Blockchain has transitioned from its origins as a ledger for supporting peer-to-peer cash systems to a transformative force in the centralized ecosystem. Its immutable, decentralized, secure, and transparent features have propelled it into mainstream technology, driving innovation across various sectors. Businesses are increasingly recognizing the benefits of integrating blockchain, which enhances speed, efficiency, and fairness within specific industries.
According to Spendmenot, a significant portion of the world’s largest public companies, approximately 81%, acknowledge their utilization of blockchain technology. Moreover, around 80% of global executives perceive blockchain as “very important.” Projections suggest that global spending on blockchain solutions will surge to $19 billion by 2024, underlining the growing significance of blockchain in business operations.
In this article, we will look into use cases for blockchain across industries and explore how it addresses existing limitations and challenges.
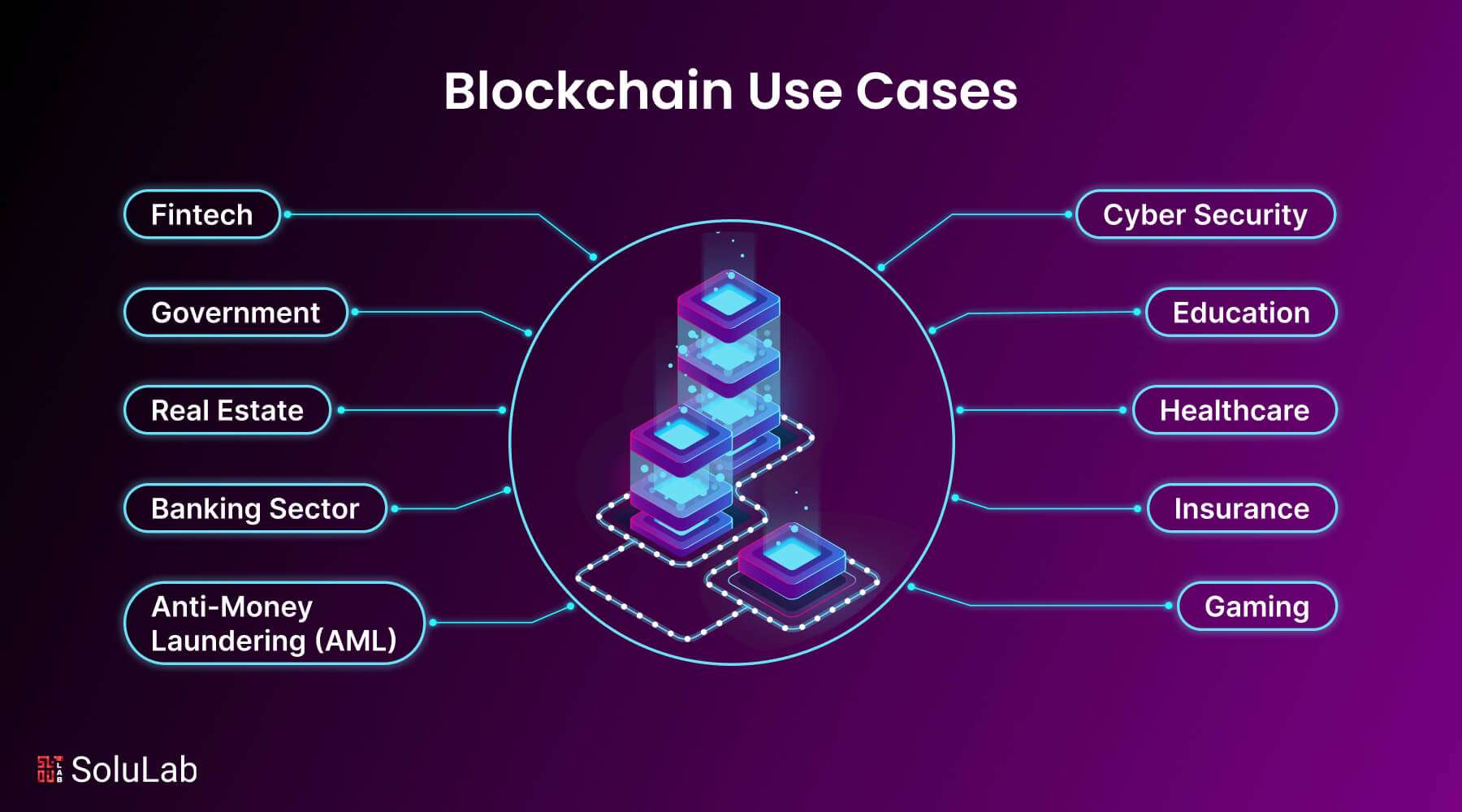
Top Blockchain Technology Use Cases in 2026
The top blockchain use cases by industry include the following:
- Fintech
- Digital Identity
- Government
- Supply Chain
- Real Estate
- Banking Sector
- Asset tokenization
- Blockchain Advertising
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
- Cyber Security
- Education
- Healthcare
- Patent Ecosystem
- Insurance
- Gaming
So, without any further ado, let’s start exploring the use cases and applications of blockchain technology.
