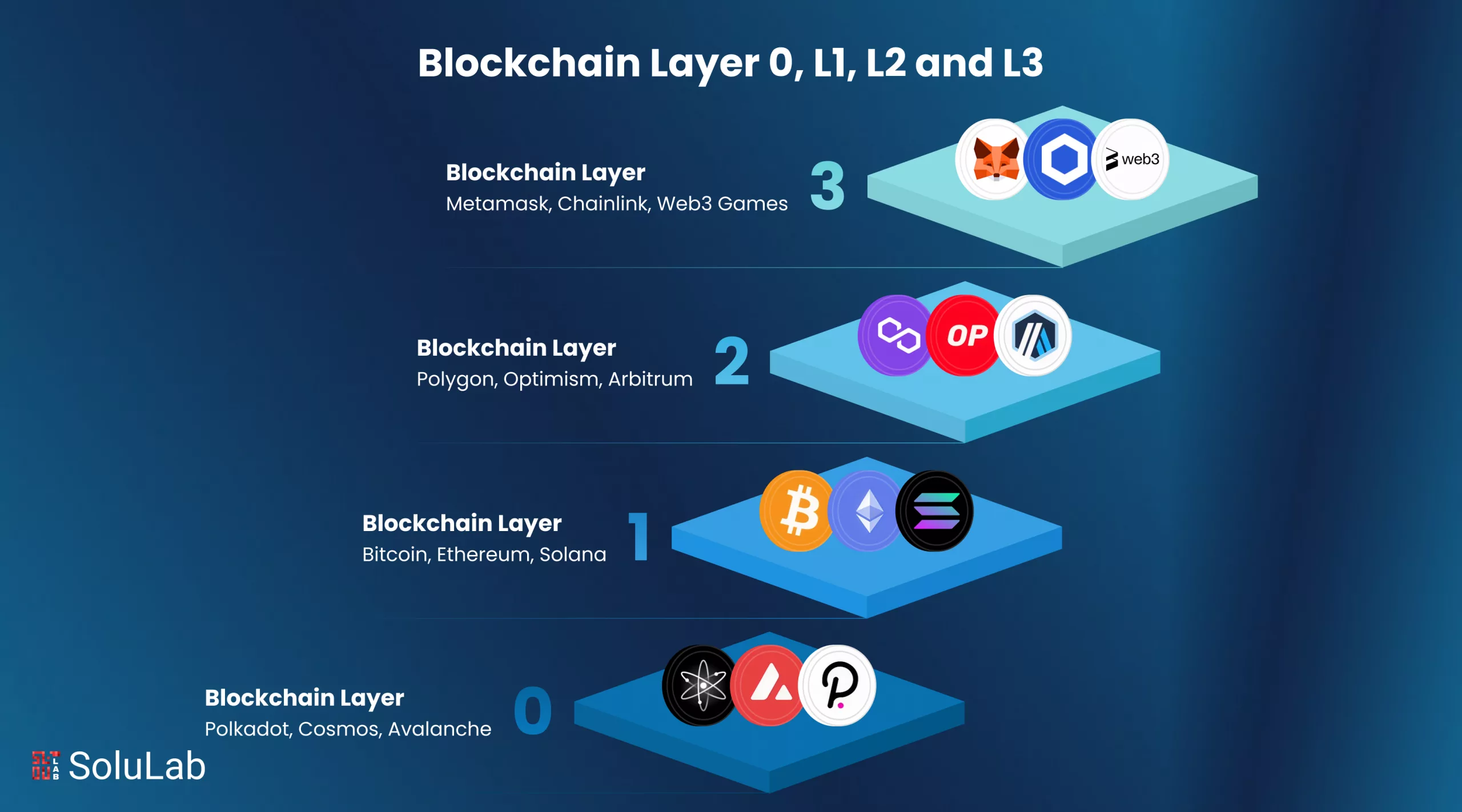
Blockchain technology is growing fast to meet the rising need for better speed, security, and decentralization. As per the World Economic Forum, the total value of crypto assets has passed $1.7 trillion, with more than 3,000 decentralized apps (dApps) live on various blockchain platforms.
As more people and businesses adopt this tech, it’s important to understand how different layers in blockchain work together. From the base infrastructure of Layer 0 to the user-facing apps in Layer 3, each layer plays a key role in making the system faster, safer, and easier to use.
This blog will break down each of the different layers in blockchain in simple terms, so you can clearly see how they work and what role they play in building powerful, scalable Web3 and AI products.
A blockchain isn’t just one system or a single line of code, it’s made up of multiple blockchain architecture layers, each playing a unique role. These layers of blockchain technology work together to make blockchains more secure, faster, and easier to use.
This structure also helps solve the well-known blockchain trilemma: balancing security, scalability, and decentralization.
Here they are:
Using layers in blockchain technology makes the system more organized and flexible. It lets developers upgrade certain features without changing everything. For example:
It also supports more complex systems like cross-chain multi-asset management platforms, which let users interact with different blockchains all in one place, improving blockchain interoperability.
