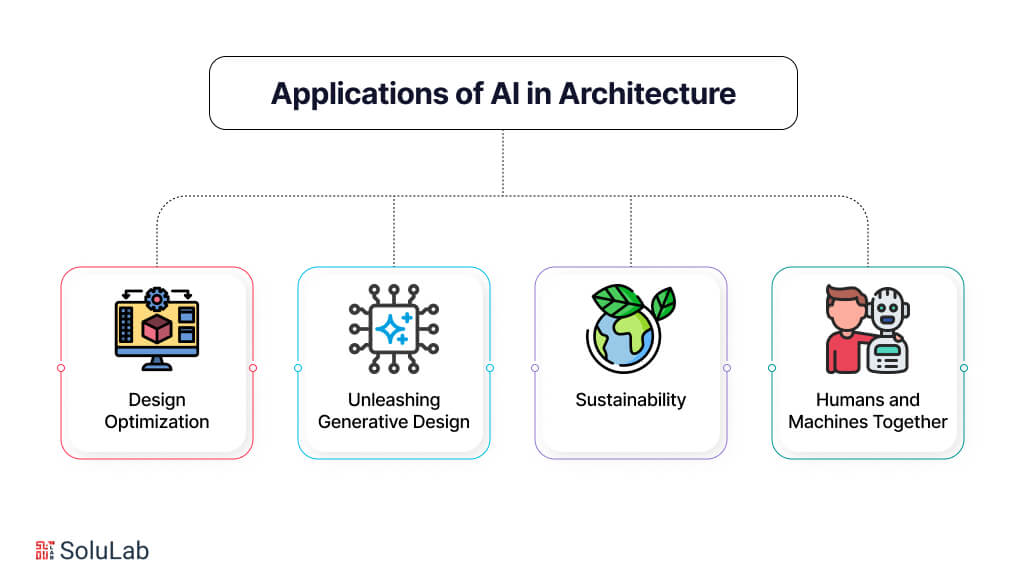
AI agents are improving enterprise workflows by operating as a coordinated crew, with each agent specializing in different business functions. Just like a well-structured team, they collaborate to understand employee intents, route requests, retrieve information, and resolve issues. Whether it’s resetting passwords, processing time-off requests, or managing software access, these AI agents work together to deliver smooth and efficient support experiences.
According to Statista AI agents are poised to become the next step in the evolution of AI for businesses in our increasingly digital society, whether they are used to automate mundane tasks or optimize complex workflows. Their learning capacity, adapting, and making smart choices create novel possibilities for innovation and applications in various fields.
If you are planning to adopt AI agents for your enterprise, this article is for you as it explores their key use cases across various business functions, including IT support, HR, finance, sales and marketing, and more.
Future of AI Agents in Business
1. Innovations and trends
AI agents in business have a bright future due to various trends and advancements. AI agents—AI-powered virtual assistants—are becoming smarter with advances in natural language processing, machine learning, and cognitive computing. AI agents can better comprehend and forecast consumer demands with these technologies, improving customer service and operational efficiency.
Integration of AI agents across corporate functions is a major trend. In addition to customer support, AI agents are employed in sales, marketing, and HR. This wide range of applications helps firms automate activities, analyze big data, and make quick decisions. These platforms simplify the creation of sophisticated AI bots that can have complex conversations and do complex jobs.
2. Estimates for the Next Decade
Technology is likely to impact healthcare and transportation in the coming decade. AI agents in the healthcare industry are improving and automating tasks assisting in diagnosis, and personalizing treatment plans, ultimately improving efficiency and patient outcomes. In artificial intelligence (AI), tremendous advancement is expected. Experts expect AI to improve its natural language processing and problem-solving skills, making human-machine interactions more natural. The adoption of driverless vehicles is a significant AI prediction over the next decade.
Real-World Examples of AI Agents
Take a look at some AI agent applications in different industries:
1. E-Commerce AI Agents
AI agents are being used by e-commerce platforms to improve the buying experience. These agents can Place orders automatically. Even they can track and send out shipment updates and make image-based product searches easier. This AI agent can remind people about carts that are left behind. For example, 35 percent of Amazon’s revenue comes from its AI-powered recommendation system.