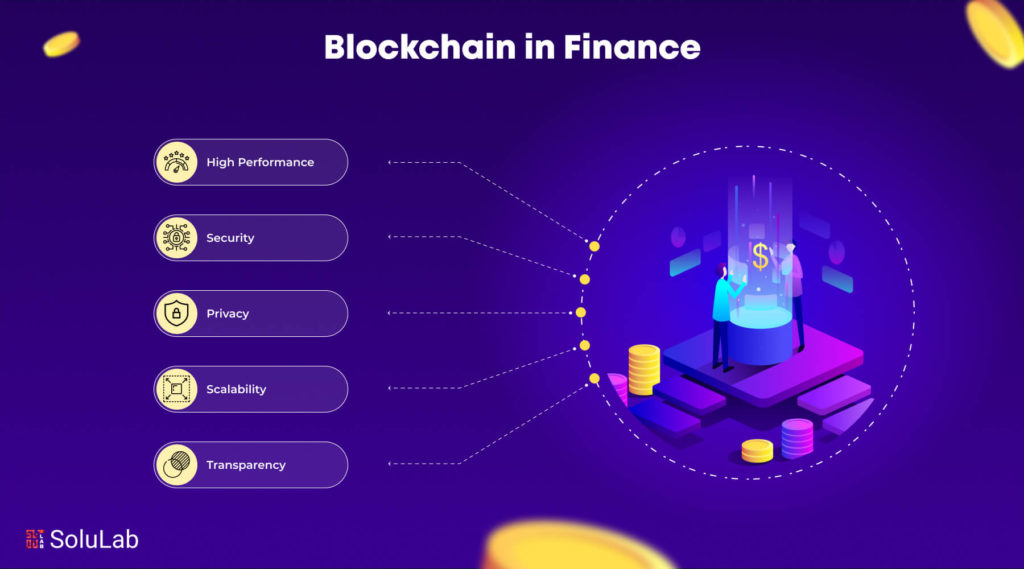
1. Fintech
Since they have been using blockchain technology for more than ten years, the finance industry is an early user of the technology. There are a number of blockchain use cases in finance. Major industrial problems including unethical conduct, long settlement and auditing times, high prices, security risks, and irregular compliance are all resolved by blockchain technology. Thus, it can offer improved audits, instantaneous settlements, risk control, security, and transparency at a lower cost. Through the use of smart contracts, blockchain has also brought Decentralized finance(DeFi) development to the banking sector, eliminating any third-party influence in financial services.
Here are some of the blockchain finance use cases:
- Cross Border Payments
- Credit Score
- Stock Exchange
- Lending Platforms
- Financial Record Keeping
- Invoice Management and Billing Solution
- Fund Investment
Related: How Blockchain Is Revolutionizing the Fintech Industry?
2. Digital Identity
Major drawbacks with the existing centralized Web 2.0 include identity theft, giving personal information to unaffiliated parties, confusion between identities and passwords, and more. It is unable to provide users with a self-sovereign identity (SSI). On the other hand, blockchain can offer consumers complete control over their digital identities and the data contained in them, opening the door for SSI.
