
The internet has undergone two major transformations, each marked by a shift in how we interact with it. The first, Web 1.0, was characterized by static websites that served as online brochures. Web 2.0 brought about the rise of social media and user-generated content, transforming the internet into a dynamic and interactive platform. Now, we stand at the precipice of Web 3.0 and DeFi, a new era of the internet that promises to be even more decentralized, democratized, and driven by user-ownership.
At the heart of Web3.0 lies the concept of decentralized finance (DeFi), a rapidly evolving ecosystem of financial applications built on blockchain technology. DeFi aims to remove the barriers and inefficiencies of traditional finance, creating a more open, transparent, and accessible financial system for all.
Web 3.0, often referred to as the “Semantic Web” or the “Decentralized Web,” represents the third generation of the internet. Unlike its predecessors, Web 3.0 is characterized by the convergence of advanced technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT), to create a more intelligent, decentralized, and interconnected web.
Web 3.0 is based on enhancing the understanding of information. It aims to enable machines to comprehend and interpret information in a more human-like manner, fostering improved search capabilities and personalized user experiences.
In contrast to the centralized models of Web 1.0 and Web 2.0, Web 3.0 emphasizes decentralization. Blockchain technology plays a crucial role in achieving this by providing a secure and transparent way to store and manage data.
Web 3.0 aims to break down silos between different platforms and applications, promoting interoperability. This ensures that data and services can seamlessly interact and integrate across diverse systems.
Users in the Web 3.0 era have greater control over their data and digital identities. Decentralized technologies allow individuals to manage and share their information on their terms, enhancing privacy and security.
AI is a cornerstone of Web 3.0, enabling machines to learn, reason, and understand context. This facilitates the creation of intelligent applications that can anticipate user needs and deliver more personalized experiences.
Blockchain, the technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, is a fundamental building block of Web 3.0. Its decentralized and tamper-proof nature ensures trust and transparency in transactions and data management.
Web 3.0 leverages the vast network of interconnected devices in the IoT. This integration allows for the seamless exchange of data between devices, creating a more dynamic and responsive internet.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) technologies contribute to the immersive experiences offered by Web 3.0. These technologies blur the lines between the physical and digital worlds, opening up new possibilities for communication and interaction.
While blockchain is a foundational technology for Web 3.0, scalability remains a challenge. As the number of transactions increases, there is a need for scalable solutions to maintain efficiency.
Establishing interoperability standards is crucial for the seamless functioning of Web 3.0. Efforts are underway to develop protocols that enable different blockchain networks to communicate effectively.
The regulatory environment surrounding Web 3.0 technologies, especially blockchain and cryptocurrencies, is evolving. Striking a balance between innovation and compliance remains a complex challenge.
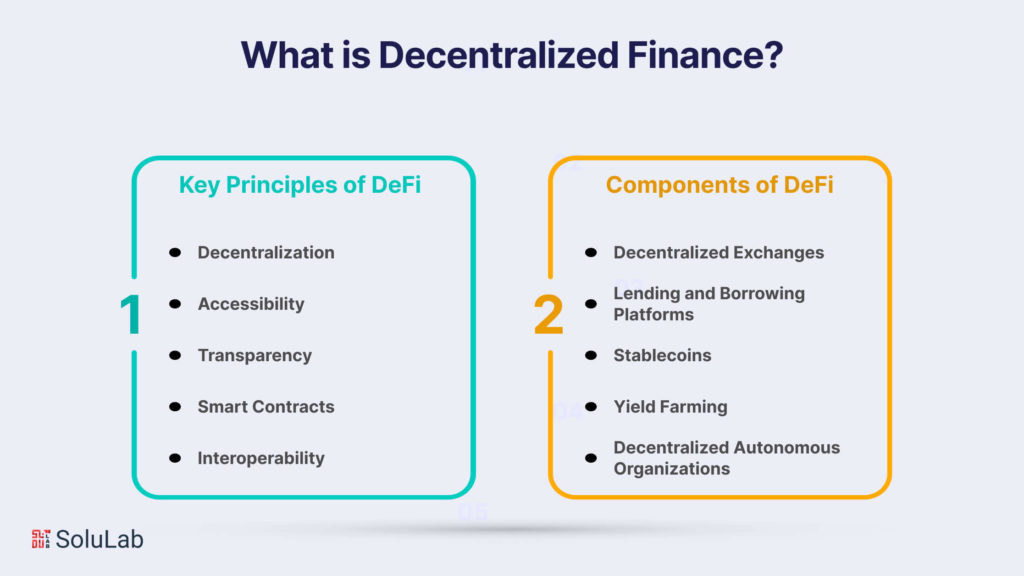
Decentralized Finance, commonly referred to as DeFi, represents a revolutionary shift in the traditional financial landscape. At its core, DeFi leverages blockchain technology to create an open and decentralized financial system that operates without the need for traditional intermediaries such as banks, brokers, or other financial institutions.
