There’s a moment every crypto founder dreads when your institutional investor asks that Has this been audited? However, what most people don’t realize is that having a basic audit and having the right audit are two completely different things, based on our experience.
| In 2025 alone, $3.1 billion was stolen from DeFi protocols, yet only 20% of the hacked projects had undergone formal security audits. |
The gap is about incomplete audits that miss what matters. As we move through 2026, how to audit a smart contract has become the defining question for any serious blockchain deployment, especially with MiCA enforcement kicking in across the EU and institutional investors tightening their due diligence requirements like never before.
Let’s be direct, the crypto industry is maturing, and maturity means scrutiny. In 2023 or 2024, you could launch a protocol, get hacked, and move on. But in 2026, you launch unaudited, you don’t launch at all, at least not with institutional backing, exchange listing, or EU users.
Thank God the shift is real. The global smart contracts market is growing at 22% annually, reaching $2.69 billion in 2025 and projected to hit $12.07 billion by 2034. That growth isn’t happening in dark corners; it’s happening in boardrooms, exchanges, and regulatory offices where audit reports matter more than code quality because the audit report is proof of quality.
Smart contract audit readiness used to mean did someone check our code? but in 2026, it means something harder: Does this system survive institutional pressure, adversarial conditions, and regulatory scrutiny?
The most successful protocols work with audit partners early, not as a final checkpoint before launch, but as an architecture decision that shapes every line of code. Your smart contract design should reflect auditability from day one, not auditability as an afterthought.
In 2026, regulatory agencies like Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA) stopped waiting and started enforcing, which caused panic in crypto products that are unaudited. For you, it means that if your smart contract processes crypto-assets in the EU, it’s now subject to MiCA’s transparency, security, and user protection requirements. Not someday or pending clarification. Now.
MiCA isn’t just a compliance checkbox anymore. It’s baked into audit requirements. Leading audit firms like CertiK, Hacken, and Quantstamp now include MiCA compliance checks as a standard part of their smart contract audit services for any protocol targeting EU users. This wasn’t the case 18 months ago.
And 75% of major exchanges have already submitted their MiCA licensing applications. Meanwhile, 60% of crypto businesses are still in partial compliance mode, scrambling to adapt. If you’re not auditing for MiCA alignment, you’re auditing for yesterday’s market.
Simultaneously, institutional investors have tightened their pre-investment audit requirements. They no longer ask, Is this audited?
They ask:
They’re entry requirements. So here are 10 Audit Areas you should not miss.

This is where most audits fail, and where preparing for a smart contract audit becomes essential.
Too many teams bring code to an audit firm expecting the auditors to find problems with the underlying architecture, they won’t. An audit firm can validate that your code matches your design, but they can’t redesign your protocol mid-audit. That’s why threat modeling happens before code is frozen.
Real threat modeling asks:
These aren’t hypothetical edge cases. They’re scenarios that actually play out in production.
A proper architecture audit includes mapping trust assumptions, who controls admin keys, which components rely on off-chain data, and where human intervention can override on-chain logic. Document this clearly, because your auditors need to understand your trust model to validate it and Institutional investors definitely need to see it.
This is where the sophistication gap becomes obvious.
Most audit teams run automated tools first, like static analysis, fuzzing, and symbolic execution. These tools are fantastic for catching obvious bugs like integer overflows, reentrancy patterns, and basic access control flaws, but they catch maybe 60% of what matters.
The other 40% requires human expertise. It’s logic flow analysis, state transition validation, and complex economic attack surface modeling.
These questions require auditors who’ve seen 500+ DeFi protocols and understand how they fail. This is also where smart contract security audit firms differentiate themselves. Top-tier firms like CertiK have completed over 5,500 audits and uncovered nearly 83,000 vulnerabilities, and they bring pattern recognition that pure automation can’t provide.
Your token mechanics might be elegant on paper mathematically, but in the real world, under market stress, they might break.
Who can mint tokens, and under what conditions? So, poorly controlled mint logic has repeatedly caused irreversible dilution and complete loss of market confidence. This isn’t a technical bug, rather It’s an economic vulnerability that audits need to catch.
Distribution and vesting are equally critical.
Auditors simulate months of operation, testing whether your economic model survives
Without this economic stress testing, your audit report is incomplete.

Oracles are the most fragile layer in crypto systems, as your smart contract is only as secure as the data it trusts. An oracle outage during volatile market conditions can turns into systemic failure. So Auditors need to test what happens when your price feed lags, diverges, or breaks entirely.
Real audits include fallback logic review.
These aren’t theoretical concerns, as they’re specific vulnerabilities that auditors actively test for.
Governance security determines who ultimately controls your protocol after deployment. This is where institutional investors focus hard.
