Gone are the days when people spent hours creating graphics, videos, and even writing blogs and social media posts. But now you don’t have to spend hours. Generative AI development is there to make tools available that you can use to create content and automate repetitive tasks.
Additionally, you can use generative AI as a virtual assistant. No need to invest in the workforce.
In fact, according to industry research, 78% of companies worldwide are using generative AI in at least one area of operations.
In this blog, you’ll learn everything you need to know about generative AI. Let’s get started!
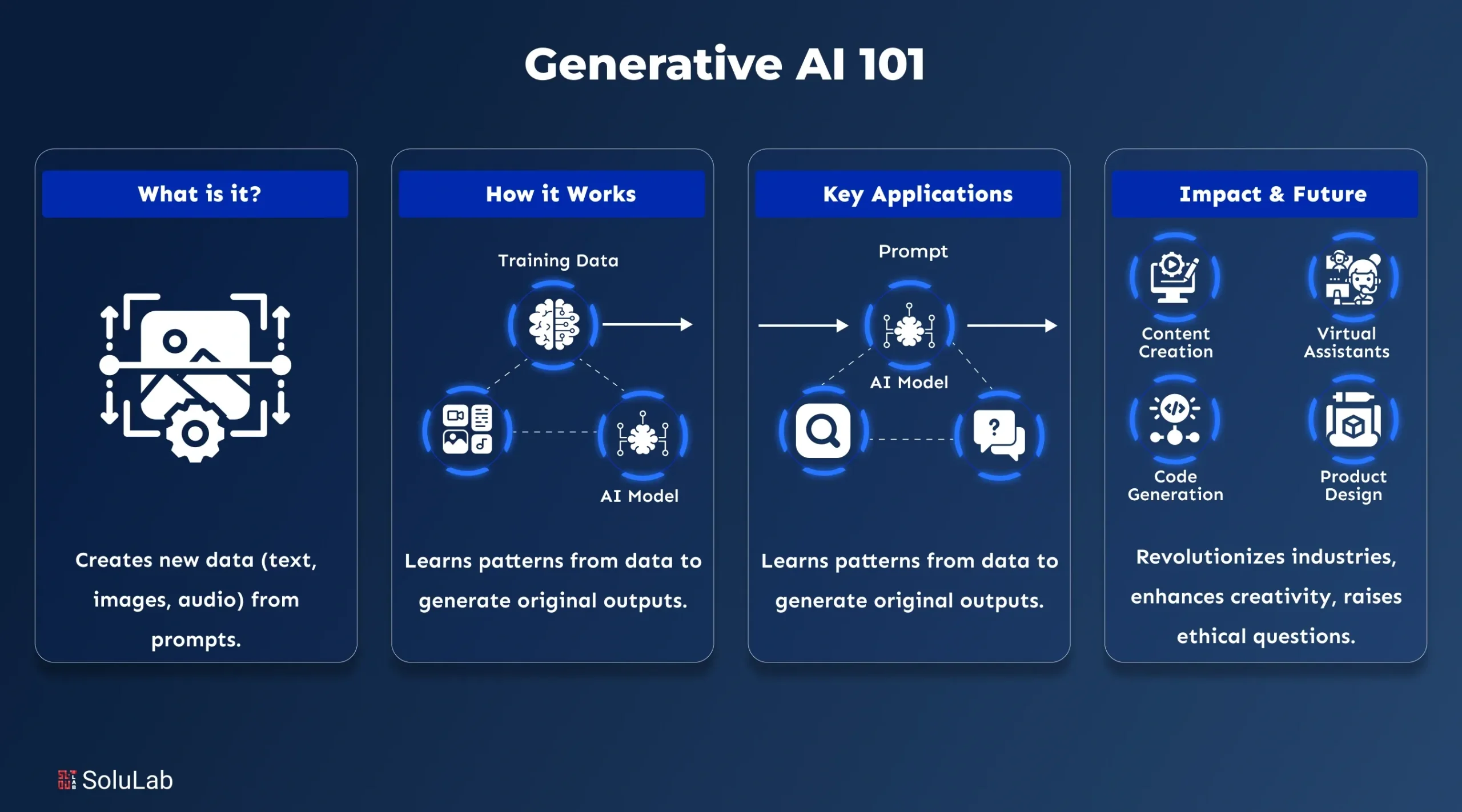
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that can create new content such as text, images, videos, music, and code instead of just analyzing existing data. It works by learning patterns from large amounts of data and then using those patterns to generate human-like outputs.
