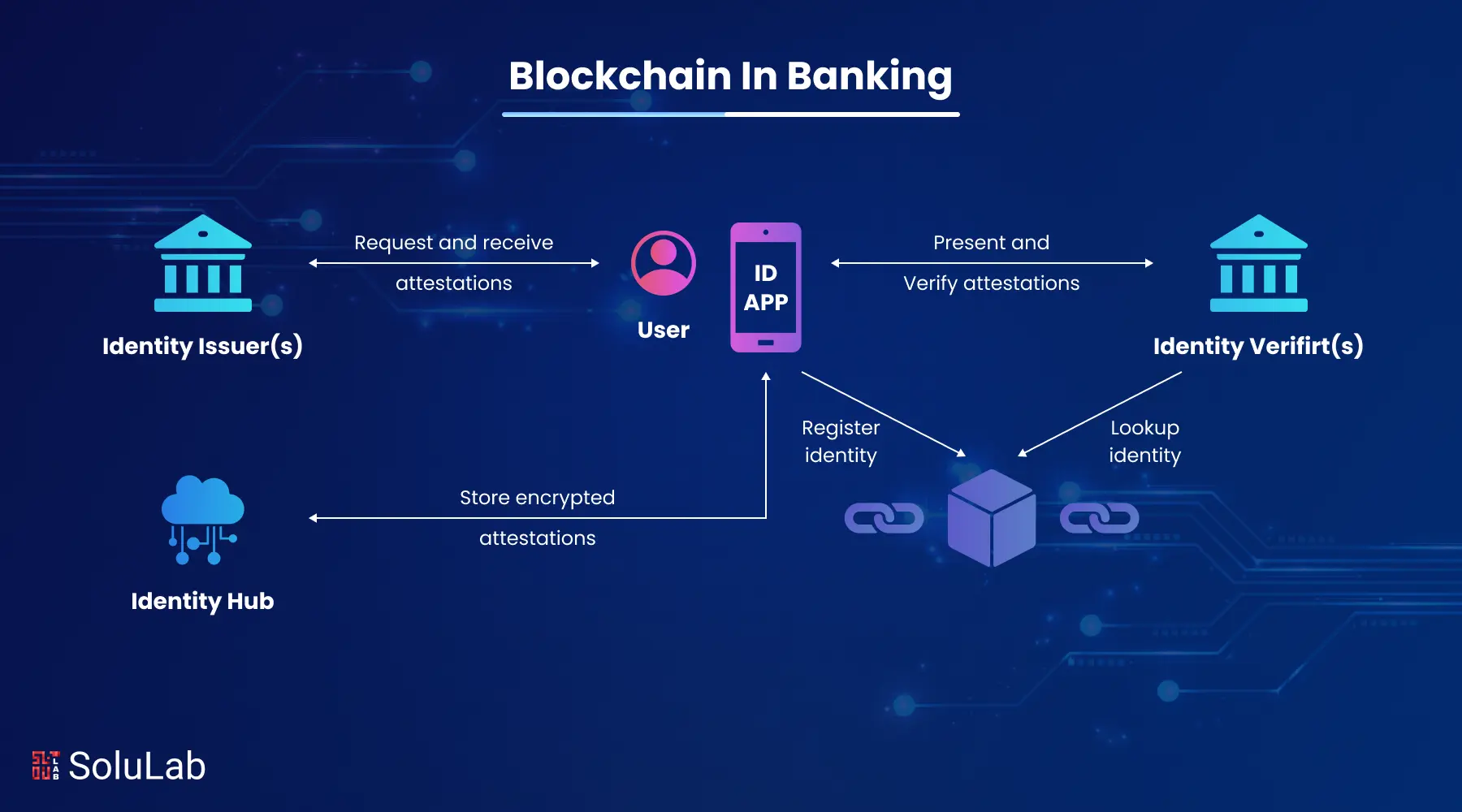
Traditional banking systems are often slow, expensive, and heavily dependent on intermediaries. Whether it’s cross-border payments taking days or the risk of fraud in financial transactions. Blockchain technology is solving these challenges by offering faster transactions, enhanced transparency, and security. It eliminates the need for middlemen.
