The global carbon market is projected to reach $2.68 trillion by 2028, yet most people, founders, startups, and even large enterprises still don’t fully understand what carbon credits are or how carbon credits work.
This lack of awareness is a massive opportunity. A carbon credit education platform can solve this gap by teaching users what carbon credits mean, how they reduce emissions, and how individuals or businesses can take real climate action. It’s more than education, it’s empowerment, transparency, and growth.
If you’re a sustainability startup, NGO, or a founder looking to build a mission-driven platform with monetization potential, now’s the time. This guide will show you how to build a carbon credit learning platform that blends blockchain, transparency, and user-friendly design, all built by a team that understands both climate impact and tech execution
Before we explore how a carbon credit platform can create impact, let’s start with the basics: what are carbon credits, and how do carbon credits work?
Carbon credits give companies or individuals the legal right to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide (usually one metric ton). These credits can be bought or sold, which creates a system where those who reduce emissions can earn and sell extra credits. It’s a market-based approach to fight climate change.
But here’s the problem: most people don’t fully understand how these credits are created, verified, or traded. That’s why education is essential.
A carbon credit education platform helps bridge this knowledge gap. It teaches users how carbon markets work, clears up misinformation, and promotes transparency. This builds trust, which is essential for any climate-related initiative.
Many people also struggle to understand what carbon assets are or how they relate to real-world offset projects like planting trees or building renewable energy sources. If they don’t understand it, they won’t get involved. And without involvement, there’s no meaningful impact.
This is exactly where a carbon credit learning platform makes a difference. It simplifies complex topics, explains key concepts, and motivates users to participate. Whether you’re building for a nonprofit, startup, or government program, these platforms are key to turning awareness into action.
Traditional systems used in the carbon credit space are often slow, hard to trust, and lack transparency. This leads to confusion, low participation, and even fraud. Blockchain technology helps solve these problems by making the entire process transparent, secure, and tamper-proof.
These are real blockchain use cases that directly improve how users learn and engage with carbon credits:
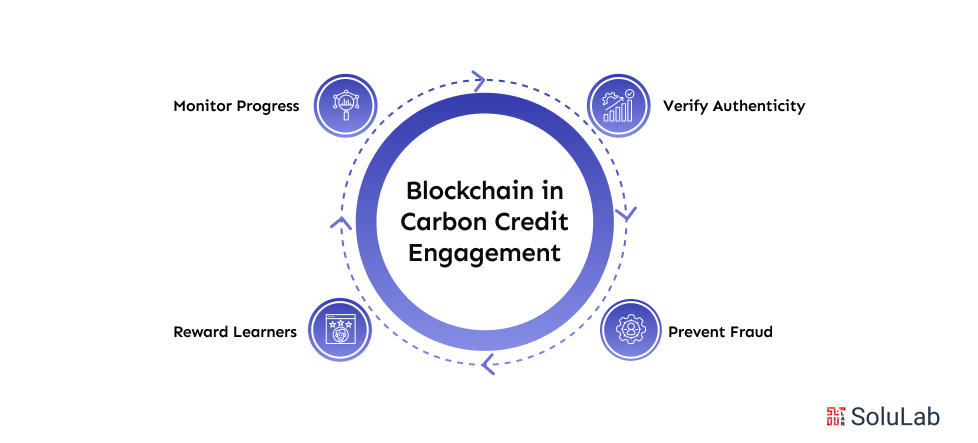
This isn’t just hype; these are practical tools that build trust and drive real results.
Understanding the difference between Layer 1 vs. Layer 2 is important when scaling your platform:
The right choice depends on your user base, budget, and growth plans
Want to discuss which blockchain setup is right for your project? Our team can guide you
A well-designed carbon credit education platform should be simple to use, easy to scale, and built to drive real engagement. It helps people understand how carbon credits work while making learning interactive and trustworthy.
