Blockchain technology, a groundbreaking innovation originally devised for the cryptocurrency realm, has now transcended its initial confines and is making significant inroads into diverse industries. One sector where its transformative potential is particularly conspicuous is the real estate industry. This introduction aims to provide a concise yet comprehensive overview of blockchain technology, its relevance in real estate, and the challenges facing the real estate industry today.
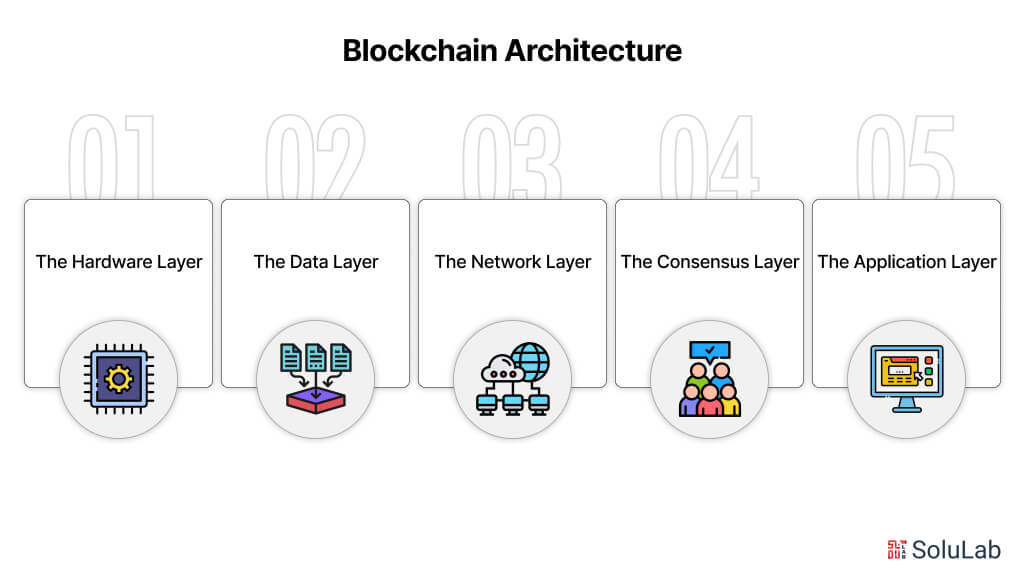
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across a network of computers securely and transparently. Utilizing cryptographic principles, each block in the chain is linked to the previous one, creating an immutable and tamper-resistant record. This technology ensures trust and transparency by eliminating the need for intermediaries and central authorities, offering a peer-to-peer approach to transactions.
The real estate industry is confronted with a myriad of challenges, ranging from cumbersome and time-consuming processes to issues of transparency and fraud. Traditional methods of property transactions involve numerous intermediaries, leading to inefficiencies, delays, and increased costs. Additionally, the lack of transparency in property records and the susceptibility to fraudulent activities have created a pressing need for innovative solutions.
What are the Fundamental Principles of Blockchain?
Blockchain, at its core, is a decentralized and distributed ledger technology that underpins a secure and transparent system for recording and verifying transactions. The fundamental principles of blockchain include decentralization, transparency, immutability, and consensus. Unlike traditional centralized systems, blockchain operates on a network of nodes, each contributing to the validation and verification of transactions.
The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that no single entity controls the entire network, fostering trust and eliminating the need for intermediaries.
A. Decentralization and Security Aspects
Decentralization is a cornerstone of blockchain, ensuring that data is not stored in a single location but is distributed across the network. This mitigates the risk of a single point of failure and enhances the system’s resilience. Security in the blockchain is achieved through cryptographic techniques, making it nearly impossible for malicious actors to tamper with or alter the stored information. The use of consensus mechanisms, such as proof-of-work or proof-of-stake, further fortifies the integrity of the blockchain network.
B. Blockchain in Real Estate
The application of blockchain in the real estate sector has the potential to revolutionize traditional processes, offering benefits that include increased transparency, efficiency, and security. One notable advantage is the reduction of fraud, as blockchain’s immutability ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered. Additionally, smart contracts, self-executing agreements with predefined rules, automate and streamline various real estate processes, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of errors.

