Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks, or DePINs, are gaining popularity among enterprises that recognize DePIN’s potential to handle actual hardware services in a decentralized manner.
DePIN integrates blockchain and artificial intelligence (AI), two transformative modern technologies. By combining these latest technologies, DePIN seeks to improve access to vital resources and systems, promoting equality and transparency for all. This innovative approach can transform a wide range of sectors and significantly impact our daily lives by changing how we interact with digital and physical objects. Over 650 projects were developing these DePIN solutions last year, according to Messari’s“The DePIN Sector Map” publication.
This explains why DePIN’s market value reaches $25 billion. So, if you want to learn more about DePIN, how it works, and why it is essential, this blog is worth reading!
In this blog, we will discuss DePIN (decentralized physical infrastructure network) and the use cases of decentralized physical infrastructure networks. So, without any further ado, let’s get started!
DePIN, an abbreviation for Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks, is a novel concept for developing and managing physical infrastructure using decentralized technologies. It blends blockchain technology alongside physical assets in order to create a more effective, transparent, and secure approach to infrastructure development, operation, and maintenance.
Traditionally, huge organizations or centralized entities take care of physical infrastructure such as data centers, telecommunications networks, and energy grids. These systems may suffer from inefficiencies, excessive costs, and a lack of transparency. DePIN shifts this paradigm by enabling individuals and organizations to contribute resources, which allows people and organizations to give resources to a decentralized network, such as processing power, storage space, or even renewable energy. In exchange, players are rewarded with tokens or other types of incentives, resulting in a more collaborative and efficient method.
