Using Machine Learning and AI for credit risk modeling has become a key tactic in the financial sector, revolutionizing how lenders evaluate borrower risk. Credit risk modeling has always depended on statistical methods and historical data, but AI-driven models provide a more accurate and dynamic approach thanks to the development of sophisticated algorithms and computer capacity.
Organizations may find new insights and development prospects while also reducing credit risk by utilizing AI and machine learning. By enabling the integration of disparate data sources, such as social media activity, and transaction histories, these technologies improve risk assessments and increase loan availability for marginalized groups. Furthermore, the AI for credit risk modeling assessment methodology is more scalable and flexible, allowing it to adapt to changing market conditions and regulatory requirements.
In this guide, we will present a complete approach to overcoming the complexities of developing credit risk models with AI and ML techniques. Financial institutions may get deeper insights into borrower creditworthiness, enhance lending choices, and reduce default risk by utilizing sophisticated data analytics, predictive modeling, and algorithmic methodologies. From comprehending the basics of credit risk to examining advanced AI breakthroughs, this article offers readers with a comprehensive overview of the major ideas, approaches, and concerns involved in constructing AI-driven credit risk models.
Credit risk is the potential loss incurred by an investor or lender as a borrower fails to repay a loan or meet financial obligations. It is a natural element of the loan and investing process, resulting from the uncertainty surrounding borrowers’ capacity or desire to repay their obligations. loan risk is determined by a variety of variables, including economic circumstances, industry trends, borrower profiles, and loan agreement terms.
Credit risk models are important in the financial industry because they assist lenders and investors in accurately assessing and managing credit risk. These models of credit risk use statistical approaches, historical data, and financial indicators to assess the possibility of debtors defaulting or not paying. The significance of credit risk models is stated as follows:
Read Blog: A Brief Guide to AI in Portfolio Management

There are several ways that credit risk might appear, and each one has different challenges and ramifications for investors and lenders. Understanding the different types of credit risk is vital for proficiently overseeing and alleviating possible damages. Three main categories of credit risk are as follows:
Also known as default probability or default hazard, default risk is the likelihood that a borrower would fail to make debt payments as agreed upon, so breaching the terms of the loan. This kind of risk occurs when borrowers are unable or unwilling to pay back their debts, which causes lenders or investors to suffer financial losses. The default risk is influenced by several factors such as unfavorable economic conditions, declining borrower financial stability, and shifts in market dynamics.
Spread risk or credit spread volatility is the possibility of unfavorable changes in the yield difference between credit-sensitive assets (like corporate bonds and credit default swaps) and securities without risk (like government bonds). This risk results from shifts in how the market views the quality of credit, liquidity, and macroeconomic factors that have an impact on credit instrument value. The return on investment and valuation of fixed-income portfolios, especially those that contain credit-sensitive assets, can be impacted by credit spread risk.
Excessive dependence on a single borrower, industrial sector, geographic area, or asset class within portfolio results in concentration risk, sometimes referred to as exposure risk or portfolio concentration risk. A portfolio’s total risk exposure increases when a sizable number of its assets are concentrated in a single business or industry. This is because the potential impact of unfavorable events on that entity or industry is amplified. Inadequate diversification tactics, market conditions, or investor strategy choices can all lead to concentration risk.
Knowing the various types of credit risk empowers lenders, investors, and financial establishments to establish comprehensive risk mitigation plans, diversify their holdings, and fortify themselves against possible setbacks. In order to maintain long-term financial stability and increase their resistance to unfavorable market conditions, stakeholders should proactively identify and manage credit risk exposures.