What is the Transformative Impact of Blockchain on Real Estate?
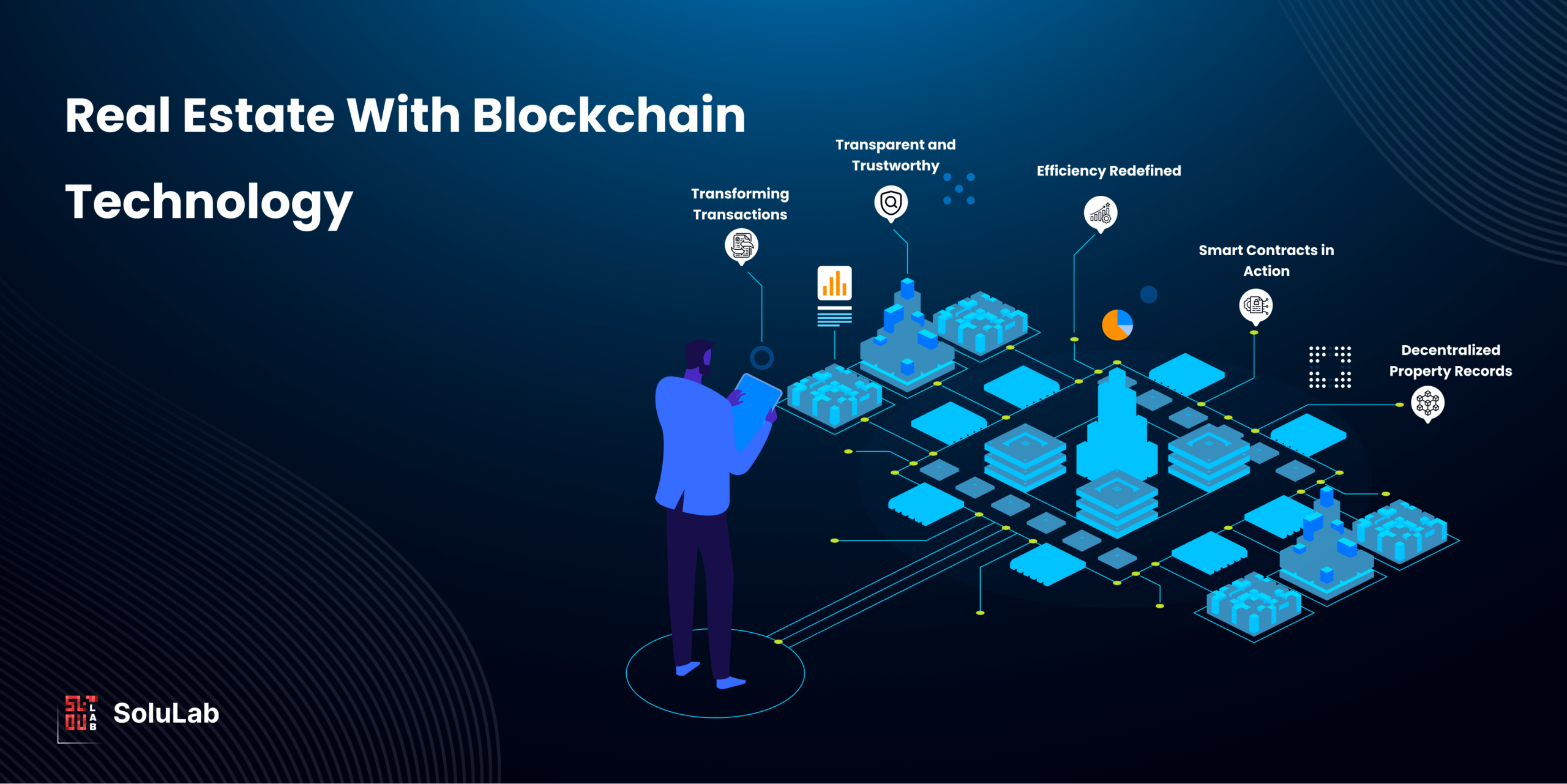
Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary force across various industries, and the real estate sector is no exception. Its decentralized and transparent nature brings forth a myriad of benefits, fundamentally reshaping the way property transactions are conducted. This article delves into the profound impact of blockchain on real estate, exploring key aspects such as transparency, smart contracts, and the tokenization of real estate assets.