Tools like ChatGPT, image generators, and video creation platforms are common examples of generative AI in action. It can generate things like:
In 2026, growing competition and higher customer expectations are pushing enterprises to rethink how they operate. Generative AI for enterprises is no longer optional– it is a critical enabler of productivity, innovation, and long-term digital competitiveness.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a broad field of computer science focused on creating systems that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence, such as reasoning and problem-solving. Generative AI is a specific subset of AI designed to create entirely new content rather than just analyzing or making decisions based on existing data.
| Feature | Traditional AI | Generative AI |
| Primary Goal | To analyze data and provide specific outputs like predictions, classifications, or recommendations. | To create new, original content such as text, images, audio, video, or code. |
| Learning Method | Often uses supervised learning with labeled datasets to recognize patterns and make decisions. | Often uses self-supervised learning on vast, unstructured datasets to learn how to generate new data. |
| User Interaction | Interaction is typically structured through dashboards, alerts, or predefined command systems. | Users interact via natural language prompts, allowing for a conversational and iterative experience. |
| Transparency | Generally, more transparent and interpretable (e.g., decision trees), making it easier to explain decisions. | Often operates as a “black box” due to complex neural network architectures, making its logic hard to trace. |
| Common Examples | Spam filters, fraud detection, recommendation engines (Netflix/Amazon), and chess bots. | ChatGPT, Gemini, DALL-E, and Midjourney. |
Contemporary generative AI is driven by a combination of sophisticated technologies that will handle the information, learns trends, and create content that resembles humans, including text, image, audio, and code.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) allows the generative AI to comprehend, analyze, and generate human language. It assists models to interpret context, grammar, intent, and sentiment and makes conversations, translations, summaries, and content creation feel natural and meaningful.
Deep Learning is a neural network method that applies several layers to massive datasets to detect complicated patterns. It enables generative AI to generate extremely precise text, images, and videos by emulating the process of the human brain learning through experience.
Machine learning enables the AI systems to become better as time goes by, and they learn through data without any programming. It enables generative models to learn, improve results, and provide more pertinent, personalised, and accurate results as they are used.
Generative AI systems are based on neural networks. They work with input data and across interconnected layers, which assist models to identify patterns, make predictions, and produce outputs that are close to content created by human beings.
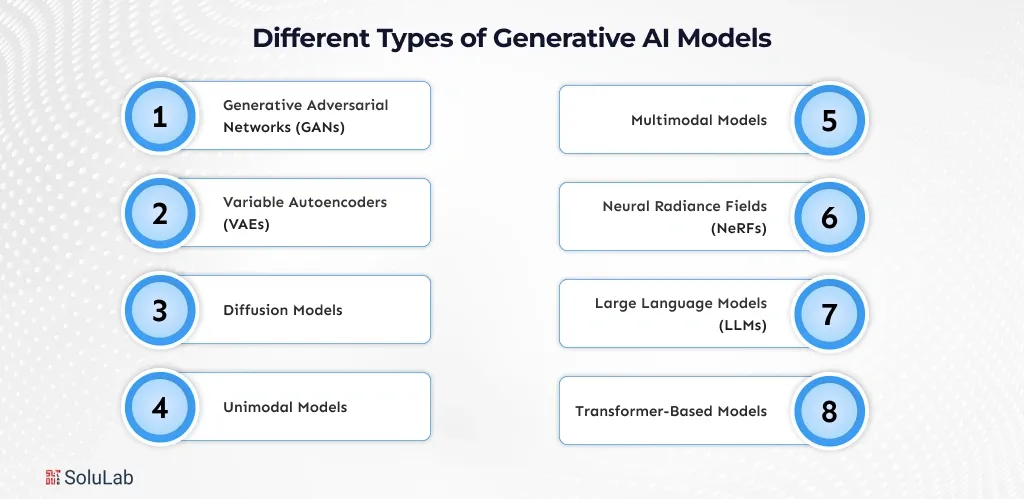
There are numerous types of generative AI models, and each one of them is intended to address a variety of problems, including the creation of images and text as well as the comprehension of various patterns in multiple types of data and real-life contexts.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) involve two neural networks: a generator and a discriminator, which compete. This is used to generate the very realistic images, videos and designs in applications where it is more often applied in art generation, fashion and image enhancement work.
VAEs are trained to pack data into a latent space and reassemble it with minor deviations. They can be applied to generate images, detect anomalies, and produce a variety of outputs without distorting the structure of the original data.
Diffusion models create information by progressively eliminating noise in random inputs until a transparent output is created. They are also reputable to generate high-quality images and are common with the current image and video generation tools.
Unimodal models operate with one type of data, e.g., text, pictures or audio. They are also easy to construct and are usually applicable in activities such as text classification, speech recognition, or image detection.
Multimodal models are able to process and comprehend multiple data types simultaneously, including text, images, and audio. This enables them to do more complicated jobs such as image captioning, video analysis, and chatbots.
The Neural Radiance Fields generate 3D scenes based on 2D images by learning light behaviour in space. They are applied in virtual reality, games, digital twins, realistic reconstruction of a 3D environment.
