
In the ever-expanding digital landscape, the importance of robust cybersecurity measures cannot be overstated. With cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated, the need for intelligent, adaptable defense mechanisms has grown exponentially. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a game-changer in this realm, revolutionizing the way we protect our digital assets.
This blog delves into the captivating journey of AI in cybersecurity, tracing its evolution from the rudimentary rule-based systems to the cutting-edge realm of deep learning.
Before AI made its presence felt, cybersecurity heavily relied on rule-based systems. These systems operated on predefined sets of rules and signatures. They were effective to some extent in thwarting known threats but had glaring limitations, which is why many companies today depend on managed IT services Dallas providers for proactive protection. Rule-based systems struggled with zero-day attacks and evolved threats that didn’t fit neatly into predetermined patterns.
For example, an antivirus software employing rule-based systems could detect and quarantine a virus only if it matched a predefined signature. If a new strain of malware emerged, the system remained blind to it until a new rule was created. This reactive approach left systems vulnerable during the crucial time gap between a new threat’s emergence and the update of the security rules.
Machine learning marked the first significant leap in AI cybersecurity. Unlike rule-based systems, machine learning systems/algorithms could learn from data. They analyzed patterns, anomalies, and behaviors to detect threats, even those with no predefined rules. This proactive approach opened new possibilities in the battle against cyber adversaries.
Supervised learning, a branch of machine learning, allowed security systems to be trained on labeled datasets. By learning from historical data, these systems could make informed decisions about the nature of incoming data and identify potential threats. For instance, a supervised learning model could identify known phishing emails by recognizing common characteristics shared among them.
Unsupervised learning algorithms, on the other hand, didn’t rely on labeled data. They analyzed incoming data to identify anomalies or deviations from the norm. This made them effective in detecting novel threats or insider attacks, where the patterns might not be predefined.
Semi-supervised learning blended the best of both worlds, combining labeled data for known threats with unsupervised techniques to uncover new ones. This approach improved detection accuracy and reduced false positives.
Reinforcement learning, often associated with AI in gaming, found its application in cybersecurity as well. It enabled systems to adapt and learn in real-time, making them more agile in responding to evolving threats.
Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, brought about a paradigm shift in AI cyber-security. At its core were neural networks, models inspired by the human brain’s interconnected neurons. These networks could process vast amounts of data, automatically extract features, and make complex decisions.
Neural networks, with their ability to analyze unstructured data like images, texts, and network traffic, became invaluable in cybersecurity systems. They excelled in tasks such as anomaly detection, where identifying subtle deviations from normal behavior was critical. Deep learning models could recognize not only known malware but also previously unseen variants based on their underlying characteristics.
Deep learning also revolutionized the fight against phishing attacks. Neural networks could analyze email content, sender behavior, and contextual information to flag potentially malicious emails, even if they lacked familiar hallmarks of phishing attempts.
The use of deep learning in malware detection was another breakthrough. These models could identify malicious code by scrutinizing its structure and behavior, without relying on predefined signatures.
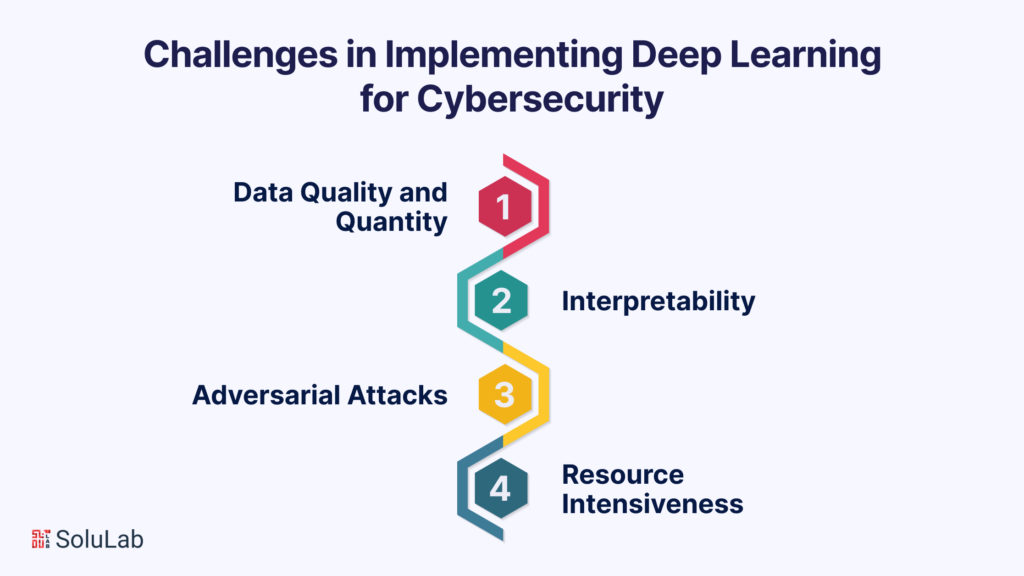
While deep learning has ushered in a new era of AI development companies, it’s not without its challenges and ethical considerations.