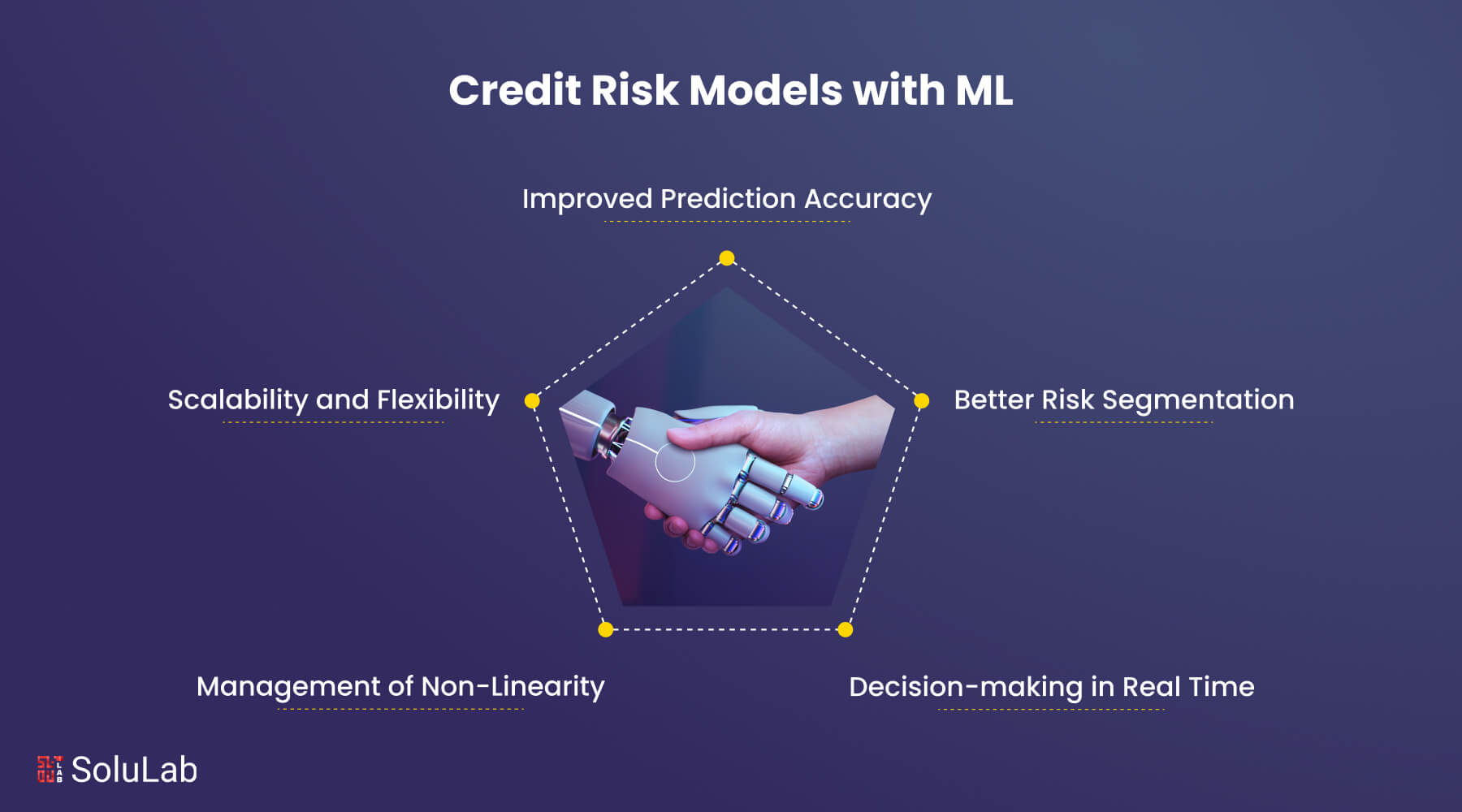
With its superior analytical skills and predictive insights, AI and machine learning (ML) has become a potent tool for credit risk modeling as the financial sector continues to grow. When it comes to credit risk modeling, machine learning has a number of benefits over conventional statistical techniques that enable financial firms to improve risk management procedures and streamline decision-making. The following are some of the main benefits of credit risk machine learning:
1. Improved Prediction Accuracy: Compared to traditional models, machine learning systems are more adept at capturing complex patterns, nonlinear correlations, and exchanges in credit risk data. ML models may achieve improved prediction accuracy and discriminating power by utilizing complex algorithms like gradient boosting machines, random forests, and neural networks. This helps lenders make better credit judgments and reduces the chance of defaults.
