
Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands as a pioneering advancement in the realm of artificial intelligence, bringing to life the ability to create original and unique content, such as images, text, music, and more. At its core, Generative AI refers to the technology that empowers machines to generate content that closely resembles human-created creations. It operates on complex algorithms and models that learn from vast datasets, allowing them to produce new content that exhibits patterns, styles, and characteristics present in the training data.
The concept of Generative AI revolves around the idea of enabling machines to autonomously create content that goes beyond simple replication. Unlike traditional AI systems that primarily focus on classification and prediction, Generative AI goes a step further by creating something novel, often presenting unforeseen combinations or variations that challenge conventional creativity boundaries.
Read Our Blog Post: Top 10 Generative AI Development Companies
At the crossroads of technology and creativity, Generative AI beckons us to peer into a future where machines and human creativity collaborate, weaving a tapestry of possibility that was once confined to human hands alone. As we immerse ourselves in this in-depth analysis, we uncover the intricacies of this remarkable technology and its potential to reshape industries, redefine artistic expression, and inspire a new era of innovation.
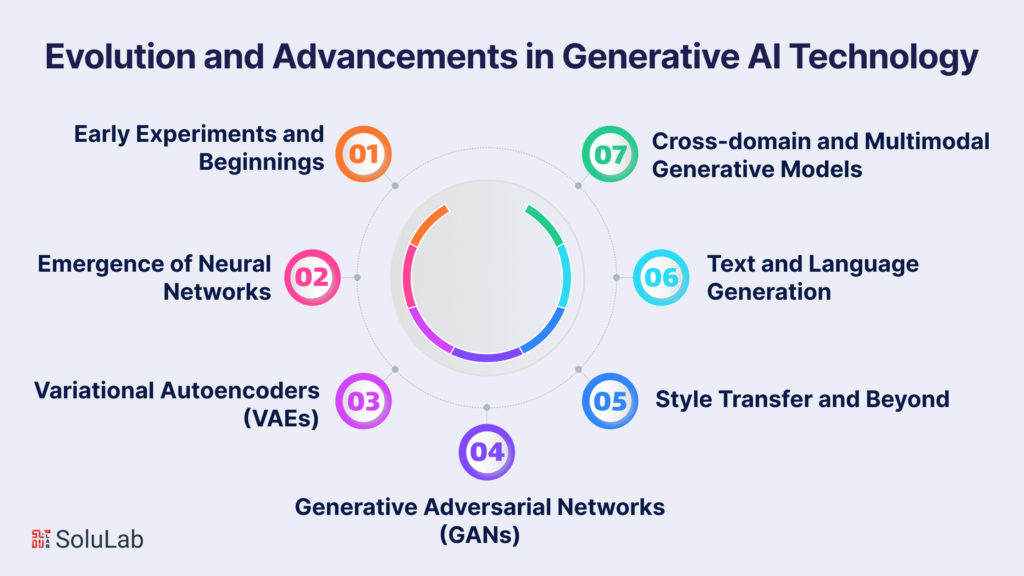
The evolution of Generative AI technology is a remarkable journey that spans multiple decades, marked by significant milestones and breakthroughs:
In the early days of AI, researchers began experimenting with simple rule-based systems that generated basic patterns. These rudimentary systems laid the groundwork for later advancements.
The resurgence of neural networks, particularly deep learning, brought a new wave of progress in the field of Generative AI. Neural networks allowed for more sophisticated learning from data and better capturing of complex patterns.
VAEs introduced probabilistic thinking into Generative AI. These models could generate new content by learning the underlying statistical distributions of data, enabling them to generate similar but distinct outputs.
GANs, introduced by Ian Goodfellow in 2014, revolutionized the Generative AI landscape. GANs consist of two neural networks – a generator and a discriminator – engaged in a competitive learning process. The generator aims to produce content that is indistinguishable from real data, while the discriminator tries to differentiate between real and generated data. This adversarial training results in remarkably realistic content generation.
Generative AI models like GANs paved the way for style transfer, where the style of one image or piece of content could be applied to another, merging art and technology in novel ways.