Additionally, self-sovereign identification can help with interoperability—particularly in the metaverse—and allow one to maintain their identity through avatars across various metaverse initiatives. One solution that would enable the most secure identification of the general public would also be very beneficial to them.
The answer lies in a digital identity management system built on the blockchain. Big businesses see this need as well and are attempting to create apps that will let their employees and the public create digital IDs. Even while it will take time to develop a global identity, the process has already started.
3. Government
Blockchain technology presents numerous use cases within the government sector, leveraging its core features such as decentralization, transparency, and immutability to enhance various processes. Here are some notable blockchain government use cases:
- Secure Identity Management: Blockchain can revolutionize identity management systems by providing a secure and tamper-proof database for storing citizen identities. Each citizen could have a unique digital identity stored on the blockchain, ensuring privacy and reducing the risk of identity theft or fraud.
- Transparent Voting Systems: Blockchain-based voting systems offer a solution to enhance the transparency and integrity of elections. Each vote is recorded on the blockchain, ensuring that it cannot be altered or manipulated. This helps to prevent voter fraud and ensures the accuracy of election results.
- Efficient Public Records Management: Governments can use blockchain to manage public records such as land titles, birth certificates, and business registrations more efficiently. By storing these records on a blockchain, they become easily accessible, tamper-proof, and can be updated in real time, reducing administrative overhead and the risk of data loss.
- Tax Compliance and Fraud Prevention: Blockchain can streamline tax collection processes and prevent tax evasion by providing transparent and traceable transactions. Smart contracts can automate tax calculations and payments, reducing errors and ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
- Secure Data Sharing: Governments often need to share sensitive information across departments or with other government agencies. Blockchain-based solutions enable secure and encrypted data sharing while maintaining data integrity and confidentiality.
4. Supply Chain
The fundamental characteristics of blockchain technology, such as its immutability, transparency, and decentralization, make it an ideal fit for the modern supply chain. This supply chain is prone to errors because of a number of factors, such as high costs, corruption, and rapid changes in the market.
Blockchain technology has the potential to replace sluggish, manual supply chain processes that mostly rely on paperwork with quick, end-to-end digital processes that provide visibility and transparency. Blockchain makes it possible for supply chain activities to be tracked and traced, as well as for greater inventory utilization, faster delivery, higher quality, and less income loss from items sold on the black or grey market. Consequently, the use case of blockchain technology may be applied to the following supply chain areas:
- Supply chain finance
- Reducing counterfeit products
- Supplier payments
- Supply chain logistics
- Food safety
- Diamond tracking
- Oil supply chain

5. Real Estate
Blockchain real estate use cases offer a transformative solution to the complex and time-consuming process of purchasing or selling real estate. Currently, the traditional method involves extensive documentation, verification, and ownership transfer, often exacerbated when involving loans, leading to increased complexity and susceptibility to fraudulent activities.
However, blockchain technology provides a streamlined approach to real estate transactions, significantly reducing the time and effort involved. Through the tokenization of physical assets, sellers can leverage smart contracts to facilitate the sale of real estate properties.
By embedding legal procedures within smart contracts, transactions can be executed automatically once predefined conditions are met. For example, upon payment from the buyer, ownership of the property is swiftly transferred, eliminating the need for lengthy paperwork and manual verification processes.
Furthermore, blockchain real estate solutions ensure security, transparency, and immutability, mitigating the risk of fraud and enhancing trust among parties involved in the transaction. This innovative application of blockchain technology revolutionizes the real estate industry, offering efficiency, reliability, and convenience to both buyers and sellers.