2. Better Risk Segmentation: Lenders may better target different customer categories with their pricing and risk assessment methods thanks to machine learning’s ability to provide precise segmentation of borrowers based on their credit risk profiles. Machine learning algorithms have the ability to detect minute changes in risk indicators and tailor credit scoring models or underwriting standards to particular sectors, loan products, or groups of people.
3. Decision-making in Real Time: Machine learning makes it possible to process and analyze enormous volumes of data in real time, which helps lenders make credit decisions quickly and adapt to changing borrower needs or market conditions. Machine learning algorithms have the ability to evaluate credit applications instantly, automate credit approval processes, and identify fraud or abnormalities in credit risk in real time. This improves client satisfaction overall, speeds up processing, and increases operational efficiency.
4. Scalability and Flexibility: Financial institutions may easily update and modify their credit risk models in response to changing market conditions, legal mandates, and new risk variables thanks to the scalability and adaptability of machine learning models. Without the need for human involvement, ML algorithms may absorb new data sources, modify model parameters, and react to shifting risk situations, assuring the continued stability of credit risk models.
5. Management of Non-Linearity: Machine learning is particularly good at managing the non-linear interactions and linkages between variables, which are typical in credit risk modeling. By using strategies like feature engineering, kernel approaches, and deep learning architectures, machine learning (ML) algorithms are able to capture intricate non-linearities and interactions, in contrast to typical linear models that presume linear correlations between predictors and outcomes. With this capacity, machine learning models may find hidden trends and risk variables that could show non-linear associations with credit risk outcomes, producing risk assessments and prediction insights that are more precise.
Machine learning has revolutionized credit risk modeling by providing advanced analytical techniques and predictive abilities. Here are some use cases of machine learning in credit risk modeling:
1. Default Prediction: Machine learning algorithms like logistic regression, random forests, and gradient-boosting machines revolutionize default prediction by leveraging historical loan data, borrower attributes, and economic indicators to estimate the likelihood of borrowers defaulting on their loan obligations. These models excel in identifying high-risk borrowers and flagging potential default events before they occur, enabling financial institutions to assess credit risk more effectively and mitigate potential losses in their loan portfolios.
2. Credit Scoring: In credit scoring, machine learning automates the process of evaluating creditworthiness by analyzing vast amounts of historical credit data. By employing advanced modeling techniques and alternative data sources, ML-based credit scoring models can provide more accurate and fair assessments of borrowers, improving the overall reliability of credit decisions.
3. Risk-Based Pricing: By examining borrower characteristics, market conditions, and rivalries, machine learning makes dynamic risk-based pricing techniques possible. In order to match loan price with risk exposure, maximize profitability, and reduce risks, machine learning algorithms divide borrowers into risk groups, estimate the likelihood of default, and compute risk-adjusted pricing measures.
4. Fraud Detection: Leveraging machine learning algorithms, financial institutions can analyze transaction data in real time to detect unusual patterns or anomalies indicative of fraudulent activities. ML models continuously learn from historical data, improving detection accuracy and enabling proactive measures to mitigate the risks associated with credit fraud.
Related: Machine Learning Use Cases in the Automotive Sector
5. Automation of Credit Decisions: Machine learning expedites the credit approval process by quickly assessing applicant creditworthiness, reducing errors and biases associated with manual decision-making. By minimizing human intervention, ML enhances efficiency and consistency in credit decisions, ultimately improving customer experience and operational workflows.
6. Customer Segmentation: ML algorithms analyze extensive customer data to identify patterns and behaviors indicative of varying risk profiles and credit behaviors. By segmenting customers into distinct groups, financial institutions can tailor products, services, and communication strategies to meet the specific needs and preferences of each segment, enhancing customer satisfaction and fostering loyalty.
7. Dynamic Pricing of Loans: By using the power of data analytics, machine learning enables lenders to dynamically adjust interest rates based on real-time assessments of borrower credit risk and market conditions. This flexibility allows financial institutions to offer fair and customized loan terms, maximizing profitability while meeting the diverse needs of borrowers.
Read Our Blog: AI Use Cases and Applications in Key Industries
8. Early Warning Systems: Machine learning algorithms detect subtle patterns indicative of impending financial distress by analyzing borrower behavior and economic indicators. Early warning systems empower lenders to identify borrowers at risk of default before the situation escalates, facilitating timely intervention measures to prevent losses and preserve borrower-lender relationships.
