For more than ten years, blockchain technology has proven reliable and has been utilized in several specialized fields. While the idea of a chain of cryptographically secure blocks was initially put out in the early 1990s, it wasn’t until 2008 with the introduction of Bitcoin that blockchain technology gained widespread attention. It is anticipated that worldwide expenditure on Blockchain-based solutions is projected to climb from $4.5 billion in 2020 to around $19 billion in 2024. The potential of this technology is so immense that its relevance has expanded to practically every area; whether it is Blockchain in healthcare or agriculture.
Hedera Hashgraph, on the other hand, made its debut in the IT world nine years after Blockchain. Given how quickly and efficiently technology may presently evolve, it would be misleading to say that one technology is more developed than another despite this time disparity. The amount of continuous work put into the development is all that matters.
Will blockchains be replaced by hashgraphs then? Let’s examine it in more detail by contrasting Hashgraph vs Blockchain detail.
What is a Distributed Ledger Database?
A distributed ledger database is a decentralized database system that is dispersed among several network nodes or participants. It is sometimes referred to as distributed ledger technology (DLT). It makes it possible for everyone to obtain a copy of the database and come to an agreement on the ledger’s current status, facilitating safe and open record-keeping.
With the use of cryptographic techniques, this strategy increases security, reduces fraud, and promotes transparency. Distributed ledger databases cut expenses and simplify procedures by doing away with the need for middlemen.
Although Hedera Hashgraph and Blockchain are well-known examples of distributed ledger databases, other technologies also provide unique features and consensus procedures.
Distributed ledger databases, in general, offer the framework for developing decentralized applications and systems, transforming markets by permitting dependable and effective peer-to-peer interchange of data.
Essential Principles of DLTs
Here are some of the essential principles of Distributed Ledger Technology:
- Decentralization: DLTs disperse control over a network of nodes (computers), as opposed to conventional ledgers that are controlled by a single entity. Because every node has a copy of the ledger, there isn’t a single point of failure or control.
- Transparency and Immutability: DLT transactions are both transparent and unchangeable when they are recorded. Because it keeps hacking and revisionism at bay, its immutability is essential to security and trust.
- Consensus Mechanisms: To verify transactions and maintain the ledger across all nodes, DLTs utilize consensus methods. To attain consensus across nodes, protocols such as Delegated Byzantine Fault Tolerance (dBFT), Proof of Stake (PoS), and Proof of Work (PoW) are utilized.
Types of DLTs
Various types of DLTs are as follows:
- Public DLTs: These are accessible to all users and allow them to join and exit the network anonymously. Among the subset of DLTs known as public blockchains are Ethereum and Bitcoin.
- Private DLTs: Usually utilized by corporations for internal procedures, they are limited to certain members. Although they come at the expense of decentralization, they provide more control and quicker transaction times.
- Consortium DLTs: Combined elements of public and private DLTs, administered by a consortium of organizations. They achieve a balance between decentralization and control.
Now, that you have understood the basics of distributed ledger technology, let’s get to know what is Blockchain and Hashraph in brief!
Overview of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has been rather popular in the last several years, especially in the financial industry. It has advanced to an unparalleled degree to become more user-friendly and accessible since its launch in 2008. But what is it exactly?
Thus, as the name implies, a blockchain is a network of blocks made up of systems connected to one another via “nodes” that resemble chains. Transactional records are distributed and maintained by this structure throughout the whole network of systems that make up the Blockchain.
The fact that this distributed ledger technology is extremely safe and makes data manipulation nearly impossible is one of the factors contributing to its popularity. The owners’ digital signature is required to confirm each transaction, helping to ensure its authenticity and guarding against tampering. The finest thing is that no one can tamper with the records, even if everyone can view them.
How Is Blockchain Technology Operational?
When considering how Blockchain is changing the digital landscape, it makes sense that this technology is advancing so rapidly. But one question can cross your mind: just how does blockchain technology operate?
Given the optimistic outlook for Blockchain in the business sector, it is imperative that this technology be made more understandable. So let’s have a little conversation on how Blockchain functions.
Thus, the main elements of blockchain are the following three crucial ones:
- Cryptographic keys
- Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks
- Virtual computing systems that store and keep track of transactional data.
There are two different kinds of cryptography keys: public and private. This pair of keys is held by every member in a blockchain system and is primarily utilized to create a safe and distinct reference for digital identities.
The most important aspect of transactions taking place in a Blockchain system is the safe identity that is generated with these keys. Because of this, the significance of public and private keys in facilitating an effective transaction between two parties cannot be overstated.