Layer 0 is the base layer of a blockchain network. It includes all the core systems like networking, hardware infrastructure, consensus protocols, and peer discovery mechanisms. It is the operating system of a blockchain.
Layer 0 allows different blockchains to talk to each other using technologies like Cosmos’ IBC and Polkadot’s Relay Chain. This enables multi-chain vs. cross-chain transactions and boosts blockchain interoperability.
These are widely used blockchain platforms for building scalable and secure ecosystems.
Layer 1 is where the actual blockchain protocol lives. It defines how the network operates, how consensus is reached, and how transactions are verified.
These are strong examples of layer 1 blockchains and are among the top blockchain development companies by adoption.
Layer 1 can get slow and expensive. Layer 2 helps by processing transactions faster and more cheaply, then reporting back to Layer 1.
This is where the Layer 1 vs Layer 2 vs Layer 3 trade-off becomes important for businesses looking to optimize cost and speed.
Layer 3 is the user-facing part of the blockchain. It includes apps, interfaces, and APIs that connect users to the blockchain.
With more demand for intelligent systems, AI agents and AI development companies are being integrated into layer 3 blockchain platforms to enhance automation and personalization.
The blockchain ecosystem is made up of multiple layers, each playing a unique role in how decentralized networks function, scale, and interact. Here’s a simple breakdown of Layer 0 to Layer 3 and how they differ:
| Layer | Main Function | Key Technologies | Examples | Who It’s For |
| Layer 0 | Base infrastructure for blockchains; handles networking and consensus | IBC (Cosmos), Relay Chain (Polkadot), Avalanche consensus | Polkadot, Cosmos, Avalanche | Developers building interoperable or multi-chain ecosystems |
| Layer 1 | Core blockchain protocol manages transactions and consensus | PoW, PoS, Smart Contracts | Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana | Startups & enterprises launching tokens, smart contracts, or DeFi apps |
| Layer 2 | Offloads transaction load to scale Layer 1; enhances speed and reduces cost | Rollups, Sidechains, State Channels | Polygon, Optimism, Arbitrum | Projects needing faster, cheaper transactions for scalability |
| Layer 3 | Application layer that connects users with the blockchain | dApps, APIs, Wallets, Oracles, AI agents | Metamask, Chainlink, Web3 Games | Businesses focusing on UI/UX, user growth, or integrating AI with Web3 |

Blockchain layers aren’t isolated; they’re designed to work together as a stack, each serving a unique purpose while enhancing the overall functionality, scalability, and user experience of blockchain networks.
Here’s how these layers interact:
Blockchain layers stack vertically. Layer 2 builds on Layer 1, which runs on Layer 0. They also connect horizontally through chain abstraction for blockchain interoperability.
Each of the different layers of blockchain can evolve independently. This modular setup supports better upgrades and innovations, vital for blockchain in healthcare and blockchain in trade finance.
Choosing the right combination depends on your application’s goal, whether performance, decentralization, or user experience is the priority.
Scalability in blockchain refers to a network’s ability to handle a growing number of transactions, users, and applications efficiently, without slowing down or becoming too expensive to use.
In simple terms, a blockchain is scalable if it can grow and serve more people without sacrificing speed, cost, or security.
Scalability, decentralization, and security by achieving all three is challenging. Layers of blockchain solve this by dividing responsibilities across layers.
These highlight the importance of blockchain use cases in designing performant applications.
Layer 2 can deliver 100x throughput over Layer 1 alone.
The future of decentralized tech lies in how we leverage each of the blockchain layers. Whether you’re building a DeFi protocol or a retail app powered by AI, understanding this layered model helps you make smarter blockchain architecture layers decisions.
If you’re looking to scale or optimize your blockchain strategy, SoluLab is a trusted blockchain development company in the USA with real-world experience in implementing multi-layer systems. The team is well-versed in rendering top-notch solutions powered by a next-gen tech stack. Recently, SoluLab enabled OBORTECH to utilize Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) to launch scalable blockchain applications without backend complexity, showcasing our expertise in enterprise blockchain development.
Whether you are planning to integrate blockchain or have a unique idea to build, we can cater to all your needs with the best solutions. Contact us!
It depends on the project. Layer 1 is ideal for building secure and decentralized protocols. Layer 2 offers speed and cost-efficiency for apps that need scalability. Layer 3 is great for building user-friendly front-end experiences.
No, Layer 0 is the base. Layer 3 isn’t required for technical function but is essential for real-world usability.
Yes! Many modern blockchain projects use a combination of layers. For example, a DApp (Layer 3) might run on a Layer 2 solution like Arbitrum, which itself is secured by a Layer 1 blockchain like Ethereum, all connected via a Layer 0 protocol like Cosmos.
Enterprises can use Layer 0 for cross-chain operations, Layer 1 for secure data storage, Layer 2 for scaling high-volume use cases, and Layer 3 for creating user-friendly apps, making the tech stack modular, scalable, and enterprise-ready.