9. Credit Limit Management: Machine learning dynamically adjusts credit limits based on recent financial behavior, changes in income, and broader economic indicators. This personalized approach optimizes risk management by aligning credit exposure with customer risk profiles, enhancing customer satisfaction, and minimizing credit-related risks for financial institutions.
10. Collections Optimization: By predicting the likelihood of repayment, machine learning enables financial institutions to tailor collection strategies to individual borrower profiles. This nuanced approach optimizes resource allocation within collections departments and enhances the borrower experience by avoiding unnecessarily harsh measures for those in temporary financial distress, ultimately improving loan recovery strategies and safeguarding institutional assets.
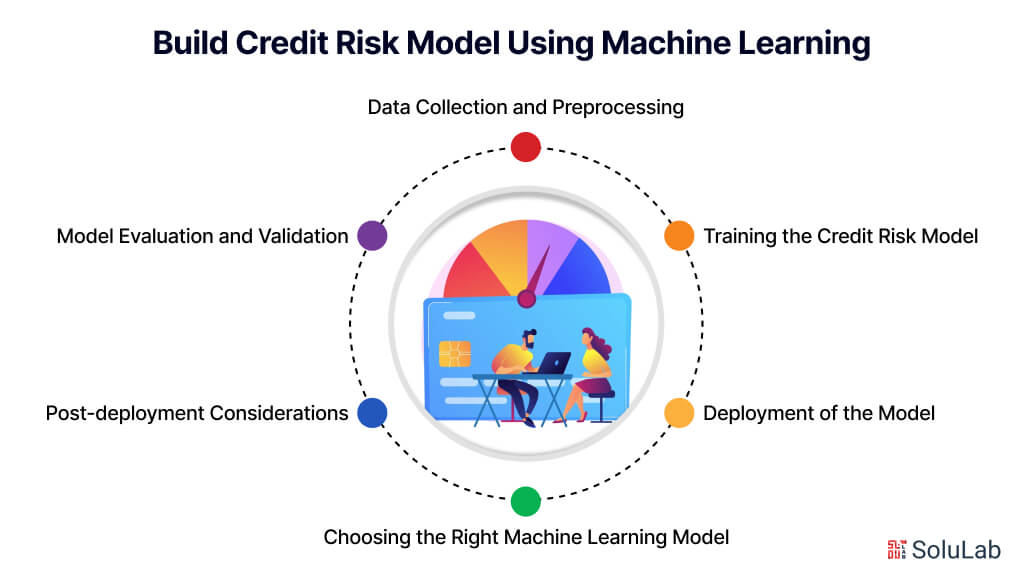
Building a credit risk model using machine learning encompasses several critical steps, each vital for ensuring the model’s precision and efficacy. Let’s look into a detailed breakdown of each phase:
By following these steps meticulously, financial institutions can build robust credit risk models that accurately assess risk and support informed decision-making in lending operations.
When employing artificial intelligence (AI) for credit risk modeling, several crucial considerations must be addressed to ensure ethical and compliant utilization of these advanced technologies. Here are three key factors:
1. Data Privacy and Ethics: AI-driven credit risk models rely on vast amounts of sensitive borrower data, necessitating robust measures to safeguard privacy and uphold ethical standards. Implementing encryption, access controls, and anonymization techniques is crucial to protect individuals’ privacy rights. Furthermore, ethical principles like fairness, transparency, and accountability should guide model development and deployment to mitigate biases and discrimination in credit decisions.
2. Regulatory Compliance: Financial institutions operating in regulated environments must comply with stringent standards governing credit risk management and data protection. Adhering to relevant regulatory requirements, conducting thorough impact assessments, and establishing governance frameworks are essential when employing AI for credit risk modeling. These measures ensure oversight of AI implementation and monitoring of compliance with regulatory mandates.
3. Interpretability of Models: The interpretability of AI models is pivotal for stakeholders to comprehend credit risk decisions and assess influencing factors. While complex machine learning algorithms offer superior predictive accuracy, their opacity can hinder interpretability, making it challenging to explain model outputs and identify potential biases. Prioritizing transparent modeling techniques and implementing validation processes enhance model interpretability, enabling effective scrutiny by stakeholders, including regulators and consumers, and fostering trust in decision-making processes.