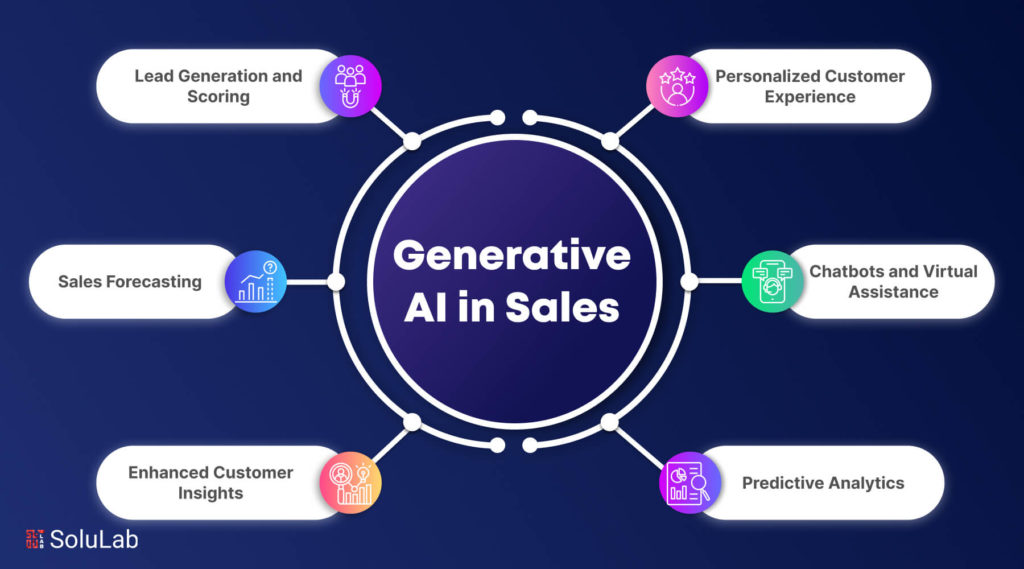
2. Sales and Marketing AI Agents
Sales and marketing procedures are being improved by AI sales agents by creating lists of leads. They can customize messages. Plan and carry out advertising campaigns and analyze competitors.
One excellent illustration of an AI agent enhancing lead creation is Find AI. Find AI’s agents can identify and qualify leads with remarkable accuracy by letting users define extremely specific search parameters. By using AI, users can give more targeted results by understanding the user intent and going beyond basic keyword searches.
3. Customer Support AI Agents
AI-driven customer service is progressing beyond basic chatbots. Chatbase and other contemporary AI customer service representatives perform tasks on behalf of users, such as processing refunds and changing passwords. Customers support AI agents can make product recommendations and address complicated technical support concerns.
Read Also: Top 10 Web3 Custom AI Agent Builders & Companies For Enterprises in 2026
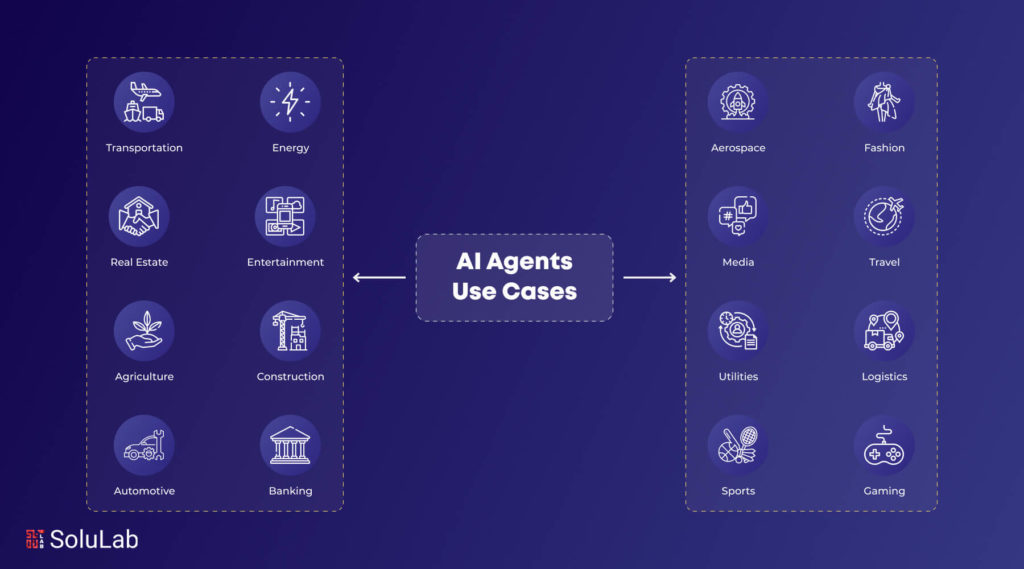
Top AI Agents Use Cases in 2025
AI agents, with their ability to process vast amounts of data and make decisions, are transforming various industries. Here are 15 detailed use cases of AI agents across different sectors:
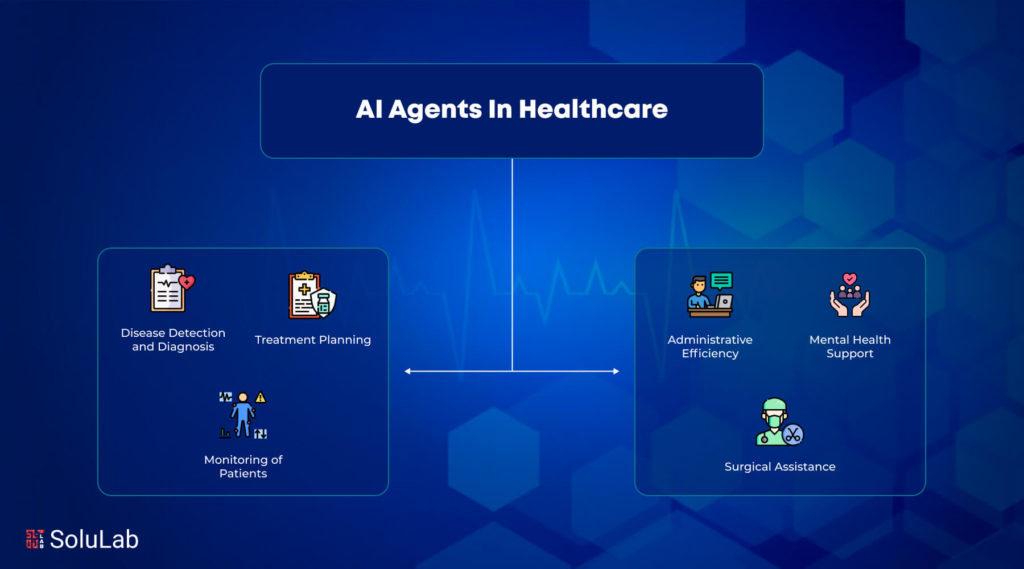
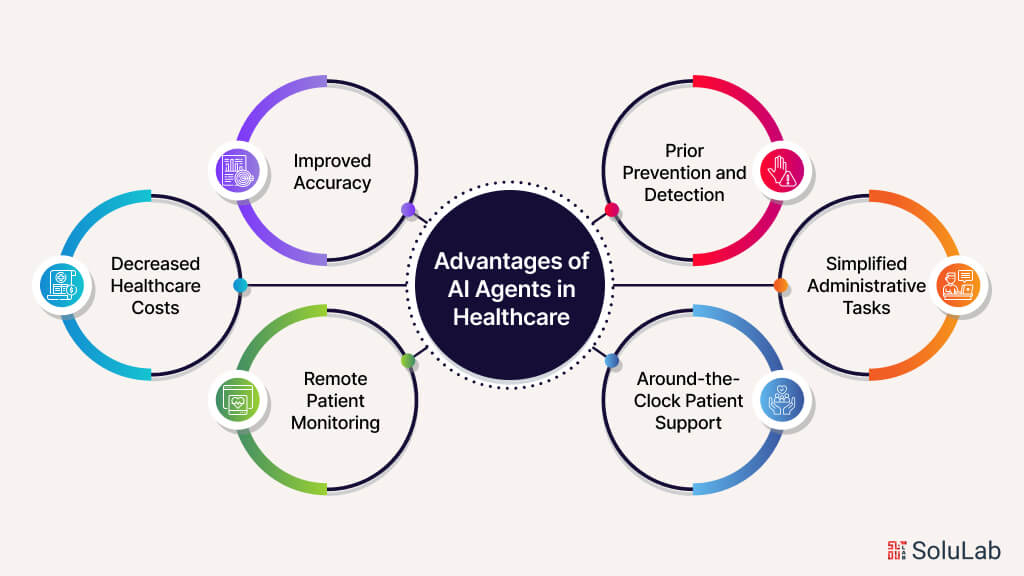
1. AI Agents in Healthcare
AI agents are revolutionizing the healthcare industry by enhancing patient care, streamlining administrative tasks, and aiding in medical research. Here are some specific use cases:
a. Patient Diagnosis and Treatment
AI healthcare agents analyze medical records, lab results, and imaging data to assist doctors in diagnosing diseases. For instance, IBM’s Watson can read millions of pages of medical literature and compare patient data to suggest potential diagnoses and treatment plans.
b. Predictive Analytics
AI agents in healthcare use predictive analytics to foresee patient outcomes. By examining historical data, these agents can predict the likelihood of readmissions, complications, or the progression of diseases, allowing for proactive intervention.
c. Virtual Health Assistants
Virtual health assistants, powered by AI, interact with patients through chatbots or voice assistants. They provide medical advice, answer health-related queries, and remind patients to take their medications, improving adherence and health outcomes.
d. Administrative Efficiency
AI agents streamline administrative tasks such as scheduling appointments, managing patient records, and handling billing. This reduces the workload on healthcare staff, allowing them to focus more on patient care.
e. Drug Discovery and Development
AI agents accelerate drug discovery by analyzing biological data and predicting the efficacy of new drugs. They identify potential drug candidates, optimize clinical trial designs, and reduce the time and cost involved in bringing new medications to market.