You may now be asking how digital signatures fit into the Blockchain. In the realm of crypto, the distinct identity you create with the cryptographic keys is referred to as a “digital signature.” The P2P network becomes subject to this digital signature. This digital signature is used by a large, sufficiently powerful group of people to reach an agreement on transactions and other relevant matters. Following authorization, a transaction between two parties connected to the same network is successfully completed by the use of a mathematical verification procedure.
Now, let’s get into what is Hedera Hashgraph in more detail!
Related: Top Blockchain Technology Companies
What is Hashgraph?
Even though Hashgraph has only been around for five and a half years, its partnerships with several IT behemoths, like IBM and Swirlds, demonstrate how remarkable it is.
Hashgraph is yet another kind of DLT and consensus method that was developed as a substitute for Blockchain. However, the main goal of this technology was supposed to be to overcome the problems that Blockchain has encountered and continues to encounter.
Hashgraph was created by Hedera, a business, to offer a quicker, safer, and more effective way to come to a consensus in a decentralized network. This technology stores and manages data using the Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) structure. In addition, it swiftly and effectively achieves mutual consensus between networked nodes by combining voting and gossip processes. As a matter of fact, a number of experts have observed that Hashgraph is able to perform thousands of transactions per second and is more secure than standard Blockchain technology.
How Is Hashgraph Technology Operational?
Hashgraph is a distributed ledger technology that uses a directed acyclic graph (DAG) and a “gossip about gossip” protocol to achieve fast, secure, and fair consensus. Nodes randomly share information with each other, and each exchange incorporates cryptographic hashes of previous events into a new event. This structure allows rapid synchronization of information across the network. Hashgraph employs virtual voting, where nodes independently calculate votes based on the Hashgraph’s history, eliminating the need for actual vote transmission. Nodes then determine the consensus order and timestamp of transactions through a series of virtual votes over multiple rounds.
Hashgraph is Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT), capable of reaching consensus even with some malicious nodes, ensuring security. Its gossip protocol and virtual voting mechanism enable efficient consensus with less computational effort than traditional blockchains. The consensus timestamp method ensures fair transaction ordering, making Hashgraph suitable for applications needing high throughput and fairness.

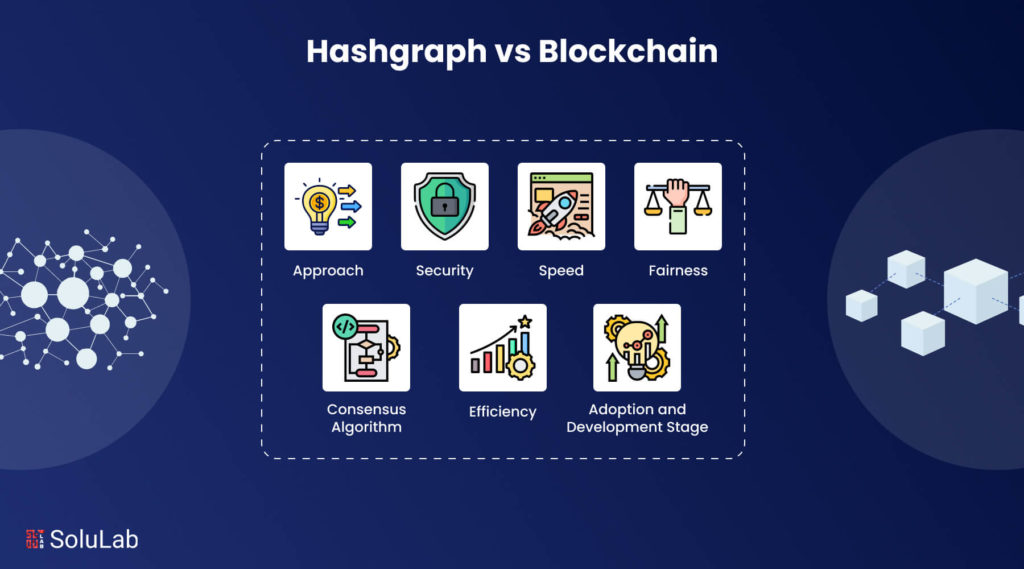
Difference Between Hedera Hashgraph and Blockchain
Here are some key differences between Hedera Hashgraph vs Blockchain Technology:
The primary difference between Hashgraph and blockchain lies in their structural approach. Blockchain organizes data into linear blocks appended sequentially, which works well but has limitations. In contrast, Hashgraph employs a directed acyclic graph (DAG) for storing and accessing information. Despite these differences, both DLTs ensure decentralization by maintaining copies of the ledger across all nodes.
