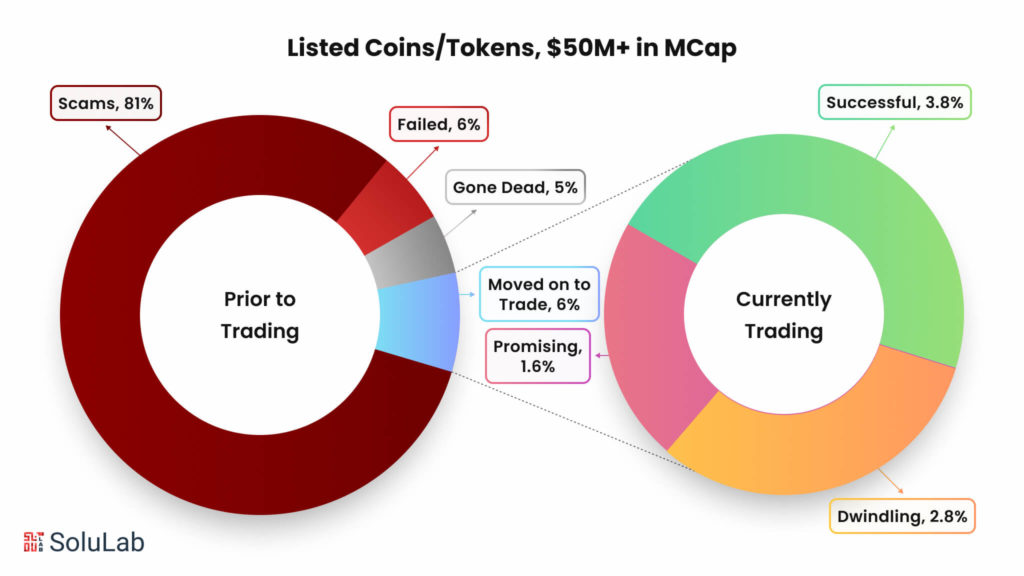
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and Initial Exchange Offerings (IEOs) are both popular methods for cryptocurrency startups to raise funds. However, they differ significantly in their processes, security measures, and the roles of third parties. In this blog, we’ll dive into what IEO crypto is, how it works, and how it differs from ICO crypto. a large number of SCAMs. According to 2017 research by Satis Group LLC, 80% of ICO are fraudulent projects. The data from the TokenData site for 2018 says that there are more than 90% of these (normal teams have switched to IEO and STO). No scammers have yet been discovered among IEO projects.
Pros & Cons of the ICO Process
Prior to exploring the advantages and disadvantages of the ICO process, it is imperative to establish a comprehensive understanding of the foundational principles underlying this fundraising mechanism. Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs), commonly known as ICO crypto, emerged in 2017 as an innovative approach for blockchain projects to secure funding from the general public, akin to initial public offerings in traditional markets.
Pros of ICO
- Initial Coin Offering (ICO) project setup and initialization are relatively straightforward compared to other crowdfunding methods.
- The ICO crypto funding model allows individuals to invest in projects without being exceptionally well-funded.
- Government intervention is minimal or non-existent in ICO launches, providing a relatively unregulated environment.
- ICOs offer high liquidity due to the ultra-short launch process time, enabling investors to quickly buy and sell tokens.
Cons of ICO
- One of the biggest issues attached to ICOs is security limitations. The whole mechanism is very susceptible to fraud and scams.
- ICO crypto is not considered a good option when it comes to long-term investments.
- Even when developed in a way that the scope of security breaches is next to none, there are times that investors might find themselves invested in Shitcoins, meaning they are left with no hope of ever making money from the investment.
The advantages and disadvantages associated with ICO crypto have created an opportunity for improvement, which Initial Exchange Offerings (IEOs) aim to address. The process of initial exchange offering involves more secure and regulated environments provided by exchanges, potentially leading to the best IEO crypto opportunities. However, like with ICO crypto currencies, careful evaluation is necessary to identify the best crypto ICO options.
What is an Initial Exchange Offering (IEO)?