Read Also: Vertical AI Agents
2. AI Agents in Finance
The finance industry is leveraging AI agents to enhance security, improve customer service, and optimize investment strategies. Here are some prominent use cases:
a. Fraud Detection
AI agents detect fraudulent activities by analyzing transaction patterns and identifying anomalies. They can flag suspicious transactions in real time, helping financial institutions prevent fraud and protect customers.
b. Customer Service
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants provide 24/7 customer service, answering queries, resolving issues, and guiding customers through financial products and services. This agent in AI improves customer satisfaction and reduces operational costs.
c. Investment Management
AI agents analyze market trends, financial news, and economic indicators to provide personalized investment advice. Robo-advisors like Betterment and Wealthfront use AI to create and manage investment portfolios tailored to individual risk profiles and financial goals.
d. Risk Management
AI agents assess risk by analyzing vast amounts of financial data. They predict market fluctuations, identify potential risks, and suggest strategies to mitigate them, helping financial institutions make informed decisions.
e. Compliance and Regulation
AI helps financial institutions comply with regulatory requirements by monitoring transactions, ensuring adherence to rules, and generating compliance reports. This reduces the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties.
3. AI Agents in Retail
AI Agents in Retail: Retailers are using AI agents to enhance customer experiences, optimize supply chains, and increase sales. Here are some specific use cases:
a. Personalized Shopping Experiences
AI agents in retail industry analyze customer behavior, preferences, and purchase history to recommend products tailored to individual tastes. This personalization increases customer satisfaction and drives sales.
b. Inventory Management
AI agents predict demand for products by analyzing sales data, market trends, and seasonal patterns. This helps retailers manage inventory more effectively, reducing overstock and stockouts.
c. Pricing Optimization
AI agents dynamically adjust prices based on factors such as demand, competition, and market conditions. This ensures competitive pricing while maximizing profits.
d. Visual Search
AI-powered visual search allows customers to upload images of products they are interested in. The AI agent then finds similar products in the retailer’s catalog, enhancing the shopping experience.
Related: Generative AI In Retail Industry
e. Customer Support
AI chatbots provide instant customer support, answering queries, handling returns, and assisting with purchases. This reduces the workload on human staff and improves customer satisfaction.

4. AI Agents in Insurance
The insurance industry is harnessing the power of AI agents in insurance to improve processes, customer service, and risk assessment. Here are some key use cases:
a. Claims Processing
AI agents automate the claims processing workflow by verifying documents, assessing damages, and determining claim validity. This speeds up the process and reduces errors, leading to faster payouts and improved customer satisfaction.
b. Risk Assessment
AI agents analyze data from various sources, such as social media, sensors, and historical claims data, to assess risk more accurately. This helps insurers price policies appropriately and reduce fraudulent claims.
c. Underwriting
AI agents assist underwriters by analyzing applicant data and predicting the likelihood of claims. This enables more accurate risk evaluation and policy pricing, leading to better decision-making.
Read Also: Impact of AI on the Insurance Sector
d. Customer Service
AI chatbots and virtual assistants handle customer queries, provide policy information, and assist with claims. This AI agent use cases improve customer experience by providing quick and accurate responses.
e. Fraud Detection
AI agents detect fraudulent activities by analyzing patterns and anomalies in claims data. They identify suspicious claims and flag them for further investigation, reducing the incidence of fraud.
5. AI Agents in Hospitality
The hospitality industry is leveraging AI agents in hospitality to enhance guest experiences, streamline operations, and improve efficiency. Here are some notable use cases:
a. Personalized Guest Experiences
AI agents analyze guest preferences and behavior to offer personalized recommendations and services. This includes room preferences, dining options, and activity suggestions, enhancing the overall guest experience.
b. Automated Check-In and Check-Out
AI-powered kiosks and mobile apps allow guests to check in and check out seamlessly without human intervention. This reduces wait times and improves operational efficiency.
c. Virtual Concierges
AI virtual concierges provide guests with information about the hotel, local attractions, and services. They can also handle requests such as room service, reservations, and transportation, improving guest satisfaction.
d. Predictive Maintenance
AI agents monitor equipment and systems within the hotel to predict maintenance needs. This prevents breakdowns, reduces downtime, and ensures a smooth operation.
e. Revenue Management
AI agents analyze market trends, demand patterns, and competitor pricing to optimize room rates and maximize revenue. This helps hotels achieve higher occupancy and profitability.