Despite these challenges and ethical concerns, numerous organisations have embraced deep learning for cybersecurity, achieving remarkable results:
These examples illustrate the practical application of deep learning in real-world cybersecurity scenarios. Organizations are increasingly relying on AI to bolster their defenses and respond swiftly to emerging threats.
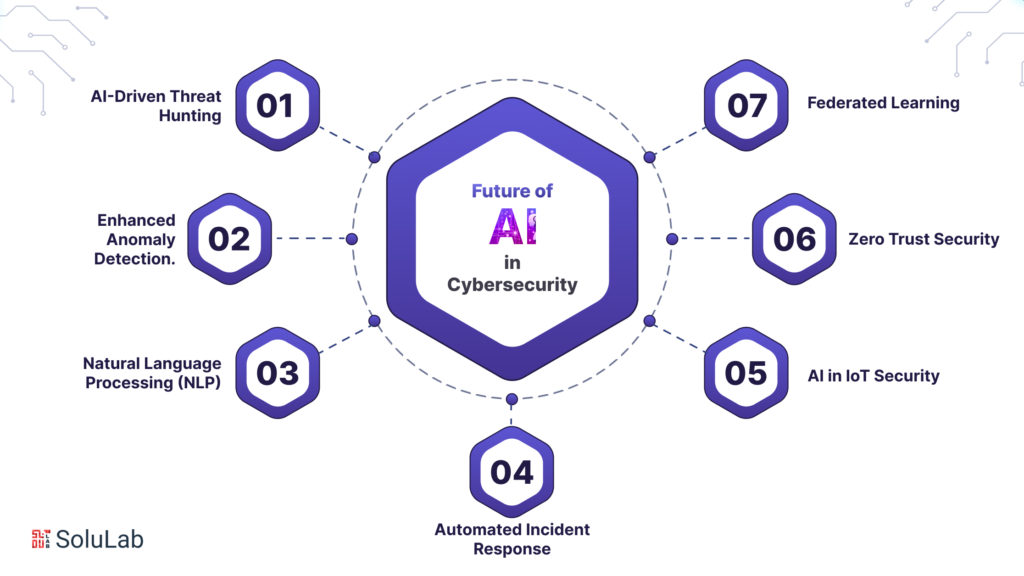
As we look ahead, the future of AI in cybersecurity promises continued evolution and transformation. Several key trends and developments are shaping the landscape:
While AI is a powerful ally in the fight against cyber threats, human expertise remains irreplaceable:
In essence, the future of AI in cybersecurity is a collaboration between human expertise and artificial intelligence. AI enhances the capabilities of cybersecurity professionals, enabling them to work more efficiently and effectively.
The evolution of AI in cybersecurity, from rule-based systems to deep learning, has been a remarkable journey. It has equipped us with powerful tools to defend against an ever-evolving threat landscape. As AI continues to advance, we must remain vigilant, addressing challenges such as data privacy and bias, while also recognizing the crucial role that human experts play in keeping our digital world secure.
In this era of rapid technological change, the fusion of human intelligence and AI-driven automation will be the key to staying resilient in the face of cyber threats. As we move forward, the synergy between human expertise and AI innovation will be our strongest defense in the dynamic and complex world of cybersecurity.
SoluLab, a forward-thinking technology company, is renowned for innovative solutions across domains, including cybersecurity. They excel in AI development services and hire AI developers, contributing significantly to AI’s evolution in cybersecurity. Leveraging advanced AI and deep learning, they shape a proactive defense against evolving threats. SoluLab exemplifies how tech companies integrate AI to create adaptive, proactive, and robust defense mechanisms, shaping the future of cybersecurity and providing AI development services and AI developer hiring solutions for organizations.
Rule-based systems rely on predefined rules and signatures to detect threats, while deep learning uses neural networks to analyze data and make decisions based on learned patterns. Deep learning is more adaptable to evolving threats.
AI in cybersecurity must be implemented with strict privacy policies and data protection measures. To address bias, diverse and unbiased training data should be used, and models should be regularly audited for fairness.
No, AI complements human expertise but cannot replace it entirely. Human professionals bring contextual understanding, ethical decision-making, and adaptability that AI lacks. They play a vital role in complex investigations and decision-making.
Organisations like Darktrace, Cylance, FireEye, and Google’s Chronicle have successfully implemented AI-driven cybersecurity solutions. These companies employ AI for threat detection, incident response, and real-time monitoring.
The future of AI in cybersecurity is marked by trends such as AI-driven threat hunting, enhanced anomaly detection, natural language processing (NLP), automated incident response, AI in IoT security, zero-trust security models, and federated learning for threat intelligence sharing. These trends aim to bolster cyber defenses and adapt to evolving threats.