In the crypto market, Initial Exchange Offering (IEO) is often referred to as ICO 2.0, and there’s a clear reason behind it. The fundamental mechanism of IEO crypto development and the process of launching it on exchange platforms are inherently similar to those of an ICO.
However, the critical difference that defines what is IEO is the platform on which it’s launched. Unlike ICOs, which are launched on the startup’s website, IEO offerings are hosted on cryptocurrency exchange platforms.
This means that established crypto exchange websites like Binance, OK Jumpstart, Bitmax Launchpad, Bittrex IEO, etc., house the IEO on their websites, allowing investors to participate easily and securely. This distinction underlines the IEO meaning in crypto, highlighting the role of exchanges in enhancing security and accessibility for investors.
How To Do an IEO?
Launching an IEO crypto follows a similar process as an ICO. The first step is to create a Whitepaper detailing the purpose of your initial exchange offering, token economics, and the benefits it will provide to investors and the public. Next, you will need to develop your cryptocurrency coin to form the basis of the IEO offering. Once these steps are complete, you will differentiate what is IEO from an ICO by selecting a cryptocurrency exchange platform and pitching your IEO blockchain model to them. If they accept, they will list your IEO on their website. From that point on, the exchange platform will handle everything, including marketing and running the entire campaign. This simplifies the process and provides numerous advantages for IEOs. The speed at which IEOs can be launched and the positive outcomes they can generate make them a strong contender in the IEO vs ICO debate. Here is an overview of the timeline for launching an IEO and achieving results through collaboration with an IEO development company, highlighting the IEO meaning in crypto.
1. Exchange: Binance Launchpad
Startup: BitTorrent
- Speed: 18 minutes (18 seconds if you remove the system lags)
- Cost: 7,2 million dollars
Startup: Fetch.ai
- Speed: 22 seconds
- Cost: 6 million dollars
Startup: Celer Network
- Speed: 17 minutes 35 seconds
- Cost: 4 million dollars
2. Exchange: JumpStart
Startup: BlockCloud
- Speed: 1 second
- Cost: 1 million dollars
3. Exchange: KuCoin Spotlight
Startup: MultiVAC
- Speed: 2 second
- Cost: 3.6 million dollars
4. Exchange: LBank Solar
Startup: OATH
- Speed: 2 second
- Cost:4 million dollars
5. Exchange: Bittrex International
Startup: VeriBlock
- Speed: 10 second
- Cost: 2 million dollars
Pros and Cons of the IEO Process
Initial Exchange Offerings (IEOs), a recent concept in the cryptocurrency realm, bear resemblance to Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) with a distinct difference. While ICOs are launched on a startup’s website, IEOs are launched on cryptocurrency exchanges. To gain a comprehensive understanding, let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages associated with the IEO process:
Pros of IEO
- In an IEO (Initial Exchange Offering) blockchain, creators send tokens to an exchange, which then sells those tokens to users through its platform at a set price. This model introduces a middleman, usually a well-known brand, which increases the trustworthiness of the crowdfunding process due to the added layer of centralization.
- Token issuers benefit from the exchange’s established customer base, increasing their project’s chances of gaining traction.
- The exchange handles the entire KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) processes, saving issuers significant time and effort.
- The exchange takes responsibility for all promotional and marketing activities, eliminating the need for issuers to invest extra resources in these areas. This is one of the key advantages of IEOs over ICOs and other investment methods.
- IEO platforms operate within a structured legal framework that protects startups from potential regulatory issues. Many exchanges also provide legal advice and guidance to help young startups navigate regulations and compliance requirements.
Cons of IEO
- IEO platforms, particularly smaller ones unconcerned with brand reputation, remain susceptible to fraud. Coin generators can mitigate this risk by carefully selecting the exchange on which they conduct their IEO offering.
- A significant disadvantage of IEOs is the potential for well-connected projects to receive preferential treatment in exchange listings.
- Price manipulation could occur if a small group of investors holds the majority of coins, a concern reminiscent of the crowdfunding ICO era.
- The liquidity level of IEOs is generally lower compared to ICOs.
Understanding the IEO meaning in crypto is crucial for navigating this evolving landscape, and recognizing what is IEO will help investors make informed decisions.