A. Transparency and Trust in Property Transactions
One of the primary advantages of integrating blockchain in real estate is the enhanced transparency it brings to property transactions. Traditional real estate processes often involve multiple intermediaries, leading to a lack of transparency and increased potential for fraud. With blockchain, a decentralized and tamper-proof ledger ensures that all transaction data is securely recorded and easily accessible to relevant parties.
Related: Blockchain Technology in dApp Development
Blockchain technology promotes trust by providing a single source of truth for property records. This transparency mitigates the risk of fraudulent activities, as every transaction is verifiable and cannot be altered retroactively. Real estate stakeholders, including buyers, sellers, and regulatory bodies, can confidently rely on the accuracy and immutability of the information stored on the blockchain, fostering a more trustworthy and efficient property transaction ecosystem.
B. Smart Contracts Revolutionizing Deal Processes
Smart contracts, enabled by blockchain technology, are automating and revolutionizing deal processes in the real estate industry. These self-executing contracts automatically enforce and execute the terms of an agreement when predefined conditions are met. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, streamlining the overall transaction process and reducing the potential for errors or disputes.
Smart contracts in real estate facilitate quicker and more secure transactions, as they eliminate the need for manual verification and approval. From property sales to lease agreements, the automation provided by smart contracts not only increases efficiency but also reduces transaction costs. This innovation is a testament to the transformative power of blockchain in simplifying complex real estate processes.
C. Tokenization of Real Estate Assets
The concept of asset tokenization involves representing real-world assets, such as real estate properties, as digital tokens on a blockchain. This fractional ownership model allows investors to buy and trade fractions of real estate assets, providing liquidity and access to a broader pool of potential investors.
Blockchain facilitates the tokenization of real estate assets by dividing them into tradable tokens, each representing a share of the property. This democratizes real estate investment, allowing individuals to participate in high-value properties with smaller investments. Tokenization not only enhances liquidity but also reduces the barriers to entry, opening up new opportunities for both investors and property owners.
What are the Key Challenges Associated With the Adoption of Blockchain Technology in the Real Estate Industry?
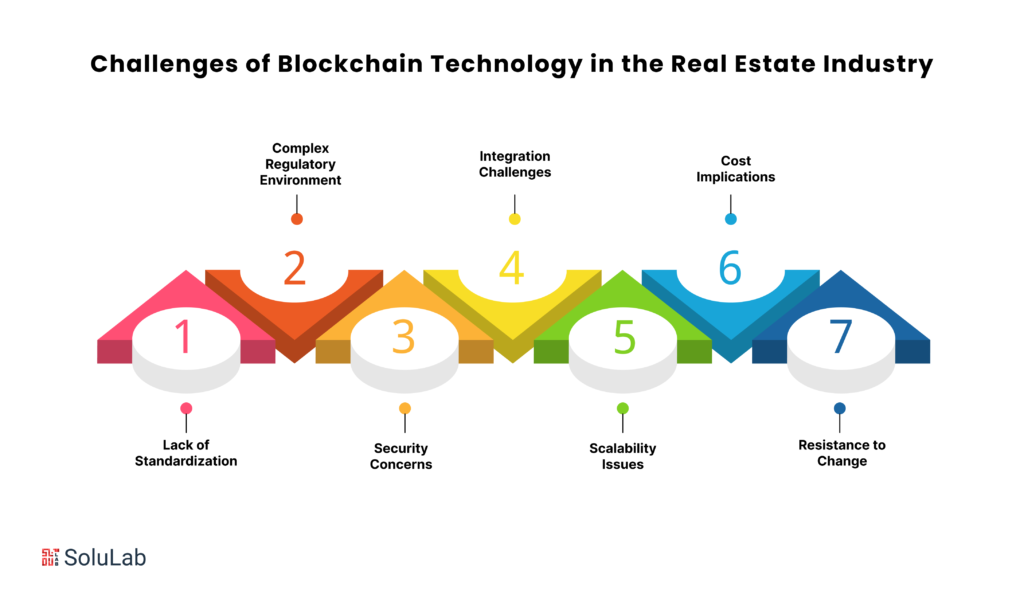
The adoption of blockchain technology in the real estate industry has gained significant traction, promising transformative benefits and revolutionizing traditional processes. However, like any innovation, it is not without its challenges and concerns. In this article, we delve into the key obstacles associated with incorporating blockchain in real estate and explore potential solutions.