Large Language Models are modeled using huge amounts of text to learn how to comprehend and produce natural language. They drive chatbots, content creators, code assist, and advanced search systems in any industry.
Transformer-based models rely on attention mechanisms to comprehend word/data point relationships. They are the foundation of the current AI systems and allow them to be trained faster, comprehend the context better, and have scaled language and vision models.

Generative AI functions by training patterns on large data sets and generating new, human-like art (text, images, audio, and code) with the use of advanced models.
By 2026, the use of generative AI will become a requirement rather than an experiment, as businesses automate their processes, personalise their experiences, reduce their costs, and keep up with an AI-driven market.
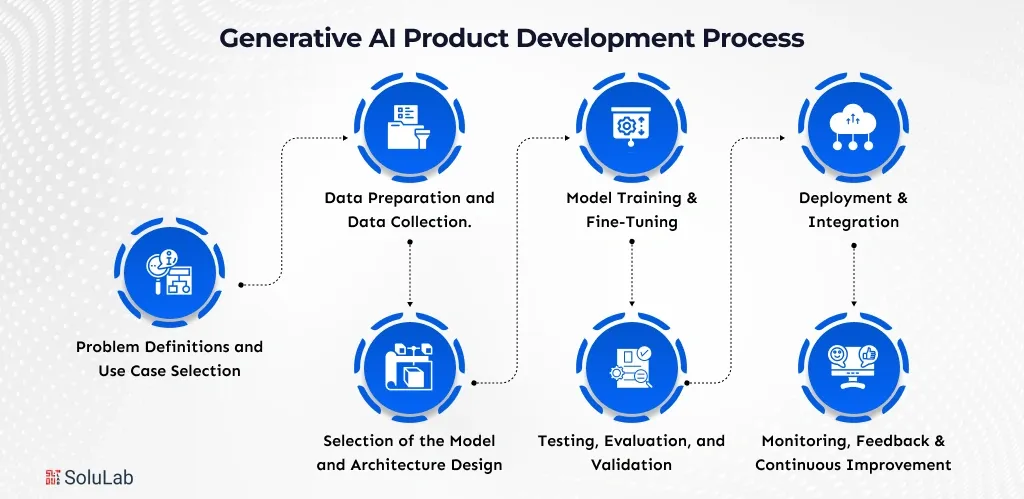
The development of generative AI solutions is a systematic process that transforms an idea into a scalable and stable solution through the combination of data, models, testing, and continuous improvement.
Begin by formulating the business problem and determining where the use of generative AI can create real value. This will help this product address a particular need of the user, and not merely apply AI because it is innovative.
Generative AI is based on high-quality data. This task includes the acquisition of relevant datasets, cleaning up of noisy data, bias elimination, and putting them in an appropriate format that allows models to learn the correct patterns and context.
Depending on your use case, select the appropriate type of model between large language models or diffusion models. Architecture choices influence performance, cost, scalability and response of real-life inputs of the product.
You can do AI model training on existing data and adjust it with new examples that are related to a domain. This enhances accuracy, relevance, and quality of output, making the AI responses more business and user-oriented.
Check the model on the accuracy, bias, safety, and edge cases. This is the measure taken to make sure that the AI is responsible, follows standards of quality, and produces stable results before it is revealed to actual users.
Implement the model into the production environment and combine it with applications, APIs, or workflows. In this stage, performance monitoring, latency control, and cost optimisation are important for the smooth experiences of users.
Monitor model actions in the post-launch phase based on user feedback and analytics. The generative AI product can be kept relevant, accurate, and competitive in the long run with frequent updates, retraining, and improvements.
Modern generative AI use cases go beyond experimentation, enabling enterprises to build intelligent systems that create content, automate workflows, and support real-time decision-making.
Generative AI assists in the generation of blogs, social media content, videos, images, and marketing copy through the recognition of user intent and brand tone. It is time-saving, more consistent, and helps teams to create high-quality content in large quantities.
The AI can help developers write and fix bugs, propose optimisations and clarify complicated logic. This accelerates development steps, minimizes mistakes, and is useful for both the new and experienced developer to work more effectively.
Chatbots and virtual agents, which are fuelled by generative AI, respond to frequently asked questions, troubleshoot, and answer instantly. Such systems enhance customer service, lower the support price, and offer 24/7 service without human reliance.
Generative AI in drug discovery can speed up the process by analyzing complicated biological data and simulating molecules. It assists scientists in finding a possible cure sooner and shortening the development time and enhancing patient outcomes.
The works of AI-based virtual assistants for enterprises include scheduling, reminding, information search, and voice search. They customise themselves to user behaviour with time, which enhances productivity in personal and professional life.
Generative AI is changing the way industries work; it is automating creative work, enhancing decision-making, and accelerating innovation in industries that have scalable data-driven solutions.