IEO vs ICO
The distinction between ICOs and IEOs suggests that the latter may offer certain advantages, particularly for stakeholders in the funding model. Now, let’s delve into the next phase of our IEO vs ICO exploration. We will examine the specific benefits that IEOs provide to each stakeholder. Understanding what is initial exchange offering and how does IEO work compared to ICOs is crucial. The dynamics between IEO and ICO reveal unique advantages that can significantly impact the success of a project, offering enhanced security, trust, and convenience for both issuers and investors.
Related: ICO Vs IPO
IEO’s Offerings To Its Stakeholders
When comparing technologies, the key factor is determining which one offers the most benefits to stakeholders. In the case of IEO vs ICO, IEO emerges as the clear winner. Understanding what is initial exchange offering is highlights how IEOs address the shortcomings of ICOs and provide evident solutions to the drawbacks associated with the Initial Coin Offering model.
IEOs have a significant positive impact on stakeholders involved in Blockchain-based crowdfunding models. To understand how does IEO work and its specific impacts, let’s examine the advantages and disadvantages of IEO and ICO for each stakeholder group. This comparison will elucidate why IEOs are increasingly favored in the crypto space.
1. IEO Benefits For Investors
Before exploring the advantages of Initial Exchange Offerings (IEOs) for investors, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental distinctions between IEOs and Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs). Although both involve raising funds through token issuance, IEOs provide several benefits over ICOs, especially in terms of security, investor protection, and the simplicity of participation.
-
Effort Minimization
By leveraging a reputable exchange for the IEO process, investors can bypass the time-consuming verification process, including KYC/AML and complex procedures for launching an IEO. Additionally, they are relieved from the burden of studying investment conditions, devising strategies to acquire startup tokens, and undertaking legal and economic due diligence on the startup or its developers.
-
Greater Security
One of the primary challenges associated with ICOs lies in the opacity surrounding the organizers behind the Blockchain project. This lack of transparency exposes investors to increased risks of falling prey to hacking attempts and fraudulent activities. In contrast, IEOs offer an elevated level of security for the crowdfunding model due to the support provided by exchanges. This exchange backing significantly enhances the reliability and trustworthiness of the fundraising process, ensuring that investors have a greater degree of confidence in the legitimacy and credibility of the project.
-
No Barrier to Entry
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) occur in three distinct stages: Private Sale, Pre-Sale, and Main Sale. During the Private Sale, tokens are typically offered with substantial discounts, often 50% or more. In the Pre-Sale phase, discounts range from 30-50%, and finally, in the Main Sale, discounts are typically around 20-30%.
Unfortunately, this system favors large investors, limiting opportunities for small and medium-scale investors to participate in these investment opportunities. In contrast, Initial Exchange Offerings (IEOs) address this disparity by allowing investors from all backgrounds to participate in all investment stages, eliminating discrimination and providing equal access to all.
2. IEO Benefits For Startups
Startups can reap significant advantages by leveraging Initial Exchange Offerings (IEOs), such as expedited token sales, enhanced listing rates, and the opportunity to tap into a substantial customer base.
-
Speed of Tokensale
The confidence of investors is bolstered by the fact that exchanges not only conduct mandatory checks but also distribute the funds collected. This is the primary reason why many IEOs can be completed in as little as 20 seconds, in contrast to the monthly valuation of ICOs.
-
Listings Rate
Upon the approval of an IEO project, the time required for listing on the Exchange is substantially shorter compared to ICOs. The time frame and probability of success for ICOs are considerably limited in contrast to IEOs.
-
Attracting a Large Customer Base
In the ongoing debate between IEOs and ICOs, entrepreneurs who invest in an IEO launch gain a distinct advantage: access to a pre-existing customer base. This eliminates the need for extensive marketing efforts and substantial financial investments in customer acquisition, providing a compelling reason to select IEOs over ICOs.
3. IEO Benefits For Exchanges
The Initial Exchange Offering (IEO) model has emerged as a viable alternative to Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs), addressing many of the challenges associated with ICOs. IEOs provide various advantages to all stakeholders involved in blockchain-based crowdfunding, including investors, exchanges, and project issuers.