Both blockchain and Hashgraph provide robust security measures. Blockchain uses cryptographic methods to secure stored and transmitted data, making the digital blocks tamper-proof. Any attempt to alter the data invalidates the signature, alerting nodes to possible breaches. Hashgraph utilizes Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT) to protect the network from malicious actors, ensuring that recorded events remain unaltered. Unlike blockchain, Hedera Hashgraph’s consensus algorithm avoids a leader-based format, protecting the network from DDoS attacks.
Blockchain employs various consensus algorithms, including Proof-of-Work, Proof-of-Stake, and delegated Byzantine Fault Tolerance, depending on the platform or cryptocurrency. On the other hand, Hashgraph, particularly Hedera Hashgraph, uses virtual voting to achieve network consensus. The Hedera Consensus algorithm, intrinsic to Hashgraph, offers unique advantages through its detailed approach.
Hashgraph significantly outpaces blockchain in transaction speed. While blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum handle between 100 to 10,000 transactions per second, Hashgraph theoretically supports up to 500,000 transactions per second. This speed advantage is due to Hashgraph’s Gossip protocol, which requires less information to be propagated as more events occur.
In blockchain systems, miners have considerable influence over transaction processing, leading to potential unfairness. Hashgraph addresses this by random node allocation and consensus timestamping, ensuring transaction order does not favor any individual.
Hashgraph is more efficient than blockchain due to its event-based approach, eliminating the issues of simultaneous block mining and discarded blocks. This results in a more streamlined and efficient network operation compared to blockchain’s block-based system.
-
Adoption and Development Stage
Blockchain enjoys a higher adoption rate and a more advanced development stage, being a decade old and benefitting from early market entry. Technologies like Ethereum have introduced smart contracts and dApps, enhancing blockchain’s utility. In contrast, Hashgraph, especially Hedera Hashgraph, is newer and less widely adopted. Though currently used by over 300 companies, its adoption rate still lags behind that of blockchain technologies.
DAG: Another Take on Distributed Ledgers
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) represent an innovative approach to distributed ledger technology (DLT). Unlike traditional blockchain, which structures data in linear, sequential blocks, DAGs organize data in a graph format where nodes are connected without forming cycles. This architecture allows for more flexible and scalable data management, making DAGs a compelling alternative in the realm of distributed ledgers.
Structure and Operation
In a DAG-based ledger, each transaction or event is recorded as a node in the graph. These nodes are connected to multiple previous nodes, rather than to a single preceding block. This structure results in a web of interconnected transactions that can be processed concurrently, enhancing efficiency.
1. Transactions as Nodes: Every transaction is a vertex in the graph. To add a new transaction, it must reference one or more previous transactions (parents).
2. No Cycles: The acyclic nature ensures there are no loops, meaning you cannot start at one node and eventually loop back to it. This prevents issues like double spending and ensures the integrity of the ledger.
3. Concurrency: Multiple transactions can be added simultaneously since they don’t need to wait for a block to be mined. This parallelism increases the throughput of the network.
Consensus in DAGs
Consensus mechanisms in DAGs differ significantly from those in blockchain systems. Rather than relying on a single chain of blocks agreed upon by all nodes, DAGs employ a more decentralized approach where each node independently verifies and adds transactions.
1. Gossip Protocol: Information about transactions spreads rapidly across the network through a gossip protocol, where each node randomly shares data with other nodes.
2. Virtual Voting: Instead of actual votes being cast, nodes infer the state of the network by analyzing the structure of the DAG. They use the history of connections (who referenced whom) to deduce consensus.
3. Transaction Confirmation: Transactions are confirmed based on their references. If a transaction is indirectly referenced by many future transactions, it is considered more secure and confirmed.
Security and Robustness
DAG-based systems offer robust security features. The interconnected nature of the graph makes it difficult for malicious actors to alter the ledger without being detected.
1. Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT): Many DAG systems, like Hedera Hashgraph, utilize aBFT to secure the network. This ensures that consensus can be reached even if some nodes act maliciously.
2. Tamper-Proof: Once a transaction is included and referenced by subsequent transactions, altering it would require changing all subsequent transactions, which is computationally infeasible.
3. No Centralization Risks: Unlike blockchain systems that might centralize around mining pools or validators, DAGs distribute validation work across all participating nodes, enhancing decentralization.