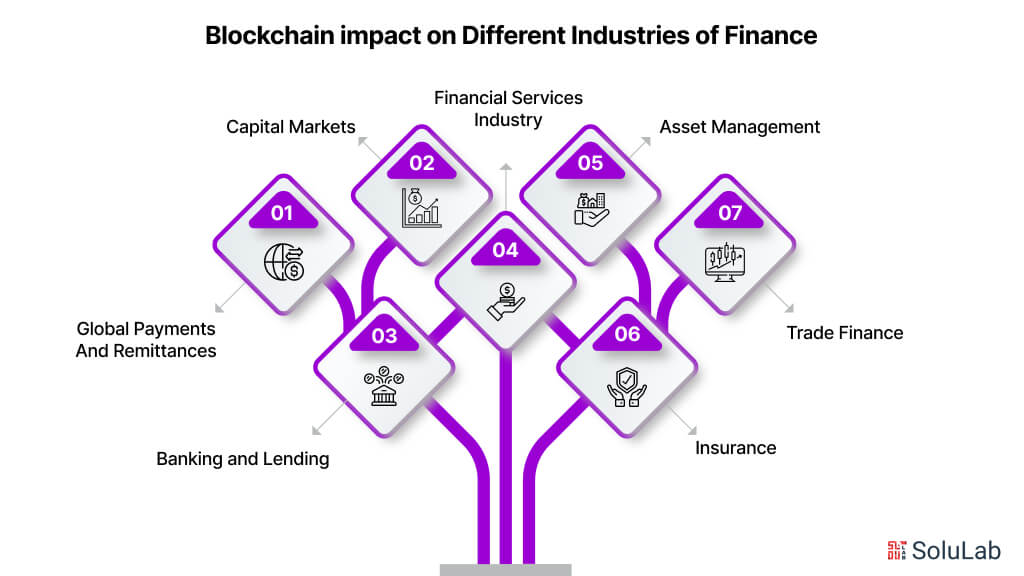
6. Banking Sector
Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize the financial industry by addressing key challenges such as inefficient record-keeping, security vulnerabilities, regulatory inconsistencies, and high transaction costs and times. In banking, blockchain technology operates on a decentralized network where each participant serves as a node, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
One of the notable advantages of blockchain in banking is the execution of smart contracts, which enable swift transactions at lower costs. Additionally, blockchain ensures secure, transparent, and private data management, with technologies like zero-knowledge proof authenticating financial information without revealing sensitive details.
Blockchain’s applications in banking encompass various areas such as clearance and settlement, lending and borrowing, trade finance, accounting, bookkeeping, and generating credit reports. These blockchain banking use cases highlight how blockchain enhances efficiency, reliability, and security in banking operations.
7. Asset Tokenization
Blockchain technology empowers Asset Tokenization development by enabling the transformation of real-world assets, digital assets, and corporate shares into secure, tradable tokens. Additionally, users may convert tangible assets into digital assets, which they can then use as fungible and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) for representing them on the blockchain. From traditional asset classes like bonds, real estate, venture capital funds, and commodities to unique asset classes like artwork, sports teams, and racehorses, almost any kind of asset may be tokenized.
Because blockchain is an unchangeable public ledger, it guarantees that the ownership of the tokens you have acquired cannot be removed. The following advantages come with tokenizing assets:
- Removal of Third Parties
- Absence of Borders
- Transparency
- Fast and Less Expensive Transactions
- Availability
- Enhanced Liquidity
- Broader Investor Base
- Fractional Ownership
8. Blockchain Advertising
The advertising business is currently dealing with issues such as costly middlemen, a dearth of accountability and transparency, inefficiencies, ad fraud, and more.
With Blockchain-based smart contracts, it is possible to design efficient advertising funnels with several levels of verification that offer better targeting and return on investment. Furthermore, Blockchain networks can improve overall security for the advertising industry as they necessitate majority consent from all of its nodes, or members.
In the advertising sector, blockchain offers the following:
- Consumer Data Privacy
- Absence of Intermediaries
- Reduction in Ad Fraud
- Improved Ad Exchanges
- Decentralized Network
- Consumer Trust
9. Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
As globalization and technology progress enhance company operations, new technologies have also been leveraged by digital financial crimes, including money laundering. Based on in-depth analysis, Zippia estimates that the United States launders about $300 billion a year.
The use of blockchain in AML can assist mitigate money laundering risks and streamline the Know-Your-Customer procedure. The whole history of every transaction can be tracked, verified, and recorded in a public blockchain ledger that cannot be changed or erased. Rather than overseeing the points of entry and departure, it helps with system analysis in general.