1. Lack of Standardization
One major challenge in the integration of blockchain in real estate is the absence of standardized protocols. The industry requires universally accepted standards to ensure interoperability, data consistency, and seamless collaboration between different stakeholders.
2. Complex Regulatory Environment
Real estate transactions are subject to a myriad of regulations, varying across jurisdictions. Navigating this complex regulatory landscape poses a significant hurdle for the widespread adoption of blockchain in real estate. Developing a framework that aligns with existing regulations is crucial for fostering trust and compliance.
3. Security Concerns
While blockchain is renowned for its robust security features, the real estate industry’s adoption is hindered by the fear of cyber threats and unauthorized access. Building trust in the technology necessitates implementing robust security measures, and encryption techniques, and educating stakeholders on the resilience of blockchain against cyber attacks.
Related: Blockchain Technology in Cybersecurity
4. Integration Challenges
Many real estate processes are deeply entrenched in traditional systems, making the integration of blockchain a daunting task. Overcoming technical challenges and seamlessly integrating blockchain applications in real estate workflows requires a comprehensive strategy, skilled professionals, and a phased approach.
5. Scalability Issues
As the real estate industry generates vast amounts of data, scalability becomes a concern. Ensuring that blockchain technology can handle the scale of transactions and data storage required for real estate applications is vital for its successful adoption.
6. Cost Implications
Initial setup costs and infrastructure investment can be a deterrent for real estate businesses considering blockchain adoption. Convincing stakeholders of the long-term benefits and potential cost savings is essential for overcoming this challenge.
7. Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is a common hurdle in any industry, and real estate is no exception. Overcoming skepticism and convincing stakeholders, including property owners, buyers, and regulatory bodies, about the advantages of blockchain in real estate is a critical aspect of its successful implementation.
Check out Case Study: acreage
How is Blockchain Technology Reshaping the Future of the Real Estate Industry?
In recent years, the real estate industry has witnessed a paradigm shift with the integration of blockchain technology. This transformative force is not only reshaping traditional processes but also paving the way for numerous emerging trends that promise to redefine the sector. Let’s delve into the future trends of Blockchain in Real Estate, exploring potential advancements, innovations, and the benefits that this revolutionary technology brings to the industry.
A. Emerging Trends in Blockchain and Real Estate
-
Tokenization of Real Estate Assets
Blockchain facilitates the fractional ownership of real estate through tokenization. This allows investors to own a share of high-value properties, making real estate investment more accessible and liquid.
-
Smart Contracts Streamlining Transactions
Smart contracts, powered by blockchain, automate and streamline various processes in real estate transactions, from property listings to payments and contract execution. This not only reduces the need for intermediaries but also enhances transparency and security.
-
Decentralized Property Listings
Blockchain enables the creation of decentralized and tamper-proof property listings, preventing fraudulent activities and ensuring the authenticity of property information. This contributes to a more trustworthy and efficient real estate market.
B. Potential Advancements and Innovations
-
Enhanced Security and Transparency
Blockchain’s immutable and decentralized nature ensures the security of sensitive data in real estate transactions. This reduces the risk of fraud and ensures that all parties involved have access to a transparent and unalterable record of the transaction history.
-
Blockchain-Based Real Estate Platforms
Innovative blockchain platforms are emerging, utilizing blockchain for property transactions, rental agreements, and property management. These platforms enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and provide users with a seamless and secure experience.
-
Integration with Emerging Technologies
The integration of blockchain with other emerging technologies like AI and IoT is on the horizon. This convergence can lead to intelligent property management systems, automated maintenance, and even predictive analytics for property values.
What are the Risks and Mitigations in Harnessing Blockchain for Real Estate?
Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary force in various industries, including real estate. Its decentralized and secure nature promises to streamline processes, enhance transparency, and reduce fraud. However, as with any innovative technology, implementing blockchain in real estate is not without its challenges. In this section, we delve into the risks associated with blockchain in real estate and explore effective strategies to mitigate these challenges for a successful implementation.
