift enhances transparency, alters ownership structures, and opens up new avenues for artists, collectors, and galleries to engage with and trade art in innovative ways.
2. Can you provide examples of successful collaborative art projects facilitated by Web3?
Certainly! Web3’s influence is evident in projects where decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) support collaborative initiatives. Notable examples include artists coming together globally to create art via DAOs, enabling transparent decision-making, funding, and ownership structures through blockchain technology.
3. How does Web3 address concerns about the environmental impact of blockchain technology in the arts?
Web3 is evolving to address environmental concerns by exploring energy-efficient consensus mechanisms and eco-friendly blockchain networks. The community is actively working on solutions to make Web3 in the arts more sustainable, ensuring that the transformative power of blockchain doesn’t compromise ecological considerations.
4. How does the tokenization of art assets work in the context of Web3?
Tokenization involves representing ownership of digital or physical art assets through blockchain-based tokens. Web3 enables fractional ownership, making art investments more accessible. These tokens, often traded as NFTs, allow for transparent provenance, automated royalties through smart contracts, and democratized access to the art market.
5. How does SoluLab contribute to the integration of Web3 in the arts?
SoluLab, as a leading web3 development company, plays a key role in revolutionizing the art industry. The company provides robust web3 development services, empowering individuals and organizations to tap into the true potential of Web3 in art. From facilitating the adoption of NFTs to implementing smart contracts and decentralized platforms, SoluLab is committed to guiding you through the dynamic intersection of technology and artistic expression. To explore the transformative possibilities of Web3 in the arts, consider contacting SoluLab for unparalleled web3 development expertise.