DeFi platforms operate on decentralized networks, usually blockchain, where no single entity has control. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, fostering a more inclusive and transparent financial ecosystem.
DeFi aims to make financial services accessible to anyone with an internet connection, thereby promoting financial inclusion globally. Users can access DeFi services without the constraints imposed by traditional banking systems.
The use of blockchain ensures transparency in transactions. Every transaction is recorded on a public ledger that can be audited and verified by anyone, enhancing trust and reducing the risk of fraud.
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code, play a pivotal role in DeFi. These programmable contracts automate and enforce the terms of agreements, reducing the need for intermediaries and minimizing the potential for disputes.
DeFi protocols are designed in a way that they are interoperable, meaning they can easily interact and integrate with each other. This interoperability enhances the efficiency and flexibility of the decentralized financial ecosystem.
DEXs enable users to trade cryptocurrencies directly with one another without the need for a centralized exchange. Popular examples are Uniswap, SushiSwap, and PancakeSwap.
DeFi platforms allow users to lend their cryptocurrencies and earn interest or borrow assets by providing collateral. Notable examples include Compound, Aave, and MakerDAO.
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged to the value of traditional fiat currencies, providing stability in a volatile market. USDC, DAI, and Tether (USDT) are popular examples.
Yield farming involves staking or lending cryptocurrencies to earn rewards, often in the form of additional tokens. This practice is prevalent in DeFi protocols seeking to attract liquidity.
DAOs are entities governed by smart contracts and run by community members who hold tokens. They make collective decisions on the development and governance of the protocol.
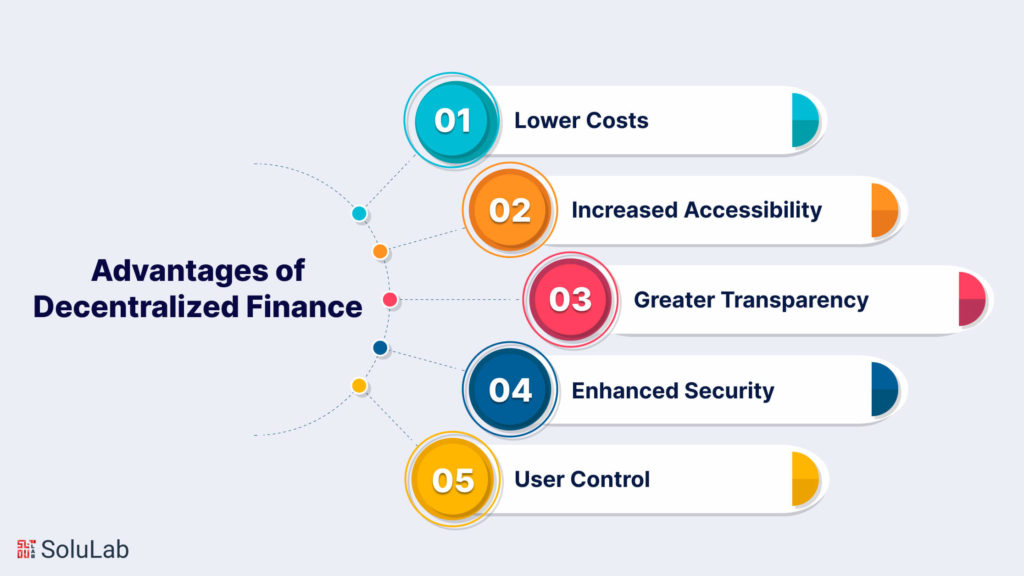
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is a rapidly growing ecosystem of financial applications built on blockchain technology. It offers a several advantages over traditional finance, including:
In addition to these general advantages, DeFi also offers a number of specific benefits depending on the type of application being used. For example, DeFi lending platforms can offer borrowers lower interest rates than traditional lenders, while DeFi savings platforms can offer savers higher interest rates than traditional banks.
Here are some specific figures that illustrate the benefits of decentralized finance:
In 2020, the total value locked in (TVL) DeFi protocols reached over $14 billion. In 2021, the number of unique Ethereum addresses interacting with DeFi protocols increased by over 250%.