Here are the key features your platform should include:
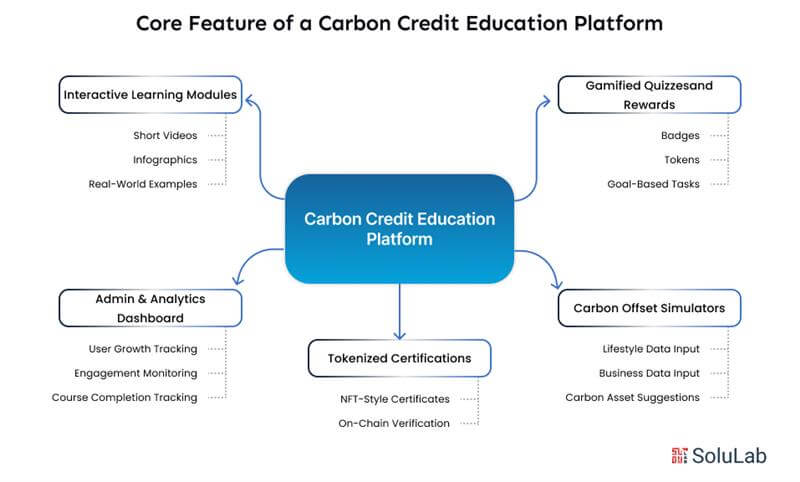
Quick, engaging lessons that explain the basics of what are carbon credits and why they matter.
Make learning fun and rewarding with built-in gamification.
Allow users to see their personal or business emissions and how to offset them.
Read Our Blog: What Makes Germany a Natural Fit for Carbon Credit Tokenization?
Reward learners with blockchain-based certificates for each milestone.
Give your organization full control and visibility.
At our blockchain development company, we integrate all these features with custom branding, secure backend systems, and smart contract logic.
We also ensure that the platform supports carbon credit tokenization, allowing users to learn about and take climate action by buying or retiring carbon credits as part of their educational journey.
The cost of building a carbon credit education platform depends on a few key factors. If you’re a startup founder or enterprise looking to build a platform that educates users on what carbon credits are and how carbon credits work, here’s what you need to consider:
| Cost Factor | Details |
| Feature Set | Basic education modules, tokenization, gamification, multilingual access |
| Blockchain Choice | Depends on using Layer 1 vs. Layer 2 blockchains (Ethereum, Polygon, etc.) |
| Time-to-Market | Faster timelines may increase development costs |
| Custom vs. White-Label Solution | Custom builds cost more, white-label options are quicker and cost-effective |
| Maintenance & Scaling | Ongoing updates, new features, and security upgrades |
| Project Type | Estimated Cost | Description |
| MVP (Minimum Viable Product) | $20,000 – $60,000 | Covers essential features: education modules, dashboards, token support |
| Full-Scale Enterprise Platform | $60,000+ | Includes automation, multilingual content, analytics, and regulatory tools |
| Using Blockchain-as-a-Service | Flexible pricing | Ideal for faster deployment and reduced in-house technical requirements |
Here are five real examples of how companies are using blockchain to improve how carbon credits are tracked, traded, and understood. These stories show how carbon credit tokenization, education, and compliance can be made easier and more trustworthy with the right tech.

A creative project blending nature with tech.
Why it matters: It’s a great example of making carbon credit education platforms more engaging by connecting digital assets with physical impact. Also helps fight double-counting.
Turning traditional carbon credits into tradable tokens.
Lesson learned: Tokenizing low-quality credits caused issues. This shows why blockchain use cases in carbon trading must prioritize quality control and verified standards.
A real exchange for buying and selling tokenized carbon credits.
Why it’s relevant: Shows how a blockchain development company can help create efficient B2B platforms with fast, transparent carbon trading tools.
Industrial-level blockchain for government-backed systems.
Impact: This project proves how blockchain can go beyond education, enabling compliance for entire countries and industries.
A Web3 company leading by example.
Takeaway: Shows how Web3 development companies and tech teams can merge carbon assets tracking with education and corporate responsibility.
As a full-stack blockchain development company, we help businesses, climate-focused startups, and NGOs bring their carbon credit education platform ideas to life. We focus on building custom, scalable, and easy-to-use platforms that solve real problems.
Here’s how we do it:
We also offer dedicated developer teams for faster execution and long-term support. Whether you’re an established company or a new venture, you can hire blockchain developers from our team to build and grow your platform with confidence.
If you’re planning to build a carbon credit platform, there’s no better time than now. Education is key to creating real impact, and using blockchain technology makes that education reliable and transparent.
A well-designed, scalable, and engaging carbon credit education platform can help turn passive users into informed, climate-conscious decision-makers, driving both awareness and action.
As a trusted blockchain development company in the USA, we’re here to help you bring this vision to life. Let’s create something impactful together.