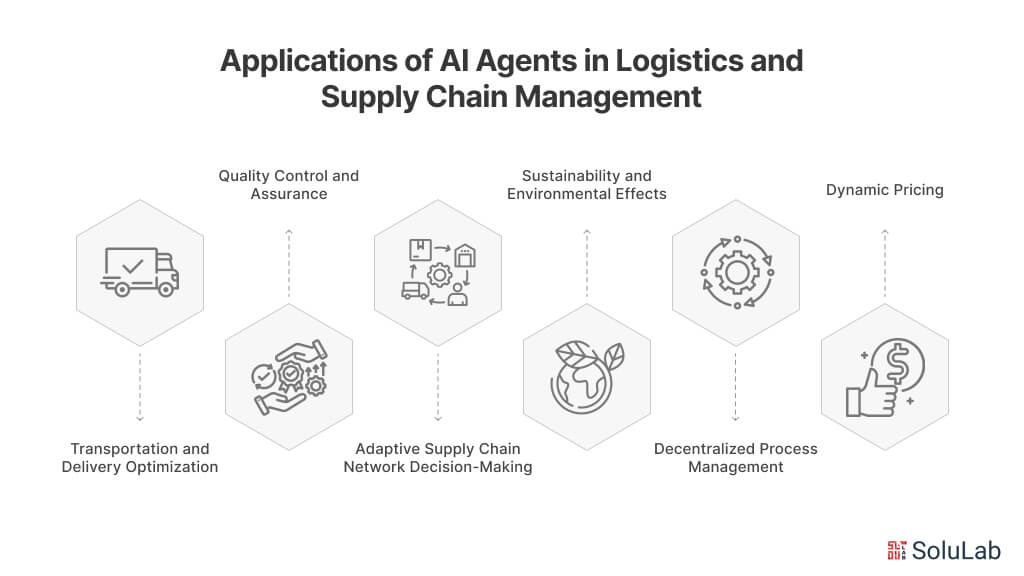
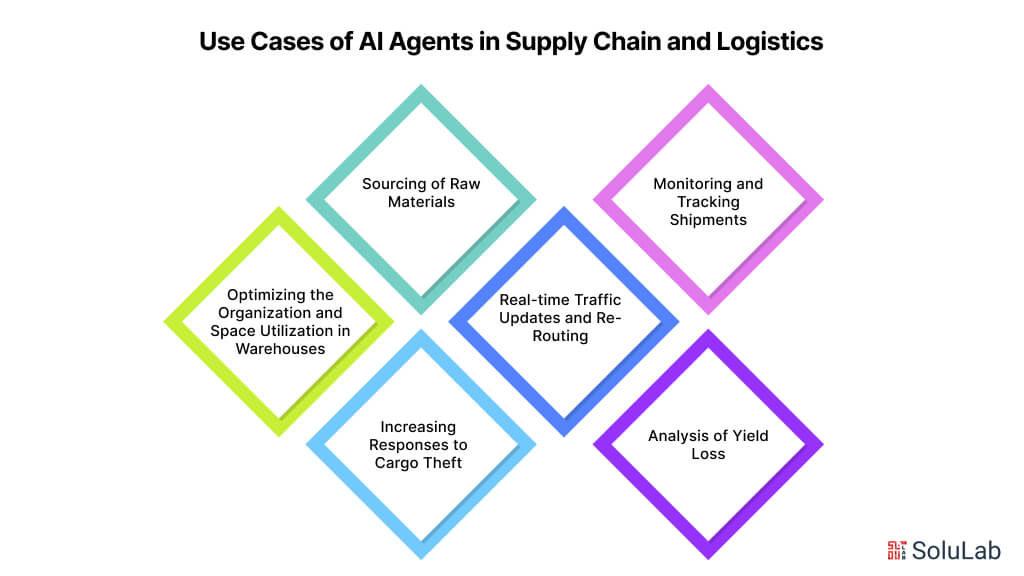
6. AI Agents in Supply Chain Management
AI agents are changing supply chain management by enhancing visibility, optimizing logistics, and improving decision-making. AI agents for supply chain are used for demand forecasting, inventory management, and route optimization, helping businesses streamline operations and reduce costs. Here are some specific use cases:
a. Demand Forecasting
Artificial intelligence agents analyze historical sales data, market trends, and external factors to predict demand for products. This helps businesses plan their inventory and production more accurately.
b. Inventory Optimization
AI agents optimize inventory levels by predicting demand, monitoring stock levels, and suggesting replenishment orders. This reduces carrying costs and minimizes stockouts.
c. Route Optimization
AI agents optimize delivery routes by considering factors such as traffic conditions, weather, and delivery windows. This reduces transportation costs and improves delivery efficiency.
d. Supplier Management
AI agents evaluate supplier performance by analyzing data on delivery times, quality, and costs. This helps businesses choose the best suppliers and negotiate better terms.
Related: Generative AI for Supply Chain
e. Risk Management
AI agents identify potential risks in the supply chain, such as disruptions, delays, or quality issues. They suggest mitigation strategies to ensure smooth operations and minimize impact.
7. AI Agents in Legal Services
The logistics industry is making use of AI agent logistics to optimize supply chains, enhance efficiency, and improve decision-making. Here are some key use cases:
a. Legal Research
AI agents assist lawyers in legal research by analyzing vast amounts of legal documents, case law, and statutes. They provide relevant information and precedents, saving time and improving accuracy.
b. Contract Analysis
AI agent for law firms analyzes contracts to identify key terms, potential risks, and compliance issues. They can also automate contract generation, review, and management, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
c. Document Review
AI agents for the legal industry streamline document review processes by identifying relevant documents, categorizing information, and highlighting key points. This speeds up the review process and reduces the workload on legal professionals.
d. Predictive Analytics
AI agents predict case outcomes by analyzing historical data, case law, and judge rulings. This helps lawyers assess the strength of their cases and make informed decisions.
e. Client Management
AI agents enhance client management by automating tasks such as scheduling, billing, and communication. This improves client service and allows lawyers to focus on legal work.