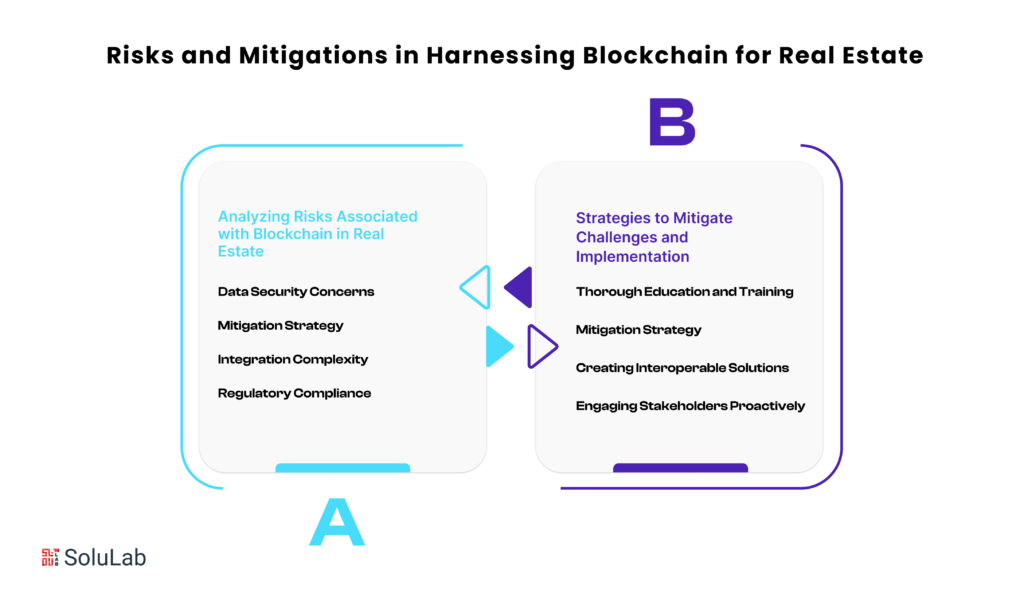
A. Analyzing Risks Associated with Blockchain in Real Estate
The decentralized nature of blockchain is both its strength and potential weakness. While it minimizes the risk of a single point of failure, it introduces concerns related to data security. Unauthorized access to sensitive information could compromise the integrity of real estate transactions.
Employing robust encryption protocols and implementing permissioned blockchain networks can enhance data security, ensuring that only authorized parties have access to sensitive information.
The existing real estate infrastructure may not seamlessly integrate with blockchain technology, leading to complexities in implementation. This could result in disruptions to ongoing processes and hinder the adoption of blockchain.
The real estate industry is subject to stringent regulations that may vary across regions. Adhering to these regulations while incorporating blockchain poses a significant challenge, potentially leading to legal issues and setbacks.
Related: Creating the Next Decentralized Application
B. Strategies to Mitigate Challenges and Ensure Successful Implementation
-
Thorough Education and Training
Educating stakeholders, including real estate professionals, on the benefits of blockchain in real estate is crucial. Training programs should cover both the conceptual understanding of blockchain technology and its practical applications.
Elaborating with educational institutions and industry experts to develop targeted training programs can ensure that all parties involved possess the necessary knowledge to harness the benefits of blockchain.
-
Creating Interoperable Solutions
Developing blockchain solutions that seamlessly integrate with existing real estate systems is essential. Interoperability ensures a smooth transition and minimizes disruptions during the implementation phase.
-
Engaging Stakeholders Proactively
Involving all relevant stakeholders in the planning and implementation process fosters collaboration and addresses concerns at an early stage. Proactive engagement ensures that everyone is aligned with the objectives of integrating blockchain in real estate.
How is Blockchain Technology Reshaping the Global Real Estate Landscape?
Blockchain technology has rapidly gained traction across various industries, and the real estate sector is no exception. The adoption of blockchain in real estate has witnessed a global surge, with notable benefits reshaping traditional practices. This article delves into an overview of the international adoption of blockchain in real estate, highlighting regional variances and success stories that underscore the transformative potential of this technology.