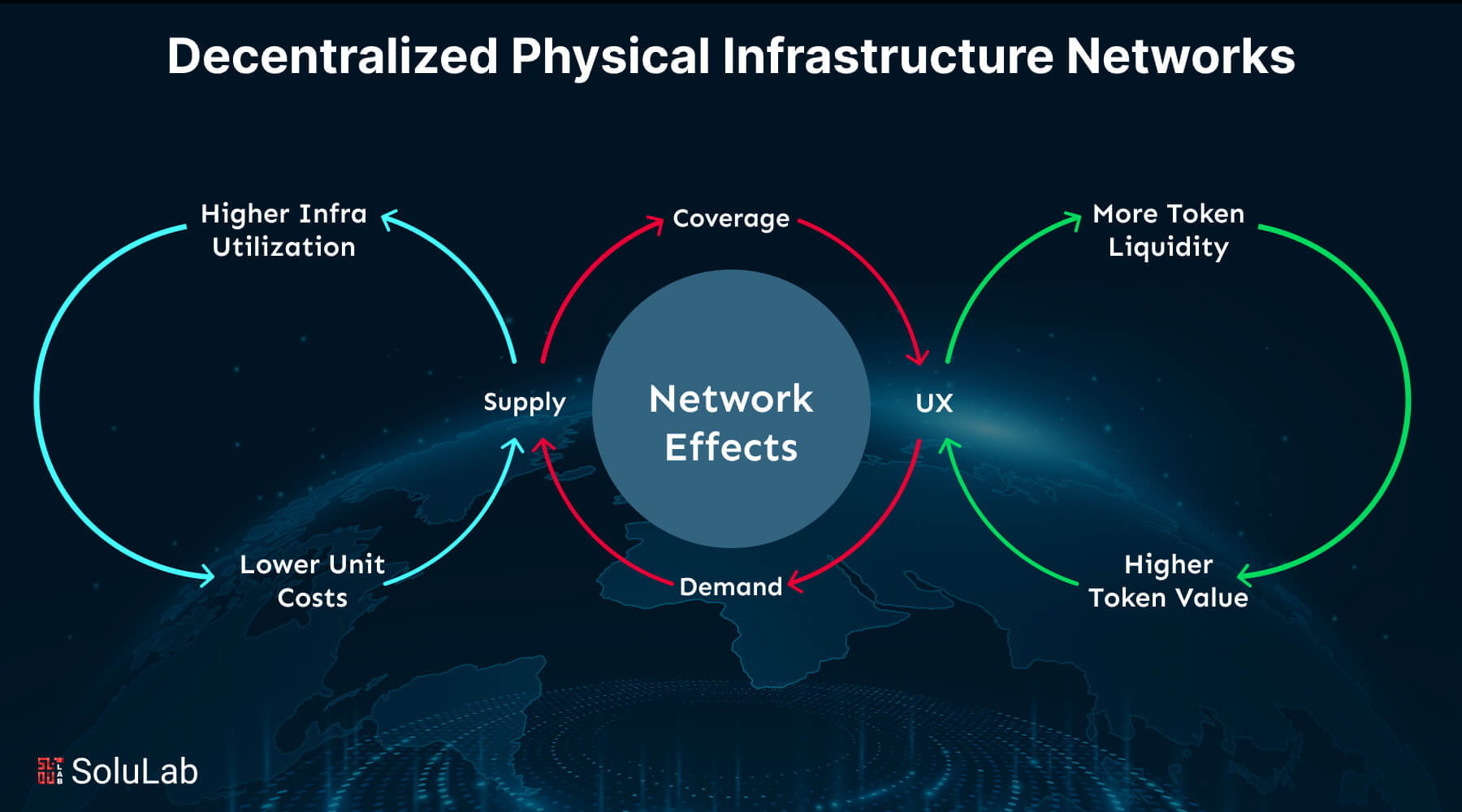
DePIN’s major characteristic is its capacity to assure trust and transparency. Blockchain technology records all transactions and activity inside the network in a tamper-proof ledger. This not only guarantees that resources are used properly, but also enables the seamless connection of scattered assets over a worldwide network.
As the world shifts toward digital transformation, DePIN has an opportunity to redefine the way we think about and engage with physical infrastructure. By decentralizing crucial system management, it provides a viable alternative to traditional methods that may be sluggish, expensive, and prone to central points of failure. DePIN improves infrastructure resilience, flexibility, and accessibility to a greater spectrum of people, resulting in a more inclusive and sustainable future.
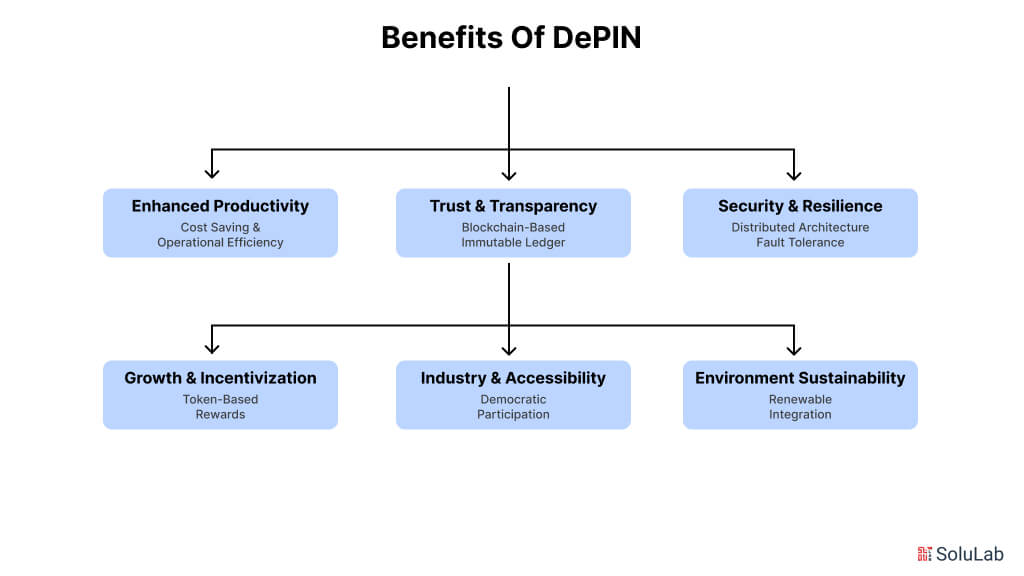
The many benefits of Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN) transform the way we design and maintain infrastructure. Besides only making systems more effective, decentralized physical infrastructure can also promote innovation, improve accessibility, and promote long-term sustainability. Here are some of the top benefits of DePIN:
DePIN’s ability to streamline infrastructure operations is among its primary benefits. Multiple levels of management are frequently used in traditional centralized systems, which can result in inefficiencies and increased expenses. DePIN, on the other hand, eliminates needless middlemen and lowers operational overhead by enabling direct communication among participants. Both suppliers and customers benefit from more affordable solutions as a result.