By storing data and information concerning KYC and AML on a decentralized ledger, developing a blockchain-enabled AML/KYC platform contributes to the simplification of AML/KYC procedures. Since the data in a blockchain ledger is constantly visible to all users of the network, AML/KYC data management on the blockchain can help financial companies manage their data more effectively.
10. Cyber Security
Decentralized storage systems and blockchain technology can improve cybersecurity. Predators won’t have a single point of entry since data is kept decentralized and the danger is distributed across several nodes. Many businesses rely heavily on centralized systems, which are not the greatest for storing data—at least not in terms of security.
Blockchain can improve Domain Name System (DNS) security and perhaps reduce Distributed Denial of Service (DD0S) assaults due to its distributed and decentralized architecture. Other elements of the system, including communications, can also benefit from increased security. Additionally, immutability stops fraud and hackers from stealing data. Therefore, blockchain has the following cybersecurity use cases:
- Safe private messaging
- Secure DNS and DDoS protection
- Internet of Things security
- Decreased risk to human safety as a result of cyberattacks
- Source of software validation
Related : Blockchain Technology in Cybersecurity
11. Education
Over time, there has been a significant shift in the educational system. Aspirants may currently fake a degree, diploma, or other educational qualification from any university they want. Even phony degrees are produced and used to pretend to be graduates of particular universities. Such occurrences make it difficult for hiring managers or employers from any business to verify the accuracy of a candidate’s educational background.
The use of blockchain technology in education can stop fake diplomas by keeping all student data in a digital ledger with tamper-proof features. Additionally, in order to establish digital certificates and eliminate paper in the system, educational certifications can be created and maintained on the blockchain. Only a URL must be provided by universities or colleges to verify the educational credentials. Other examples of applications of blockchain in education are:
- Keeping academic records secure in the blockchain
- Preserving records of information on grants, teacher payments, and other funds that improve the legitimacy of credentials
- Economical storage of big files
- Platforms for automated learning
12. Healthcare
Patients sometimes find it difficult to keep their records organized and undamaged, and this problem is exacerbated when they see several doctors. Health information exchange (HIE), the digital mobilization of health care data, can assist in tracking medical records, however, it is vulnerable to security and privacy problems.
On the other hand, patient data may be safely stored using blockchain technology. They are accessible at any time and may be updated each time a patient sees their physician. A Hipaajournal article states that between 2009 and 2021, the Health and Human Services (HHS) Office for Civil Rights received reports on 4,419 healthcare security breaches involving 500 or more records. Similarly, blockchain technology may be used to track pharmaceuticals, making it possible to eliminate counterfeit drugs from the medical supply chain. Blockchain technology may be applied to healthcare to enhance interaction between providers and patients and to analyze genomes, or whole sets of an organism’s DNA, comprising its genes.
Related: Blockchain in Healthcare
13. Patent Ecosystem
Due to incomplete asset ownership records or difficulty selecting the best patent for a company, the old patent system has many drawbacks. It’s also challenging to maintain the ownership, transparency, and privacy of digital material. For example, it’s common practice to utilize a music, film, or other digital asset that has been put online without the owner’s consent.
This problem can be largely resolved by using blockchain in the payment industry. On the blockchain, patents are exclusive rights bestowed by a governing authority, be it an international organization or a sovereign state. The exclusive right to reveal the creation’s details to the wider public is given to the author. Blockchain patents, which provide a commercial value of confidence, have grown in importance since the creation of Bitcoin. Rather than relying on a third party for its operations, it stores, broadcasts, verifies, and exchanges data across a dispersed network. This enhances prolonged IP safety, progressive protection, and secure collaboration. It provides value and trust at a reasonable price.

14. Insurance
Currently, obtaining insurance involves difficult procedures when submitting a claim, requiring a substantial quantity of paperwork and ongoing communication with your insurance agent.
Because the blockchain can securely store data that has to be validated in order to process a claim, it helps expedite the claims settlement process. After having been uploaded to the blockchain network, the claims are subsequently sent to the relevant parties. The parties issue the insurance after examining the data. Additionally, smart contracts can improve the automation of the claims procedure, making it easier for consumers to file and receive approved claims. Blockchain has the potential to drastically change insurance procedures by doing away with paper contracts, speeding up turnaround times, and disclosing fictitious claims.