Your voting system might be mathematically sound, but
Audits need to simulate governance under adversarial conditions, not just validate that voting math works. Multi-signature wallet for controls, timelock mechanisms, and transparent admin documentation matter massively here.
Even secure code fails when deployment environments are misconfigured like Network parameters, gas optimization settings, and compiler version consistency, these operational details have caused irreversible smart contract failures. Your audit should include a pre-deployment configuration review that validates:
This is where operational security becomes part of your audit scope.
MiCA compliance is now a pre-deployment audit standard, at least for EU-facing protocols. Your audit should validate:
1. Transparency requirements:
2. Security compliance measures:
3. User protection mechanisms:
4. Developer liability readiness:
If you’re targeting EU users, MiCA isn’t background reading. It’s part of your audit checklist. 40% of DeFi platforms still report uncertainty about whether they fall under MiCA scope, so don’t be one of them.
Static code analysis alone can’t predict real-world behavior at scale. Proper audits include simulation:
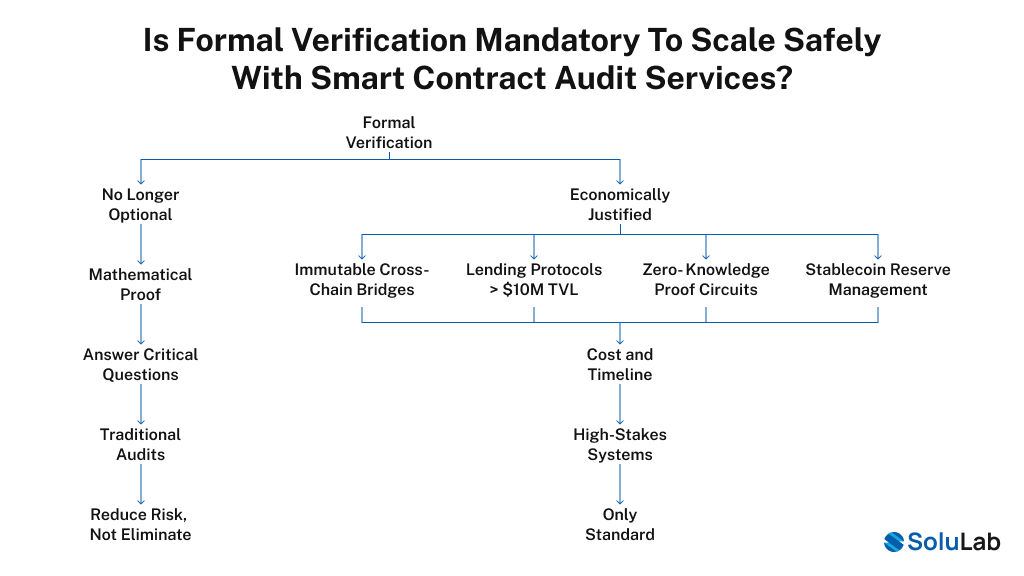
This is where formal verification sometimes enters the picture, a mathematical proof that critical invariants hold under all conditions. For immutable bridges, high-TVL lending protocols, and zero-knowledge proof circuits, formal verification is becoming a prerequisite. It typically adds $20,000-$50,000 to audit costs and 4-12 weeks to timelines, but for high-stakes systems, it’s justified.
An audit report that your team can’t understand is an audit report that won’t prevent failures. Quality audits include clear documentation of threat assumptions, architectural decisions, remediation guidance, and admin procedures. Post-launch, your team needs to know how to maintain the system, respond to incidents, and escalate issues.
This also matters for regulatory conversations. If an auditor asks your team how your contract handles certain edge cases and no one knows, that’s a red flag for institutional investors.
Before your protocol goes live, your team needs to be crystal clear on responsibility.
Audits that ignore ownership and accountability fail institutional expectations. This is also where continuous monitoring services come into play. Top teams don’t just do one audit and call it done; they retain ongoing security services like real-time monitoring, flash loan attack detection in the mempool, and incident response readiness. Continuous monitoring services run $2,000-$10,000 per month, but they’re the difference between detecting exploits in milliseconds and discovering breaches on X.
AI isn’t replacing auditors, it’s amplifying them. Machine learning models trained on historical vulnerabilities and past exploits can scan code patterns, identify anomalies, and flag high-risk areas at scale. This reduces audit scope by 15-25% and accelerates early-stage detection. But AI can’t catch economic exploits, governance vulnerabilities, or architectural flaws that require domain expertise. The most effective audit approach combines three layers:
This hybrid model is becoming standard because it works. AI finds what it’s trained to find, Humans find what matters, and together, they’re comprehensive.
Here’s what’s changed in 2026: formal verification is no longer optional for certain categories of systems. Formal verification provides mathematical proof, not probability. It answers the question: Can this code ever violate critical invariants under any input condition?