Use Cases of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has a wide range of applications due to its decentralized, secure, and transparent nature. Here are some key use cases:
1. Financial Services
Cryptocurrencies: The most well-known use of blockchain technology is in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Blockchain provides a decentralized, transparent, and secure ledger for recording transactions, ensuring trust without the need for intermediaries.
Cross-border Payments: Blockchain can streamline cross-border transactions by reducing the need for intermediaries, lowering costs, and speeding up processing times. Ripple is an example of a blockchain-based solution aimed at facilitating international payments.
Smart Contracts: Platforms like Ethereum allow for the creation of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. These contracts automatically enforce and execute the terms of agreements when predefined conditions are met.
Related: Blockchain in Trade Finance
2. Supply Chain Management
Traceability: Blockchain can enhance transparency and traceability in supply chains. Companies like IBM and Walmart are using blockchain to track the origin and journey of products from suppliers to consumers, ensuring authenticity and quality control.
Anti-counterfeiting: By recording every transaction and movement of goods on an immutable ledger, blockchain helps prevent counterfeiting and fraud, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals, luxury goods, and electronics.
3. Voting Systems
Secure Voting: Blockchain can create tamper-proof voting systems, ensuring the integrity and transparency of elections. Each vote can be recorded on the blockchain, making it nearly impossible to alter the results once they are submitted.
4. Healthcare
Medical Records: Blockchain can securely store and manage medical records, providing patients and healthcare providers with a unified and tamper-proof health history. This enhances data sharing while protecting patient privacy.
Drug Traceability: Blockchain can track the production and distribution of pharmaceutical drugs, helping to prevent counterfeit drugs and ensuring the authenticity of medications.
Use Cases of Hashgraph
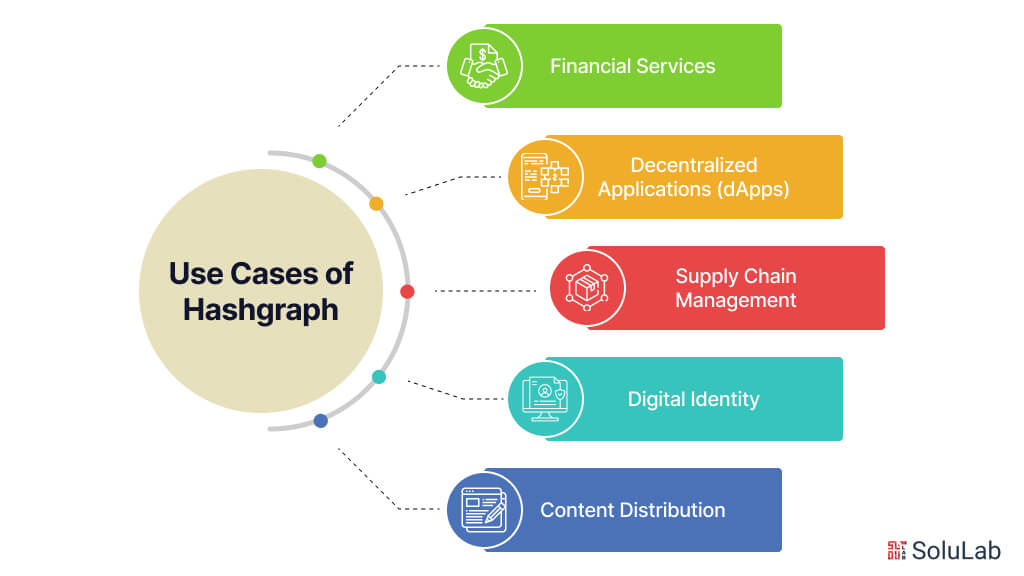
Hashgraph offers high-speed and efficient solutions for various industries. Here are some notable use cases:
1. Financial Services
- Micropayments: Enables efficient, low-cost transactions for digital services such as content monetization and IoT device interactions, allowing for seamless microtransactions.
- Stablecoins: Provides a scalable and secure platform for issuing and managing stablecoins, digital currencies that maintain a stable value by being pegged to fiat currencies.
2. Decentralized Applications (dApps)
- Gaming: Supports high-speed, low-latency transactions necessary for in-game purchases, rewards distribution, and real-time interactions, enhancing the gaming experience.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Powers DeFi platforms with efficient and secure transaction processing, enabling services like lending, borrowing, and trading of digital assets without intermediaries.