DePIN makes use of blockchain technology to guarantee that every activity and transaction within the network is documented in a safe, unchangeable ledger. Since every action made within the network can be confirmed by all members, this transparency increases participant trust. Additionally, it removes the possibility of fraud or resource abuse, increasing the dependability and accountability of decentralized infrastructure.
Decentralized physical infrastructure also has the important advantage of being less susceptible to single points of failure. Cyberattacks, natural catastrophes, and other disturbances that could impact significant swaths of the infrastructure are common threats to centralized systems. By distributing resources and operations among numerous participants, DePIN’s decentralized architecture, on the other hand, produces a more resilient system that is more difficult to hack or disable.
DePIN gives people and organizations the chance to get involved in infrastructure development and upkeep in ways that were previously impossible with conventional procedures. It promotes broad participation and creativity by giving participants tokens or other rewards. In addition to encouraging community-driven solutions, this guarantees that infrastructure develops to satisfy the many demands of its users.
No matter their size or location, participants can contribute resources to decentralized infrastructure. This makes it possible for smaller actors to join and profit from the network, democratizing access to vital infrastructure. Anyone with the required resources can participate in DePIN’s more inclusive model, whether they are giving storage capacity, processing power, or renewable energy.
Another significant advantage is the integration of renewable energy sources into decentralized infrastructure networks. To run more sustainably, many DePIN projects seek to use resources like hydroelectric, solar, or wind power. In addition to lessening infrastructure’s negative environmental effects, this emphasis on sustainability promotes the wider use of green technologies.
Related: Why are Startups, Businesses, and Governments Looking for DePIN Development?
Many components work together to create a cooperative, blockchain-based physical infrastructure, which is what makes a Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN) successful and effective. These contributions, which vary from human users to technological elements, are all essential to the smooth and successful operation of the network.
Participants—individuals, companies, and organizations that provide resources—are the backbone of every DePIN network. Depending on the particular DePIN use cases, these resources might vary greatly and could include physical assets like infrastructure gear or renewable energy sources, as well as processing power, storage capacity, and bandwidth. Anyone may engage in a decentralized system, allowing for a more diversified ecosystem where the network as a whole is shaped by a range of inputs.
Participants may provide extra energy from solar panels, empty data center storage space, or idle computer resources, for instance, in blockchain-based physical infrastructure initiatives. DePIN networks can build bigger, more effective systems without depending on conventional centralized authority by combining these contributions.
Blockchain technology, which guarantees security, transparency, and immutability, is the foundation of any DePIN network. Blockchain is the distributed ledger that keeps track of every activity and transaction that takes place on the network. It fosters confidence among participants by guaranteeing that each activity, trade, and contribution is authenticated and unchangeable. The blockchain’s decentralized structure also eliminates the need for a central authority, enabling the network to function independently by established standards.
Blockchain not only protects transactions but also makes asset tokenization easier. In return for their efforts, members of a DePIN network might get tokens or other digital rewards. The network becomes more dynamic and sustainable as a result of the incentives provided by this token-based economy.
The actual assets are essential to a DePIN network’s operation, even though blockchain technology is also quite important. These can include energy grids, sensor networks, data storage facilities, and telecommunications infrastructure. Underutilized or dispersed physical infrastructure that can be decentralized and improved for increased efficiency is what DePIN networks rely on to function well.
For example, persons or companies with solar panels can provide extra energy to the network in DePIN use cases linked to energy grids, and people with extra hard drives can donate space for distributed storage systems in data storage networks. The secret is in the way these tangible assets are linked together and controlled by blockchain protocols, which enable resource sharing and coordination in real-time.
Another essential component of the DePIN network is smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements encoded in the blockchain. These contracts eliminate the need for manual intervention by automatically executing and enforcing provisions when specific conditions are satisfied. They guarantee that donors receive just and timely payment for their contributions, which builds confidence and promotes further involvement.