These figures show that DeFi is a rapidly growing and increasingly popular alternative to traditional finance. As the technology matures and more people become aware of its benefits, DeFi is likely to play an even greater role in the future of finance.
It is important to note that DeFi is still a relatively new technology, and there are some risks associated with using it. For example, DeFi applications can be subject to smart contract bugs, which can lead to the loss of funds. Additionally, the DeFi market is still relatively volatile, and the value of DeFi assets can fluctuate significantly.
However, the potential benefits of DeFi are significant, and it is a technology that is worth watching closely. DeFi has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with money and financial services, and it could have a major impact on the global economy.
Decentralized finance (DeFi) and Web 3.0 are two closely intertwined concepts that are revolutionizing the way we interact with the internet and financial services. Web 3.0 is a vision for a more decentralized, democratized, and user-centric internet, while DeFi is a suite of financial applications that are built on blockchain technology to provide peer-to-peer financial transactions without the need for intermediaries such as banks or brokerages.
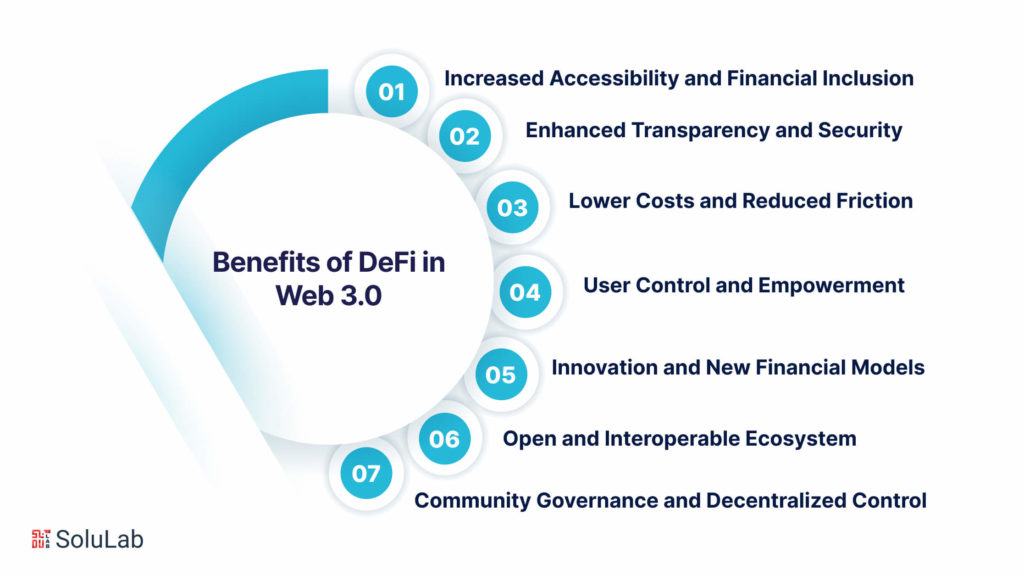
Here are some of the key benefits of DeFi in Web 3.0:
1. Increased Accessibility and Financial Inclusion: DeFi breaks down the barriers to financial inclusion by providing access to financial services to anyone with an internet connection. This is particularly beneficial for individuals and communities that have been underserved by traditional financial institutions.
2. Enhanced Transparency and Security: DeFi transactions are recorded on a public blockchain, making them transparent and traceable. This transparency promotes trust and accountability within the system. Additionally, blockchain technology provides a secure and tamper-proof environment for financial transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and manipulation.
3. Lower Costs and Reduced Friction: DeFi eliminates intermediaries, significantly reducing transaction fees and other costs associated with traditional financial services. This makes financial transactions more affordable and accessible to a wider audience.
4. User Control and Empowerment: DeFi users retain control over their own funds and financial decisions, empowering them to make informed choices about their finances. This contrasts with traditional finance, where users often have to relinquish control of their funds to intermediaries.
5. Innovation and New Financial Models: DeFi fosters innovation and the development of new financial models and services that are not possible in traditional finance. This openness encourages experimentation and the creation of novel solutions that cater to the needs of the Web 3.0 community.
6. Open and Interoperable Ecosystem: DeFi promotes an open and interoperable ecosystem where applications and protocols can interact seamlessly, enabling the creation of complex financial products and services. This open architecture fosters collaboration and innovation within the Web 3.0 space.