This is different from traditional audits, which reduce risk but don’t eliminate it. Formal verification is economically justified for:
Here’s what you actually need to budget for:
| Audit Category | Typical Cost (USD) | Timeline | Scope & Notes |
| Simple ERC-20 Token | $8,000–$20,000 | 2–5 days | Boilerplate logic, automated tooling, limited manual review |
| Standard DeFi Protocol (DEX, Lending) | $50,000–$100,000 | 3–6 weeks | 3 – 4 auditors, complex contract interactions, manual + AI analysis |
| Solana Protocol (Equivalent Complexity) | $60,000–$130,000 | 4–8 weeks | Around 20 – 30% premium vs Ethereum due to Rust expertise scarcity |
| Complex Systems (Bridges, L1s, ZK-Rollups) | $150,000–$500,000+ | 2–6 months | Formal verification required, highest risk surface |
| Continuous Monitoring (Retainer) | $2,000–$10,000 / month | Ongoing | Real-time on-chain monitoring, exploit & flash-loan detection |
Urgency premiums are real, as requesting a 2-week turnaround for a protocol that normally requires 6 weeks adds 30-50% to costs, so plan early.
Here’s where your audit strategy diverges from your competitor’s:
| Audit Strategy Model | Ownership & Setup | Typical Cost (USD) | Timeline | Key Limitations / Advantages |
| Model 1: Developer-Led Audit ( Higher Risk but Lower Cost ) | Internal dev team and 1 – 2 external auditors | $20,000 – $50,000 | 2 – 4 weeks | Limitation: Gaps in formal verification, governance design, and regulatory interpretation; higher post-launch risk |
| Model 2: Integrated Audit-Led Development ( Institutional Standard ) | Single tier-1 firm involved from architecture to deployment | $75,000 – $150,000 | 3 – 8 weeks (runs alongside development) | Advantage: Architecture is designed for auditability from day one; fewer reworks and smoother launches |
| Model 3: Boutique Specialists and Tier-1 Audit ( Highest Assurance ) | Specialist firms for formal verification, compliance, AI analysis, and tier-1 auditors | $150,000 – $300,000+ | 6 – 12 weeks | Advantage: Minimal deployment risk with full institutional-grade coverage |
For any protocol managing greater than $10M TVL or seeking exchange listing, Model 2 or 3 is standard, but Model 1 is increasingly associated with post-launch friction and investor skepticism.

In 2026, success isn’t defined by who ships the most innovative protocol– it’s defined by who proves it’s secure, resilient, and compliant before real capital goes on-chain. The numbers are clear: only 20% of hacked protocols were audited, while audited protocols experience 98% fewer security incidents and raise 37% more capital. Security is no longer optional; it’s a growth advantage.
That’s why your next deployment must look different: early audit engagement, clear architecture documentation, formal verification for high-value logic, continuous post-launch monitoring, and MiCA-ready compliance from day one. This isn’t bureaucracy; it’s how serious platforms earn institutional trust.
As a smart contract development company, SoluLab helps teams build audit-ready, regulator-aware smart contracts from the start, reducing rework, accelerating approvals, and enabling safe scale. In 2026, professionalism is the product. Get in touch to know more!
Internal testing is foundation-level, where Audits add exponentially more value. Projects with thorough audits raise 37% more capital than those without, as Institutional investors and exchanges explicitly require third-party audits, and MiCA compliance also mandates security validation by qualified personnel.
Architecture review should happen before code is finalized, as audit firms can identify scope and timeline before you’re locked into a particular design. This saves months of back-and-forth post-development, as most Top-tier firms have 2-3-month waiting lists, so plan accordingly.
Depth and breadth. A $50K audit (standard DeFi protocol) typically involves 2-3 auditors, 3-4 weeks, and automated tooling with manual review. A $100K audit adds a fourth auditor, formal verification components, economic attack-surface modeling, and a continuous monitoring setup. The difference is in the thoroughness that catches what automated tools miss.
No, AI accelerates detection of known patterns, reducing audit scope by 15-25%. But it can’t catch economic exploits, governance vulnerabilities, or architectural issues that require domain expertise. The most effective audits layer AI signal generation with human validation.
The audit report is your security baseline at a point in time. After post-launch, your team needs continuous monitoring, real-time on-chain surveillance, and catching exploits before they drain funds. This typically costs $2,000-$10,000/month. Also, maintain incident response readiness and keep your team trained on documented security procedures.
We work with enterprise teams to build audit-ready architecture from the start. We map audit requirements into your development roadmap, coordinate with tier-1 audit firms, manage MiCA compliance documentation, and support formal verification planning for high-risk systems.