In a decentralized energy network, for instance, a smart contract may automatically move tokens to a user’s wallet each time they supply the grid with more solar energy. The network becomes more efficient as a result of this smooth automation, which simplifies the procedure and lowers transaction friction.
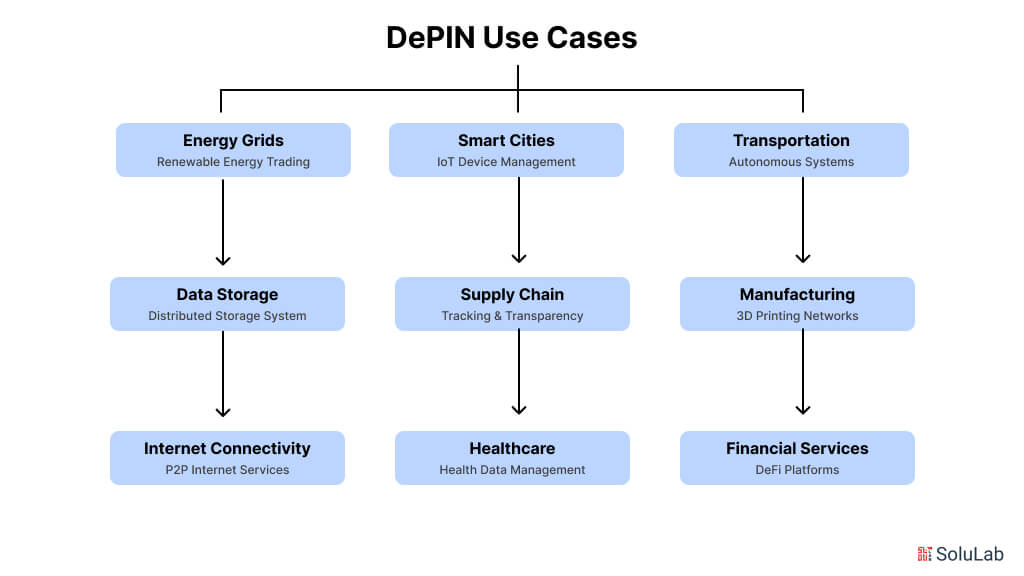
The power of decentralized physical infrastructure networks (DePIN) to transform businesses and alter conventional systems is becoming more and more apparent as they develop. DePIN use cases are anticipated to significantly grow by 2026 in a number of industries, including telecommunications and energy, providing cutting-edge solutions that promote inclusivity, sustainability, and efficiency. Here are a few of the most important DePIN use cases that will be relevant in 2026.
The energy industry is expected to be one of the most significant DePIN application examples. Decentralized energy systems will make it possible for residences and commercial buildings to pool excess energy produced by renewable resources like wind turbines and solar panels by 2026. Blockchain-based systems will enable participants to purchase and sell energy effectively, boosting the usage of sustainable energy and decreasing reliance on conventional centralized networks.
Use cases for decentralized networks in the form of distributed storage systems will be driven by the increasing demand for safe, scalable, and easily available data storage. Participants can establish an international storage network by providing unused storage space from devices like SSDs or hard disks. This concept lowers costs, gives customers more control over their data, and lessens the need for central cloud providers.
Decentralized networks will improve internet access worldwide by 2026, especially in underprivileged areas. By providing peer-to-peer services, anyone with extra bandwidth will be able to support a worldwide decentralized network use case. By giving low-income or distant areas access to dependable and reasonably priced internet, this solution will lessen the digital divide.
Decentralized systems will be essential to the creation of smart cities. Managing IoT devices, such as sensors for trash management, pollution monitoring, and traffic control, is one use case for DePIN in smart cities. Utilizing decentralized networks, these gadgets will exchange information and communicate, enhancing urban living’s sustainability and efficiency.
Top DePIN use cases will also flourish in the telecommunications infrastructure sector. Underutilized network hardware, including routers or signal towers, might be donated by people and companies by 2026 to increase global connectivity. A more robust, economical, and adaptable telecommunications system will be made possible by this example of DePIN applications.
Supply chains will use blockchain technology to track and validate transactions, giving customers and companies real-time visibility into the origin and path of commodities. By ensuring that items are supplied lawfully and ethically, this use case for decentralized networks will increase transparency, lower fraud, and foster more sustainable behaviors.