Banks now settle payments in real time while reducing costs. Smart contracts automate processes like loan disbursements and KYC, making operations more efficient and trustworthy.
Banks save up to 40% on operational costs, including compliance and document handling, by using blockchain for payments and KYC. In this blog, we’ll break down how blockchain is revolutionizing the banking industry with real-world examples
Blockchain in banking refers to the use of blockchain technology to improve how banks handle transactions, data storage, and customer verification. At its core, blockchain is a secure, decentralized digital ledger that records transactions in a transparent and tamper-proof way.
In banking, this means faster money transfers, reduced fraud, lower operational costs, and improved transparency. Instead of relying on multiple intermediaries, blockchain allows banks to complete cross-border payments almost instantly, with real-time tracking and verification.
It also enhances security through encryption and reduces the risk of data breaches. Additionally, processes like KYC (Know Your Customer) and loan approvals can be automated using smart contracts, making banking more efficient and customer-friendly.
Blockchain technology offers multiple implementation models in banking, each tailored to different levels of control, transparency, and collaboration depending on the use case and security needs.
Consortium blockchains are semi-decentralized networks governed by a group of banks or financial institutions. They offer better scalability and security while maintaining trust among known participants, ideal for shared services like interbank settlements or trade finance.
Private blockchains are controlled by a single organization, typically used within a single bank. They provide high levels of security, fast transaction speeds, and privacy, making them suitable for internal auditing, customer verification, or loan processing.
Public blockchains are open to everyone and fully decentralized. While less common in traditional banking due to privacy concerns, they are useful for issuing digital currencies or offering transparent financial services like P2P lending or crowdfunding.
Blockchain technology is transforming the banking industry by offering faster, safer, and more efficient solutions. Here are key use cases where blockchain is making a real difference in banking:
1. Cross-Border Payments: Blockchain allows near-instant international transactions with reduced fees and no need for multiple intermediaries. This not only speeds up the process but also brings transparency and real-time tracking to cross-border payments.
2. Fraud Prevention: With its tamper-proof ledger and secure encryption, blockchain helps banks detect and prevent fraud more effectively. It reduces the risk of double spending, data manipulation, and unauthorized access.
3. KYC (Know Your Customer): Banks can store and share verified customer data securely using blockchain. This reduces duplication, shortens onboarding time, and ensures compliance with regulations while improving the overall customer experience.
4. Smart Contracts: Smart contracts automate agreements between parties without human involvement. In banking, they can streamline processes like loan disbursement, insurance claims, and trade finance, ensuring faster and error-free execution.
5. Trade Finance: Blockchain simplifies trade finance by reducing paperwork, minimizing delays, and ensuring transparency across all participants in a trade deal. It allows real-time verification of documents and payments, increasing trust.
6. Syndicated Loans: Managing syndicated loans typically involves multiple banks and lots of paperwork. Blockchain ensures all parties have access to the same up-to-date information, reducing errors, delays, and operational costs.
7. Asset Tokenization: Banks can use blockchain to convert physical assets into digital tokens, making them easier to trade and manage. This opens up new investment opportunities and enhances liquidity in the market.
8. Clearing and Settlement: Traditional clearing and settlement can take days. Blockchain enables real-time or same-day settlement by providing a single source of truth, reducing counterparty risk, and freeing up capital.