By hosting the IEO on their platform, exchanges can generate multiple revenue streams, including:
- Listing fees from the project team
- Commissions on each token sale
- Increased demand for the exchange’s native token, which is often required for participation in IEOs.
These revenue streams offer exchanges a lucrative opportunity to capitalize on the growing popularity of blockchain-based crowdfunding.
-
More Attention
Listing IEOs allows the exchange to serve as a hub for numerous social mentions that lead back to its platform. This, in turn, attracts market attention, which significantly contributes to the exchange’s growth and development.
-
Access to Exclusive Coins
After each Initial Exchange Offering (IEO), the platform gains access to an exclusive token that is not available for trading on other platforms. These tokens often attract new investors interested in investing in a particular project. This, in turn, increases trading volumes and expands the customer base. Given the ongoing scrutiny of Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs), particularly by investors, IEOs have emerged as an improved version of ICOs. IEOs are poised to overshadow ICOs and swiftly gain popularity. However, the question arises: does this mean that ICOs are obsolete and that IEOs represent the future of Blockchain-based fundraising models?
What is the Future of IEO?
Although ICO is declining, IEO is not necessarily the sole future of Blockchain-based crowdfunding. Several alternative Blockchain funding models present worthy options. Comparing ICO and IEO specifically, IEO seems poised for long-term success. While IEO’s investor interest is relatively low compared to ICO’s initial stage, its future prospects are promising. IEO offers unique advantages, particularly in terms of guaranteed security and high return on investment. As a result, entrepreneurs and investors are shifting their focus toward IEO. As a Blockchain development agency involved in both ICO and IEO projects, we have observed a shift in loyalty toward IEO. The benefits offered by the IEO crowdfunding model are unmatched in the industry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding IEO crypto and ICO crypto is crucial for navigating the evolving landscape of cryptocurrency investments. The initial exchange offering (IEO) represents a more secure and regulated approach to raising funds, facilitated by cryptocurrency exchanges. What is IEO? It is a process where a crypto exchange acts as an intermediary between the project and investors, enhancing trust and reducing risks. IEO vs. ICO showcases the advantages of IEOs in terms of security and investor confidence. Understanding how does IEO work is essential for investors looking to participate in these offerings. The process of initial exchange offering involves exchanges conducting due diligence, listing tokens, and facilitating the sale.
For those seeking the best IEO crypto opportunities, platforms like SoluLab offer valuable insights and services. SoluLab specializes in blockchain and cryptocurrency solutions, guiding projects through successful IEOs and ensuring compliance with industry standards. Their expertise helps projects navigate the complexities of initial public offerings in the crypto space. staying informed about the differences and benefits of ICO and IEO will be crucial for making informed investment decisions. SoluLab stands as a reliable partner in this journey, offering expert guidance and innovative solutions for successful IEO offerings.
FAQs
1. What is IEO crypto?
IEO crypto, or Initial Exchange Offering crypto, refers to a fundraising event where a cryptocurrency exchange acts as an intermediary between the project and investors, enhancing security and trust.
2. How does an initial exchange offering (IEO) work?
An IEO works by having a cryptocurrency exchange conduct due diligence on a project, list its tokens, and facilitate the token sale directly on the exchange platform, providing a layer of security for investors.
3. What is the meaning of IEO in crypto?
IEO in crypto means Initial Exchange Offering, a fundraising mechanism where exchanges act as trusted intermediaries, conducting token sales on behalf of blockchain platforms.
4. What is the process of an initial exchange offering?
The process of an initial exchange offering involves a project submitting its proposal to an exchange, the exchange conducting due diligence, listing the project’s tokens, and managing the token sale on its platform.
5. What are the differences between IEO vs. ICO?
IEO vs. ICO: An IEO is conducted through a cryptocurrency exchange, which adds a layer of security and trust, whereas an ICO (Initial Coin Offering) is a direct fundraising event by the project itself, often with less regulatory oversight.
6. How to find the best IEO crypto opportunities?
To find the best IEO crypto opportunities, research reputable cryptocurrency exchanges, review their listing criteria, and consider the project’s fundamentals, team, and potential for growth.