
Deciding to migrate your business the cloud drastically alters how you conduct business operations. This major move requires careful strategic planning and consideration. While potential benefits exist, wrong decisions bring unwanted costs. Cloud migration impacts economics, operations, security, and more. Having answers to these strategic questions allows informed planning to fully leverage cloud promise while managing very real challenges. Deciding requires thoughtful deliberation as this is no minor choice. In this guide, we are going to discuss the key elements that are crucial for a successful cloud migration.
There are transformative cloud migration benefits across key business operations. Regardless of your starting point, transitioning to a cloud platform can greatly enhance performance, agility, scalability, and security. Key potential benefits include:
Migrating to the cloud provides flexible access to on-demand computing, storage, and network resources that can scale up and down based on real-time workload demands. Organizations are no longer constrained by fixed on-premises infrastructure capacities and capabilities. Cloud platforms offer near instantaneous access to additional resources when needed, by leveraging the provider’s massive global infrastructure and economies of scale. This enables high-performance workload processing. Cloud data migration also provides auto-scaling, intelligent load balancing across global regions, and optimizing running workloads on the latest high-efficiency hardware.
The cloud accelerates business innovation through faster ideation, development, and deployment of new products and services. Automated self-service and API access transforms deployment lead times from months to minutes, dramatically accelerating experimentation and implementation. This empowers innovation across all levels of the business, not just IT teams. Many advanced cloud services offer pre-built solutions leveraging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning, IoT and analytics that can drive innovation. New capabilities can be built, tested and deployed rapidly.
Migrating business systems to the cloud substantially strengthens organizational resilience. Leading cloud providers offer built-in business continuity and disaster recovery capabilities across isolated global regions and availability zones. This includes persistent storage replication and seamless cross-region redundancy providing unprecedented resilience to outages. Cloud also offers many other related continuity capabilities such as automated failover and instance recovery. For most organizations, cloud delivers business resilience well beyond what can realistically be achieved using traditional on-premises models.
Leading cloud providers invest billions in next-generation security tools and global threat intelligence to prevent, detect, and respond to emerging risks. Cloud platforms provide unified security controls including automated policy enforcement, data encryption, role-based access controls, and activity auditing logs across services. System updates, security patches, and compliance controls are applied automatically at global scale. By tapping advanced cloud security capabilities, organizations can reduce risk exposure related to talent shortages, legacy systems, limited budgets and more.
The cloud changes infrastructure spending from high upfront capital investments to flexible ongoing operating expenditure based on consumption. The pay-as-you-go models allow optimal spending aligned to workloads and support accurate cost allocation across teams, applications, and services based on actual usage. Cloud pricing models also benefit enormously from the providers’ economies of scale. Organizations avoid over or under provisioning by purchasing the computing resources needed versus planning for theoretical peak capacity. Cloud billing transparency and recommendation tools further empower organizations to optimize cloud expenditure
Before moving to the cloud, it’s crucial to establish a solid migration architecture. This involves planning resources, defining cloud requirements, and strategizing for data transfer. The migration architect plays a key role in making critical decisions for a successful migration process through detailed technical planning and structured design.
Selecting a cloud platform for critical applications can be challenging. The choice depends on the APIs and technology used in software development. Organizations must assess their business requirements and application technology before deciding on a single or multi-cloud platform.
Setting an affordable budget for cloud migration is essential. Companies need to estimate the total cost of resources and understand the pricing structure of cloud platforms. Evaluating existing infrastructure and internal resources is crucial before committing to a cloud migration approach. Additionally, exploring available cloud cost monitoring tools can provide insights into potential savings opportunities when migrating to cloud.
Making the right choice of cloud service provider is a crucial step. Companies should analyze providers based on technology, compatibility, international standards, and governing policies. An apt provider can work efficiently with your applications and provide 24/7 support.
Safeguarding confidential data is paramount. Organizations must scrutinize the security policies and regulations of the chosen cloud provider before deploying applications. More than 60% of companies express concerns about the security measures followed by cloud providers, highlighting the importance of thorough evaluation.