Read Also: RWA Tokenization In Traditional Banking
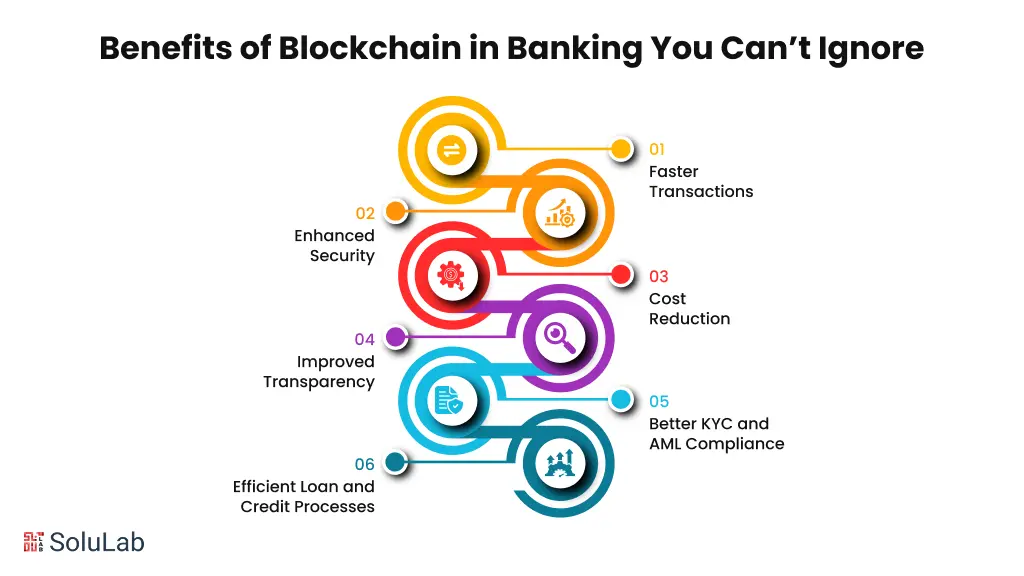
Blockchain is transforming the banking sector by making financial operations faster, safer, and more transparent. Here’s how it’s benefiting banks and customers alike:
As more banks explore their potential to change the way banking services are provided. Blockchain is expected to become an essential component of the banking system as the need for quicker, safer, and more transparent processes grows. Blockchain will likely be used more often in the upcoming years for digital identity verification, real-time settlements, and cross-border payments.
To simplify KYC, lower fraud, and save compliance expenses, banks may work together on shared blockchain networks. Smart contracts may further automate processes like trade financing and loan disbursement. Blockchain could be crucial to achieving financial equality.
This would enable rural and unbanked communities to access banking services safely. Blockchain is anticipated to transition from trials to widespread implementation as laws and technology advance, redefining innovation, efficiency, and trust in the financial industry.
Banks around the world are actively using blockchain to improve operations, security, and reduce costs in real-world applications.
JPMorgan created JPM Coin, a digital currency used for instant money transfers between institutional clients. It helps speed up transactions, especially for cross-border payments, while ensuring transparency and security using blockchain.
ICICI Bank in India has used blockchain to execute trade finance and remittance transactions. This reduces paperwork, speeds up processing, and offers real-time tracking of documentation between exporters and importers.
HSBC uses blockchain to settle billions in foreign exchange trades through its platform “FX Everywhere.” This ensures faster settlements and reduces the need for manual reconciliation between banks.
YES Bank has implemented blockchain-based smart contracts to automate vendor financing. It minimizes delays, reduces fraud, and ensures that payments are released automatically when contract terms are met.
State Bank of India is part of the BankChain consortium, using blockchain for KYC, loan processing, and fraud prevention. It improves collaboration among banks and enhances customer verification across institutions.
Blockchain is changing the banking industry by making processes faster, safer, and more transparent. Across the globe, both private and public banks are testing and adopting blockchain. As adoption grows, we can expect more efficient financial systems that benefit both banks and their customers.
Token World partnered with SoluLab to create a secure, scalable platform for emerging blockchain projects. Solutions included GenAI integration, smart contract auditing, compliance frameworks, and community engagement strategies, boosting investor confidence and delivering seamless token launches with innovative tokenomics and multi-chain interoperability.
Partner with SoluLab, a trusted blockchain development company in the USA, to build secure, scalable, and smart banking solutions.
Implementing blockchain helps banks streamline processes, improve trust through transparency, reduce fraud risks, and offer more efficient customer services—all while saving costs.
Yes, blockchain uses advanced cryptography and decentralized verification, making it highly secure and tamper-proof compared to traditional systems.
Not entirely. Instead, it will complement and enhance existing systems by making them more efficient, transparent, and secure over time.
By automating documentation and verification through smart contracts, blockchain speeds up loan approvals and reduces the chances of fraud or delays.
Absolutely. Its transparent and immutable ledger makes tampering nearly impossible, reducing the risk of internal and external fraud.