Read Also: AI Agent in Legal Document Management
8. AI Agents in Automotive
The automotive industry is leveraging AI agents to improve vehicle safety, enhance user experiences, and optimize manufacturing processes. Here are some key use cases for AI agents in the automotive industry:
a. Autonomous Driving
AI agents power autonomous vehicles by processing data from sensors, cameras, and LIDAR systems to navigate and make driving decisions. This enhances safety and reduces the need for human intervention.
b. Predictive Maintenance
AI agents monitor vehicle performance and predict maintenance needs by analyzing data from sensors and onboard diagnostics. This prevents breakdowns, reduces downtime, and extends the lifespan of vehicles.
c. In-Vehicle Assistants
AI-powered in-vehicle assistants provide drivers with real-time information, navigation, and entertainment. They can also monitor driver behavior and suggest breaks or adjustments to improve safety.
Read Also: Future of Generative AI in Automotive Industry
d. Manufacturing Optimization
AI agents optimize manufacturing processes by analyzing production data, identifying inefficiencies, and suggesting improvements. This increases productivity and reduces costs.
e. Supply Chain Management
AI agents enhance supply chain management by predicting demand, optimizing inventory levels, and managing supplier relationships. This ensures timely delivery of parts and materials, reducing production delays.
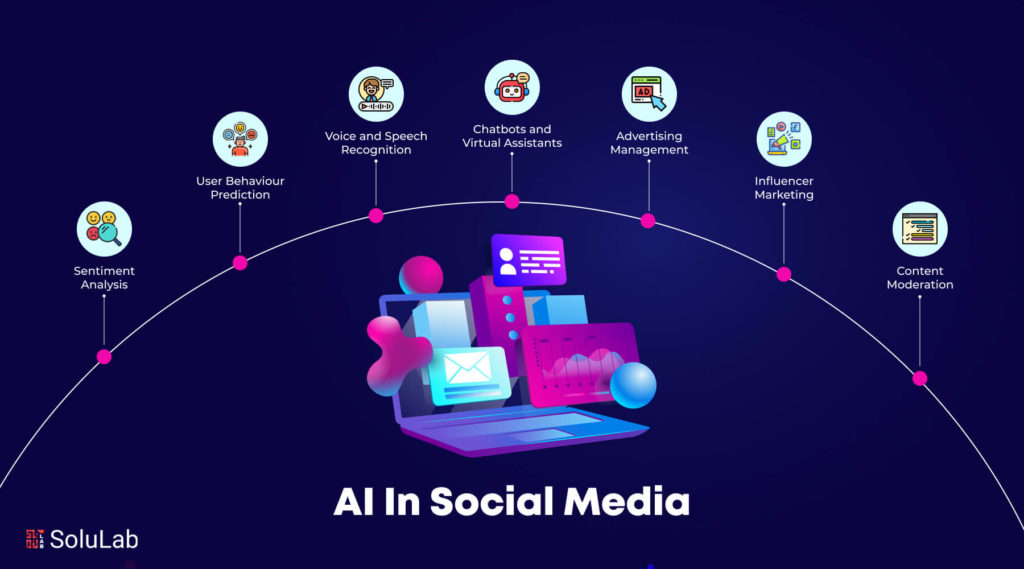
9. AI Agents in Social Media
Social media platforms are utilizing AI agents to enhance user experiences, manage content, and improve security. Here are some notable use cases:
a. Content Moderation
AI agent in media monitor and moderate content to ensure it adheres to community guidelines. They detect and remove inappropriate, harmful, or spam content, creating a safer and more enjoyable user environment.
b. Personalized Recommendations
AI agents analyze user behavior, preferences, and interactions to provide personalized content recommendations. This includes suggesting friends, groups, pages, and posts that align with individual interests, increasing user engagement.
c. Sentiment Analysis
AI agents perform sentiment analysis on user posts and comments to gauge public opinion and sentiment toward brands, products, or topics. This helps companies understand their audience and tailor their marketing strategies accordingly.
d. Social Media Advertising
Social media AI agents optimize social media advertising campaigns by targeting specific demographics, analyzing ad performance, and suggesting adjustments. This maximizes ad effectiveness and return on investment.
e. Trend Analysis
AI agents analyze social media data to identify emerging trends, hashtags, and viral content. This provides valuable insights for businesses and marketers to stay ahead of the curve and engage with trending topics.
10. AI Agents in Telecommunications
The telecommunications industry is leveraging AI agents to enhance network management, improve customer service, and optimize operations. Here are some key use cases:
a. Network Optimization
AI agents monitor network performance and predict potential issues, such as congestion or outages. They optimize network traffic and resources to ensure smooth and reliable connectivity.