Credit risk modeling is a dynamic field that is always changing due to market forces, regulatory needs, and technological improvements. In the future, a number of developments and trends have the potential to completely change the credit risk management industry. Three main areas of attention are as follows:
The demand for transparency and interpretability in credit risk modeling is growing alongside the increasing complexity of machine learning algorithms. Explainable AI methods aim to enhance understanding by shedding light on the factors influencing credit risk decisions and identifying potential biases. By providing insights into model predictions and decision-making processes, Explainable AI fosters trust supports regulatory compliance and empowers users to make informed assessments.
Federated Learning is emerging as a promising approach in environments where data sharing is restricted. This method allows multiple institutions to collaboratively train a shared machine learning model while preserving data privacy by keeping sensitive information encrypted and localized. By aggregating model updates instead of raw data, Federated Learning maintains privacy, enables scalability, and facilitates collaborative risk assessment across distributed data sources.
Credit risk modeling is evolving to incorporate alternative data sources beyond traditional financial metrics. These sources, including social media activity and transactional data, offer valuable insights into consumer behavior and financial health. By leveraging advanced analytics and data fusion techniques, financial institutions can enrich credit risk models with alternative data, improving predictive accuracy, expanding credit access, and enhancing risk differentiation.
Credit risk modeling has a bright future ahead of it because of developments in artificial intelligence, data analytics, and regulatory frameworks. Prioritizing responsible and innovative methods of credit risk management is essential for financial institutions as they negotiate changing market dynamics, technology advancements, and regulatory requirements.
Credit risk modeling may now be improved in ways never before possible thanks to machine learning and artificial intelligence. Financial organizations may create more transparent and robust credit risk models that support informed decision-making, build trust, and promote sustainable development by utilizing complex algorithms, alternate data sources, and explainable AI methodologies.
Are you prepared to redefine your credit risk modeling using AI and machine learning? Collaborate with SoluLab, a top AI development company, to utilize advanced technology and expertise in crafting resilient credit risk models. Our AI consulting and development services are tailored to your requirements, ensuring accuracy, dependability, and regulatory compliance throughout the process. Partner with SoluLab to navigate the evolving landscape of credit risk management with confidence.
A credit risk model is a statistical tool used by financial institutions to assess the likelihood of a borrower defaulting on a loan. It analyzes various factors such as borrower characteristics, historical loan performance, and macroeconomic indicators to estimate credit risk. Credit risk models are crucial for financial institutions as they aid in making informed lending decisions, allocating capital efficiently, and mitigating potential losses in loan portfolios.
Machine learning algorithms excel in credit risk modeling by analyzing vast amounts of data to identify complex patterns and relationships. Unlike traditional statistical methods, machine learning techniques such as logistic regression, random forests, and gradient boosting machines can handle nonlinear relationships and capture intricate interactions between variables. This enables more accurate predictions of default probability, leading to improved risk assessment and management.
Credit risk models leverage a variety of data sources, including historical loan performance data, borrower information (e.g., credit scores, income), macroeconomic indicators (e.g., GDP growth, unemployment rates), and alternative data sources (e.g., social media activity, transaction history). By incorporating diverse datasets, machine learning models can capture a comprehensive view of credit risk and enhance predictive accuracy.
Financial institutions prioritize fairness and transparency in credit risk modeling by implementing explainable AI techniques and conducting rigorous model validation processes. Explainable AI methods enable stakeholders to understand how credit risk decisions are made and assess the factors influencing these decisions, promoting transparency and accountability. Additionally, model validation ensures that the model is fair, unbiased, and compliant with regulatory standards.
Some key challenges in credit risk modeling with machine learning include data quality and availability, model interpretability, regulatory compliance, and the potential for model biases. Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of input data, interpreting complex machine learning models, complying with regulatory requirements, and mitigating biases are critical considerations for building effective credit risk models. However, with proper data governance, model validation, and ethical AI practices, these challenges can be addressed to develop robust and trustworthy credit risk models.