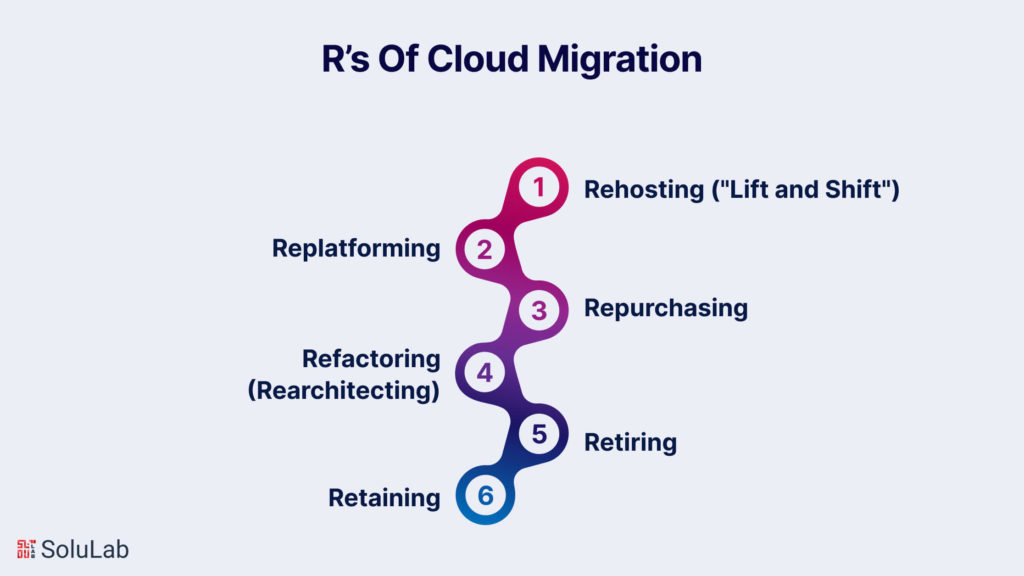
Broadly categorized as the “six R’s of migration,” these strategies offer various approaches, each tailored to different business needs and priorities. Understanding and choosing the right strategy is crucial for a successful transition to the cloud.
Rehosting involves lifting your existing infrastructure and shifting it from on-premises hosting to the cloud without making significant modifications. This approach aims for a quick return on investment (ROI) by creating an exact replica of the current environment. It is suitable for companies with a conservative culture or those lacking a long-term strategy for advanced cloud capabilities. The advantage of rehosting lies in its simplicity and speed, making it an efficient strategy for organizations looking for a straightforward migration process.
Replatforming, a variation of lift and shift, involves making additional adjustments to optimize your applications for the cloud. While the core architecture remains the same, organizations implementing this strategy aim to enhance performance and efficiency. Replatforming is a good fit for conservative organizations seeking to build trust in the cloud while realizing benefits like increased system performance. It strikes a balance between the simplicity of rehosting and the potential improvements offered by more complex strategies.
Repurchasing entails moving applications to a new, cloud-native product, commonly a Software as a Service (SaaS) platform. For example, migrating a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system to Salesforce. This strategy can be cost-effective, especially for organizations transitioning from highly customized legacy landscapes. However, it comes with challenges, such as adapting to a new platform and training teams on its usage. Repurchasing is a strategic move for organizations looking to benefit from specialized cloud services provided by third-party vendors.
Refactoring, or rearchitecting, involves rebuilding applications from the ground up. This strategy is driven by the need to leverage cloud capabilities not available in the existing environment, such as auto-scaling or serverless computing. While refactoring is generally the most expensive option, it offers compatibility with future versions and allows organizations to fully exploit advanced cloud features. Businesses adopting this strategy prioritize long-term benefits and are willing to invest in overhauling their applications for maximum cloud efficiency.
After assessing the application portfolio for cloud readiness, organizations may find some applications are no longer useful or relevant. In such cases, the retirement strategy involves simply turning off these applications. The resulting cost savings can potentially strengthen the business case for migrating other applications. This approach is a pragmatic way to streamline the IT landscape, focusing resources on essential and relevant applications, ultimately contributing to cost efficiency and improved overall performance.
Not all organizations are ready for or find value in immediate cloud adoption. The retaining cloud strategy acknowledges that cloud migration might not currently align with the organization’s priorities or constraints. This could be due to compliance reasons, data sensitivity concerns, or a recent application upgrade. In such cases, organizations plan to revisit cloud computing at a later date when it makes more business sense. Retaining allows businesses to migrate to the cloud at their own pace, aligning with their strategic goals and priorities.