The evolution of Generative AI expanded to include text and language generation. Models like OpenAI’s GPT-3 demonstrated the capability to generate coherent and contextually relevant text, revolutionizing content creation and automated text generation.
Recent advancements have focused on generating content across domains or even across different modes, such as generating images from textual descriptions or vice versa.
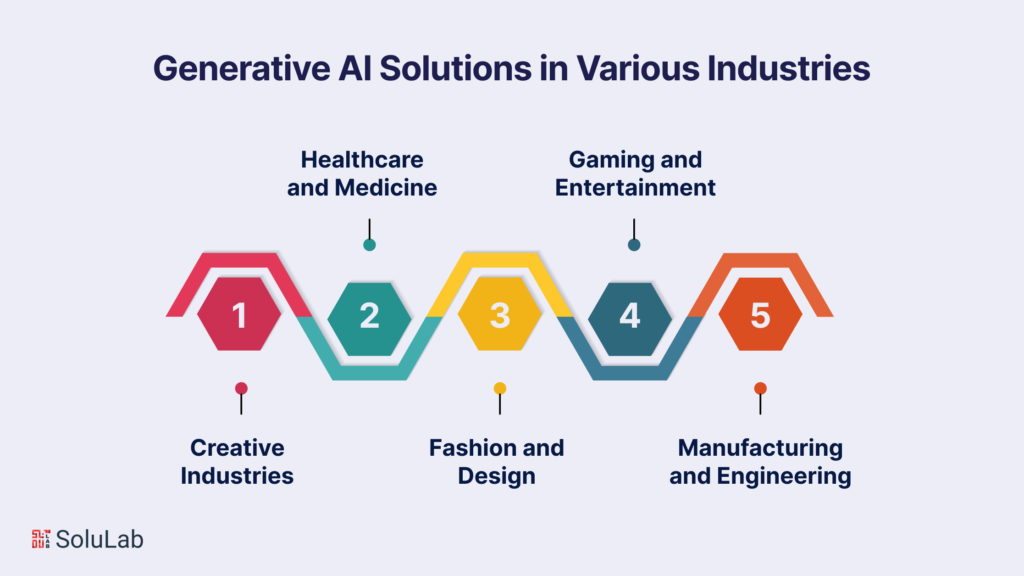
Generative AI has transcended its experimental origins and found its way into a multitude of industries, revolutionizing processes, igniting innovation, and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. As industries recognize the transformative potential of Generative AI, its applications have evolved to cater to specific needs and challenges across diverse sectors.
In the realm of creative expression, Generative AI has become a muse that collaborates with artists, designers, and musicians to produce captivating and novel works. Artists are leveraging generative models to create unique visual art pieces, blending their creativity with the algorithms’ ability to produce unexpected variations. Music composers are experimenting with AI-generated compositions that span genres, allowing them to explore new melodies and harmonies that might have never been considered.
This intersection of human ingenuity and algorithmic creativity fosters an environment where artistic boundaries are continually stretched and redefined.
Check Out Our New Blog: Generative AI and Human-AI Collaboration: A Look into the Future
The healthcare and medical sectors have embraced Generative AI to tackle complex challenges, from drug discovery to medical imaging analysis. AI models are being trained to generate molecular structures for potential drugs, expediting the drug development process.
In medical imaging, Generative AI assists in enhancing and denoising images, aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Additionally, the technology is being used to simulate biological processes, contributing to advancements in understanding diseases and their mechanisms.
Fashion designers and architects are harnessing the power of Generative AI to create innovative designs that blend aesthetics and functionality. In fashion, AI-generated patterns and textures provide designers with fresh ideas and inspirations.
Architects are using generative models to design structures that optimize space utilization and environmental sustainability. By incorporating AI-generated concepts into design processes, the industry is pushing the boundaries of creativity while maintaining a practical focus.
The gaming and entertainment sectors have embraced Generative AI to enhance user experiences and create immersive virtual worlds. Game developers are utilizing AI to generate intricate landscapes, characters, and scenarios, resulting in dynamic and evolving gameplay.
Procedural content generation driven by Generative AI ensures that no two gaming experiences are alike. Moreover, in the entertainment industry, AI-driven algorithms are used to generate realistic special effects and visualizations, elevating storytelling to new heights.