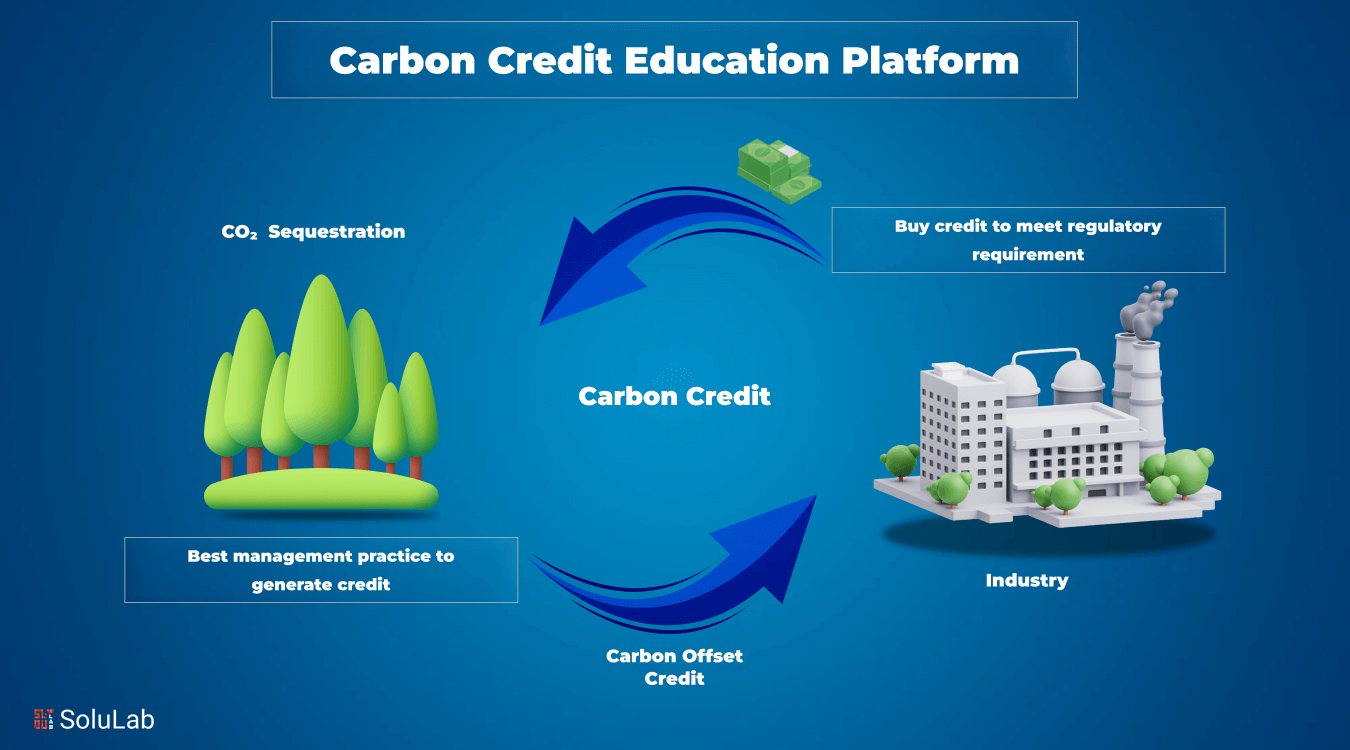
Carbon credits are tradable permits that allow an organization or individual to emit one metric ton of carbon dioxide or equivalent greenhouse gases. They create a financial incentive for reducing emissions by allowing those who reduce emissions to sell credits to others.
Carbon credits work by supporting projects that reduce or capture greenhouse gas emissions, such as reforestation or renewable energy. When a project reduces emissions, it generates credits that companies can buy to offset their own emissions, helping to meet regulatory or voluntary climate goals.
A great carbon credit learning platform offers interactive modules, real-time data, and easy-to-understand content that breaks down complex topics like carbon markets and offsets. It empowers users to grasp carbon assets and how they can participate in sustainable initiatives effectively.
A carbon credit platform is a digital marketplace or educational hub where carbon credits are issued, traded, or learned about. These platforms often use blockchain to increase transparency and prevent issues like double counting, making it easier for businesses to participate responsibly.
The cost varies based on features and scale, but typically ranges from $20,000 to $60,000 for a minimum viable product (MVP). Factors affecting price include blockchain integration, user interface complexity, and support for carbon credit tokenization.