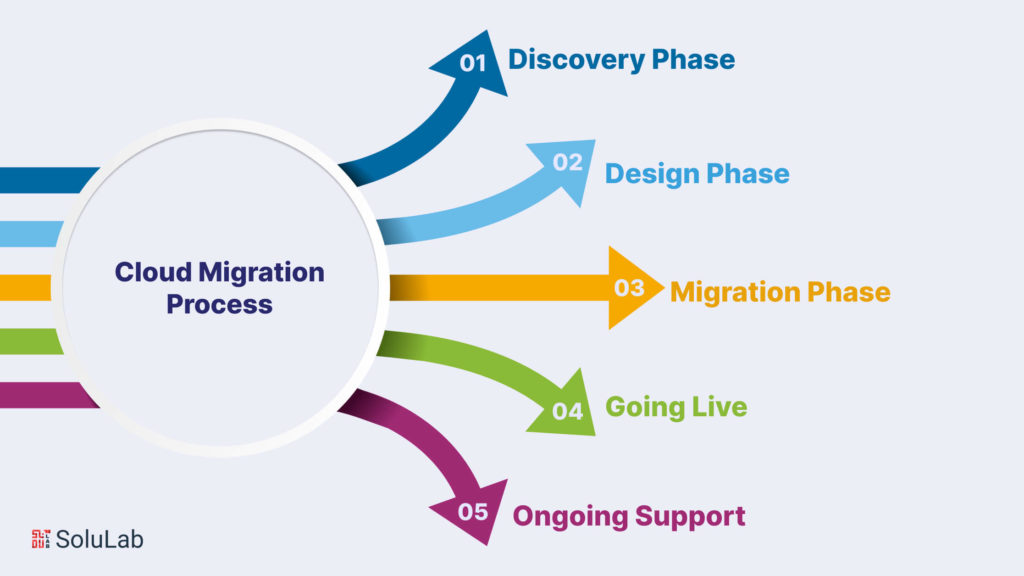
A smooth transition to a new cloud infrastructure requires a comprehensive framework and access to expert guidance. A structured migration plan helps organize the process into manageable phases while ensuring accountability. Here is how to migrate to the cloud.
Analyze Existing Infrastructure:
Formulate Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
Understand Pain Points:
Identify Success Drivers:
Select Deployment Model:
Choose Cloud Vendor:
Document Architecture:
Plan Migration Sequence:
Infrastructure Migration:
Application Migration:
Data Migration
Data Freeze:
Minimize Downtime:
Have Rollback Plan:
Regular Updates:
Performance Monitoring:
Consider Managed Services:
So, these are the cloud migration steps to carefully work on for successfully moving your business to the cloud.
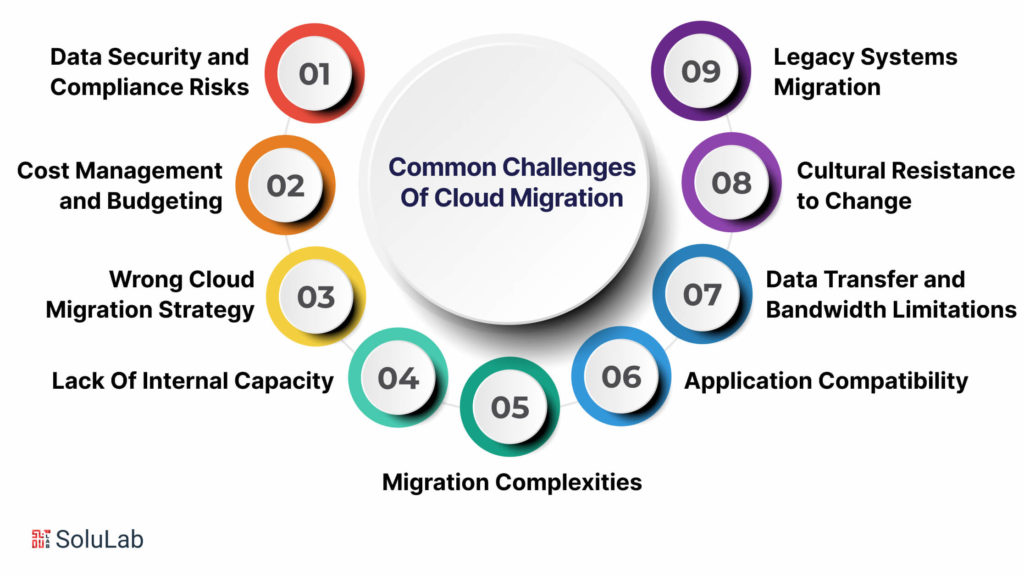
Cloud migration is not without challenges, and understanding and mitigating these challenges are crucial for a successful transition. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into various facets of cloud migration challenges, emphasizing the need for careful planning, expertise, and strategic decision-making.