Read Blog Post: Top Artificial Intelligence Solution Companies
In the domain of manufacturing and engineering, Generative AI is redefining the design and production processes. Engineers are using AI-generated designs to optimize product geometries for enhanced performance and reduced material usage.
This approach is particularly valuable in fields like the aerospace and automotive industries. Additionally, Generative AI aids in generating prototypes and testing scenarios, accelerating the iterative design process and enabling faster product development cycles.
As Generative AI continues to make strides in reshaping industries and creative processes, it brings forth a series of challenges and ethical considerations that demand careful attention. These complexities arise from the unprecedented capabilities of AI models to create convincing and realistic content, as well as the potential consequences of their misuse. Here, we explore the key challenges and ethical dimensions surrounding Generative AI.
Generative AI models can generate highly realistic but entirely fabricated content, raising concerns about misinformation and manipulation. Deepfakes, for instance, can convincingly swap faces in videos, potentially leading to the spread of falsified information or malicious intent.
Know More: From Data to Business Success: Role of AI in Sentiment Analysis
The question of who owns AI-generated content remains a legal and ethical gray area. As these models blend existing data to create new works, determining intellectual property rights and fair compensation for creators becomes complex.
Generative AI’s ability to generate art, music, and literature prompts questions about the nature of creativity. If machines can produce creative works, how does this impact the value and definition of human creativity?
Generative AI models learn from large datasets, which may inadvertently embed biases present in the data. These biases can be perpetuated in the generated content, raising concerns about the fairness and inclusivity of AI-generated outputs.
Using AI to generate content often involves using existing data, raising privacy concerns if the data used wasn’t originally intended for such purposes. Additionally, AI-generated content might inadvertently reveal sensitive information or breach privacy boundaries.
The authenticity of AI-generated content can be challenging to discern. This poses potential threats to the reliability of digital media and could undermine trust in online content.
Check Our Post: Generative AI for Enterprises: Understanding Architecture, Implementation, and Implications
The complexity of Generative AI development may lead to a technology gap, where only those with significant technical expertise can create and control these systems. This could limit equal participation and hinder widespread understanding.
Deciding how Generative AI should be used and where the line should be drawn in terms of its applications is an ongoing ethical debate. Determining which Generative AI use cases align with societal values and avoiding harmful applications is a complex task.
Generative AI development demands a specialized skill set that combines expertise in machine learning, data science, and creative problem-solving. Creating AI models that generate new and imaginative content requires a deep understanding of algorithms, neural networks, and the nuances of the data they learn from. Here are the essential skills and expertise required for Generative AI development:
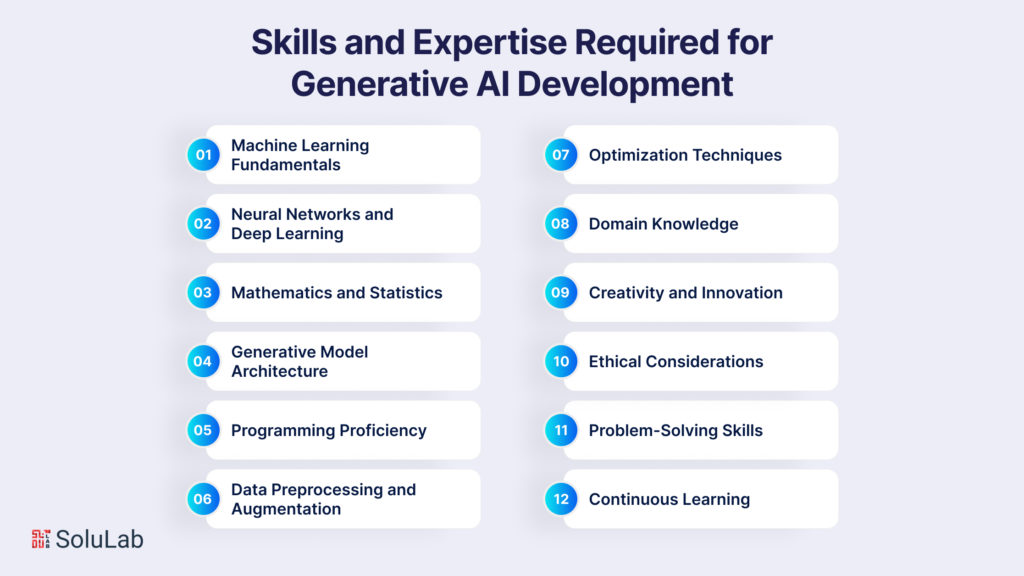
A solid grasp of machine learning concepts is foundational. Understanding supervised and unsupervised learning, classification, regression, and clustering provides the basis for more advanced Generative AI techniques.