A. Overview of International Adoption of Blockchain in Real Estate
-
Transforming Transactions
Blockchain in real estate streamlines property transactions by providing a decentralized and transparent ledger. This ensures secure and tamper-proof documentation, reducing the risk of fraud and enhancing trust among the parties involved.
-
Efficient Title Management
Blockchain facilitates efficient title management, minimizing the complexities associated with verifying property titles. Smart contracts, powered by blockchain, automate the transfer of ownership, ensuring accuracy and speed in title transfers.
Blockchain enables the tokenization of real estate assets, dividing them into tradable digital tokens. This fractional ownership model enhances liquidity in the real estate market, allowing smaller investors to participate in high-value properties.
B. Regional Variances and Success Stories
North America has witnessed significant adoption of blockchain in real estate. The use of blockchain technology for transparent and efficient property transactions has gained momentum, with success stories emerging from major cities like New York and Toronto.
European countries are exploring blockchain applications in real estate to address regulatory challenges and improve transactional efficiency. Pilot projects in countries like Sweden showcase the potential for blockchain in streamlining property registration processes.
In the Asia-Pacific region, blockchain adoption in real estate is growing, driven by initiatives in countries like Singapore and Japan. Blockchain’s role in enhancing transparency and reducing fraud is particularly crucial in markets with high property investment activities.
The Middle East and Africa are embracing blockchain for land registry systems and property transactions. Blockchain’s ability to reduce paperwork and streamline processes aligns with the region’s vision for modernizing real estate practices.

Conclusion
In conclusion, SoluLab- a blockchain development company, has emerged as a pioneering force in revolutionizing the real estate industry through the transformative power of blockchain technology. The integration of blockchain in real estate has ushered in a new era of transparency, efficiency, and security, fundamentally reshaping traditional practices.
SoluLab’s commitment to harnessing blockchain technology in real estate is evident in its innovative solutions and customizable platforms. The company’s expertise extends to diverse blockchain use cases in real estate, offering tailored applications that cater to the specific needs of clients. Whether it’s streamlining property transactions, enhancing data security, or optimizing workflow efficiency, SoluLab’s solutions leverage the full potential of blockchain technology to bring about tangible improvements in the real estate landscape.
As the real estate industry continues to evolve, blockchain technology remains a cornerstone of this transformation. SoluLab’s initiatives exemplify the impact and adaptability of blockchain in real estate, providing a glimpse into the future of a more transparent, efficient, and secure property ecosystem. In essence, the strategic incorporation of blockchain technology by SoluLab marks a pivotal moment in the ongoing narrative of how innovation is reshaping the dynamics of the real estate industry.
FAQs
1. How is Blockchain Technology Transforming the Real Estate Industry?
Blockchain in Real Estate is revolutionizing traditional practices by introducing transparent and secure transaction processes. This technology ensures tamper-proof record-keeping, reducing fraud and enhancing trust among stakeholders.
2. What Are the Key Benefits of Integrating Blockchain in Real Estate?
The Benefits of Blockchain in Real Estate include increased transparency, reduced paperwork, faster transactions, and enhanced security. Smart contracts, a blockchain application in real estate, automate and enforce agreements, streamlining processes.
3. Can You Explain Blockchain Use Cases in Real Estate?
Blockchain technology in real estate finds diverse applications. These use cases encompass property tokenization, ensuring fractional ownership, and establishing immutable property records. This decentralized approach adds efficiency to transactions and minimizes disputes.
4. How Does Blockchain Ensure Security in Real Estate Transactions?
Blockchain applications in real estate bring unparalleled security by employing cryptographic techniques. Each transaction is recorded in a block, linked to the previous one, making alteration virtually impossible. This tamper-resistant structure safeguards sensitive information.
5. How Does Blockchain Streamline Property Transactions?
Blockchain technology in real estate expedites property transactions by eliminating intermediaries and reducing the need for manual verification. This leads to faster and more cost-effective processes, making property acquisition and transfer more efficient.
6. Are There Any Challenges Associated with Implementing Blockchain in Real Estate?
While the benefits of blockchain in real estate are significant, challenges include regulatory concerns and the need for industry-wide adoption. Overcoming these obstacles is crucial for maximizing the potential of blockchain technology in the real estate sector.