Moving to a new cloud environment introduces fresh security and compliance risks. While major cloud providers have robust security measures in place, understanding the shared responsibility model is vital, especially when dealing with highly sensitive data. Thorough risk assessments and a clear grasp of the cloud provider’s coverage are essential for maintaining data security during migration. Compliance considerations, such as industry-specific and regulatory requirements, must also be diligently addressed to avoid legal and financial repercussions.
Cloud migration is a complex and resource-intensive process that demands meticulous planning to avoid unexpected costs. Businesses must carefully assess their existing infrastructure and applications, identifying potential bottlenecks and compatibility issues. Collaborating with experienced cloud providers and implementing cost management strategies, including rightsizing instances and utilizing cost-saving options, is crucial to control expenses and ensure a successful migration.
A well-planned cloud migration strategy is vital for success. Rushed decisions, such as migrating all workloads at once, can lead to increased costs, prolonged timelines, and disruptions to business operations. A comprehensive strategy should include cost estimates, workload prioritization, realistic timelines, and considerations for necessary human and technical resources. Failing to assess specific organizational needs may result in suboptimal performance and higher-than-necessary costs.
The lack of internal expertise can impede a smooth migration. Skilled cloud professionals are essential for optimizing resource utilization, troubleshooting, and understanding best practices. Engaging with cloud consultants or managed service providers with proven expertise can provide valuable guidance and support throughout the migration process.
Cloud migration is inherently complex due to factors such as data type, size, and dependencies. Incompatibility issues, both with data and hardware/software, can arise, requiring careful consideration and resolution. Differences in opinions on migration approaches can add to the complexity, emphasizing the need for a well-thought-out plan.
Applications that perform well on-premises may face performance issues in the cloud. Identifying and addressing root causes, such as poorly optimized applications or network latency, is crucial to ensure optimal performance and user adoption.
Transferring large volumes of data from on-premises to the cloud can lead to significant delays, especially with limited network bandwidth. Efficient data migration strategies, including incremental transfers and data compression techniques, are essential to overcome bandwidth limitations.
Organizations may encounter resistance from team members accustomed to legacy systems. Proactively managing change and communication, involving end-users in decision-making, and adopting a phased migration approach can help mitigate cultural resistance.
Migrating legacy systems poses unique challenges due to outdated technologies and complex interdependencies. Rigorous testing, validation, and a thorough assessment during the planning phase are essential to ensure a seamless integration with modern cloud platforms.
When choosing a new infrastructure, it’s essential for companies to carefully think about various factors while moving their applications to the cloud. A reliable Cloud service provider must provide robust security measures to safeguard your company’s sensitive data. While cloud data migration is a vital process, following the appropriate steps with the support of your cloud provider can streamline the transition to a cloud platform.
Elevate your cloud migration experience with SoluLab cloud-based development and migration services. We will guide you through the discovery and design phases, evaluating your current environment and optimizing a bespoke cloud solution.
Subsequently, we will assist you in selecting a platform, deploying your applications, and executing the migration to your new environment. Our experts will then ensure that your cloud environment consistently meets the security and performance standards vital for your business success.
For further details on cloud migration or to initiate the development of a personalized cloud migration plan for your organization, reach out to SoluLab today.
1. Can I put secret information in the cloud?
It depends on how important your data is. Sometimes, rules about where and how to store private information, like medical details, might limit your choices.
2. Can I use any technology in the cloud?
If you’re using special technology that belongs to someone else, you might not be allowed to use it in the cloud.
3. Does the cloud slow down apps?
Some apps might be slower depending on where the user and the app are. It’s called latency.
4. Can I see how well my cloud is doing?
Since someone else controls the cloud hardware, you might not have as much control when fixing problems. It can be less clear.
5. Will I ever run out of space in the cloud?
In theory, no. But it depends on your money. Cloud storage can get more expensive, but it’s flexible. You can control costs with tools like calculators and alerts.
6. How good are cloud disaster recovery systems compared to in-house ones?
They are really good. Cloud systems are faster because you don’t need to buy more hardware. They also have plans that follow industry rules.
7. Do I have to update my cloud server software?
Usually not. The cloud provider might do it automatically. Some cloud models also make hard tasks, like backups and updates, easier for you.