Deep learning is at the core of Generative AI. Proficiency in building and training various types of neural networks, including convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs), is essential.
Check This Blog Also: 10 Benefits of Incorporating Generative AI in the Manufacturing Process
Developers need a deep understanding of various generative model architectures, such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and autoregressive models. Each architecture has its intricacies and applications.
Fluency in programming languages such as Python is essential. Frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Keras are commonly used to implement and train generative models.
Manipulating and preparing data for generative tasks is vital. Skills in data preprocessing, augmentation, and normalization ensure that the input data is suitable for training the models effectively.
Understanding optimization algorithms, gradient descent, and backpropagation is crucial for training generative models and fine-tuning their performance.
Read Also: From Theory to Reality: Real-World Applications of Generative AI and GPT
Depending on the application of Generative AI, having domain-specific knowledge can greatly enhance the effectiveness of the models. For example, medical imaging requires knowledge of medical processes.
Generating novel content requires a creative touch. Developers need to think innovatively to push the boundaries of what AI-generated content can achieve.
Awareness of ethical implications and considerations related to AI-generated content, such as privacy, bias, and authenticity, is vital to developing responsible and socially aware solutions.
Generative AI development often involves solving complex challenges, from fine-tuning models to optimizing hyperparameters. Strong problem-solving abilities are a must.
Check Out Our Post: Top 7 Generative AI Integration Services For Your Business
In the quest to find skilled and proficient Generative AI developers, SoluLab emerges as a noteworthy destination that combines expertise, innovation, and a proven track record in cutting-edge AI development. As the demand for Generative AI solutions grows, the search for top-tier talent becomes crucial, and SoLulab offers a compelling solution.
SoluLab boasts a team of seasoned AI experts who specialize in Generative AI development. Their multidisciplinary skill set spans machine learning, data science, neural networks, and more. This diversity enables them to tackle complex Generative AI projects with finesse.
Generative AI often relies on frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Keras. SoluLab’s developers are well-versed in these platforms, allowing them to efficiently build and deploy generative models tailored to your specific needs.
Read Also: Top 10 Enterprise AI Development Companies
Collaboration is key in AI development, especially in a domain as intricate as Generative AI. SoluLab’s team adopts a collaborative approach, working closely with clients to understand their requirements, offer expert insights, and create tailor-made solutions that align with their vision.
SoluLab’s portfolio showcases an array of successful AI projects, including those in the realm of Generative AI. This proven track record underscores their ability to deliver innovative solutions that cater to diverse industries and challenges.
Generative AI’s applications span various industries, and SoluLab’s expertise extends across sectors like healthcare, finance, e-commerce, and more. This diverse integration showcases their adaptability and commitment to addressing industry-specific challenges.
SoluLab maintains an active presence in the AI community through research, participation in conferences, and sharing insights. Their thought leadership reflects their dedication to staying at the forefront of AI advancements.
Check Blog Post: Unleashing Business Value: How Generative AI is Transforming Industries
Addressing ethical considerations in Generative AI is of paramount importance. SoluLab prioritizes the responsible use of AI technologies, ensuring that solutions align with ethical guidelines and societal norms.
SoluLab offers end-to-end solutions, from ideation and development to deployment and maintenance. This comprehensive approach streamlines the development process.