Related: Generative AI in Telecom
b. Customer Support
AI-powered virtual assistants handle customer inquiries, troubleshoot issues, and provide technical support. This reduces wait times and improves customer satisfaction by offering prompt and accurate assistance.
c. Fraud Detection
Agent in AI detects fraudulent activities, such as unauthorized access or identity theft, by analyzing patterns and anomalies in network usage. They help prevent fraud and protect customer data.
d. Predictive Maintenance
AI agents predict maintenance needs for network infrastructure by analyzing data from sensors and equipment. This prevents downtime, reduces maintenance costs, and extends the lifespan of network components.
e. Personalized Services
AI agents analyze customer data to offer personalized services and recommendations, such as tailored subscription plans or value-added services. This enhances customer loyalty and increases revenue.
11. AI Agents in Education
The education sector is utilizing AI agents to enhance learning experiences, personalize education, and streamline administrative tasks. Here are some key use cases:
a. Personalized Learning
AI agents analyze student performance and learning styles to create personalized learning plans. They provide tailored recommendations, resources, and exercises to help students learn more effectively.
b. Intelligent Tutoring Systems
AI-powered tutoring systems offer real-time feedback and support to students. They can explain complex concepts, provide additional practice, and adapt to the learner’s pace, enhancing understanding and retention.
c. Automated Grading
AI agents automate the grading process by assessing assignments, quizzes, and exams. This reduces the workload on educators, ensures consistent evaluation, and provides students with timely feedback.
d. Student Support
AI chatbots provide students with 24/7 support, answering questions about course material, deadlines, and administrative processes. This enhances student engagement and satisfaction.
e. Administrative Efficiency
AI agents streamline administrative tasks such as enrollment, scheduling, and record-keeping. This reduces the administrative burden on staff and ensures accurate and efficient operations.
12. AI Agents in Agriculture
The agricultural industry is leveraging AI agents to improve crop management, optimize resource use, and enhance productivity. Here are some notable use cases:
a. Precision Farming
AI agents analyze data from sensors, drones, and satellite imagery to monitor crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns. This enables precise application of water, fertilizers, and pesticides, improving crop yields and reducing waste.
b. Predictive Analytics
AI agents predict crop yields and identify potential issues such as pest infestations or disease outbreaks. This allows farmers to take proactive measures and optimize their farming practices.
c. Autonomous Machinery
AI-powered autonomous machinery, such as tractors and harvesters, perform tasks such as planting, weeding, and harvesting with high precision and efficiency. This reduces labor costs and increases productivity.
d. Supply Chain Optimization
AI agents optimize the agricultural supply chain by predicting demand, managing inventory, and coordinating logistics. This ensures timely delivery of produce and reduces post-harvest losses.
e. Sustainable Farming
AI agents promote sustainable farming practices by analyzing environmental data and suggesting eco-friendly farming techniques. This helps farmers minimize their environmental impact and conserve resources.
13. AI Agents in Energy
The energy sector is adopting AI agents to optimize energy production, enhance grid management, and promote sustainability. Here are some key use cases:
a. Predictive Maintenance
AI agents monitor energy infrastructure, such as power plants and transmission lines, to predict maintenance needs and prevent failures. This ensures a reliable energy supply and reduces maintenance costs.
b. Energy Management
AI agents optimize energy consumption by analyzing usage patterns and adjusting settings in real time. This helps businesses and households reduce energy costs and improve efficiency.
c. Renewable Energy Optimization
AI agents manage renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, by predicting energy production and optimizing integration with the grid. This maximizes the use of renewable energy and reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
d. Demand Response
AI agents enable demand response programs by predicting energy demand and adjusting supply accordingly. This helps balance the grid, reduce peak load, and prevent blackouts.
e. Smart Grids
AI agents enhance the operation of smart grids by analyzing data from sensors and meters to optimize energy distribution and detect issues. This improves grid reliability and efficiency.
Read Also: x402 Protocol for Building Next-Gen AI Agents
14. AI Agents in Real Estate
The real estate industry is adopting AI agents to enhance property management, improve customer service, and optimize transactions. Here are some key use cases:
a. Property Valuation
AI agents analyze market trends, property features, and historical data to provide accurate property valuations. This helps buyers, sellers, and investors make informed decisions.
b. Virtual Property Tours
AI-powered virtual assistants offer virtual property tours, providing potential buyers or renters with detailed information and answering questions in real time. This enhances the property viewing experience and saves time.
c. Tenant Screening
AI agents assist property managers in screening tenants by analyzing application data, credit scores, and rental history. This ensures a thorough and efficient screening process.
d. Predictive Maintenance
AI agents monitor building systems and infrastructure to predict maintenance needs and prevent issues. This ensures well-maintained properties and reduces maintenance costs.
e. Market Analysis
AI agents perform market analysis by analyzing data on property sales, rental rates, and market trends. This provides valuable insights for real estate professionals and investors to make strategic decisions.