7. Community Governance and Decentralized Control: DeFi applications often incorporate governance mechanisms that allow users to participate in decision-making processes, promoting a decentralized and community-driven approach to financial governance. This decentralization aligns with the core principles of Web 3.0, empowering users to shape the future of the financial system.
Trend: The future of Web 3.0 and DeFi is likely to witness increased cross-platform integration, allowing different decentralized applications (DApps) to work seamlessly together. This interconnectedness enhances the overall user experience by providing a more comprehensive suite of financial services.
Impact: Users can navigate a diverse range of financial activities seamlessly, promoting efficiency and expanding the scope of decentralized finance.
Trend: As the adoption of Web 3.0 and DeFi grows, there will be a heightened focus on enhancing security measures. Innovations in decentralized identity solutions and secure multi-party computation will mitigate risks associated with user data and transactions.
Impact: Improved security measures will instill greater confidence among users, fostering increased adoption of decentralized financial services.
Trend: The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms within DeFi platforms will become more prevalent. These technologies will enable intelligent automation for tasks such as risk assessment, market analysis, and smart contract execution.
Impact: DeFi users will benefit from more accurate predictions, automated decision-making processes, and improved risk management, making the financial web more robust and adaptive.
Trend: AI and ML will play a pivotal role in tailoring financial services to individual user needs. Predictive analytics and personalized recommendations will be leveraged to offer customized investment strategies, lending terms, and other financial products.
Impact: Users will experience a more personalized and user-centric approach to finance, aligning with the overarching goal of Web 3.0 to prioritize individual empowerment.
Trend: Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) will continue to evolve, becoming more sophisticated in their governance structures. DAOs will play a central role in decision-making processes related to protocol upgrades, project development, and resource allocation.
Impact: Enhanced DAO structures will lead to a more inclusive and democratic financial ecosystem, where users have a direct say in shaping the future of DeFi projects.
Trend: Community governance will extend beyond project-specific decisions to address broader regulatory concerns. DeFi communities will collaborate to establish industry standards and self-regulatory frameworks to navigate the evolving regulatory landscape.
Impact: This proactive approach to regulation will contribute to the legitimacy and long-term sustainability of decentralized finance, fostering greater trust among users and traditional financial institutions.
The future outlook for Web 3.0 and Decentralized Finance is marked by dynamic trends and transformative technologies. The seamless integration of decentralized applications, advancements in AI and ML, and the maturation of community governance models will collectively shape a financial web that is more secure, personalized, and community-driven.
As these trends unfold, the intersection of Web 3.0 and DeFi will continue to redefine the landscape of finance, offering users unprecedented opportunities for financial inclusion and empowerment. In the intersection of Web 3.0 and Decentralized Finance, we witness the dawn of a new era in the financial landscape.
The shift towards decentralization, transparency, and user empowerment is reshaping how we perceive and engage with financial services. As the journey into Web 3.0 unfolds, the transformative power of decentralized finance will continue to redefine the contours of the financial web, paving the way for a more inclusive, efficient, and accessible global economy.
Web 3.0 is the next evolutionary phase of the internet, characterized by increased decentralization, semantic understanding of data, and enhanced user experiences. Unlike Web 1.0 and Web 2.0, Web 3.0 leverages technologies like blockchain, AI, and the Internet of Things to create a more intelligent, decentralized, and interconnected web.
DeFi operates on decentralized networks, typically blockchain, eliminating the need for intermediaries like banks. It provides open and accessible financial services to anyone with an internet connection, fostering global financial inclusion. Smart contracts automate transactions, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
DeFi’s permissionless nature allows individuals without access to traditional banking services to participate in various financial activities, including lending, borrowing, and trading. It transcends geographical boundaries, providing financial services to the unbanked and underbanked on a global scale.
Blockchain is fundamental to DeFi, providing a secure and transparent ledger for financial transactions. It ensures trust through decentralization, immutability, and transparency. Smart contracts, executed on blockchain platforms, automate and enforce financial agreements, reducing the need for intermediaries.
Smart contracts automate the execution of financial agreements, reducing the risk of human error and enhancing efficiency. Users can participate in various activities such as lending, borrowing, and trading with the assurance that smart contracts will execute transactions based on predefined rules.
Emerging trends include increased cross-platform integration, enhanced security measures, and the integration of AI and machine learning in DeFi. The maturation of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) and proactive community governance in response to regulatory developments are also key trends shaping the future.
Community governance in DeFi involves users having a direct say in decision-making processes related to project development, protocol upgrades, and resource allocation. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) play a central role in enabling community members to participate in shaping the future of DeFi projects.