Another industry that will be transformed by DePIN in 2026 is healthcare. Patients may have more control over their medical records if health data management is decentralized. Applications for DePINs include enhancing privacy, accessibility, and interoperability while safely storing and exchanging health data across a decentralized network.
The evolution of autonomous transportation networks will be significantly influenced by decentralized infrastructure. Through a decentralized system, vehicles will interact with the infrastructure around them and with each other, enabling safer, more effective transportation as well as real-time traffic control and route optimization. The shift to autonomous vehicles and intelligent transportation systems will heavily rely on this DePIN use case.
One of DePIN’s most popular applications in the manufacturing sector will be the decentralized 3D printing of items. By using 3D printers, people and companies may participate in a distributed manufacturing network, which eliminates the need for massive, centralized factories by creating goods or parts as needed.
Platforms for decentralized finance (DeFi) will keep growing in their capacity to offer financial services in 2026. Without depending on conventional banks, anyone can lend, borrow, or exchange assets using instances of DePIN apps. Users will have easier access to financial tools as a result, especially in areas with weak banking infrastructure.
Thus, DePIN will have a wide range of applications in 2026 that will affect every facet of contemporary life. The prospective uses of decentralized infrastructure in fields like energy distribution, healthcare, and transportation will not only improve current systems but also give rise to whole new paradigms for resource sharing and teamwork. A more equitable, environmentally friendly, and secure future where physical infrastructure is more easily available and effectively controlled by a worldwide network of contributors is what the top DePIN use cases offer.
While decentralized physical infrastructure networks (DePIN) provide various benefits, their broad acceptance and deployment present some obstacles that must be solved. These challenges span technological, regulatory, and operational dimensions, all of which can have an impact on DePIN systems’ effectiveness and scalability. The following are some of the major challenges that might impede the use of blockchain-based physical infrastructure.
1. Scalability and Network Efficiency: One of the most significant issues for DePIN networks is to make sure that they can grow efficiently. As the network expands, so does the number of participants and the volume of transactions, which can cause congestion and sluggish processing times. It is critical in blockchain-based physical infrastructure networks to ensure that the underlying blockchain can manage a huge number of transactions while maintaining speed and dependability. This problem becomes considerably more complicated when different forms of physical infrastructure—from energy grids to telecommunications—demand varying degrees of transaction speed and data storage.
2. Interoperability Between Networks: DePIN systems frequently rely on a broad set of devices and resources that must function flawlessly. Getting separate blockchain-based physical infrastructure networks to connect and exchange resources with one another is a huge difficulty. A decentralized energy grid, for example, may require connectivity to a decentralized data storage network or a telecommunications network. Without common protocols and procedures for interoperability, these networks may function in isolation, limiting the potential of DePIN applications and diminishing their overall efficacy.
3. Security and Privacy Concerns: While blockchain offers a high degree of security, DePIN systems’ decentralized structure introduces additional security vulnerabilities. Because these networks rely on a large number of players, each providing resources and information, vulnerabilities in one portion of the system have the potential to harm the entire network. Privacy is another issue, particularly when dealing with sensitive data. In areas such as healthcare and banking, protecting personal information while retaining transparency is a tricky balancing. To avoid these dangers, appropriate encryption methods and secure protocols must be implemented.
4. Regulatory and Legal Issues: DePIN networks, being relatively fresh, are not generally properly defined under existing legal and regulatory systems. This creates a substantial difficulty, particularly in areas with strong regulations such as energy, healthcare, and telecommunications. Governments and regulatory agencies are still figuring out how to categorize and govern decentralized infrastructure. Legal uncertainty may hinder adoption, as organizations may be hesitant to invest in or operate within a system that lacks clear legal guidance. Furthermore, questions of accountability, taxes, and intellectual property in decentralized contexts must be addressed to support the long-term growth of DePIN networks.
Read Blog: How DePIN Transforms Web3 Space
5. Adoption & Trust: To survive, every DePIN network requires widespread engagement and confidence from a varied range of stakeholders. Convincing individuals, organizations, and enterprises to donate resources to a decentralized network can be difficult, especially in industries traditionally dominated by centralized authority. Overcoming cynicism regarding the security, dependability, and utility of decentralized systems is a serious challenge. Furthermore, new users may struggle to use blockchain systems, which might provide a barrier to wider adoption.
6. Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact: Despite increased interest in employing blockchain-based physical infrastructure for decentralized energy grids and other systems, the environmental effect of blockchain technology is still a worry. Certain blockchains, particularly those based on proof-of-work consensus algorithms, require massive amounts of energy. This may negate the potential sustainability benefits of DePIN systems, particularly if they are used in energy-intensive industries. Discovering energy-efficient blockchain alternatives, such as proof-of-stake or hybrid models, will be critical in meeting this problem.
7. Maintenance and Reliability: DePIN’s decentralized structure implies that no central authority oversees the system’s maintenance and functioning. In classic centralized infrastructure arrangements, a single organization manages maintenance and system changes, resulting in seamless operations. However, in a DePIN system, maintenance responsibilities are split among several players, which might result in variable performance and dependability. Ensuring that the system stays robust and resilient in the face of resource restrictions or system failures is a significant problem.
8. Financial and Incentive Structures: Tokenization of resources is a key component of DePIN networks, in which players are paid for their efforts. However, developing equitable and sustainable funding mechanisms for these networks might be difficult. Token values vary, creating uncertainty for those who rely on the system for pay. Furthermore, because token-based incentive systems are complicated, new users may struggle to grasp and trust the network’s economic architecture.
Finally, DePIN use cases in 2026 have the potential to change industries throughout the world by providing a more decentralized, effective, and sustainable approach to managing physical infrastructure. As industries such as energy, data storage, telecommunications, and healthcare experiment with decentralized models, the promise for increased accessibility, openness, and resilience becomes obvious. DePIN’s most popular use cases, such as decentralized energy grids, peer-to-peer internet access, and distributed manufacturing, are only the beginning of a more connected and collaborative future.
SoluLab helped Spherium Finance create an all-in-one decentralized finance platform that consolidates a wide range of DeFi products and services, making them easily accessible. With the launch of this platform, Spherium is now empowering users outside of core IT enthusiasts to achieve high positive returns on their DeFi investments. By integrating multi-asset, cross-chain swaps, and crypto financing solutions, the platform offers low-risk, high-reward investment management.
SoluLab specializes in designing blockchain-based physical infrastructure solutions that are suited to the specific requirements of each business. As a leading decentralized physical infrastructure and blockchain development company, we can assist businesses in harnessing the potential of DePIN to create more efficient and scalable solutions. If you want to incorporate blockchain technology into your energy network, enhance data storage, or create a decentralized telecoms platform, SoluLab has the skills to make it happen. Want to transform your infrastructure with decentralized solutions? Contact SoluLab today to start building the future.
DePIN stands for Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks, where resources like energy, storage, and computing power are shared across a decentralized network rather than being controlled by a single organization. By using blockchain technology, DePIN ensures that transactions and contributions are secure, transparent, and efficient, allowing participants to contribute and earn rewards in a decentralized ecosystem.
In the coming years, DePIN will impact the energy sector by allowing individuals and businesses with renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines, to share excess energy through decentralized energy grids. This will make energy distribution more efficient, sustainable, and accessible, as participants can trade energy directly with each other, reducing reliance on traditional energy companies.
Decentralized data storage through DePIN offers enhanced security and privacy by distributing data across multiple participants rather than relying on a single centralized provider. This approach reduces the risk of data breaches, offers greater control over personal data, and makes storage more affordable. Plus, it enables scalable solutions that can grow with the increasing demand for data.
DePIN will be instrumental in building smart cities by decentralizing the management of critical urban infrastructure, such as traffic systems, waste management, and pollution monitoring. IoT devices will be connected through decentralized networks, allowing real-time data sharing and decision-making. This will lead to more efficient, sustainable, and responsive urban environments, improving the quality of life for city residents.
Although DePIN offers tremendous potential, challenges such as scalability, integration between different decentralized systems, regulatory uncertainties, and security concerns could slow its adoption. To fully realize the benefits of decentralized infrastructure, it will be essential to overcome issues related to interoperability, user trust, and the need for clear regulatory frameworks that can guide its development.