15. AI Agents in Logistics
The logistics industry is harnessing AI agents to optimize supply chains, enhance efficiency, and improve decision-making. Here are some key use cases:
a. Route Optimization
AI agents optimize delivery routes by considering factors such as traffic conditions, weather, and delivery windows. This reduces transportation costs and improves delivery efficiency.
b. Warehouse Management
AI agents manage warehouse operations by analyzing inventory levels, predicting demand, and optimizing storage space. This reduces operational costs and improves efficiency.
c. Predictive Maintenance
AI agents monitor equipment and vehicles to predict maintenance needs and prevent breakdowns. This reduces downtime and maintenance costs, ensuring smooth operations.
d. Demand Forecasting
AI agents analyze historical sales data, market trends, and external factors to predict demand for products. This helps businesses plan their inventory and production more accurately.
e. Risk Management
AI agents identify potential risks in the supply chain, such as disruptions, delays, or quality issues. They suggest mitigation strategies to ensure smooth operations and minimize impact.

Conclusion
From handling simple password resets to organizing complex workflows, AI agents are improving how enterprise teams operate. Whether you’re troubleshooting IT issues, processing leave requests, or preparing for customer calls, there’s an AI agent ready to streamline your workday.
As teams continue to explore new ways to leverage AI agents like Atom, the possibilities are limitless. The best part? This is only the beginning of how these intelligent assistants will improve workplace interactions and eliminate time-consuming tasks.
If you’re ready to identify the top AI agent use cases for your organization and start implementing them, keep reading. Sight Machine, a leading AI company in the digital manufacturing space, partnered with SoluLab to overcome resource constraints and enhance its product capabilities. SoluLab designed a scalable technical architecture, integrated generative AI models, and developed advanced analytics. Their collaboration improved Sight Machine’s digital twins’ platform, boosting performance, scalability, and user experience. SoluLab An AI agent development company has a team of experts to help you build AI agents across industries. Reach out to us today.
FAQs
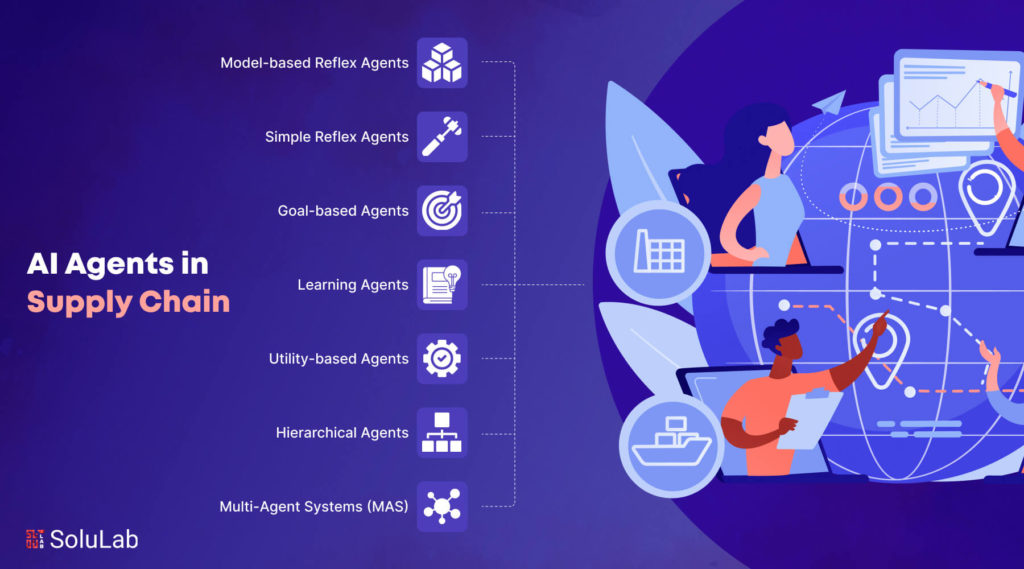
1. What are the types of agents used in development?
There are 5 types of AI agents used– simple reflex agents, model-based reflex agents, goal-based agents, utility-based agents, and learning agents. Each type varies in complexity, from basic condition-response actions to advanced learning and decision-making capabilities.
2. What are the major use cases where AI is used?
AI is used in healthcare for diagnosis and drug discovery, finance for fraud detection and algorithmic trading, logistics for route optimization and inventory management, customer service for chatbots and virtual assistants, and marketing for personalized recommendations and ad targeting.
3. What is an example of a good AI agent?
A good AI agent is Google Assistant, which uses natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to execute tasks, answer queries, and interact with users effectively, providing personalized and context-familiar assistance.
4. Are AI agents secure for business applications?
Yes, the majority of AI agents follow strict security protocols with data encryption and access controls. However, it is suggested that businesses must regularly update and monitor them to prevent any sort of vulnerabilities.
5. How do AI agents improve customer service?
AI agents automate responses, handle queries, and provide personalized support through chatbots and virtual assistants. They enhance customer experience by reducing wait times and offering 24/7 assistance.