15. Gaming
There are several promising use cases for blockchain in the gaming industry, revolutionizing how games are developed, distributed, and monetized. One significant application lies in digital asset ownership and interoperability. Through blockchain, players gain true ownership of in-game assets, such as skins, weapons, or characters, which can be securely stored and traded on decentralized marketplaces. This fosters a more transparent and equitable ecosystem where players have greater control over their virtual possessions. Additionally, blockchain enables cross-game compatibility, allowing players to use their assets across multiple gaming platforms seamlessly. This interoperability enhances user experience and encourages player engagement, as gamers can leverage their investments across various titles.
Another compelling use case of blockchain in gaming is the implementation of provably fair systems for in-game economies and rewards. By utilizing blockchain-based smart contracts, game developers can ensure transparent and verifiable distribution of rewards, loot, and digital currencies within the game environment. This not only enhances trust between players and developers but also mitigates issues like cheating and fraud. Moreover, blockchain technology enables the creation of decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) for community governance, empowering players to participate in decision-making processes regarding game development, updates, and monetization strategies. Overall, blockchain’s integration into gaming holds the potential to foster a more inclusive, secure, and player-centric gaming experience.
Related: Top 25 Blockchain-Based Gaming Companies
The Bottom Line
It is astonishing to observe how blockchain is revolutionizing a number of sectors and how use cases for blockchain keep evolving in response to shifting trends and time. Blockchain is essential to supply chains, healthcare, real estate, and financial services. Blockchain technology is undoubtedly going to be the face of the future, given the rapid expansion of use cases by sector and the widespread acceptance of blockchain across a range of industries.
SoluLab, a leading blockchain consulting company, is spearheading the integration of blockchain across various industries, revolutionizing traditional processes and enhancing efficiency, transparency, and security. With a team of seasoned blockchain experts, SoluLab is empowering businesses to leverage the full potential of distributed ledger technology.
From finance to healthcare, supply chain to gaming, SoluLab’s innovative blockchain solutions are reshaping industries worldwide. Whether it’s developing decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, implementing transparent supply chain tracking systems, or creating secure digital identities in healthcare, SoluLab’s bespoke blockchain solutions cater to diverse business needs.
Contact us today to explore how SoluLab can tailor innovative blockchain solutions to drive your business forward. Let’s innovate together for a smarter, more connected future.
FAQs
1. What are the main applications of blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology finds applications across various industries, including finance, supply chain management, healthcare, gaming, and more. Its primary applications include decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain transparency, digital identity management, smart contracts, and tokenization of assets.
2. How does blockchain enhance supply chain management?
Blockchain ensures transparency and traceability in supply chains by recording every transaction in a tamper-proof and immutable ledger. This enables stakeholders to track the movement of goods from the point of origin to the final destination, thereby reducing fraud, ensuring product authenticity, and optimizing processes like inventory management and logistics.
3. What role does blockchain play in the financial sector?
In the financial sector, blockchain technology facilitates faster and more secure transactions, eliminates intermediaries, reduces costs, and enables access to financial services for the unbanked population through decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. Additionally, blockchain-based smart contracts automate contract execution, streamlining processes like loan approvals, trade settlements, and insurance claims.
4. How can blockchain benefit the healthcare industry?
Blockchain enhances data security, interoperability, and patient privacy in the healthcare sector by enabling secure storage and sharing of medical records and facilitating the development of decentralized healthcare applications. It also enables pharmaceutical supply chain tracking to combat counterfeit drugs and ensures transparency in clinical trials by recording trial data immutably.
5. What opportunities does blockchain present in the gaming industry?
Blockchain introduces new monetization models, enhances digital asset ownership, and enables provably fair gameplay in the gaming industry. Through blockchain, players gain true ownership of in-game assets, which can be traded on decentralized marketplaces. Smart contracts ensure the transparent distribution of rewards, while blockchain-based voting mechanisms empower players in community governance.