3. Supply Chain Management
- Real-time Tracking: Facilitates the real-time tracking of goods, providing immediate updates and greater scalability compared to traditional systems, ensuring more efficient and transparent supply chains.
- Digital Provenance: Ensures the authenticity of products by tracking their entire journey through the supply chain, from origin to consumer, preventing fraud and counterfeiting.
4. Digital Identity
- Identity Verification: Offers a secure and rapid way to verify identities for financial services, access control, and online applications, enhancing security and user experience.
- Credential Management: Allows educational institutions and professional organizations to issue and verify digital credentials, such as degrees and certifications, ensuring authenticity and preventing fraud.
5. Content Distribution
- Fair Royalties: Ensures that creators in the media and entertainment industry are compensated accurately and promptly by automating royalty distributions based on content usage and rights agreements.
- Decentralized Content Platforms: Enables the creation of platforms where users can share and monetize their content directly, benefiting from the network’s speed and security, and reducing reliance on intermediaries.
Will Blockchain Be Replaced by Hashgraph?
We do not currently think that Hashgraph will take the place of blockchain. However, there are a number of advantages to adopting Hashgraph versus blockchain technology. The current wave of blockchain acceptance is just growing, and businesses are now eager to begin utilizing blockchain thanks to the usage of private blockchains.
Blockchain technology is already being used by a lot of businesses, and we think this is only the beginning of a new age. However, Hedera Hashgraph may stand alone and become more well-liked without taking the place of any other technology.
Even while blockchain has a lot of problems, they aren’t significant enough to make the technology less popular.

Concluding Remarks
Blockchain has served for more than 15 years as the foundational technology in the cryptocurrency space. However, Hashgraph is a somewhat more recent option—it was introduced in 2017.
However, even in this short period, Hashgraph has garnered a lot of praise for its high-tech speed, which is fueled by its consensus algorithms. It can really reach an agreement far faster than Blockchain—in less than three seconds.
However, there is still a long way to go and Hashgraph has to improve to become as well-liked as Blockchain. Moreover, developers continue to favor Blockchain due to its dependability, decentralization, security features, and application scenarios. Furthermore, the constantly growing Blockchain technology trends demonstrate why it is still leading the DLTs domain.
Blockchain technology, despite its transformative potential, faces several challenges such as scalability issues, high energy consumption, and slow transaction speeds. Security concerns like susceptibility to 51% attacks and regulatory uncertainties also hinder its broader adoption. SoluLab, as a leading blockchain development company, addresses these issues by offering tailored solutions like optimized consensus algorithms for enhanced scalability, energy-efficient blockchain models, and robust security frameworks. By using its expertise in developing customized blockchain applications, SoluLab ensures businesses can harness the full potential of blockchain technology securely and efficiently. Contact SoluLab today to overcome blockchain challenges and accelerate your digital transformation journey.
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between Hashgraph and Blockchain?
The primary difference lies in their data structure and consensus mechanisms. Blockchain stores data in linear blocks, whereas Hashgraph utilizes a directed acyclic graph (DAG). Additionally, Hashgraph employs a “gossip about gossip” protocol for consensus, while blockchain relies on various consensus algorithms like Proof-of-Work or Proof-of-Stake.
2. Which technology offers higher transaction speeds, Hashgraph, or Blockchain?
Hashgraph typically offers significantly higher transaction speeds compared to traditional blockchain systems. While blockchain solutions like Bitcoin and Ethereum handle between 3 to 15 transactions per second, Hashgraph theoretically supports up to 500,000 transactions per second, making it ideal for applications requiring high throughput.
3. How does each technology ensure the security and integrity of the ledger?
Both Hashgraph and Blockchain employ robust security measures to maintain the integrity of the ledger. Blockchain ensures security through cryptographic methods like hashing and digital signatures, while Hashgraph utilizes Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT) to secure the network from malicious actors, ensuring that recorded events remain unaltered.
4. What are the key use cases for Hashgraph and Blockchain?
Blockchain technology finds applications in financial services, supply chain management, voting systems, healthcare, and more. Hashgraph, on the other hand, is well-suited for micropayments, stablecoins, gaming, supply chain management, digital identity verification, and decentralized content distribution.
5. Which technology is more energy-efficient, Hashgraph, or Blockchain?
Hashgraph generally consumes less energy compared to traditional Proof-of-Work (PoW) blockchain systems like Bitcoin. Hashgraph’s consensus mechanism does not require extensive computational power for mining, making it more environmentally friendly. However, energy consumption varies depending on the specific implementation and consensus algorithm used in blockchain systems.