Collaborating with Generative AI development experts can bring transformative advantages to your projects and initiatives. As the field of AI rapidly evolves, these specialists offer a wealth of knowledge and experience that can shape innovative solutions and drive progress. Here’s a closer look at the benefits of partnering with Generative AI development experts:
Generative AI development experts possess a deep understanding of AI algorithms, neural network architectures, and cutting-edge frameworks. Their technical prowess ensures that your generative models are designed, implemented, and fine-tuned for optimal performance and innovation.
Generative AI is as much about creativity as it is about technology. Collaborating with experts allows you to harness their creative problem-solving skills to produce novel and imaginative outputs that align with your project goals.
Read Also: What is an AI-powered chatbot?
Generative AI has applications across various industries, from art and entertainment to healthcare and manufacturing. Development experts can tailor their solutions to suit your specific industry requirements, bringing a versatile approach to your projects.
Responsible AI development involves addressing ethical concerns such as bias, privacy, and authenticity. Generative AI experts are well-versed in navigating these complexities, ensuring that the AI-generated content adheres to ethical guidelines and societal norms.
Building Generative AI models from scratch can be resource-intensive and time-consuming. By collaborating with experts, you can tap into their pre-existing knowledge, tools, and workflows, saving valuable time and resources.
The AI landscape evolves rapidly, with new techniques and advancements emerging frequently. Generative AI experts stay updated with the latest developments, ensuring that your projects benefit from state-of-the-art technology and methodologies.
From ideation to deployment and maintenance, Generative AI development experts offer end-to-end solutions. This holistic approach streamlines the entire development process and ensures that your projects are seamlessly integrated and effectively managed.
Collaborating with experts provides a unique learning opportunity. You gain insights into AI techniques, best practices, and industry trends, fostering knowledge exchange that can empower your team’s future projects.
Innovation often requires thinking beyond the conventional. Generative AI development experts introduce fresh perspectives, helping your projects stand out and maintain a competitive edge in rapidly evolving markets.
No two projects are exactly alike. Generative AI experts can customize solutions to address your project’s unique challenges, ensuring that your goals are met with precision.
In conclusion, delving into the current landscape of generative AI has unveiled a realm of innovation that holds immense potential across various domains. The evolution of generative AI models has paved the way for groundbreaking solutions that redefine creativity, problem-solving, and user experiences. From art and content generation to complex data synthesis, generative AI demonstrates its prowess by producing outputs that often transcend human capabilities.
Generative AI solutions are witnessing a surge in adoption, driven by their remarkable versatility and ability to cater to a wide array of use cases. This technology has showcased its prowess in fields as diverse as art, design, music, text generation, and even scientific research. The power to create novel and contextually relevant content is empowering businesses and individuals alike, opening new avenues for exploration and expression.
However, it’s worth noting that while generative AI tools continue to astound with their capabilities, they are not without challenges. Fine-tuning these models, ensuring ethical usage, and maintaining quality control are important considerations to navigate this evolving landscape successfully.
Unlock the potential of Generative AI for your digital creations with SoluLab. Our team of experts harnesses the power of cutting-edge Generative AI models like ChatGPT, DALL-E, and Midjurney, offering tailor-made solutions for your specific AI needs. When it comes to state-of-the-art Generative AI Development Services designed specifically for your company’s requirements, look no further. We stand out in the crowded Generative AI landscape by prioritizing agile development and a steadfast commitment to delivering exceptional business outcomes. Hire Generative AI Developers from SoluLab today to harness the creative force of Generative AI for your success. Contact SoluLab Now to explore the possibilities.
Generative AI refers to a subset of artificial intelligence that involves creating or generating new content, such as images, text, music, or even entire virtual worlds, using algorithms and data.
Generative AI models work by learning patterns and features from a dataset and then generating new content that resembles the input data. These models utilize techniques like neural networks and probabilistic models to generate creative and novel outputs.
Generative AI has diverse applications, including creating realistic images, text generation, video game content generation, style transfer, music composition, drug discovery, and more. It’s used wherever creativity and content creation are needed.
Generative AI focuses on creativity and content generation, distinguishing it from other AI applications that primarily involve classification, prediction, or optimization tasks.
Generative AI solutions are software applications or platforms that leverage generative AI technology to create new content. They can range from text generators and image synthesis tools to more complex systems like virtual environment creation engines.