Generative AI tools are transforming the very nature of content creation, visuals and video in 2026, enabling creators, developers, and businesses to be more inventive and more rapid with the vast AI power of generative AI tools across text, visuals, and multimedia.
One of the most popular writing, brainstorming, coding, and conversational AI assistants. It produces natural and human- like text, responds to questions, writes content and marketing and support, and creative work workflows.
A writing assistant that summarises content, writes a report, and helps with writing assignments easily. It is excellent among students, professionals, and researchers who need to have clear, structured information within a short time.
Claude was an Anthropic-developed conversational AI assistant that is safe, capable of writing, explaining, summarising, and automating tasks, making it feel like deep work and complex workflows.
An AI-powered text-to-image generator that converts prompts into images in a variety of styles with high visual quality and quality build creative, brand, and visual stories- increasing design, branding, and storytelling by creators and businesses.
AI video maker with converting written scripts into professional movies with realistic avatars and voiceovers to train clips, market, and multilingual videos.
Businesses using a generative AI strategy can access quantifiable gains through cost-reduction, efficiency improvements, better decision-making and the generation of new revenue streams while maintaining competitiveness in business markets.
Generative AI trends are evolving rapidly, and by 2026, it will reshape how businesses create content, automate operations, and make smarter decisions while improving speed, efficiency, and customer experience.
By 2026, generative AI will enable brands to deliver deeply personalised messages, product recommendations, and support responses in real time. Businesses can improve customer satisfaction, boost conversion rates, and build stronger relationships without increasing marketing or support team size.
Generative AI will help businesses produce blogs, ads, videos, and product descriptions faster and more consistently. This allows teams to scale content production, reduce creative costs, and maintain brand consistency across multiple platforms and markets.
AI models will analyse large datasets and generate insights, forecasts, and reports instantly. Businesses can use these insights to identify trends, reduce risks, and make data-backed decisions more quickly than traditional analysis methods.
Generative AI will assist developers by writing, reviewing, and testing code automatically. This reduces development time, lowers errors, and helps companies launch products faster while optimising engineering resources.
Advanced AI agents will handle customer queries, internal workflows, and operational tasks autonomously. Businesses benefit by improving response times, reducing operational costs, and allowing human teams to focus on high-value strategic work.
As generative AI continues to evolve and expand across industries, the future of generative AI in 2026 is expected to significantly impact businesses, technology, and everyday life. The move toward multimodal AI systems that can comprehend and produce text, images, video, and audio simultaneously will be a significant trend, expanding and improving interactions for both users and organizations.
At the same time, reactive chatbots will start to give way to agent-style AI helpers that plan and carry out tasks proactively, allowing for more independent digital workflows. In order to promote automation and individualized client interactions, businesses will further integrate generative AI into commonplace applications like CRM systems and service platforms.
Another significant advancement is synthetic data, or AI-generated datasets that support model training without disclosing private information. These datasets have the potential to be a vital component of safe AI implementation in industries like healthcare and finance.
Simultaneously, as generative AI becomes more commonplace, debates over ethics, privacy, and copyright will heat up, forcing businesses and authorities to embrace more transparent guidelines for responsible AI use.

Generative AI is changing how companies create, communicate, and innovate. Its application continues to grow exponentially, in terms of content creation as well as in customer support, product design, and software development.
Generative AI increases productivity, reduces expenses, and opens creative opportunities at scale. The more the tools are available and improved, the more the business who begins to learn and experiment today will remain ahead tomorrow.
SoluLab, a generative AI development company USA, can help businesses integrate AI into their business operation and can build custom tools from scratch. Book a free discovery call today to discuss further.
Traditional AI focuses on analyzing data and making predictions, while generative AI creates original content. For example, traditional AI may detect fraud, but generative AI can write reports, design images, or generate code based on prompts.
When you hire generative AI developers, you get solutions tailored to your business needs. Custom development offers better data control, improved accuracy, stronger security, and the ability to scale AI systems as your business grows.
The cost depends on the use case, tools, infrastructure, and scale. Small pilots can start affordably, while enterprise-grade generative AI solutions may require higher investment for security, integration, and customization.
Generative AI is a broad technology that includes many models and tools. ChatGPT is one example of a generative AI application that focuses on generating text-based responses through conversation.
Cloud platforms offer the computing power necessary to train, deploy, and scale generative AI models efficiently, eliminating the need for significant upfront infrastructure investment.
Simple generative AI applications can be deployed in a few weeks, while enterprise-scale solutions may take several months depending on complexity, integration, and compliance requirements.
Companies can start by identifying simple use cases, testing AI tools through pilots, and gradually scaling solutions. Partnering with an experienced generative AI consulting company like SoluLab helps ensure faster and safer adoption. Get started now!